Session 9: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland, and Their Disorders
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Vital regulatory functions of the hypothalamus
- Temperature
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Blood osmolarity
- Goal-seeking behaviour
- Emotional behaviour
- Visceral nervous system
- Sexual activity
- Food & water intake
- Aggression
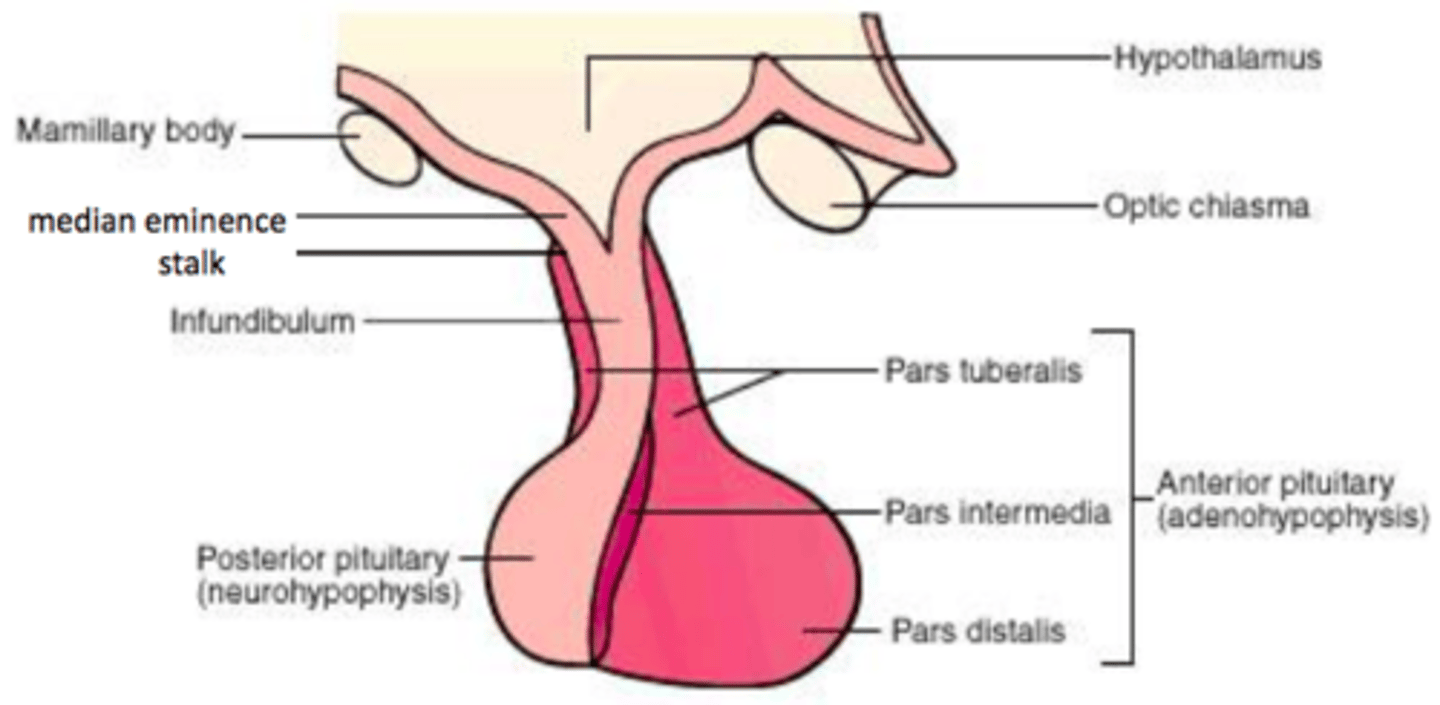
Pituitary gland is ___ fused glands...
Pituitary is two fused glands...
- Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
- Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
Anterior pituitary
adenohypophysis
Posterior pituitary
neurohypophysis
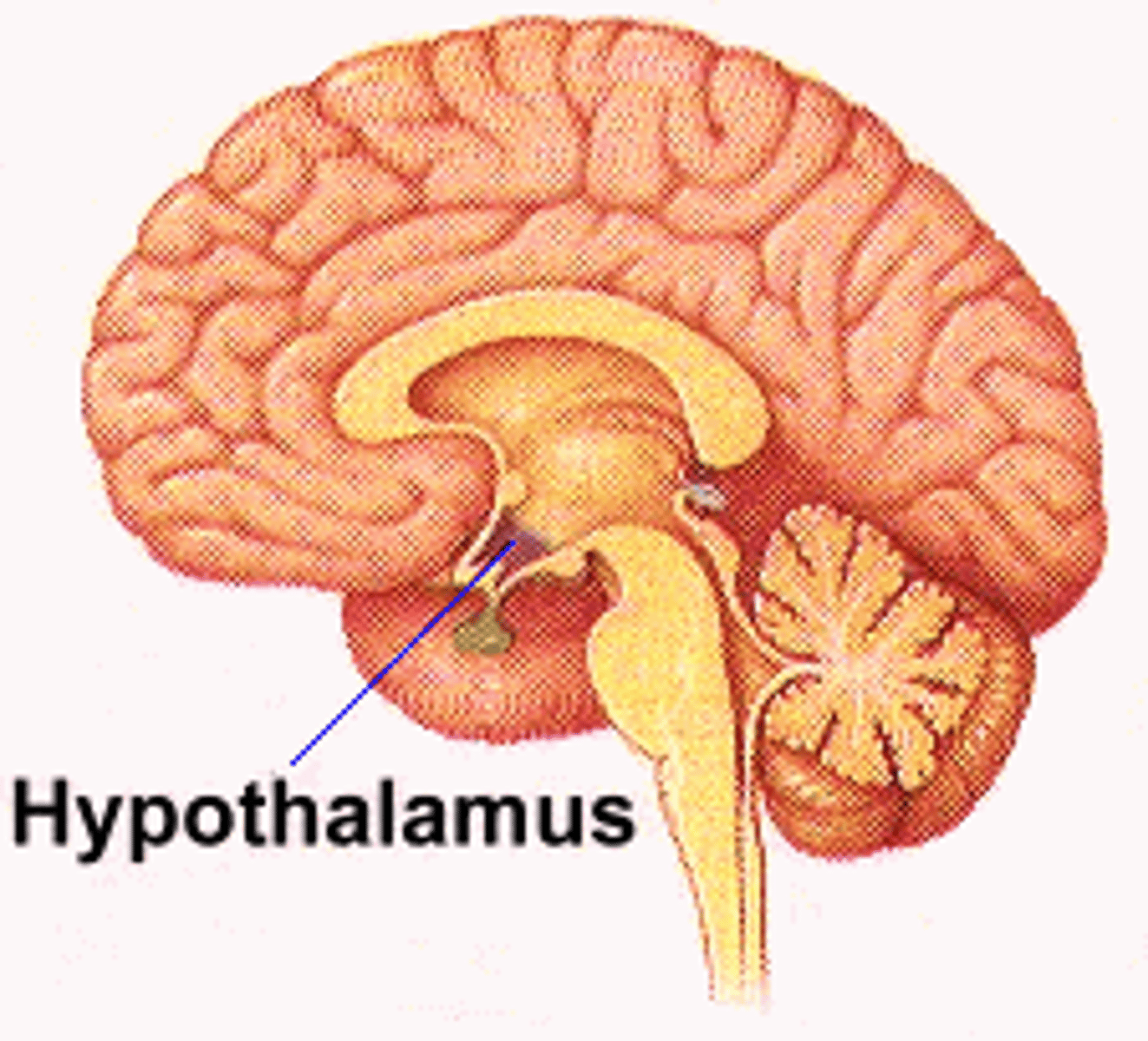
The pituitary gland lies just below the ___ in the brain
hypothalamus
The pituitary gland is connected by a stalk to the hypothalamus. This stalk is known as the ___ ___ stalk
median eminence
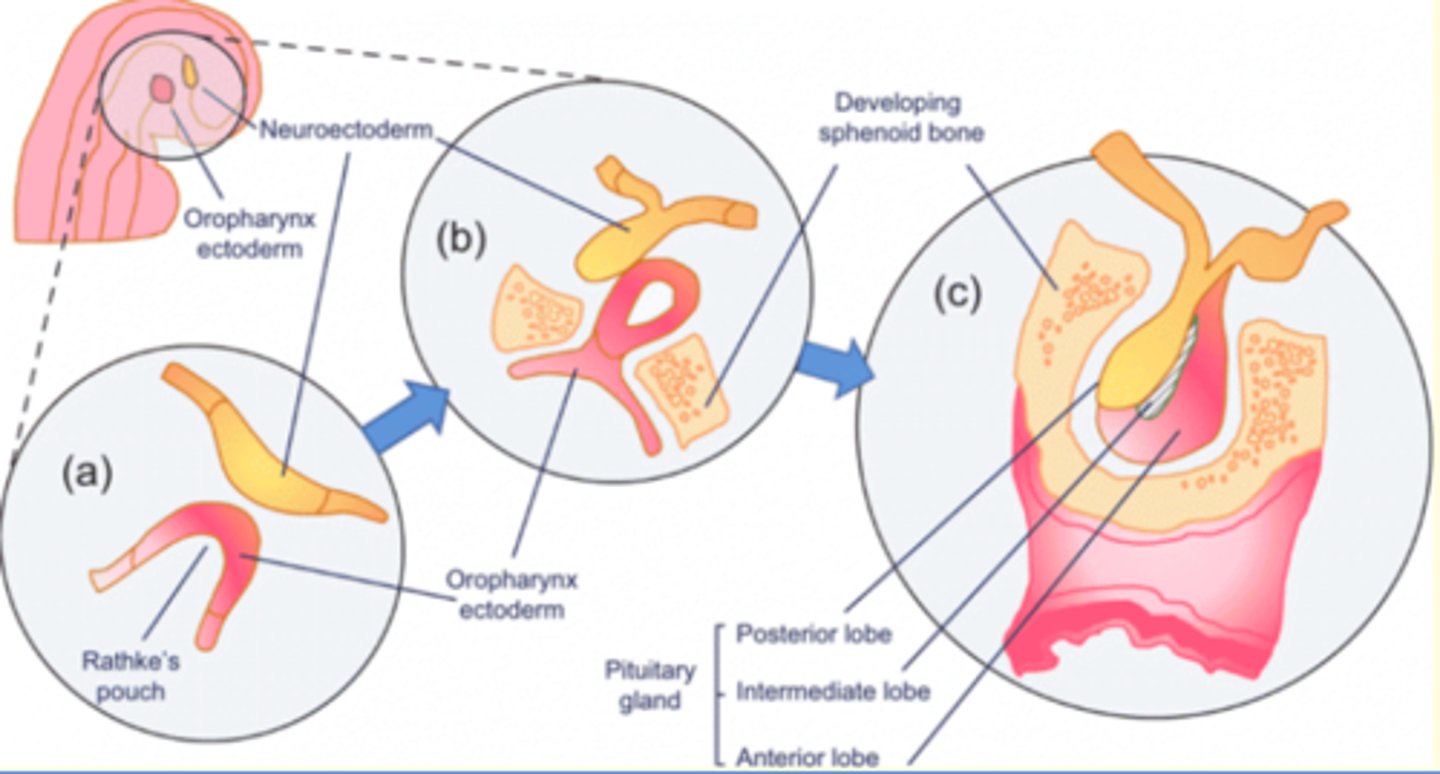
Describe development of pituitary gland in utero
Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis)
- Upgrowth of ectodermal cells from roof of primitive pharynx (buccal cavity)
- Arises from Rathke's Pouch
Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis)
- Down-growth of neural tissue from hypothalamus
- Arises from neuroectoderm
These two tissues fuse to form the pituitary gland
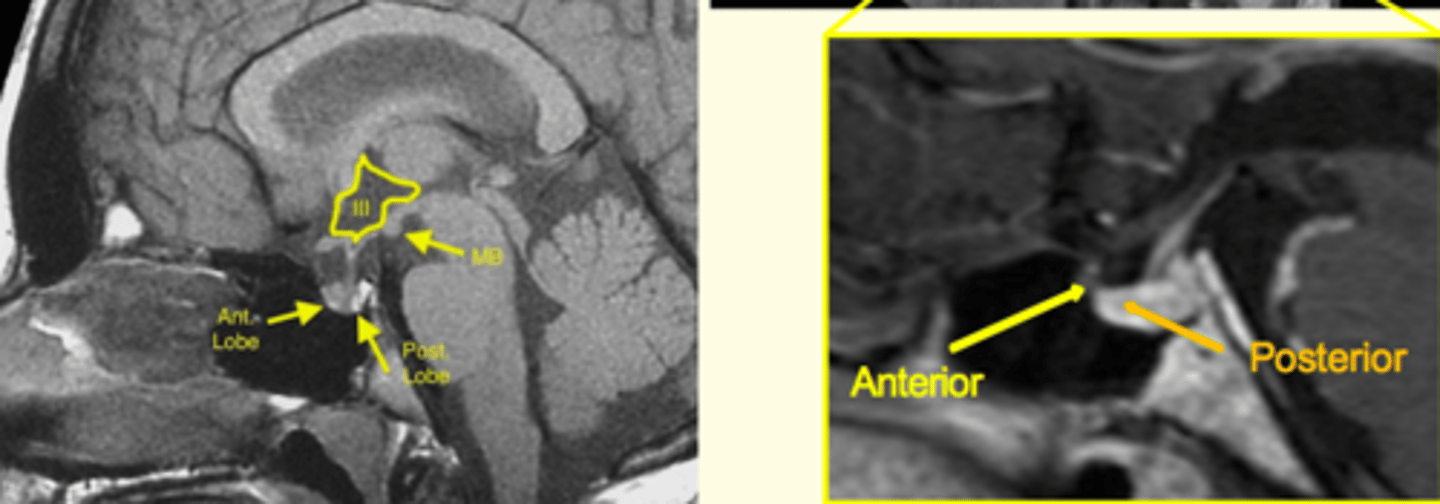
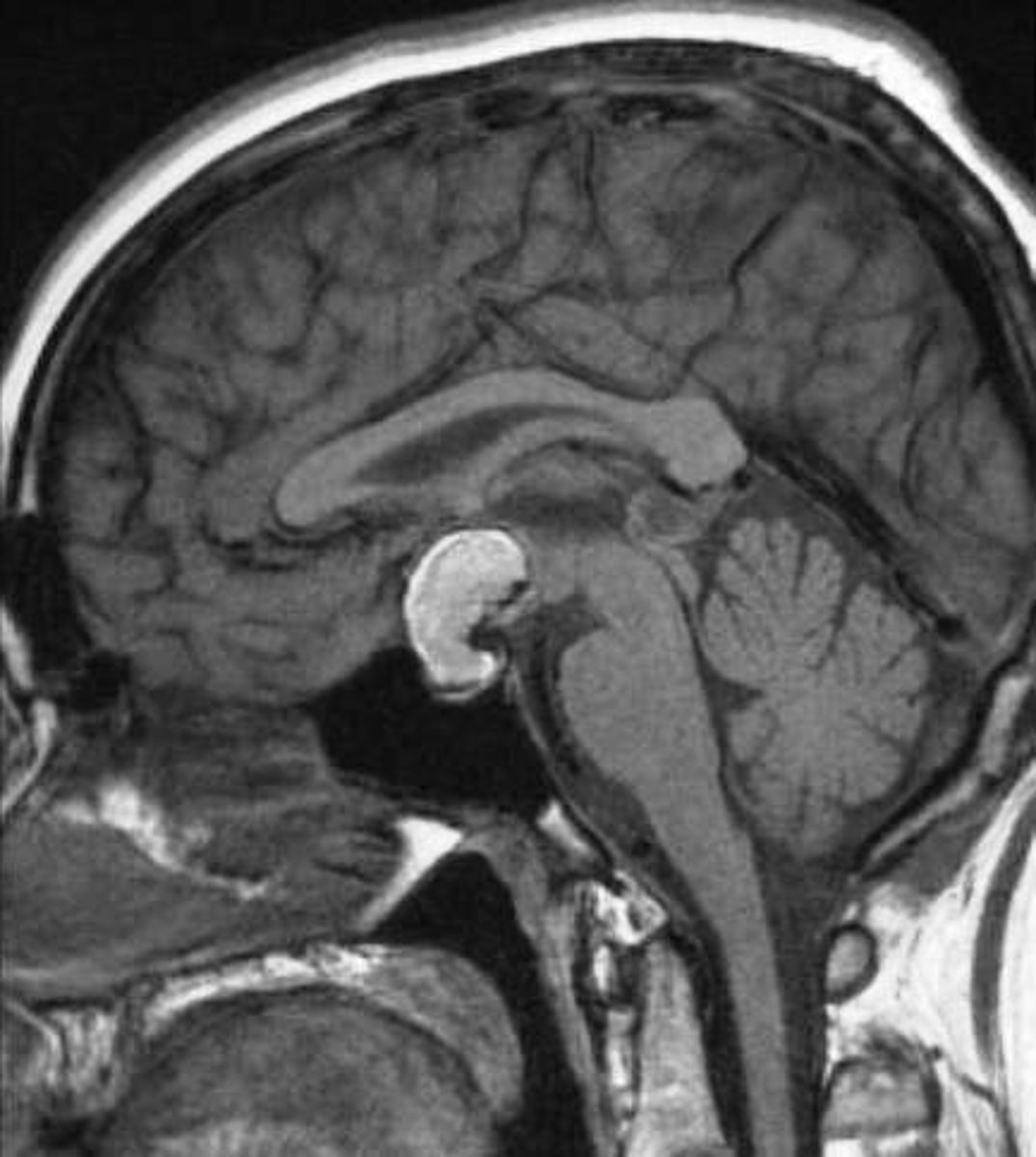
Identify anterior and posterior pituitary on this brain MRI
Name the artery connecting pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
Hypophyseal portal artery
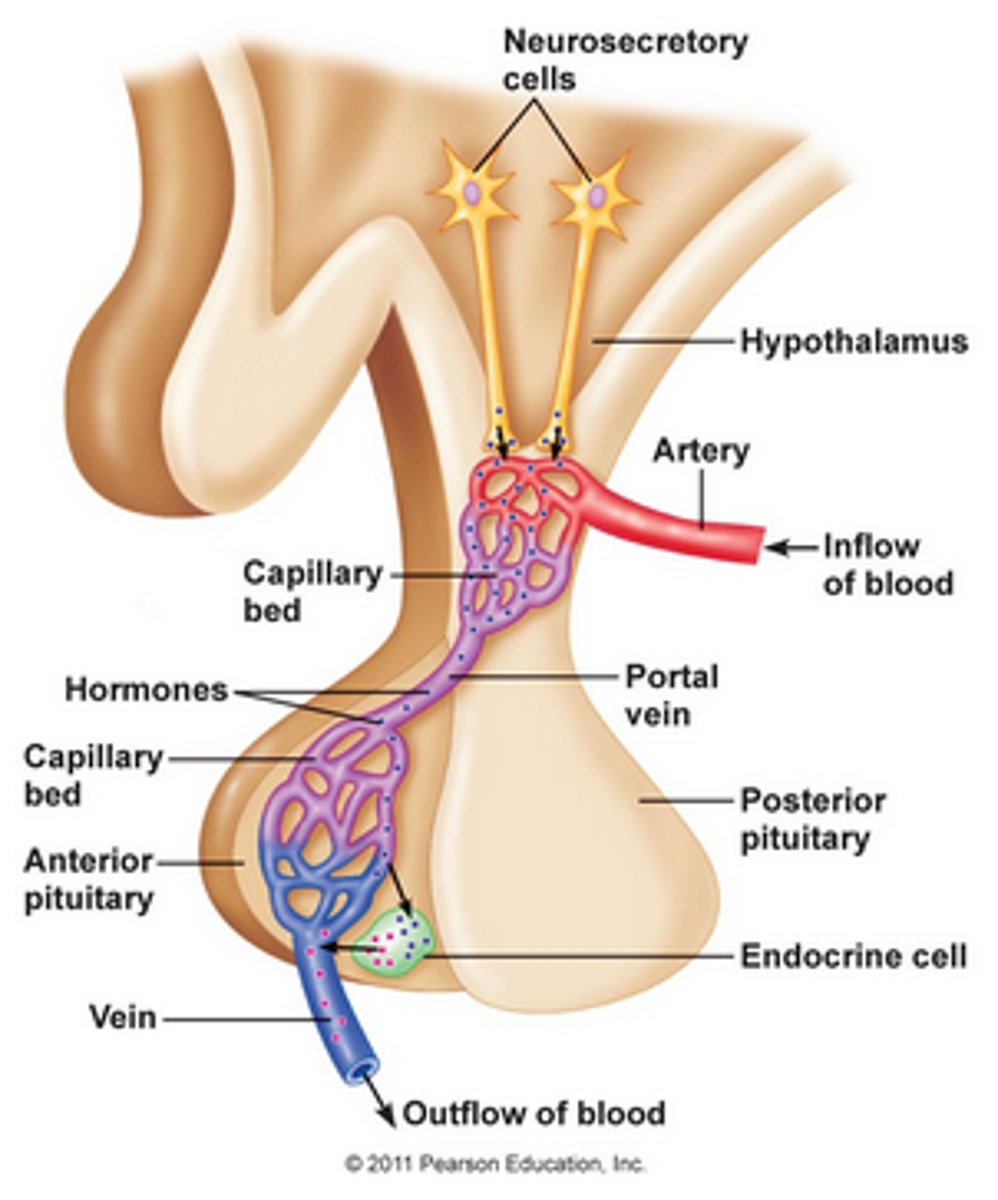
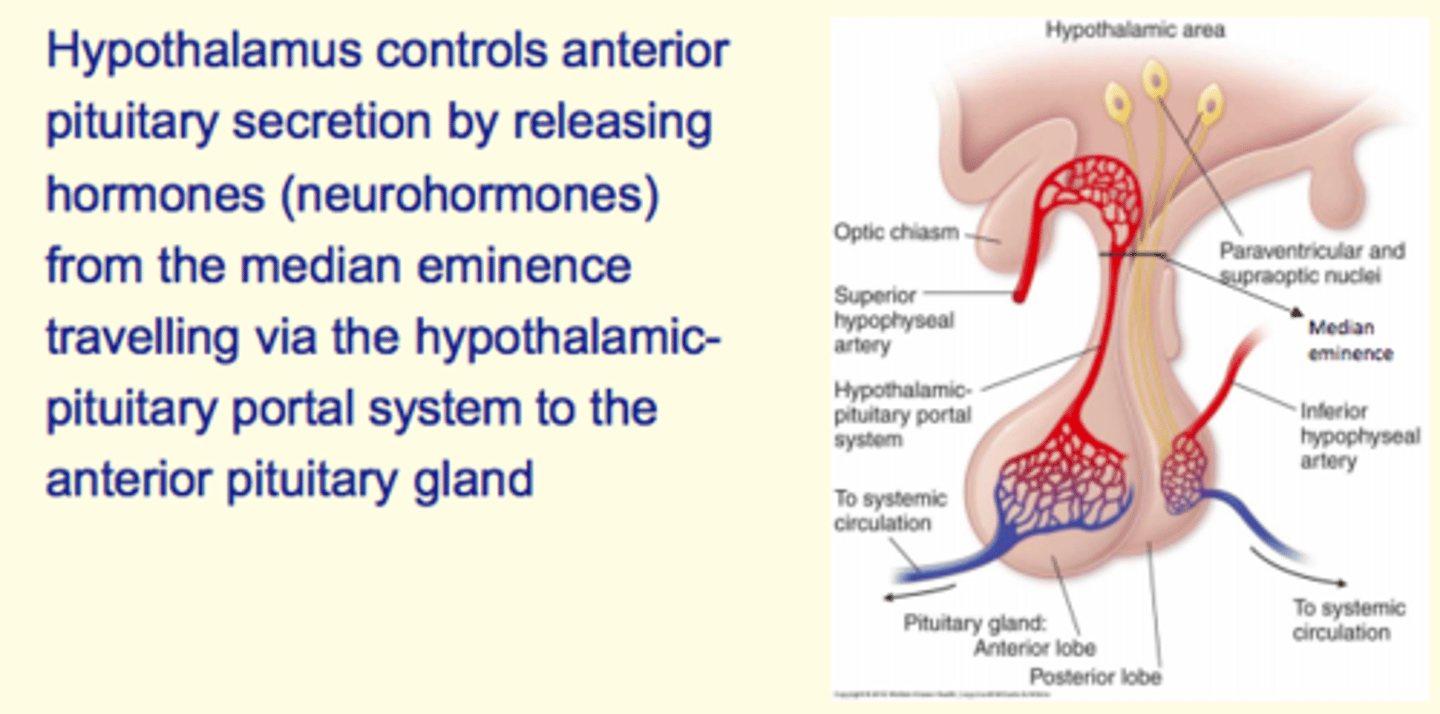
The hypothalamus controls the ___ pituitary gland secretion by releasing hormones (neurohormones) from the ___ ___
The hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary gland secretion by releasing hormones (neurohormones) from the median eminence
The anterior pituitary is connected to the hypothalamus via the ___-___ circulation
The anterior pituitary is connected to the hypothalamus via the hypophyseal-portal circulation
The anterior pituitary is made up of hormone producing glandular cells.
It produces six peptide hormones - these hormones are...
1) Prolactin
2) Growth Hormone (GH)
3) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
4) Lutenizing Hormone (LH)
5) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
6) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Name the TWO gonadotrophins secreted by anterior pituitary
1) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
2) Lutenizing Hormone (LH)
These gonadotrophins are produced by gonadotrophs and act on gonads to control reproduction
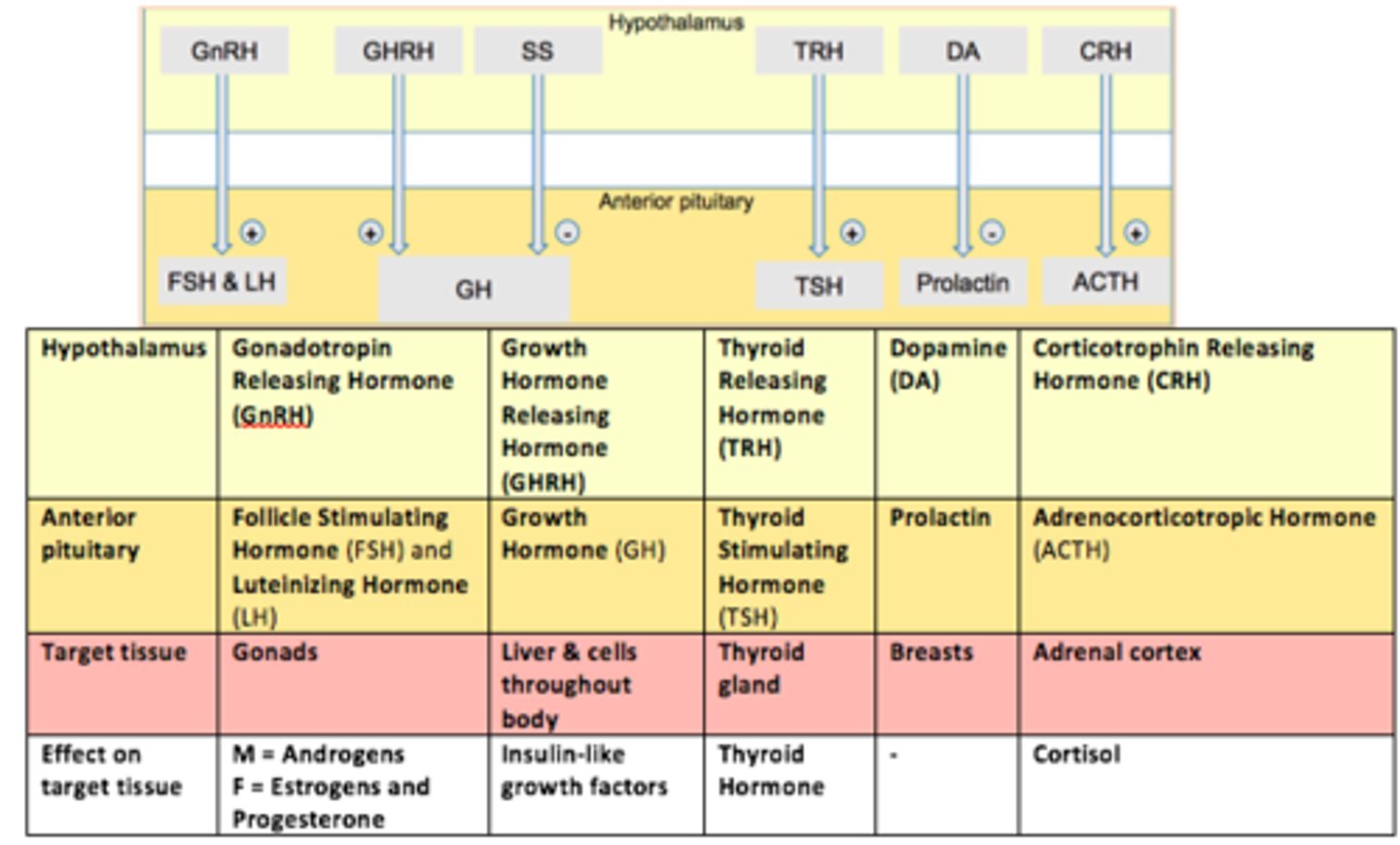
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) is produced by ___
thyrotrophs
TSH stimulates the ___ gland to secrete hormone
thyroid
Glycoprotein hormones secreted by anterior pituitary
- Gonadotrophins = FSH, LH
- TSH
Polypeptide hormones secreted by anterior pituitary
- GH
- ACTH
- Prolactin
Growth Hormone (GH) is produced by ___
somatotrophs
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is produced by ___
corticotrophs
Prolactin is produced by ___
lactotrophs
Role of ACTH
Stimulates adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids (cortisol)
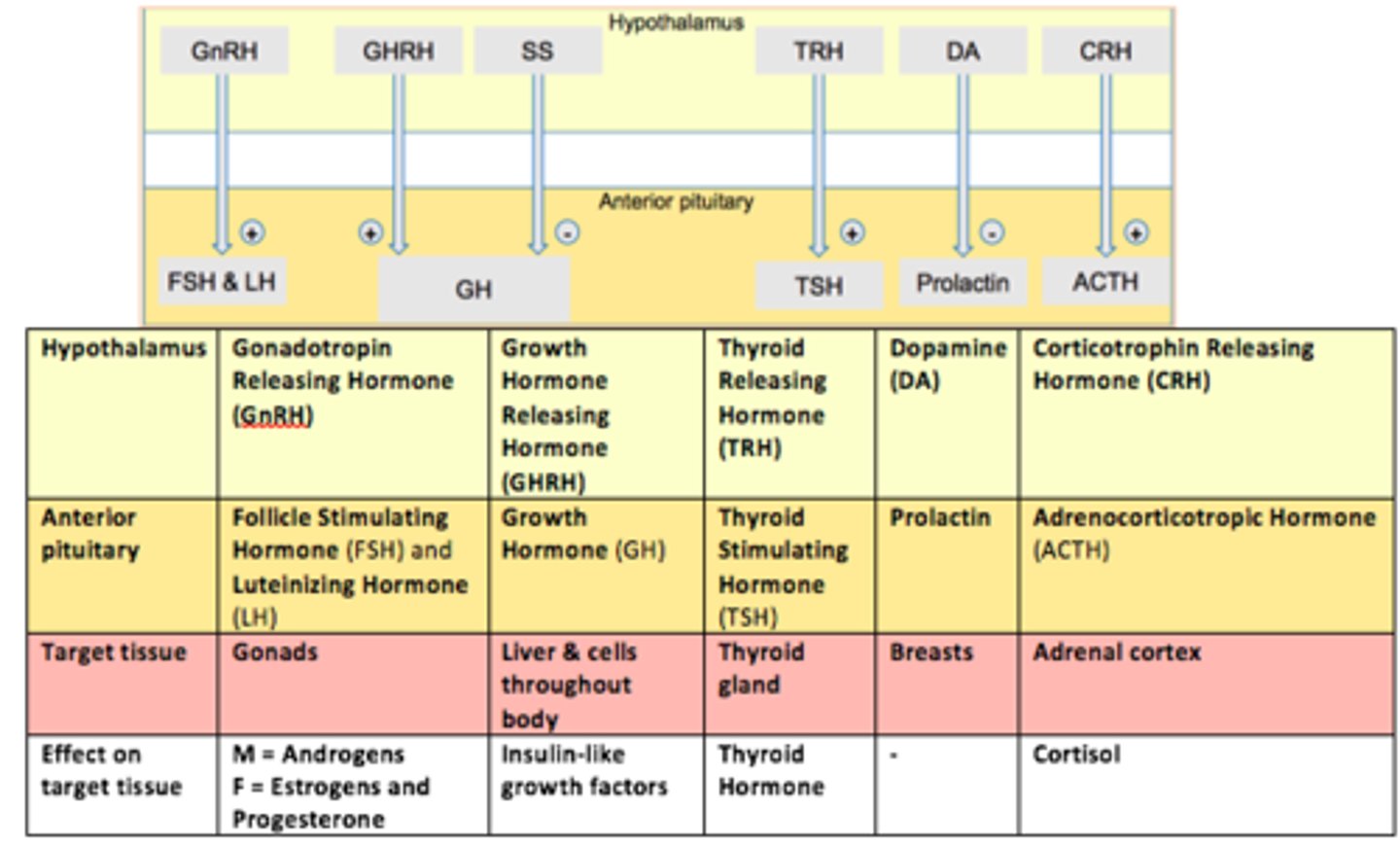
Role of GH
Influences growth and metabolism
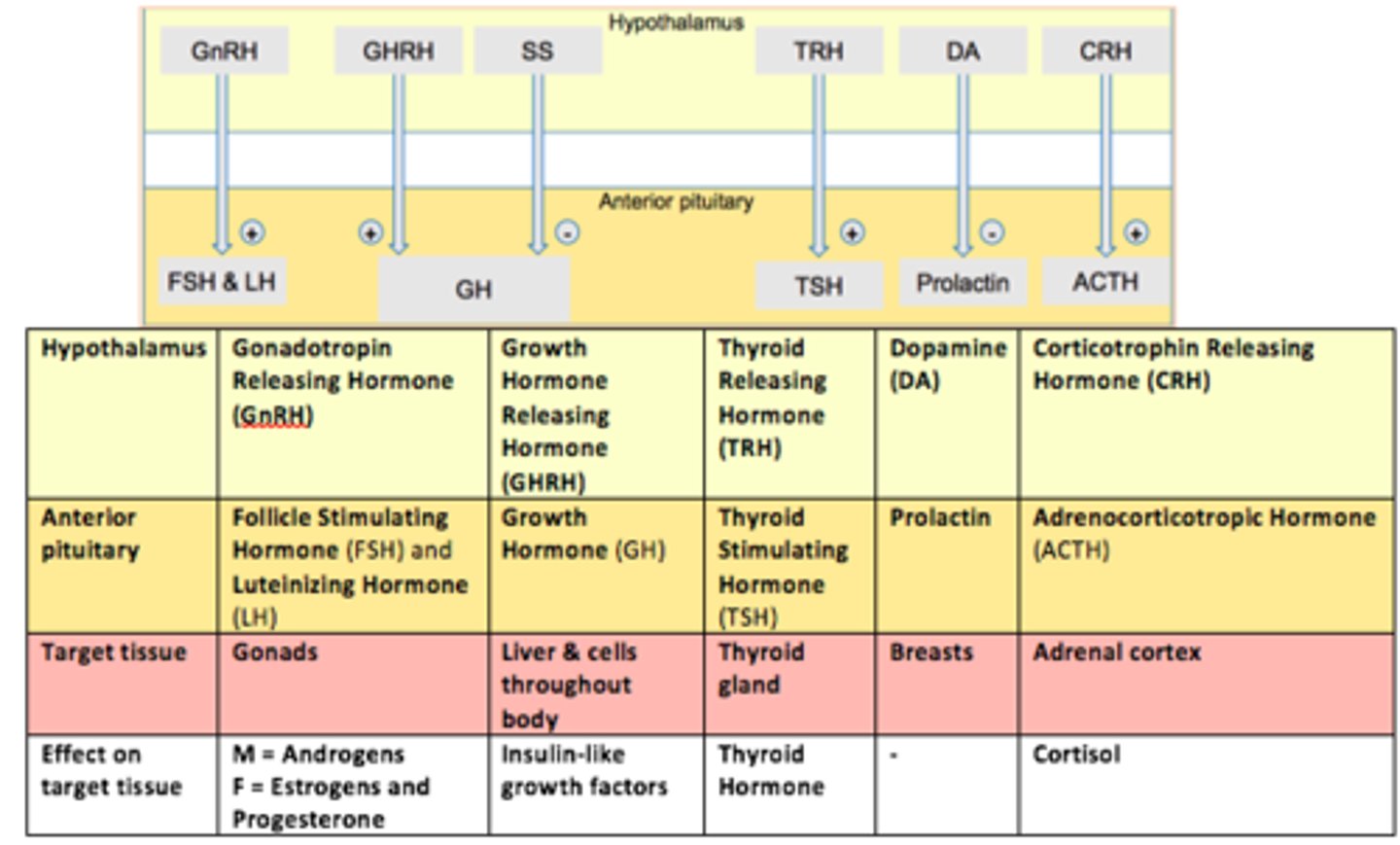
Role of prolactin
Controls milk production (from breasts) and other reproductive processes
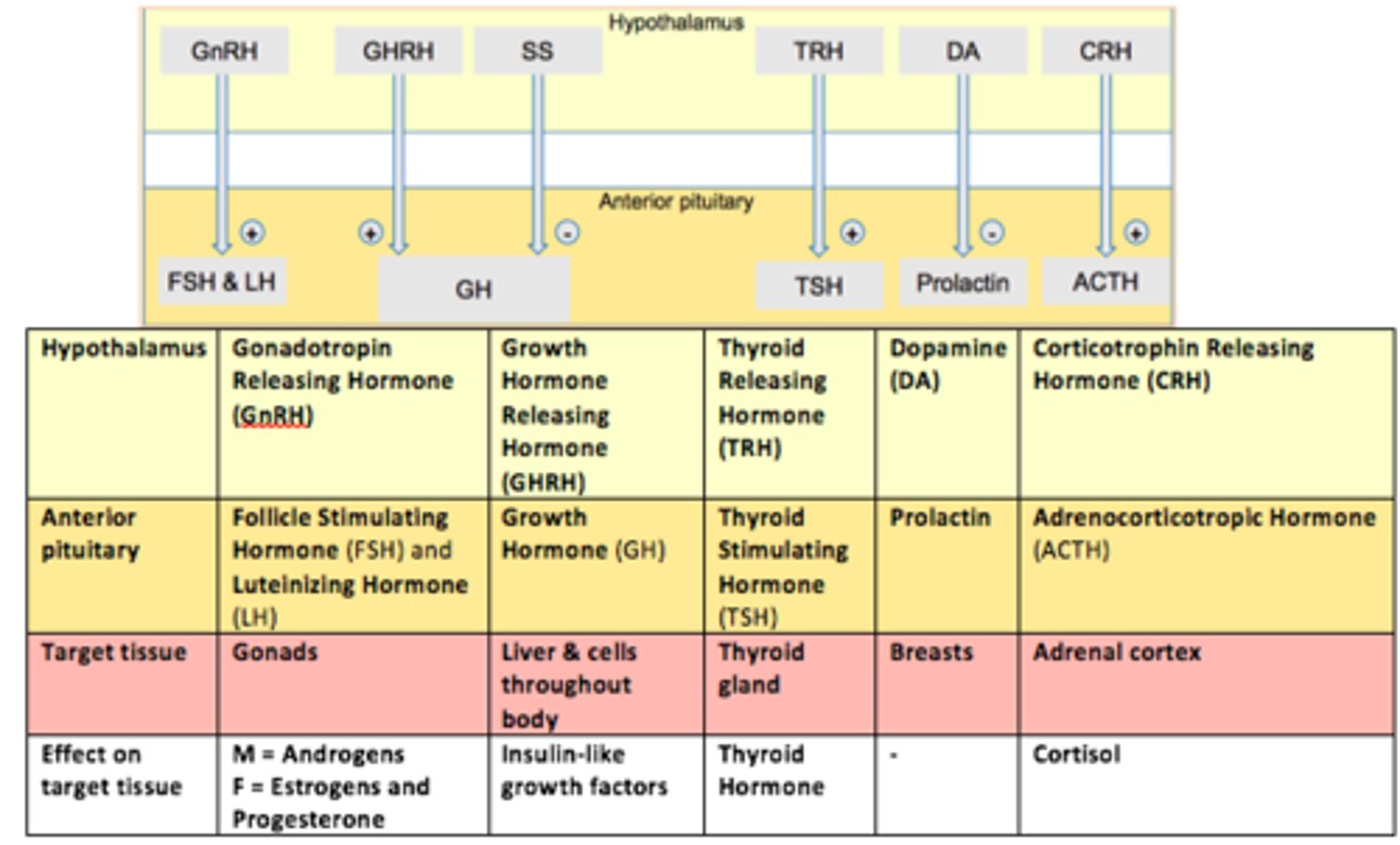
Gonadotropes are controlled by GnRH (___).
This hormone stimulates both LH and FSH secretion.
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
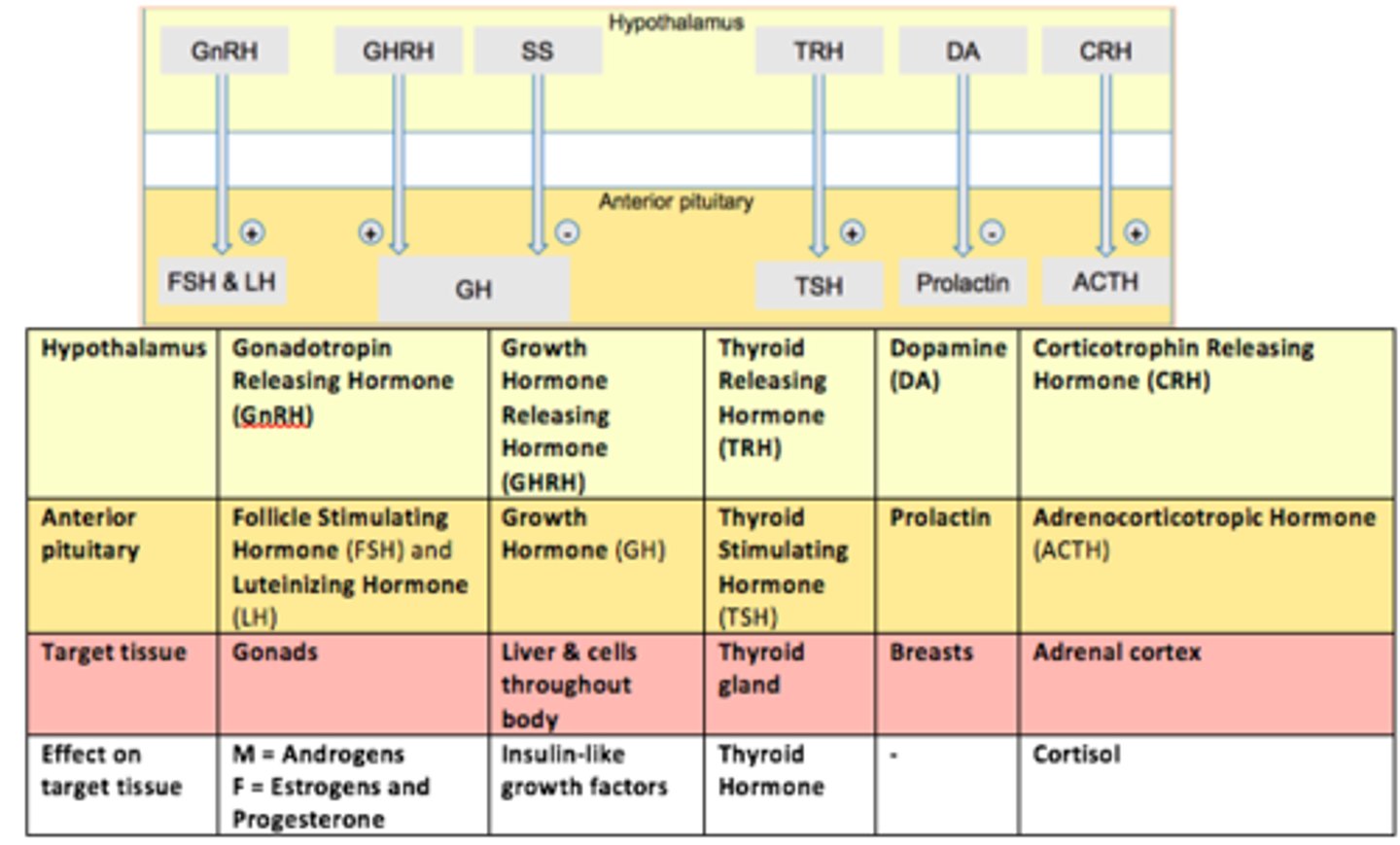
Thyrotropes are controlled by TRH (___).
This hormone stimulates Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) - stimulates thyroid gland to provide thyroid hormones
Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH)
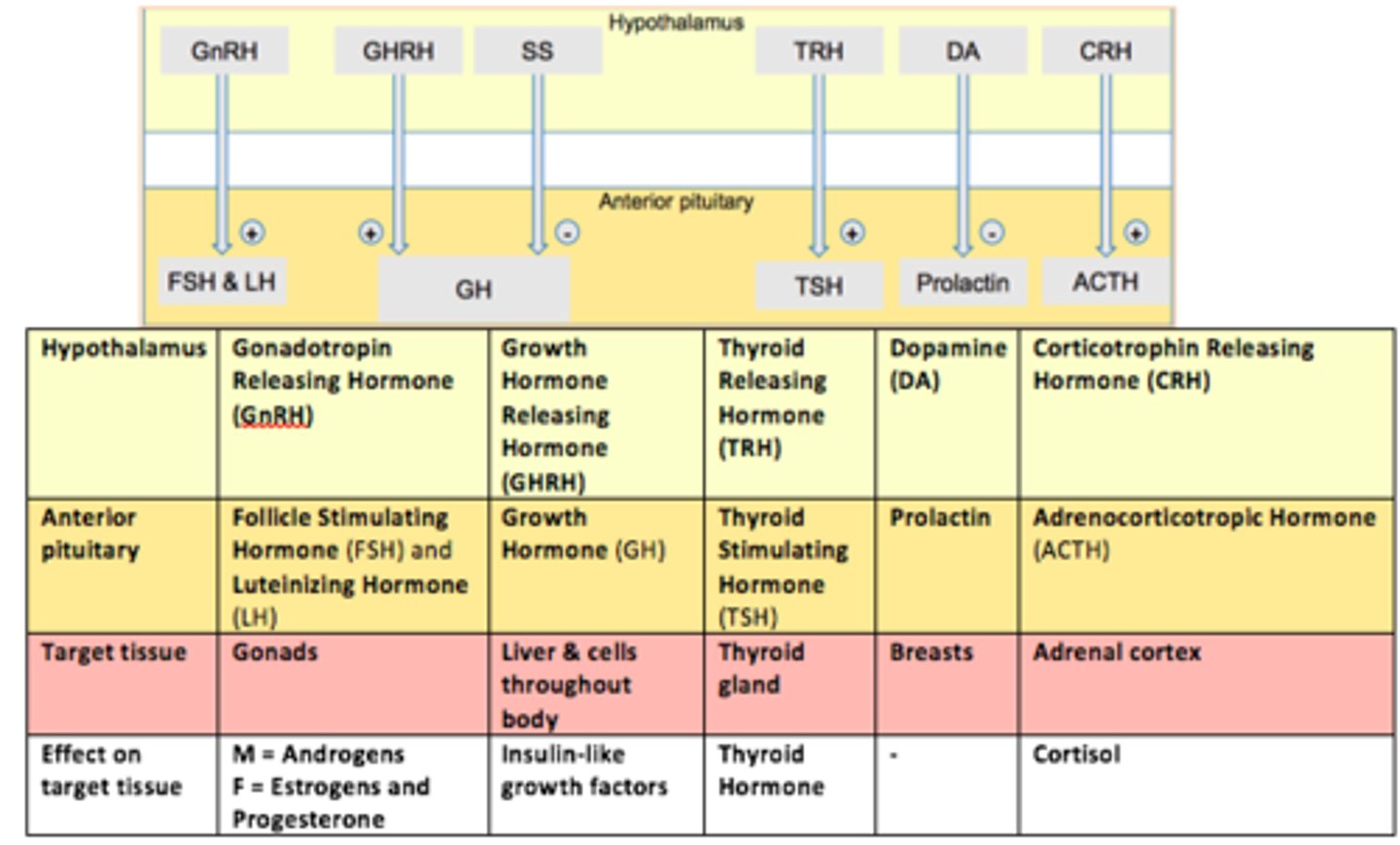
Somatotropes are controlled by GHRH (___).
This hormone stimulates Growth Hormone (GH) release.
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
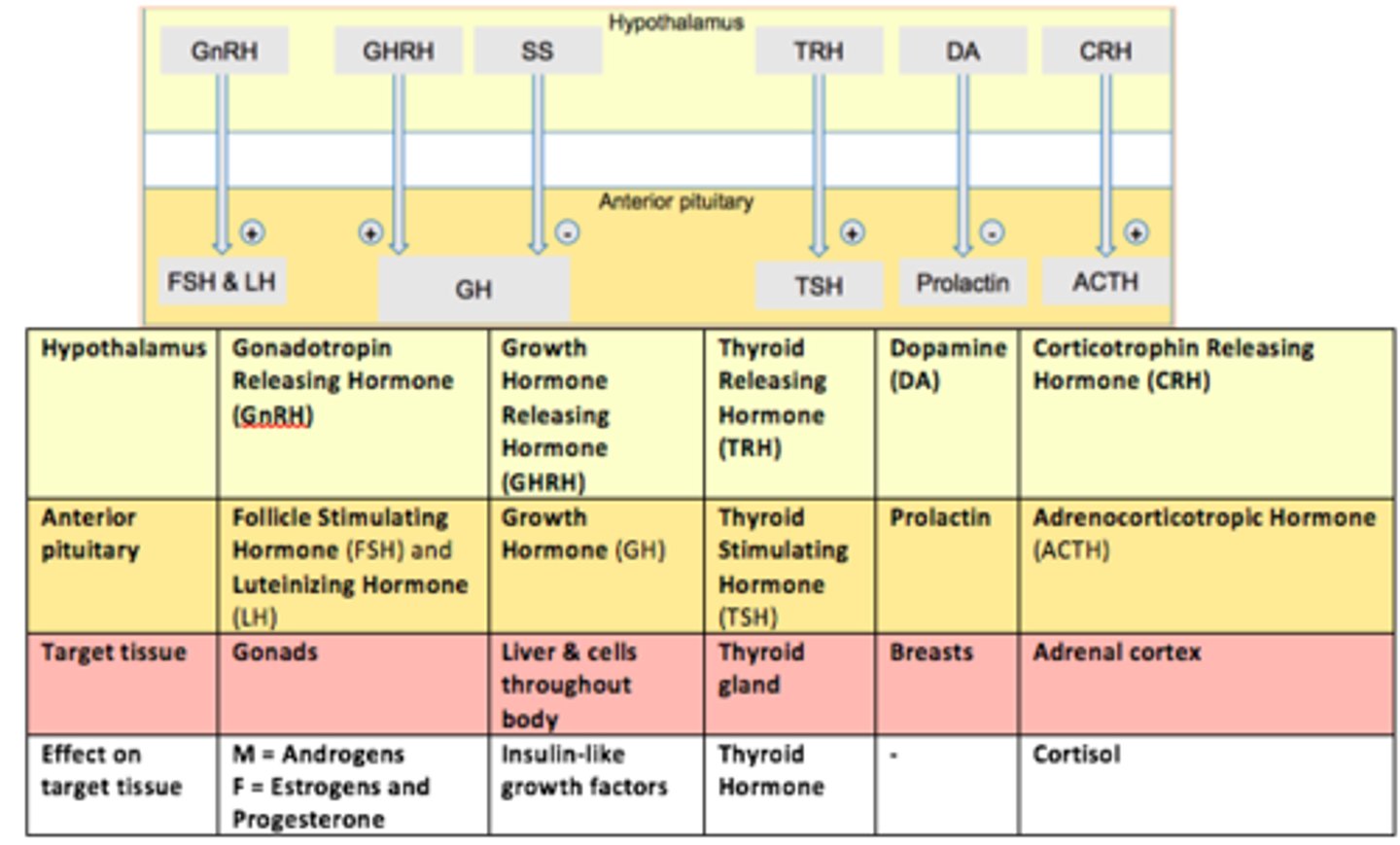
Lactotropes controlled in a different way.
The hypothalamus secretes ___.
___ inhibits prolactin secretion from the anterior pituitary.
Dopamine
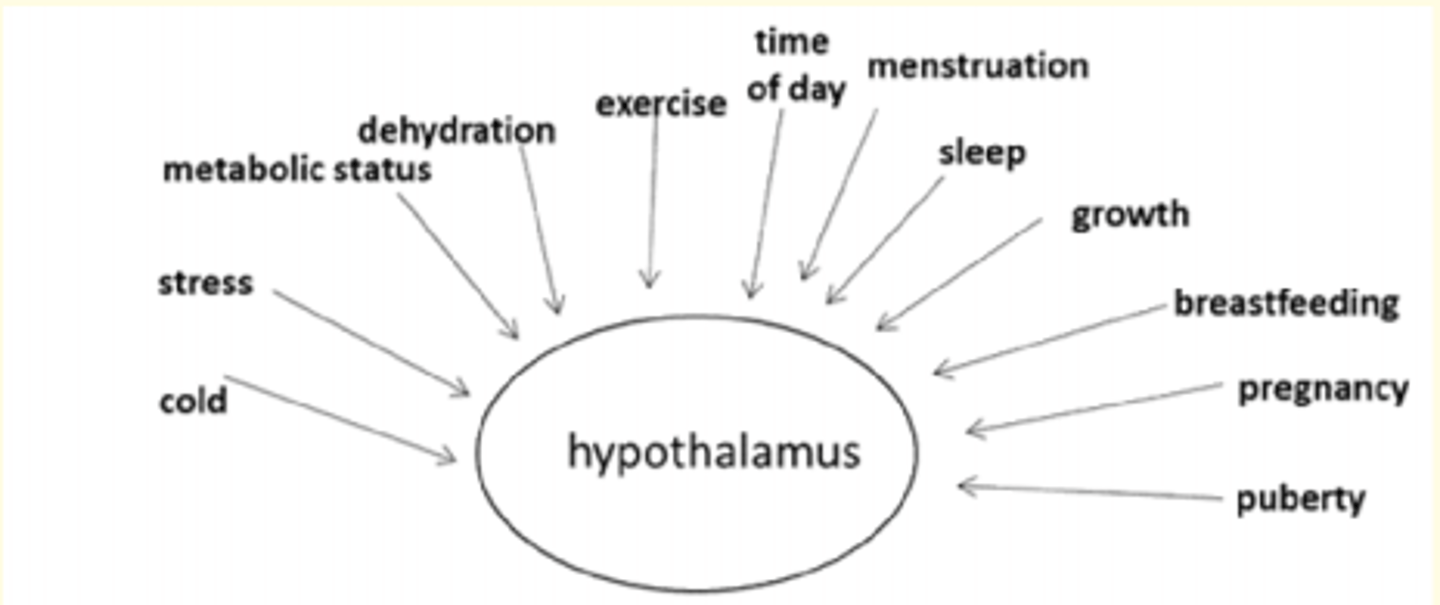
What environmental factors influence the Hypothalamus - Pituitary Gland Axis
- Cold
- Stress (HPA)
- Metabolic status
- Dehydration
- Exercise
- Time of day
- Menstruation
- Sleep
- Growth
- Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy
- Puberty
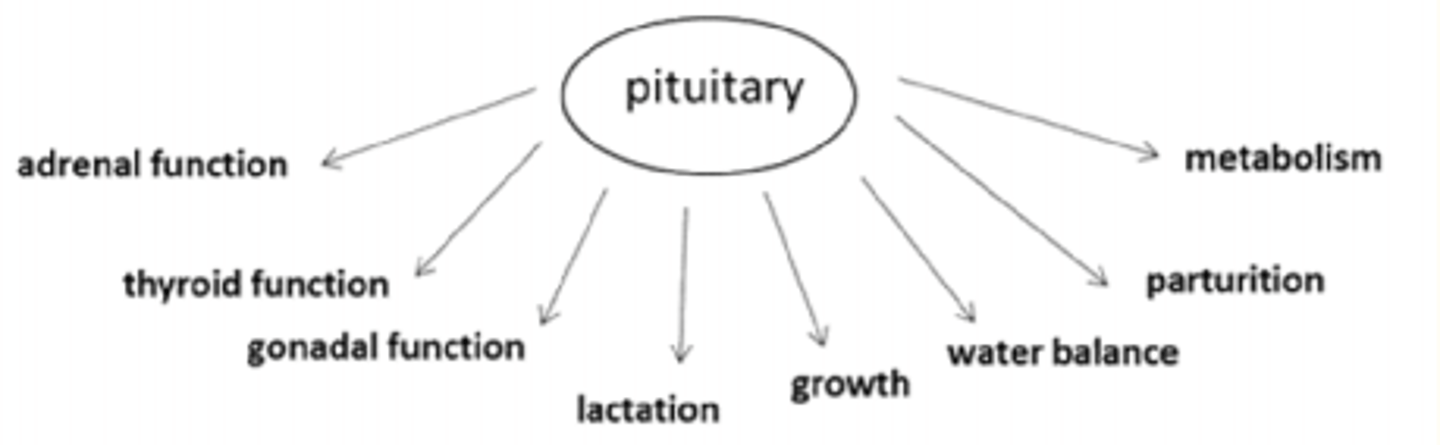
Examples of some physiological effects elicited by the pituitary gland in the Hypothalamus - Pituitary Gland Axis?
- ACTH = adrenal function
- TSH = thyroid function
- FSH/LH = gonadal function
- Prolactin = lactation
- GH = growth/metabolism
- Water balance
- Parturition
HPA axis
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
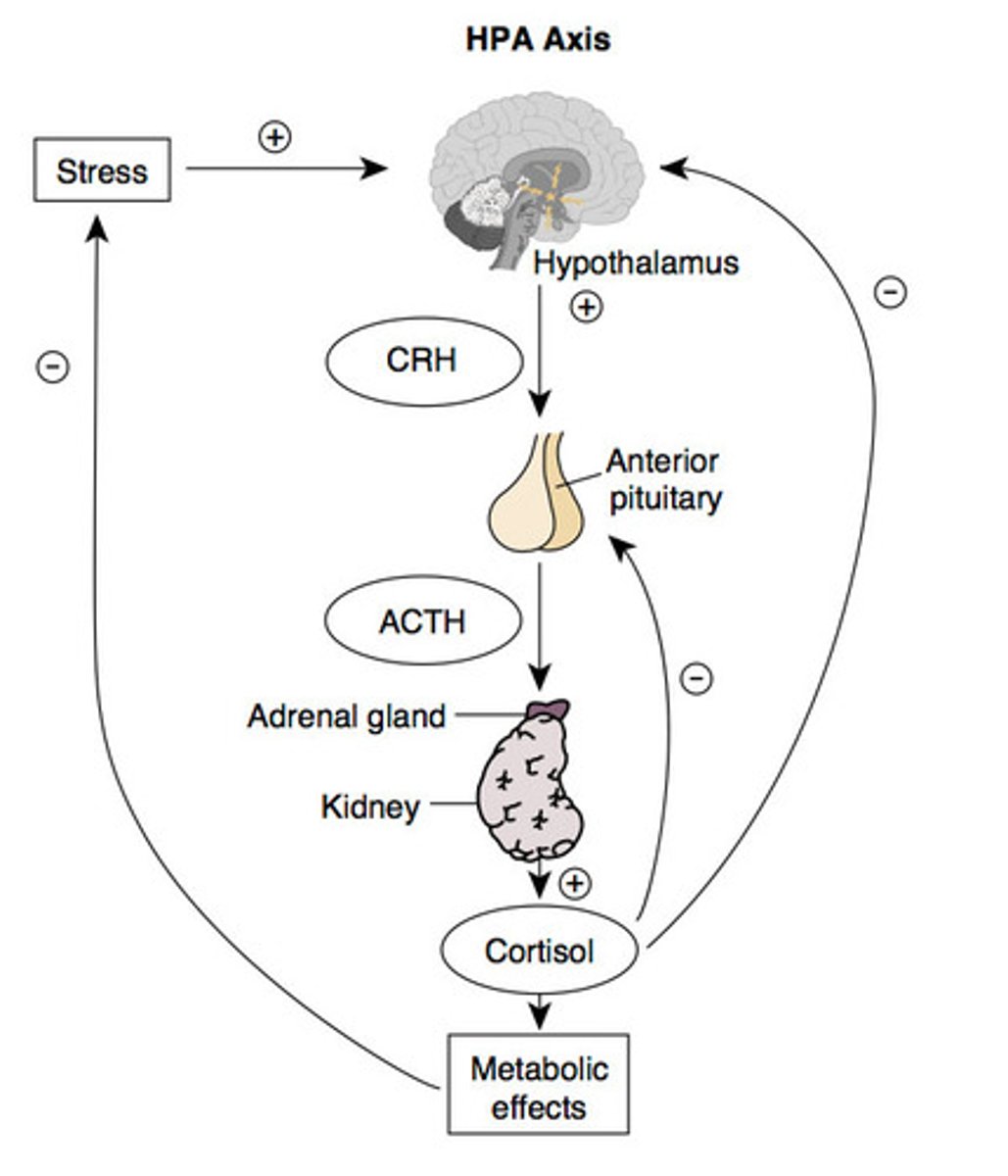
HPA axis responds to ___
Stress
What are the metabolic effects of the stimulation of the HPA axis?
- Energy stores mobilised
- Lipolysis and proteolysis
- Vasoconstriction
- Reproduction is suppressed
- Altered stress-related behaviours
- Bronchodilation
- Increased heart rate & blood pressure
- Blood flow to muscles is increased (fight/flight)
Increased risk of cognitive, emotional and behavioural dysfunctions as an effect of increased HPA axis stimulation.
Some examples of these dysfunctions...
- Major depression disorder
- Anxiety disorders
- Memory problems
Increased risk of cardiovascular dysfunctions as an effect of increased HPA axis stimulation.
Some examples of these dysfunctions...
- Cardiac hypertrophy (hypertension)
- Vascular damage
Increased risk of other diseases as an effect of increased HPA axis stimulation.
Some examples of these dysfunctions...
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Cushing's syndrome (hypercortisolism)
- Obesity
Increased risk of immune system dysfunction as an effect of increased HPA axis stimulation.
Some examples of these dysfunctions...
- Increased risk of autoimmune disorders
- Increased levels of circulating cytokines
- Chronic/low-grade inflammation throughout body
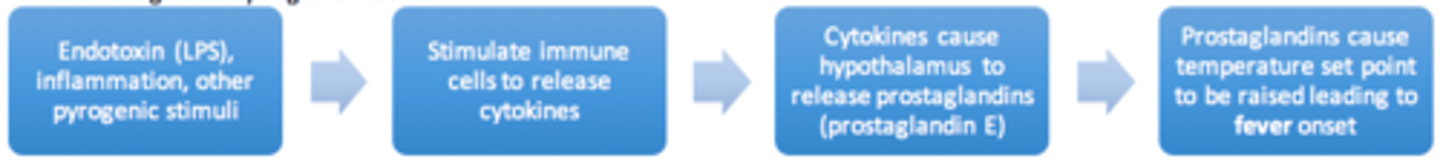
Mechanism of fever
- Exogenous pyrogens (e.g., bacterial LPS) stimulate leukocytes (monocytes, macrophages, Kupffer cells) to release cytokines
- Cytokines lead to release of prostaglandins from hypothalamus (prostaglandin E)
- Prostaglandins cause increase of temperature set point causing fever
- Fever is regulated by negative feedback
Give two examples of pituitary gland disorders
1) Hypopituitarism
2) Pituitary Adenoma
Hypopituitarism
Deficient pituitary gland activity
- Decreased synthesis of one or more pituitary or hypothalamic hormones
- Rare
- Most commonly = FSH/LH deficiency
- Mostly due to = tumours, surgical, radiotherapy treatment
- Symptoms/signs depend on the severity of deficiency
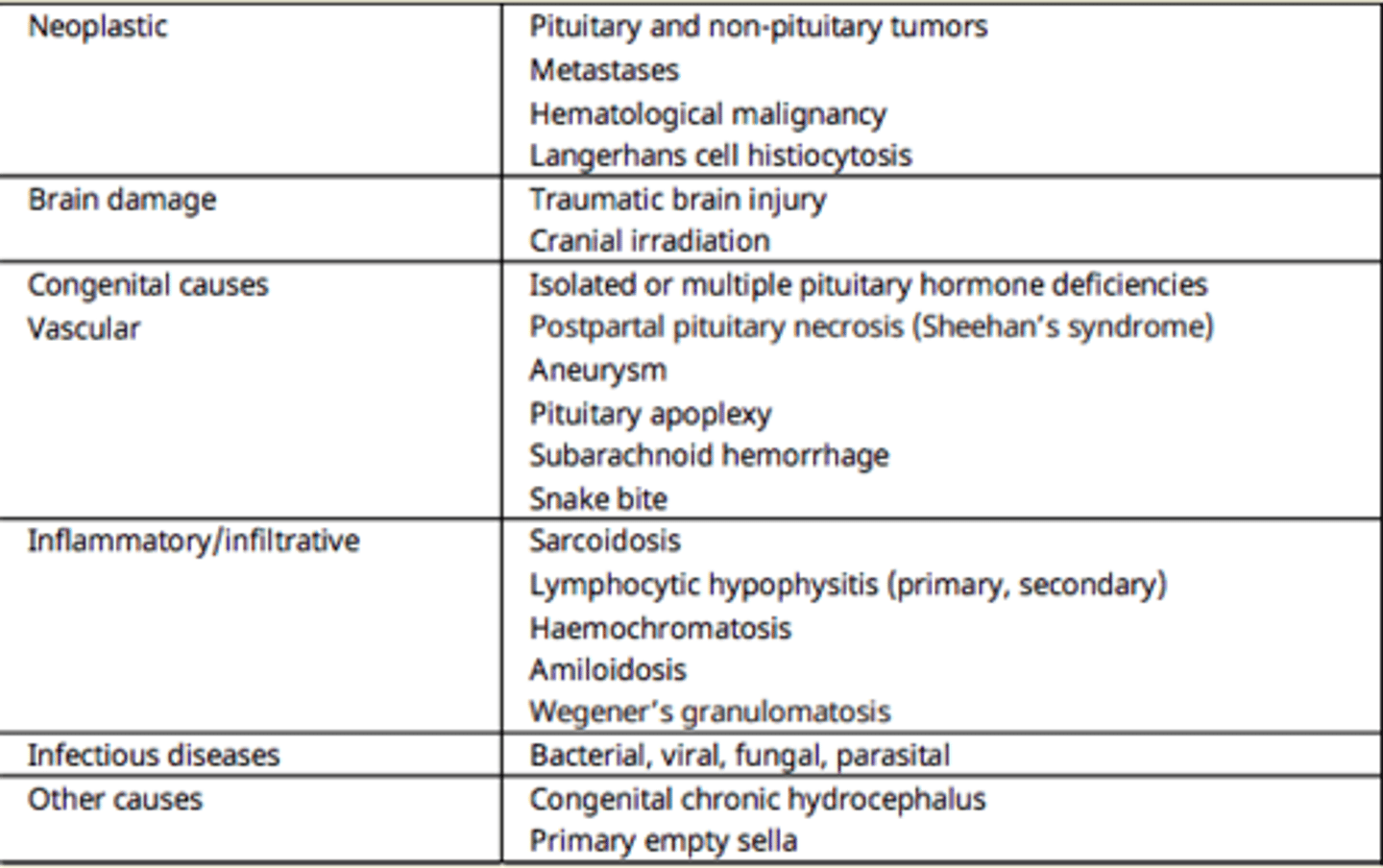
Name some causes of Hypopituitarism
bacterial/viral
subaracnoid hemorage
snake bite
TBI
Symptoms of gonadal deficiencies in Hypopituitarism
- Loss of libido
- Secondary sexual hair loss
- Amenorrhoea
- Erectile dysfunction
- Menstrual cycle deficiencies
Symptoms of GH deficiency in Hypopituitarism
- Growth failure in children
- Impaired wellbeing in adultd
Symptoms of TSH deficiency in Hypopituitarism
- Weight gain
- Dry skin
- Cold intolerance
Symptoms of ACTH deficiency in Hypopituitarism
- Mild hypotension
- Hyponatraemia (low serum sodium)
Case study
36 year old male referred by GP with 5 day history of headache that has been progressively increasing in severity and a 1 day history of visual disturbance. Further history reveals a one month history of lethargy, dizziness on standing up too quickly, loss of libido and some loss of chest hair.
Clinical Findings
• Decreased serum cortisol, TSH, LH, FSH and testosterone
• Increased prolactin
• MRI: large pituitary tumour compressing the optic chiasm
Diagnosis = Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenoma can be associated with ___ hormonal secretion which causes effects. This is called a ___ adenoma
Pituitary adenoma can be associated with excess hormonal secretion which causes effects. This is called a functional adenoma
- Hyperprolactinaemia
- Gigantism
- Acromegaly
- Cushing's disease
Gigantism
Pituitary adenoma secreting excess GH in childhood (before epiphyses have fused)
- Accelerated growth of bone, muscle and connective tissue
- Enlargement of organs

Gigantism symptoms
- Joint pain
- Delayed puberty
- Pain and limited joint mobility
- Vision problems
- Headaches
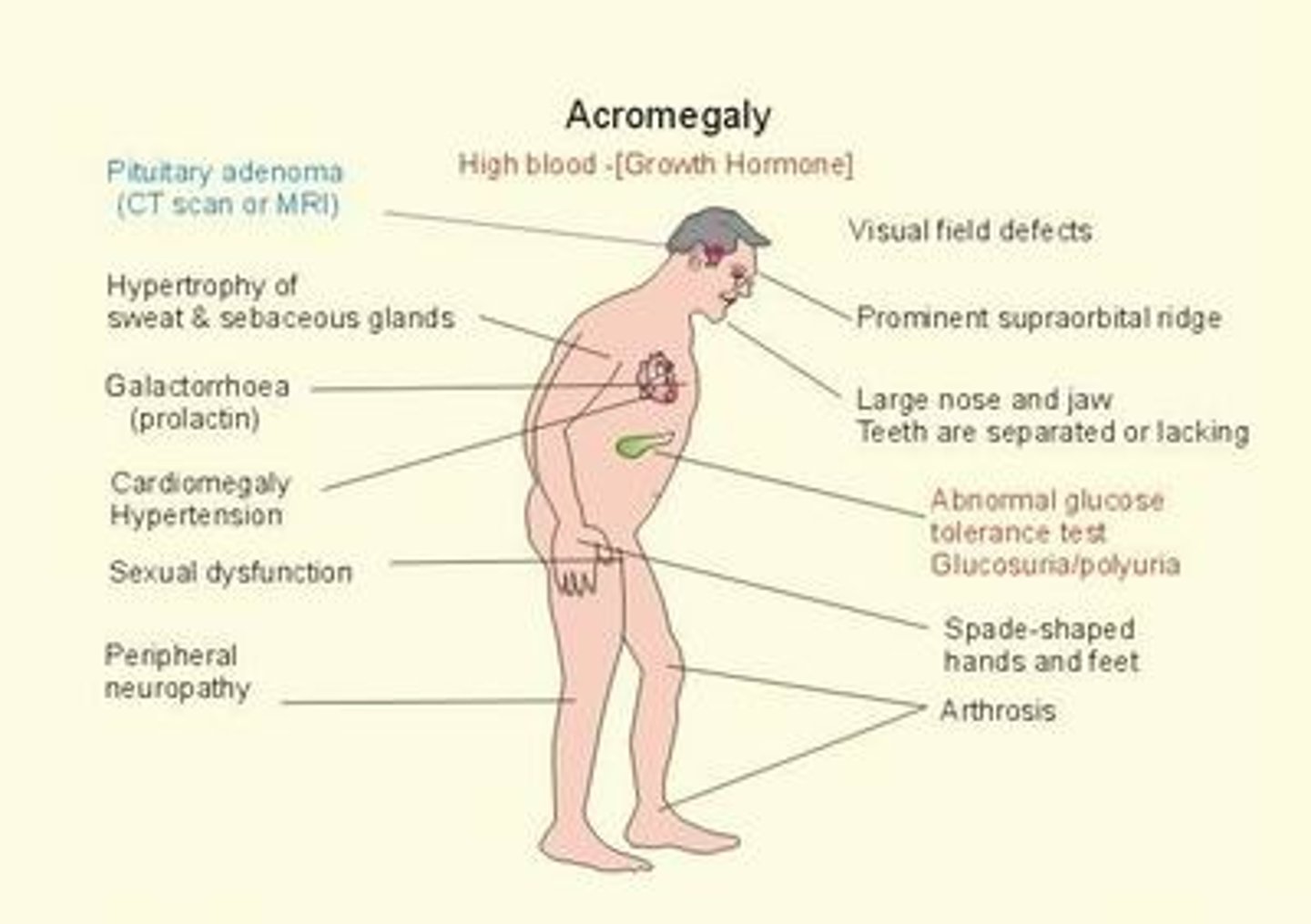
Acromegaly
Pituitary adenoma secreting excess GH during adulthood (after epiphyses have fused)
Symptoms and signs of Acromegaly
- Enlarged hands and feet
- Enlarged facial features (facial bones, lips, nose, tongue)
- Fatigue
- Joint/muscle weakness
- Pain and limited joint mobility
- Vision problems
- Headaches
- Menstrual cycle irregularities
- Erectile dysfunction
- Reduced libido
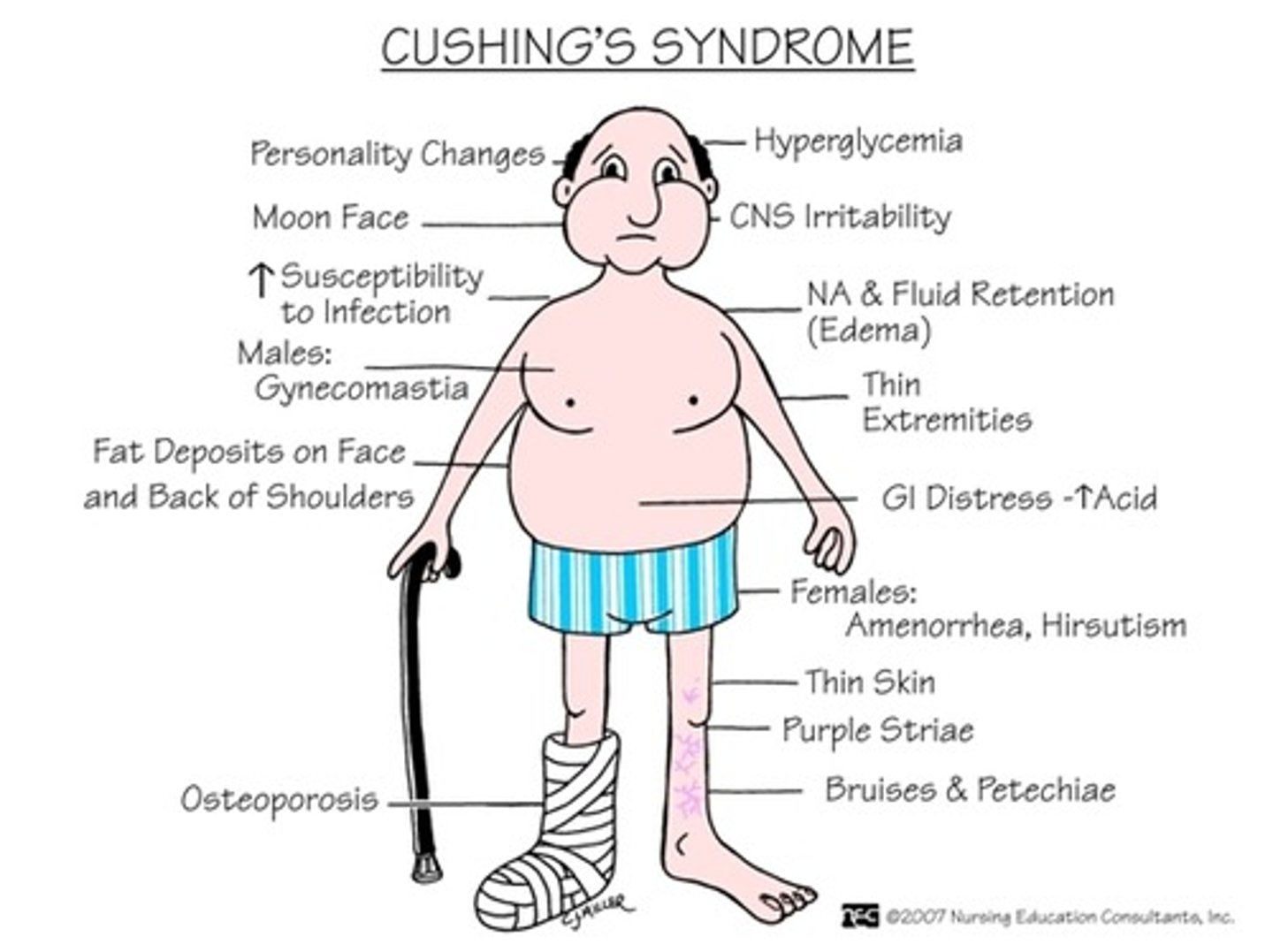
Cushing's disease
Pituitary adenoma secreting ACTH; increased cortisol, increased ACTH
Symptoms of Cushing's disease
- Weight gain and increase in body fat on abdomen/chest
- Thin arms and legs
- Build-up of fat on back of neck and shoulders
- Moon face/rounded face, puffiness, redness
- Easy bruising
- Large purple stretch marks
- Skin ulcers (poor wound healing)
- Amenorrhea
- Purpura
- Abdominal striae
- Osteoporosis
Management of Cushing's disease
- Pituitary adenoma/tumour =
Surgery, radiotherapy, medical therapy
- Pituitary hormonal secretion deficiency or excess
Hormonal therapy, medical therapy
Name the pituitary gland cells that release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
Thyrotrophs
Which hypothalamic hormone regulates secretion of TSH?
Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)