CH 1.3: Physical Foundations
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Why do concentrations of molecules such as hemoglobin and glucose stay constant?
Rate of synthesis or intake = Rate of breakdown, consumption, or conversion
What is a system?
All the constituent reactants and products, the solvent that contains them, and the immediate atmosphere
What is the a universe?
The system and its surroundings
What is an isolated system?
System exchanges neither energy or matter with its surroundings
What is a closed system?
System exchanges energy but not matter with its surroundings
What is an open system?
System exchanges both energy and matter with its surroundings
What type of system are living organisms?
Open
How do organisms get energy?
Take up chemical fuels from the environment and oxidizes them
Absorbs energy from sunlight
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Conservation of energy
In any physical or chemical change, the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant, although the form of the energy may change
What energy can cells interconvert?
Chemical
Electromagnetic
Mechanical
Osmotic
When a cell doesn’t have enough energy, what happens?
Goes from steady state towards equilibrium with its surroundings, causing the cell to decay
What are oxidation-reduction reactions?
One reactant is oxidized as another is reduced
What does it mean to be oxidized?
Loses electrons
What does it mean to be reduced?
Gains electrons
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Randomness in the universe is constantly increasing.
What is entropy (s)?
Randomness or disorder of components of a chemical system
What is G?
Gibbs free energy
What is enthalpy (H)?
The heat of a system
What does it mean if delta H is negative?
Releases heat/ exothermic
What does it mean if delta H is positive?
Absorbs heat/ endothermic
What does it mean if delta S is positive?
Randomness increases
What does it mean if delta S is negative?
Randomness decreases
What is the Gibbs free energy equation?
Delta G = Delta H - (T)*(Delta S)
What does it mean if Delta G is negative?
Energy is released
What does endergonic mean?
Requiring energy
What does exergonic mean?
Releasing energy
What Delta G is thermodynamically favorable?
Delta G is negative
What does delta G mean?
Free energy change
What are bioenergetics?
Study of energy transformations in living systems
In closed systems, chemical reactions occur until what?
Equilibrium
What is equilibrium?
The rate of product formation is equal to the rate of reactant formation
In exergonic reactions, is there available energy to do work?
Yes
If the reaction is aA + bB → cC + dD, what does Keq equal?
Keq = [C]c [D]d / [A]a [B]b
What does it mean if Keq » 1?
Reaction proceeds until reactants are completely converted to products
What does Delta G note mean?
Standard free energy change
What does Delta G equal in terms of Delta G not?
ΔG = ΔG° + RT ln ([Initial Concentration of Products]p / [Initial Concentration of Reactants]r )
At equilibrium, ΔG is?
Zero
What does delta G not equal in terms of Keq?
ΔG° = -RT ln (Keq)
If Keq »1, then ΔG° is?
Large and negative
If Keq « 1, then ΔG° is?
Large and positive
What is kinetics?
The study of reaction rates
What is thermodynamics?
The study of how energy (heat) transforms and transfers during chemical reactions and physical transformations
Why is ATP breakdown exergonic?
All living cells maintain a concentration of ATP far above its equilibrium concentration
Why does ATP breakdown drive many endergonic processes?
The net reaction will be exergonic, which is favorable
Why is the transfer of a phosphoryl group to another small molecule important?
It causes the conservation of the chemical potential that was originally in ATP, making the new reaction spontaneous
What does kinetically stable mean?
Uncatalyzed breakdown occurs slowly
What does an enzyme do?
Enhance rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process
What is an activation barrier?
The path from reactants to products has an energy barrier that needs to be surmounted for the reaction to proceed
What is a transition state?
Highest energy point where bonds are partially broken and formed
What is activation energy (ΔG‡)?
The difference in energy between reactant in its ground state and transition state
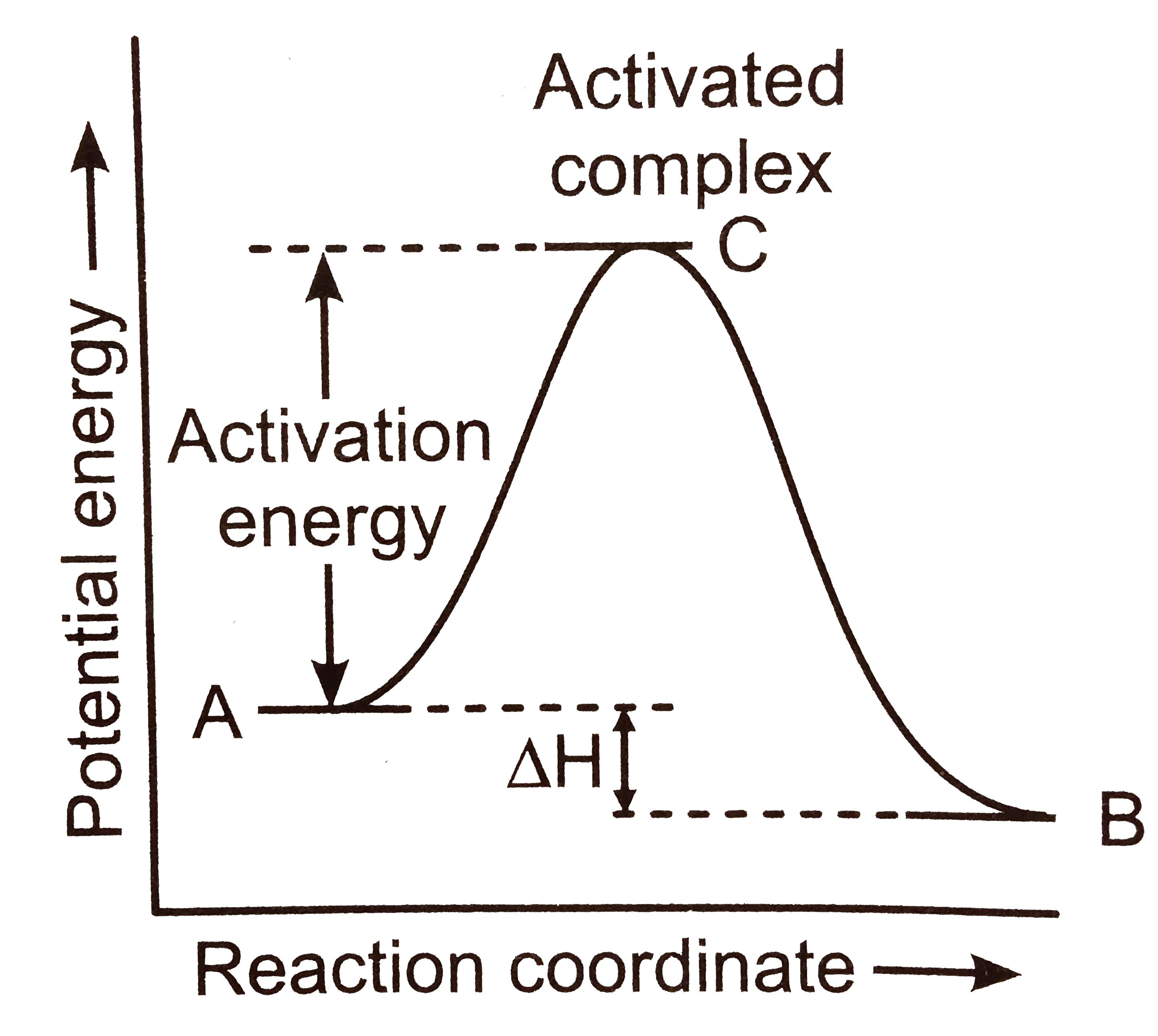
Why do enzymes lower the activation energy?
The binding of an enzyme to the transition state makes the transition state more stable, releasing energy (exergonic) which is favorable
Why is exergonic more stable?
When a reaction releases energy, the molecules are going from a higher energy to a lower energy meaning the products are more stable
Why does an enzyme-catalyzed reaction occur incredibly fast (x1012)?
The reactants have to bind to the enzyme in a stereospecific orientation. Since the reactants are held in a position that is favorable, there is an increase of probability of productive collisions between reactants
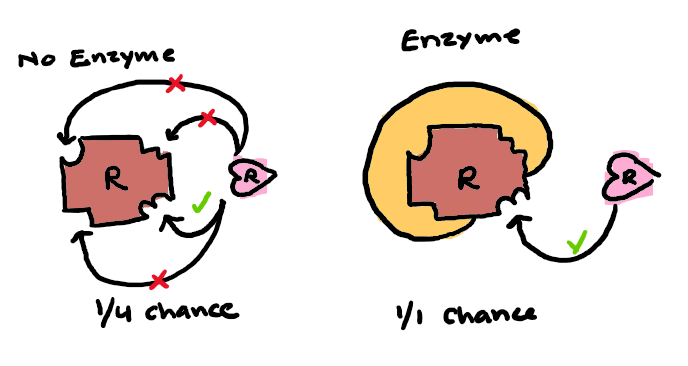
Why do enzymes lower activation energy selectively?
It’s due to the multiplicity, their specificity, and their susceptibility to regulation
What are pathways?
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are functionally organized into sequences of consecutive reactions; product of one reaction becomes reactant of next reaction
What is catabolism?
Degrade organic nutrients into simple end products to extract chemical energy and convert into its most useful form
What are some crucial molecules that catabolism produces?
ATP
NADH
NADPH
What is anabolism?
Convert smaller precursor molecules to longer, more complex molecules
What is metabolism?
Consist of catabolism and anabolism
What are the connecting links between catabolic and anabolic reactions?
ATP, adenosine triphosphate
CTP, cytidine triphosphate
UTP, uridine triphosphate
GTP, guanosine triphosphate
What is feedback inhibition?
Keeps production and utilization of each metabolic intermediate in balance