MCAT Biology Draft 2025!
1/98
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
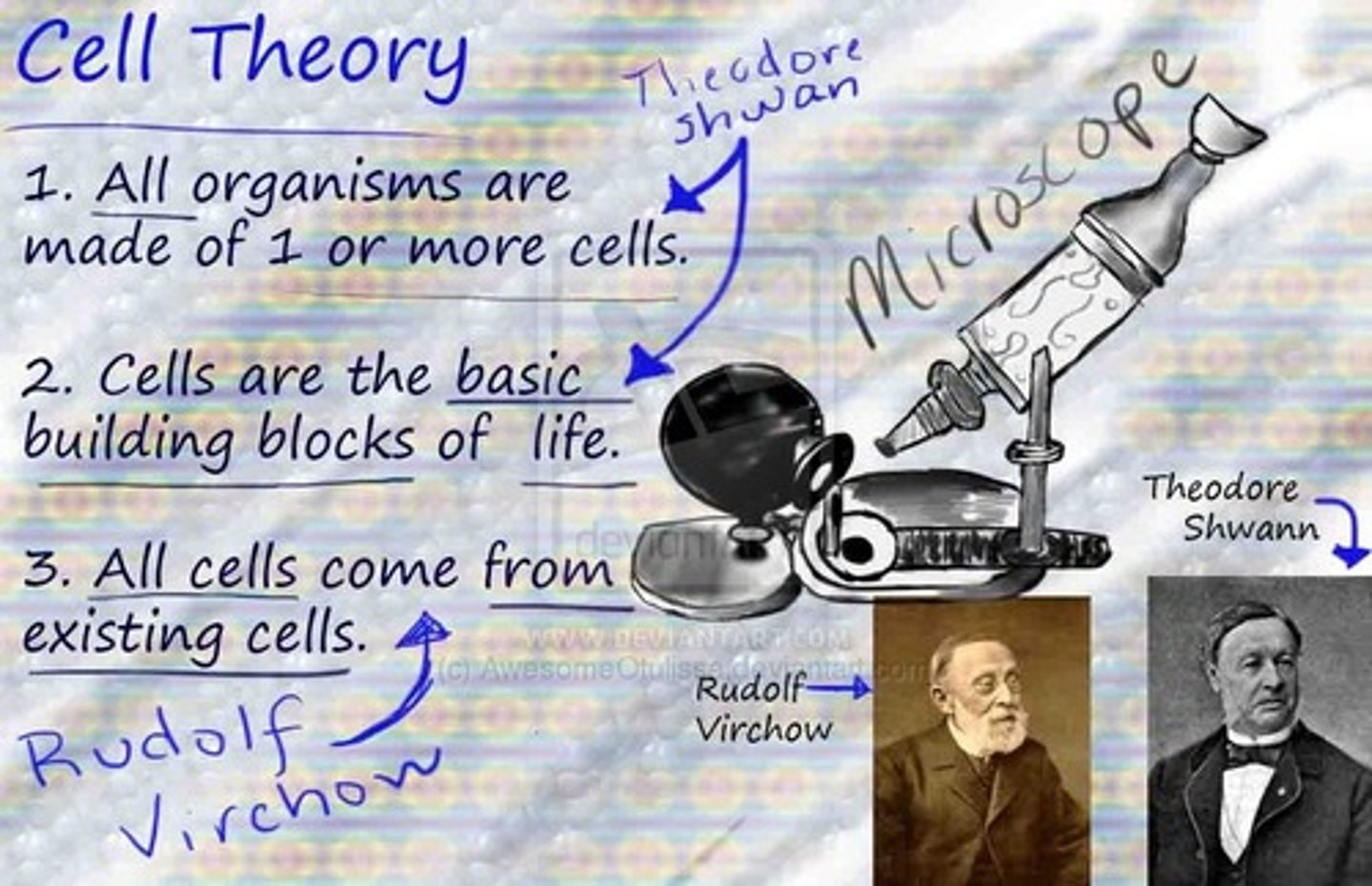
Cell Theory
1. All living things are made up of cells
2. All cells come from pre-existing cells
3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
4. Cells carry Genetic Information (DNA) in Nucleus
Central Dogma
DNA —> RNA —> Protein
Replication —> Transcription —> Translation (Occurs in Cytoplasm)
Prokaryotic Cell
Reproduce; By Binary Fission
Contains Single circular chromosome
Eukaryotic Cell
Compartmentalization
Organelles Membrane Bound
Have Nucleus
Reproduce; By mitosis
Contain Multiple Linear Chromosomes
Endomembrane System (endo- = “within”)
A group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
Nuclear envelope
Golgi apparatus
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Vesicles
Lysosomes
Vesicle
Plasma Membrane
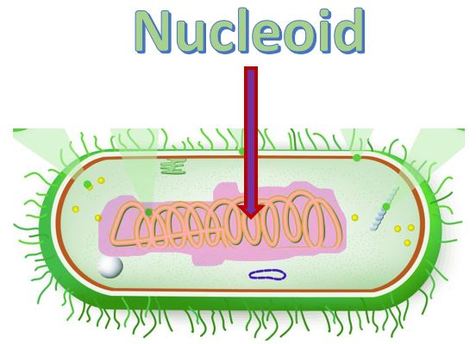
Nucleoid Region
DNA region in Prokaryotes
Nucleus
A part of Eukaryotic cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces Ribosomes
Types of RNA
mRNA (Messenger RNA): carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
tRNA (Transfer RNA): brings amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
rRNA (Ribosomal RNA): a component of ribosomes, which are the sites of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
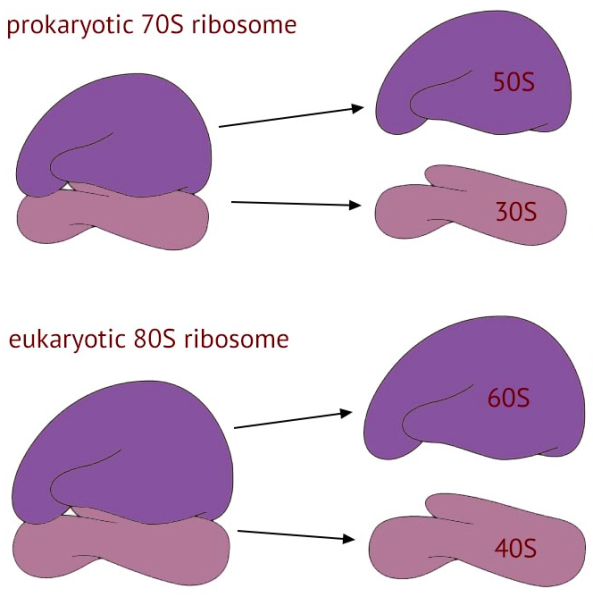
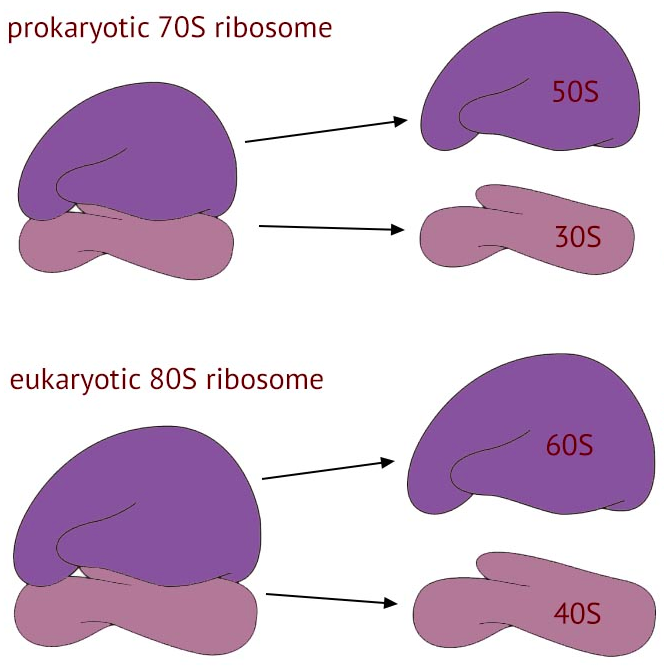
Ribosome Sizes
Prokaryotes Ribosomes
70s —> 50/30
Eukaryotes Ribosomes
80s —> 60/40
30 of Prokaryotes and 40 of Eukaryotes is where translation occurs
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth ER
Detoxification
Lipid Synthesis
Rough ER
Embedded in ribosomes
Accept mRNA to make proteins
A network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis, consisting of smooth and rough sections. Smooth ER is primarily involved in detoxification and lipid synthesis, while rough ER is studded with ribosomes and aids in protein production.
Golgi Apparatus
Package proteins - Protein secretion
Modify / distribute proteins. Only in eukaryotes.
Put proteins in vesicle and prepare them for execration (being released from the cell)
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Peroxisomes
Collect and break down material.
Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
Lysosomes
Demo & Recycling center. Made by Golgi. Single membrane.
Uses chemicals to break down food and proteins
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Glycolysis occurs here
Vacuole
a space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluid.
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Centrioles
Located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division
Example: 9 groups of microtubules, pull chromosomes apart
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome.
In prokaryotes. Carry DNA not necessary for survival.
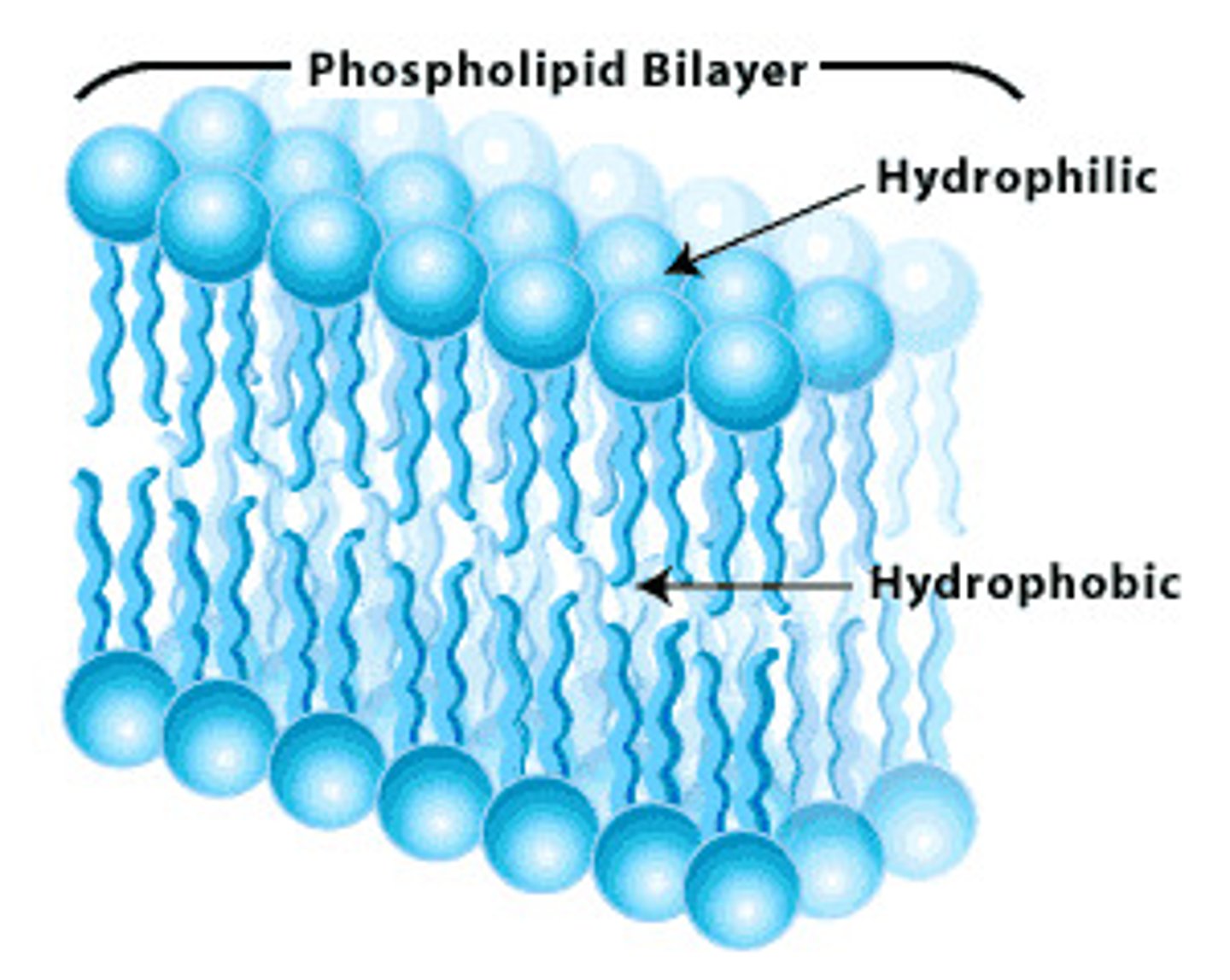
Cell/Plasma Membrane
Semi-permeable and made up of Phospholipid Bilayer
Prefers passing of small, nonpolar, and uncharged polar molecules
Phospholipid Bilayer
1. Phosphate head
2. Glycerol Backbone
3. Two Fatty Acids
Fluid Mosaic Model
Fatty acids
Long Hydrocarbon Chains that are key components of Lipids
Plasma Membrane Parts
Amphipathic - Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
Phospholipids Bilayer - Phosphate head and two Lipid tail.
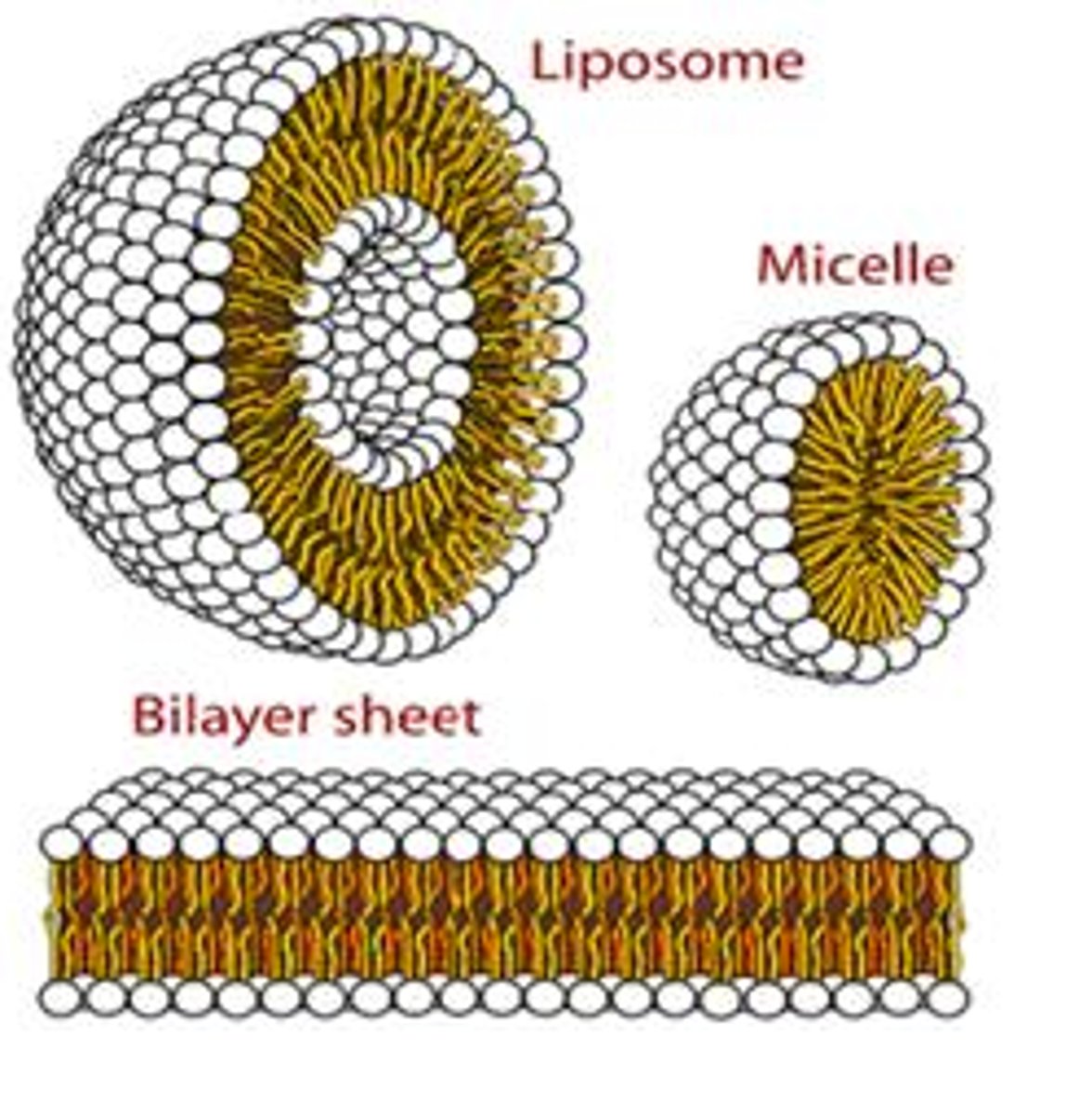
Micelles
Lipid molecules orient with polar (hydrophilic) head toward water and nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails away from water

Liposome
Small membrane bounded transport vesicles
Have been used as a drug delivery recently
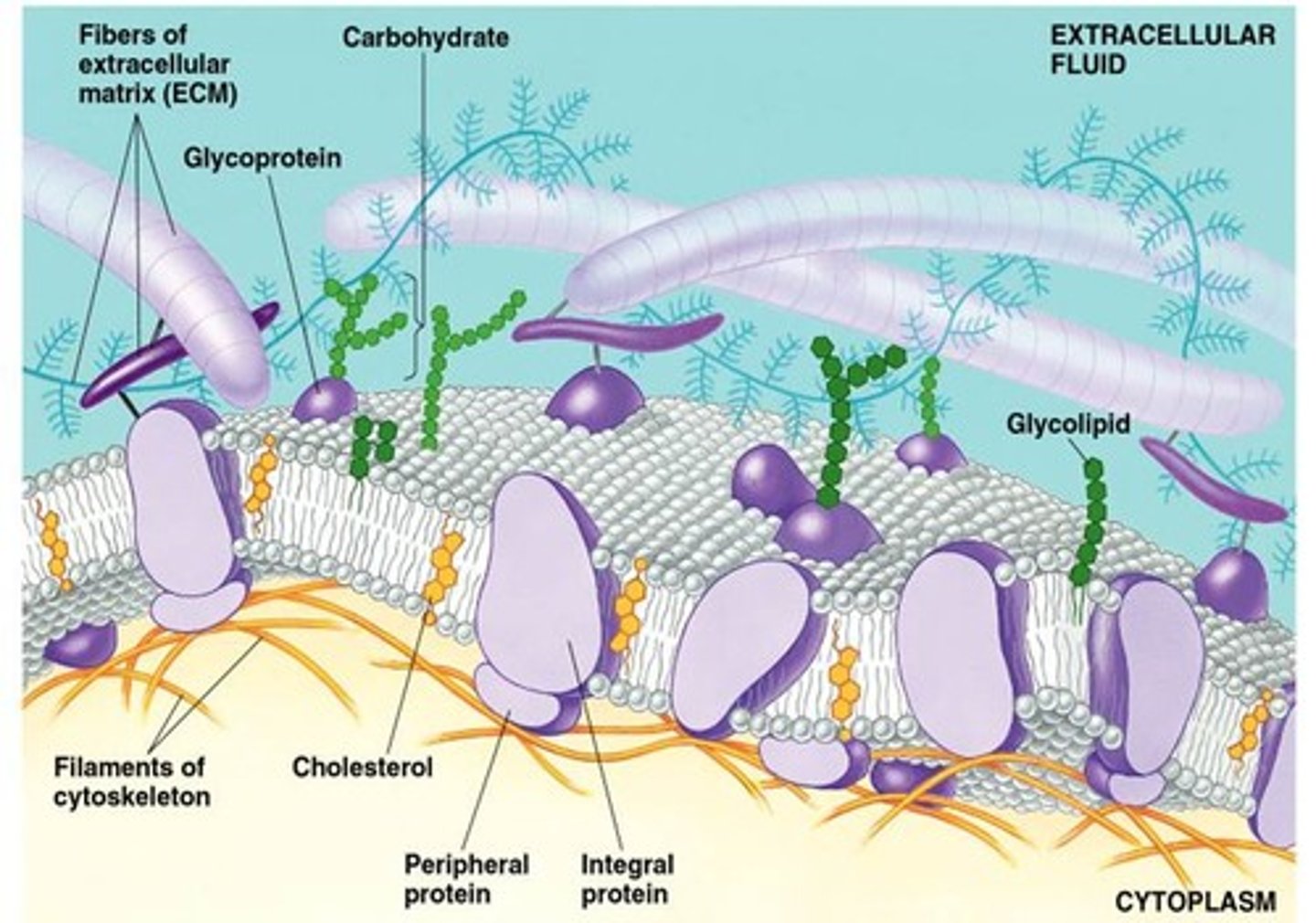
Cholesterol
Helps Phospholipid bilayer lubricate when it's cold and glues phospholipid together when its hot.
Glycolipid
A lipid covalently attached to a carbohydrate Plasma membrane
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates in Plasma membrane
Membrane Proteins
Integral proteins and Peripheral proteins
Peripheral Proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.
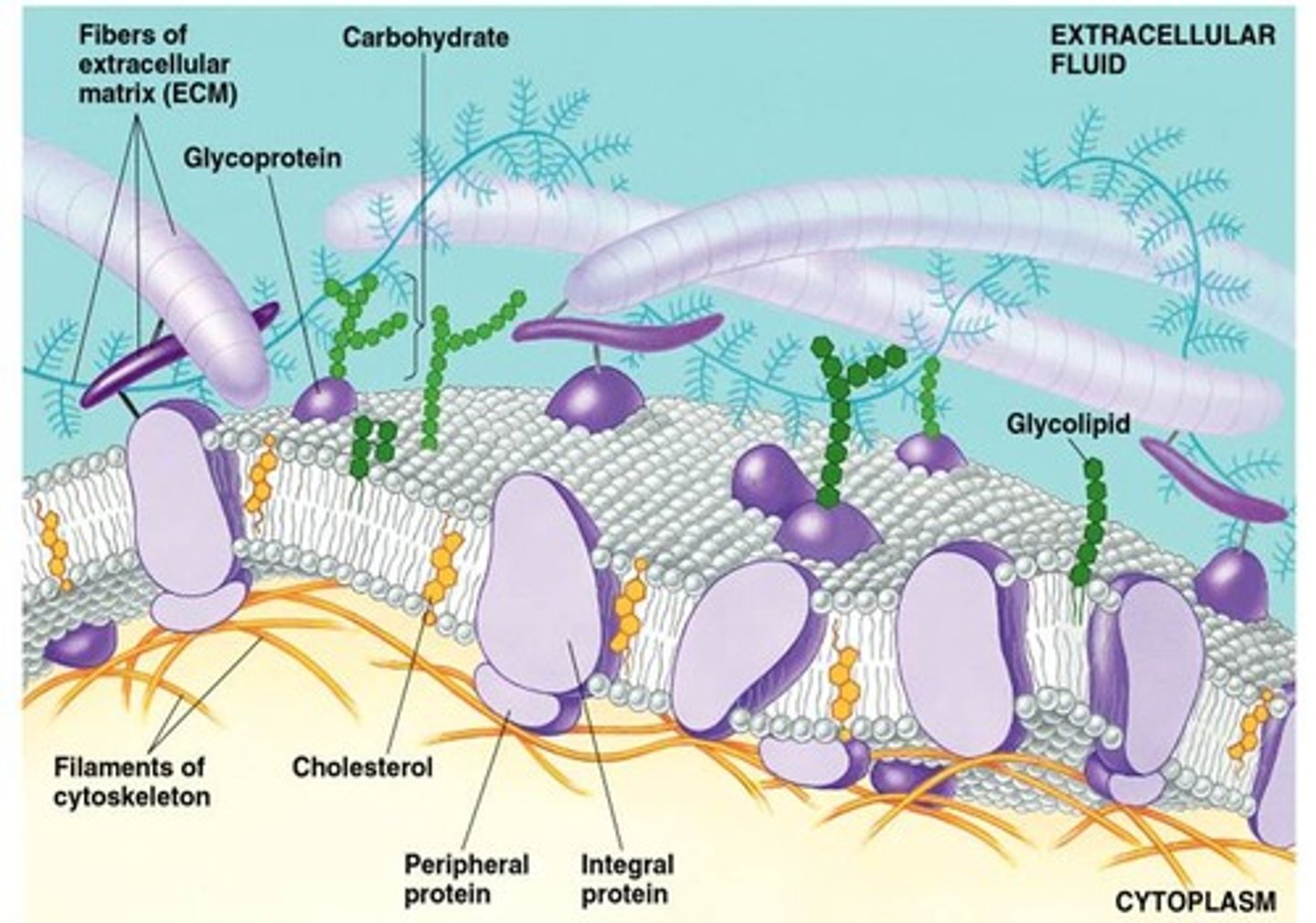
Integral Proteins
Embedded the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
Examples of Hydrophobic Molecules
O2, CO2, N2, benzene, lipids and cholesterol
Example of Small Unchanged Hydrophilic (polar)
Urea, Glycerol H2O
Examples of Large Hydrophilic (Polar) Molecules
Glucose and Sucrose
Examples of Ions
H+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, Mg2+, HCO3-
Simple Diffusion
Doesn't require energy, depends on concertation gradient
Direct transport of molecules across the cell membrane
Small uncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
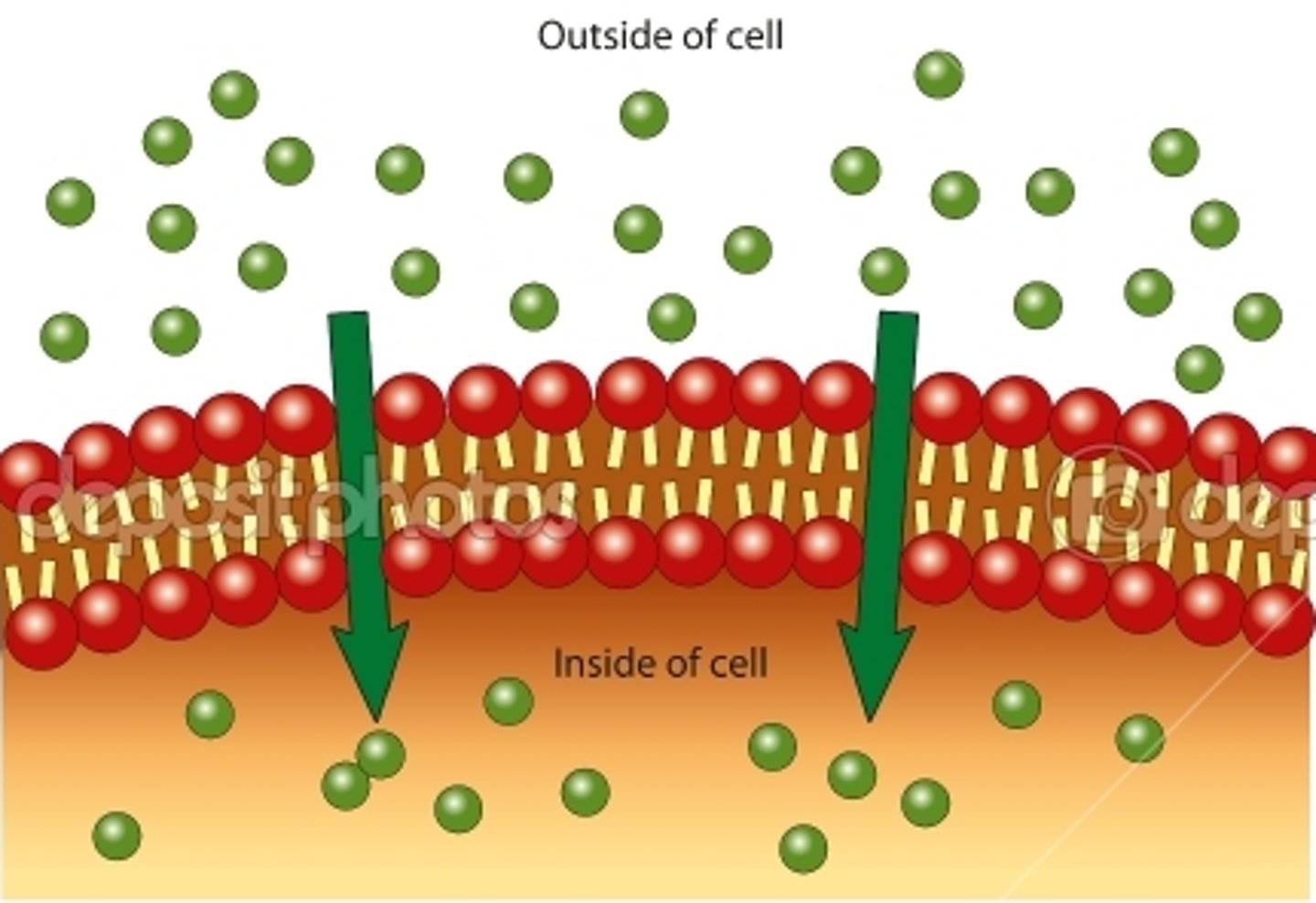
Facilitated diffusion
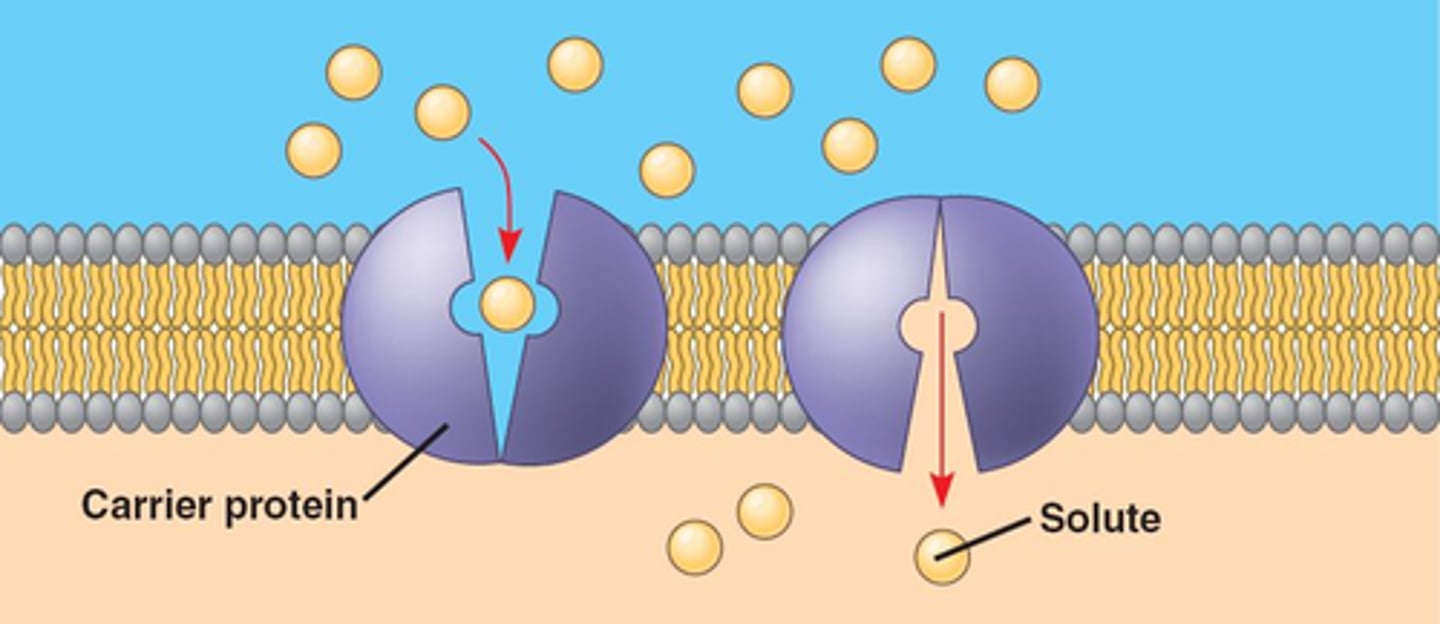
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
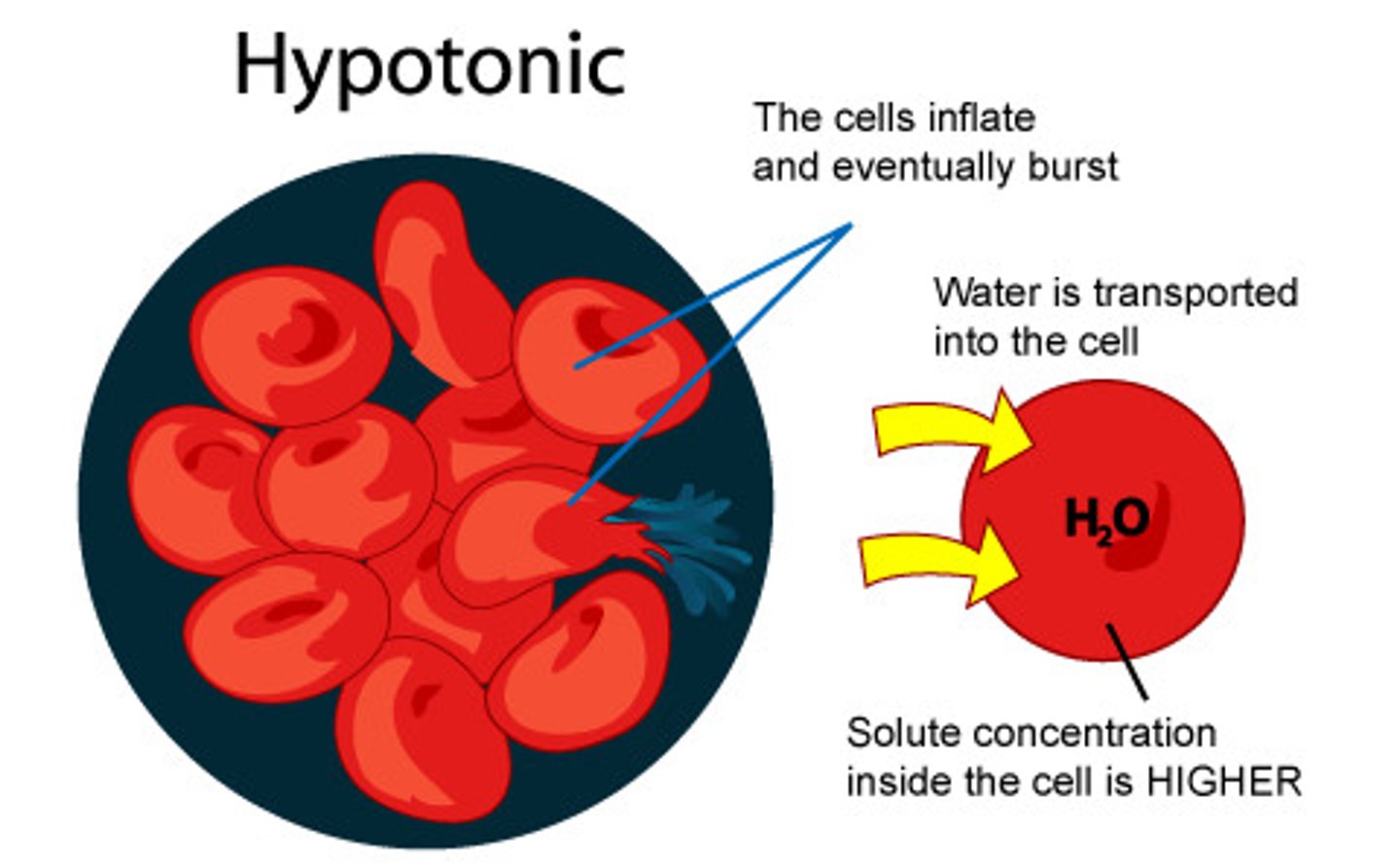
Hypotonic Solution
Cell is in a solution that is less concentrated than it self.
H2O rushes into the cell to neutralize it, cell might burst process called cytolysis OR swell
Isotonic Solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
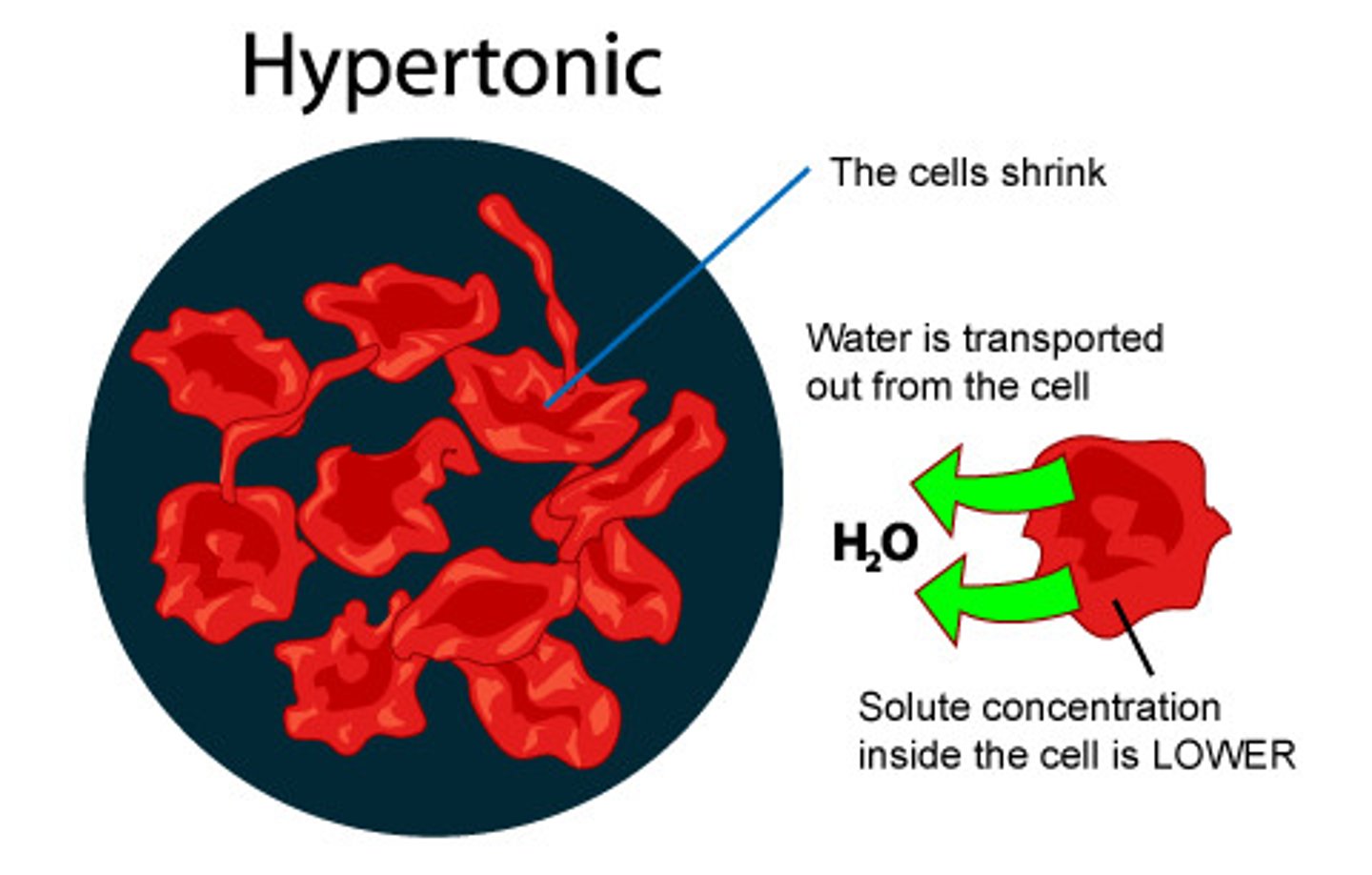
Hypertonic Solution
Cell is in a solution that is more concentrated than it self.
H2O get's out of the cell to neutralize it the outside, resulting cell to shrink
Passive Transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
High to low
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Low to high
Secondary Active Transport
Form of active transport which does not use ATP as an energy source; rather, transport is coupled to ion diffusion down a concentration gradient established by primary active transport.
We use ATP to create concentration gradient of Na+. Since we used energy to create Na+. We use the energy from this later on to to transport something else like Glucose
Why is it helpful to give Glucose, water and Sodium to someone who is dehydrated? why not just water?
Water alone doesn't get absorbed at a fast enough rate, but with Glucose and sodium they are absorbed together into the cell in the intestines. The concentration of the intestines will be high and now water will rush into the intestines through osmosis.
Solubility of Vitamins
Fat Soluble, Not water Soluble
Vitamin K
Vitamin A
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
Mnemonic: KADE
Vitamin C is not water Soluble, it's found in orange juices
Why is it harmful to drink Salt Water?
Dehydrate you more
Sea water has a high osmatic pressure, causing water to flow out of body cells into the intestines.
Proteins that are used to transport things inside Plasma Membrane
1. Pores
2. Channels
Pores and channels are passive transport
3. Carries - can be Active and Passive Transport
Pores
Holes that allow water to flow through
Can't be open/ closed, They can only be added or remove them
Aquaporins are an examples of pores
Aquaporins
Water channel proteins
Regulated by adding/subtracting the number of pores in membrane.
Example: Add pores if want to make the PM more permeable to water and vice versa.
Channels
Can be opened/ closed
Regulated by
Voltage gated (charge)
Ligand Gated
Mechanically Gated - mostly found in heart
Carries
Change conformation
Can be saturated
Have Enzyme Kinetics - Km and Vmax
Can be inhibited/competitive inhibitors and etc
Can be Active and Passive Transport
Types of Carries
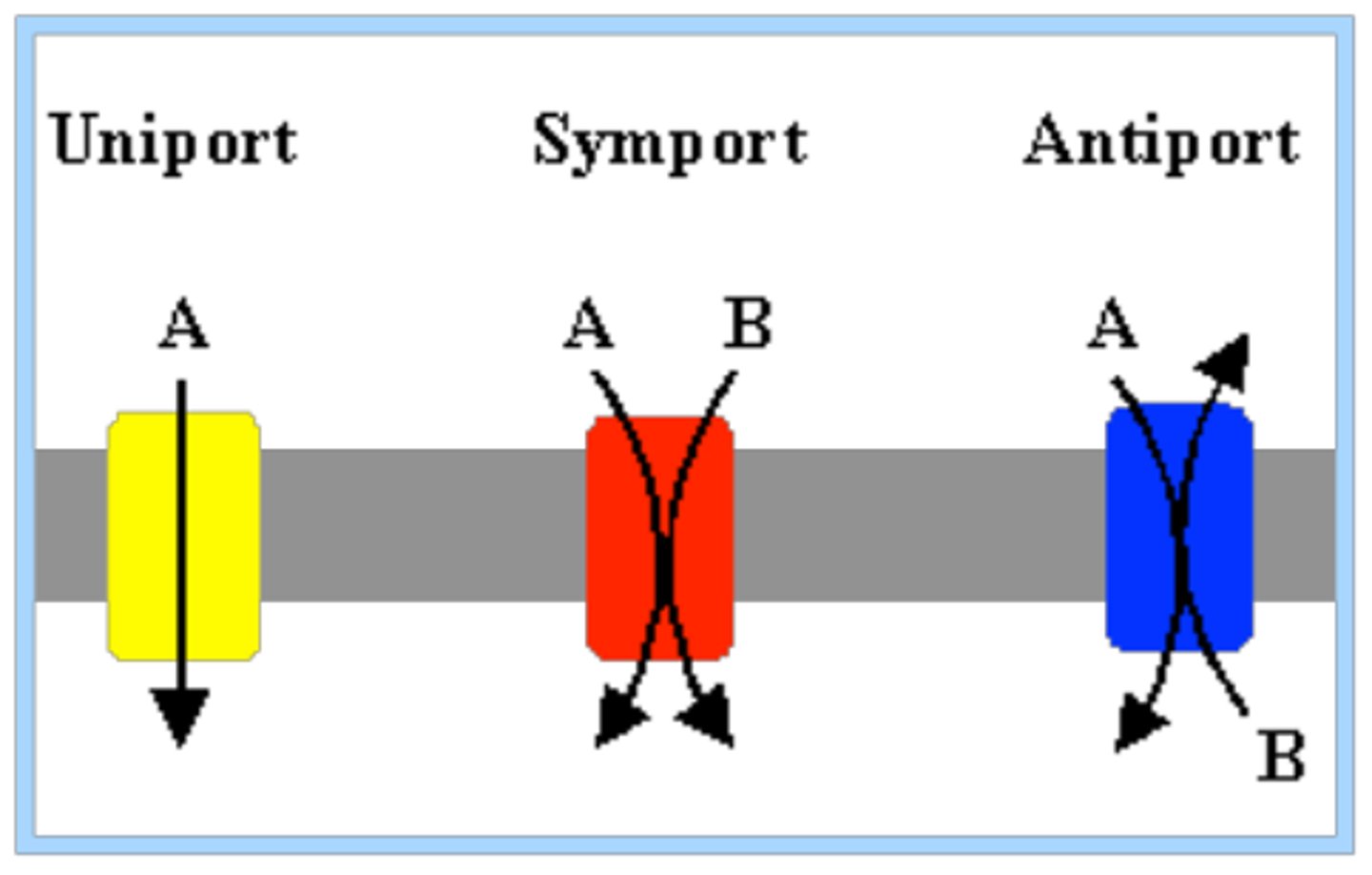
1. Uniporter
2. Symporter
3. Antiporter
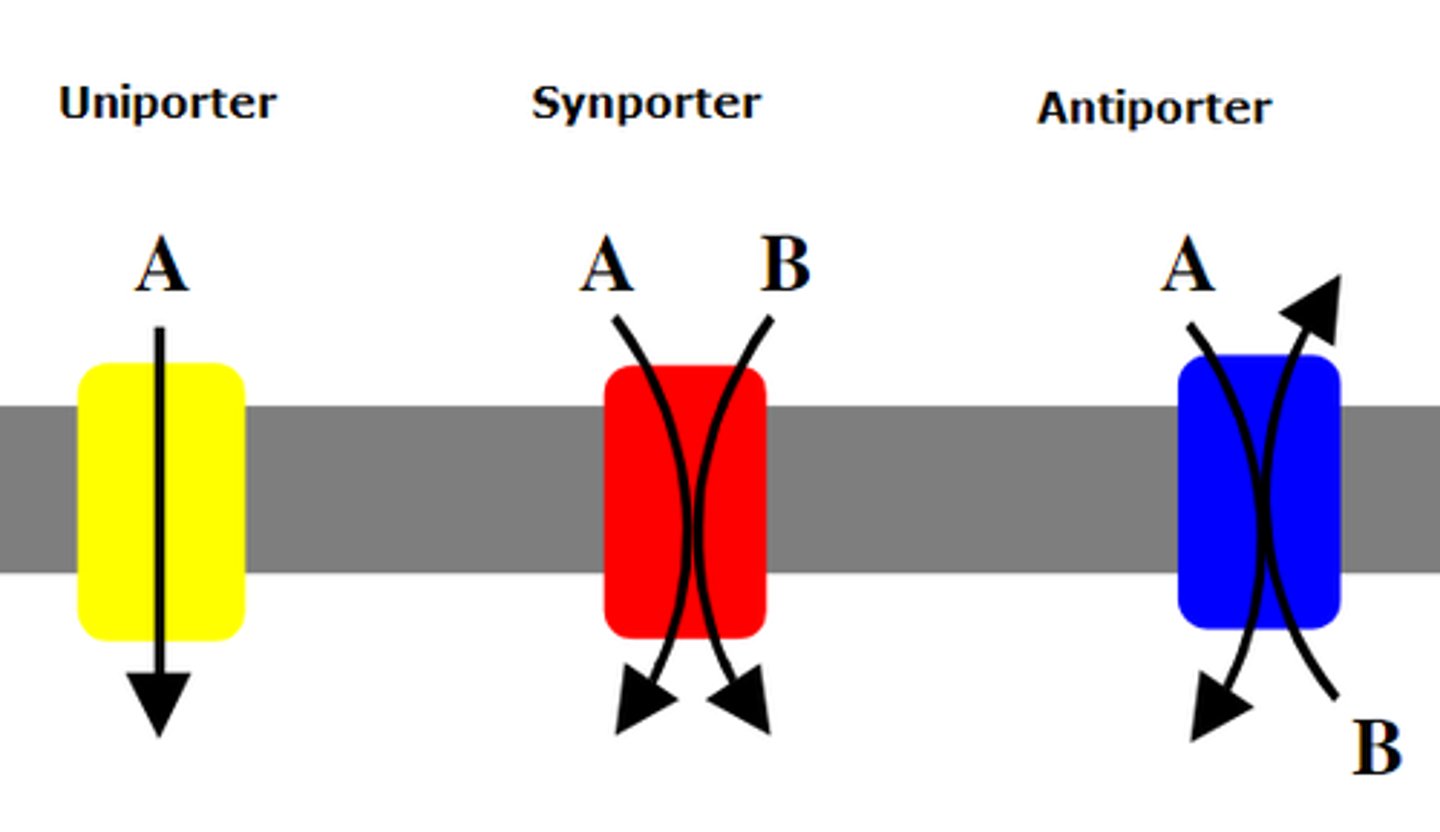
Uniporter
Transport one thing at a time
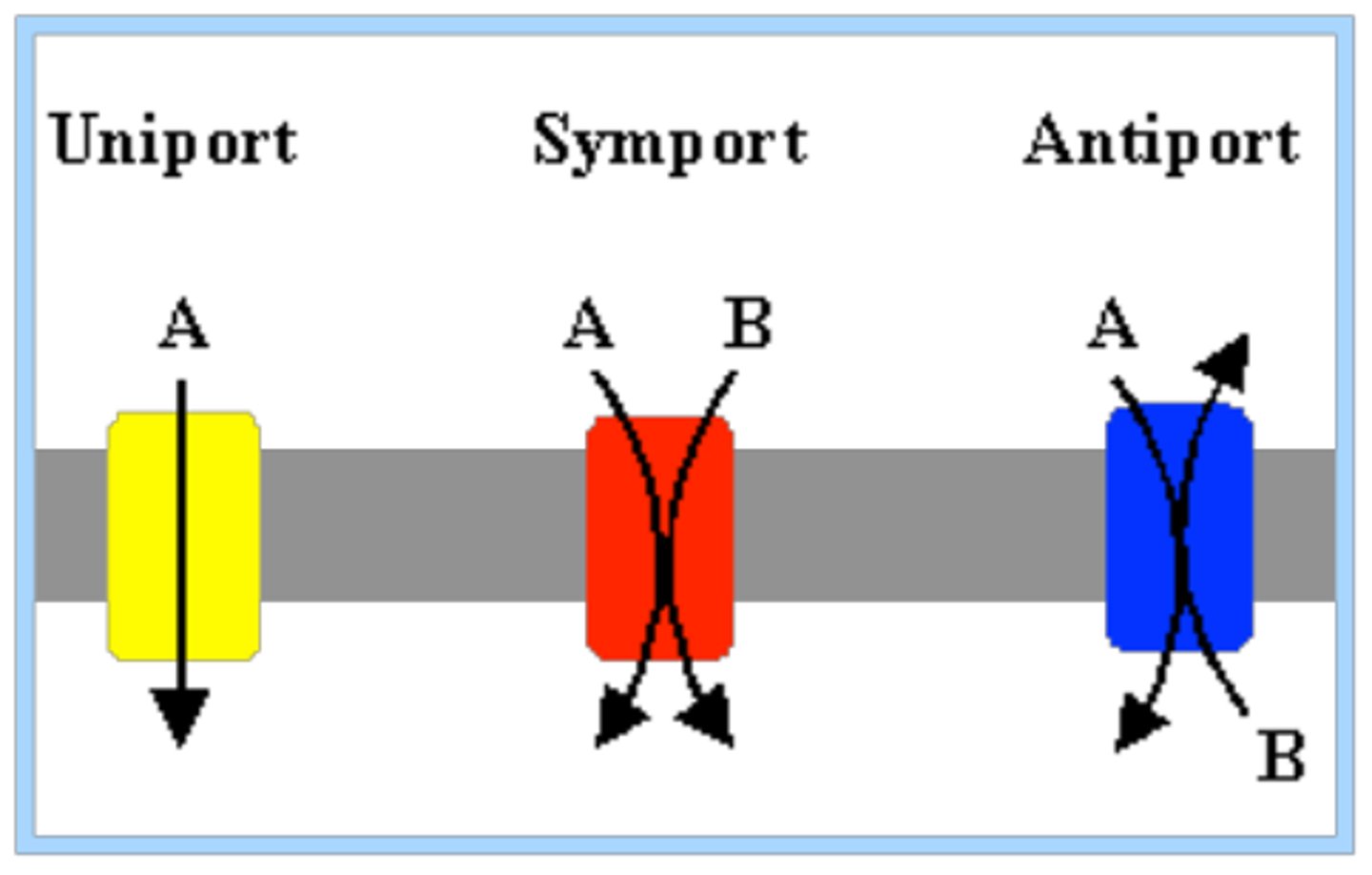
Symporter
Transports two solutes at a time in the same direction
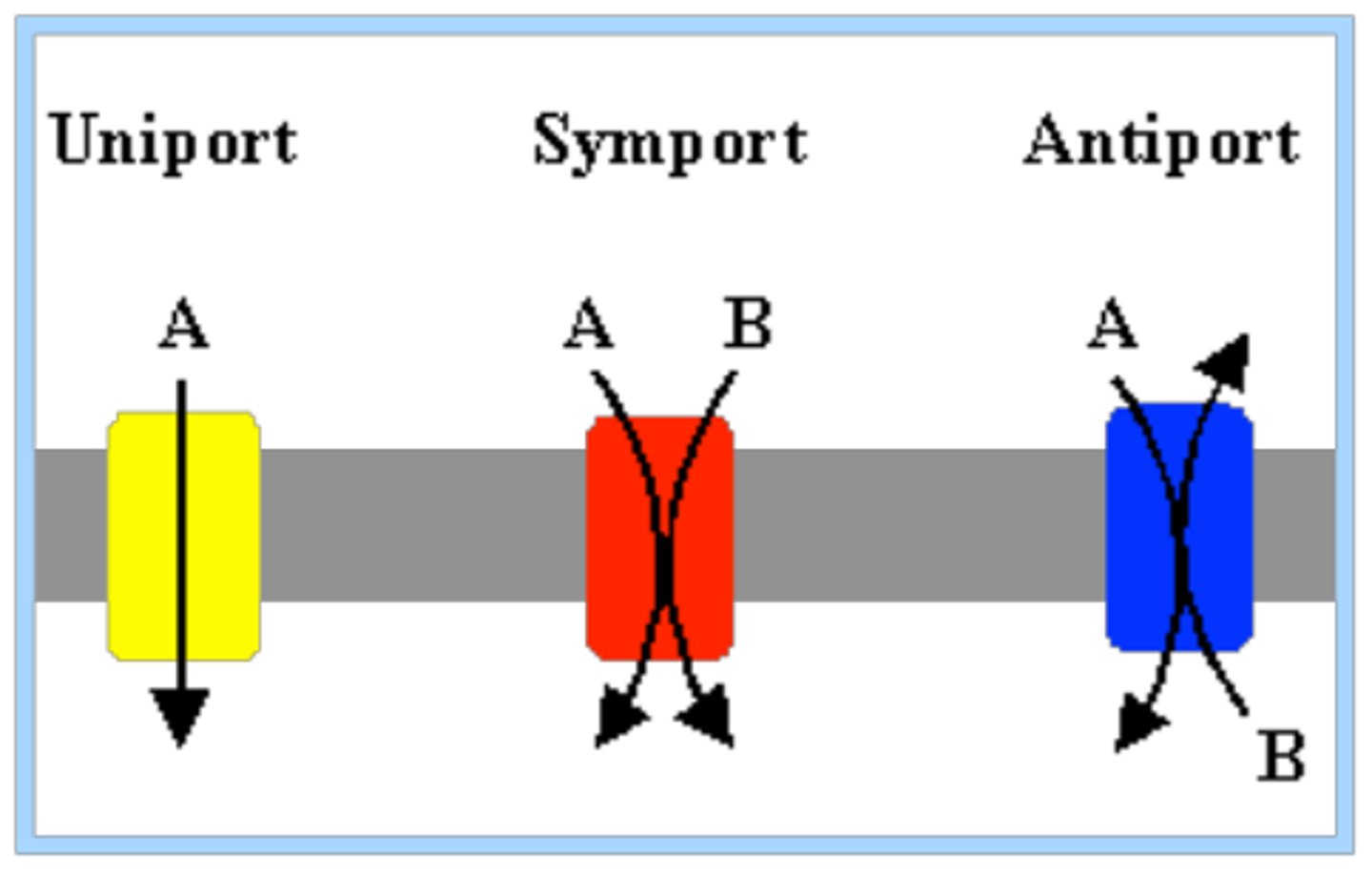
Antiporter
Transports two solutes at a time in the opposite direction. Example: Na+ and K+ ATPase. 2K+ in 3Na+ out. requires energy.
Requires input of energy Uses energy from ATP.
Action Potential
Cell typically hover around -70V
A lot sodium outside and overall charge of the cell is negative
Cells are usually at Resting Potential -70V, it gets a signal. Sodium channels open, more of Sodium Channels open.
Sodium flows into the cell, Na+ channels close and Ka+ opens
Action potential doesn't fire all the time, enough channels must be open in order to fire.
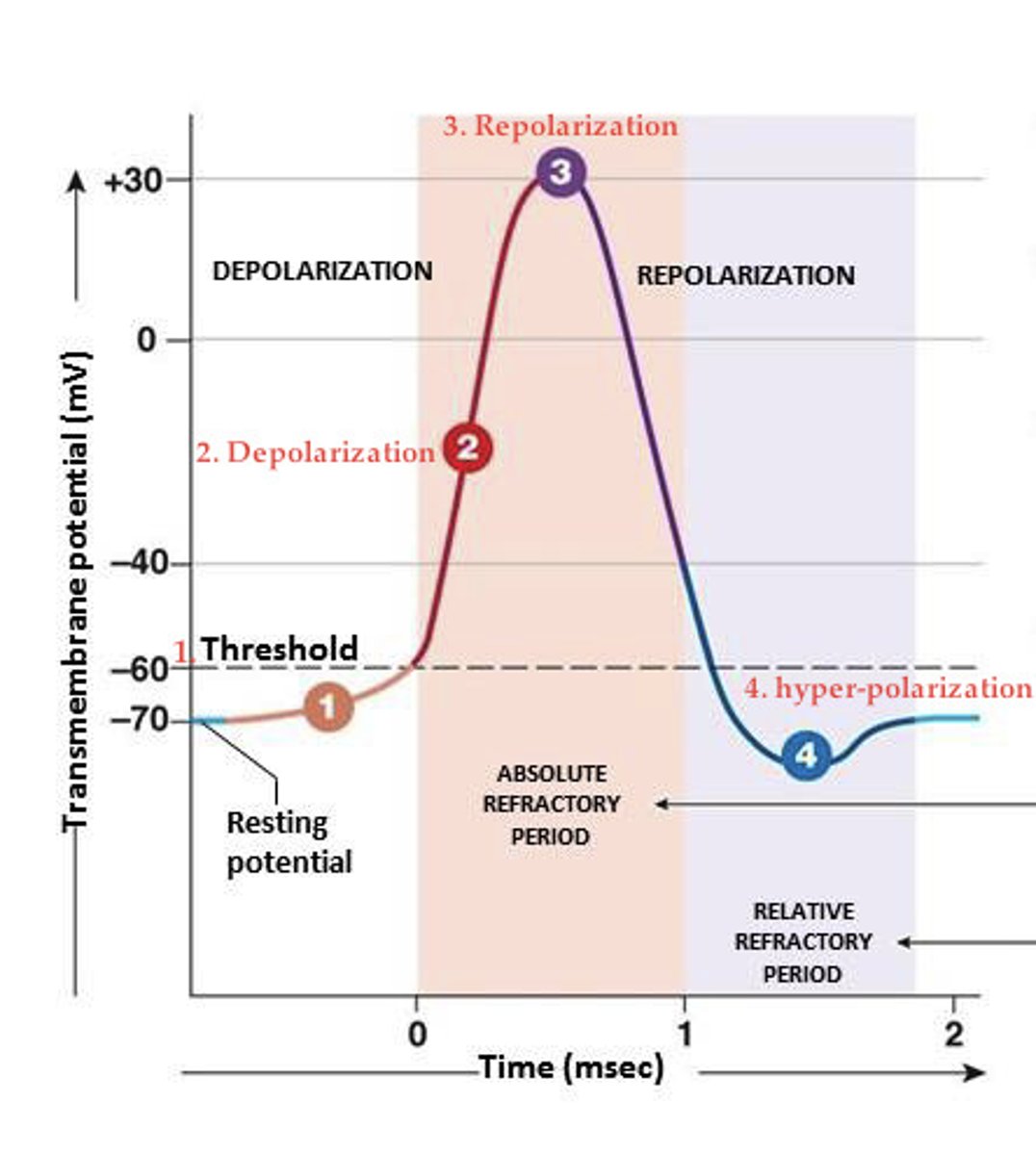
Chloride Channels
Inhibits neuron to fire
Sodium Potassium ATPase
2 K+ In
3 Na+ out
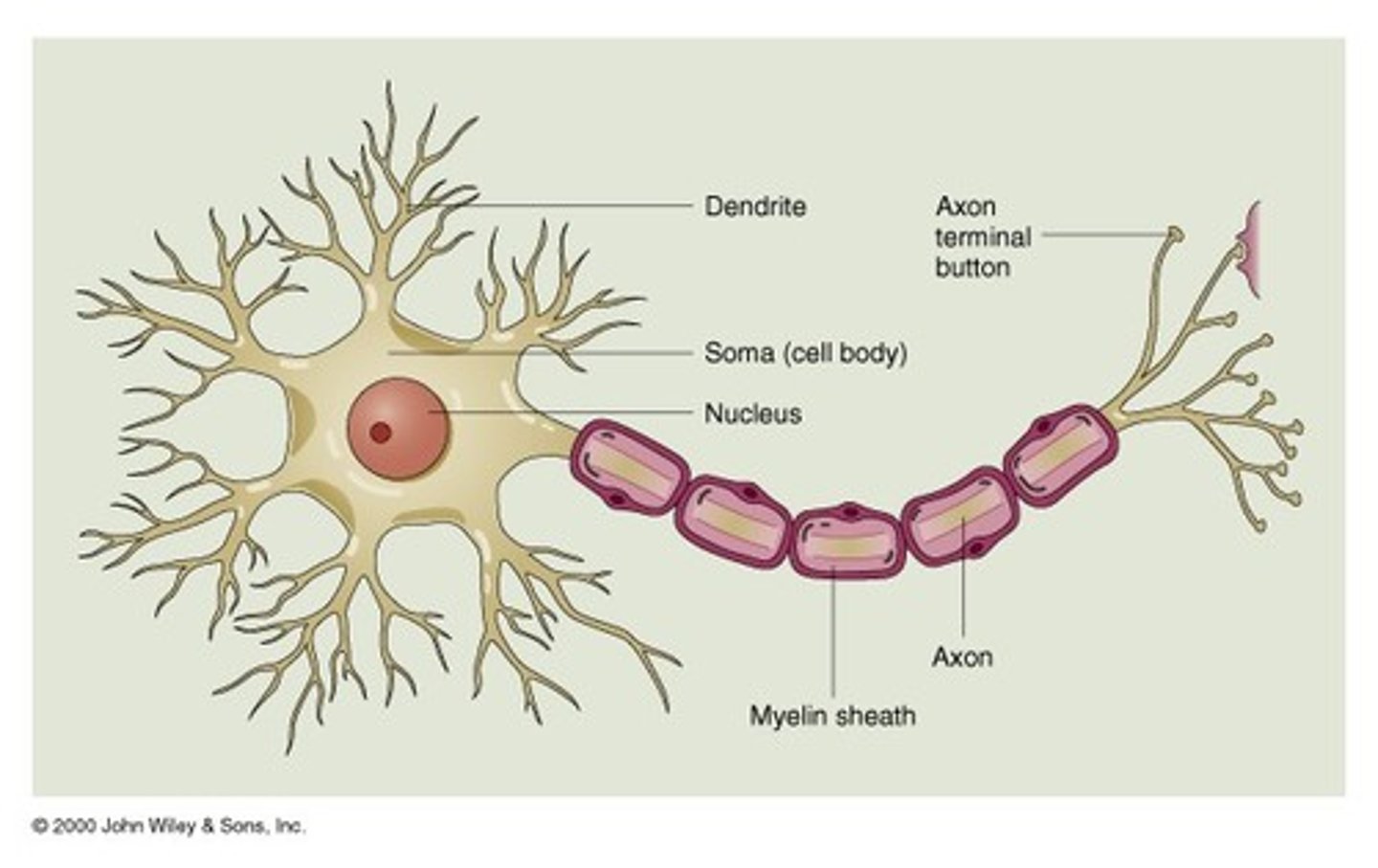
Neuron (Nerve Cell) Structure
Cell Body
Axon
Axon Terminal
Dendrites
Axon Hillock
Myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
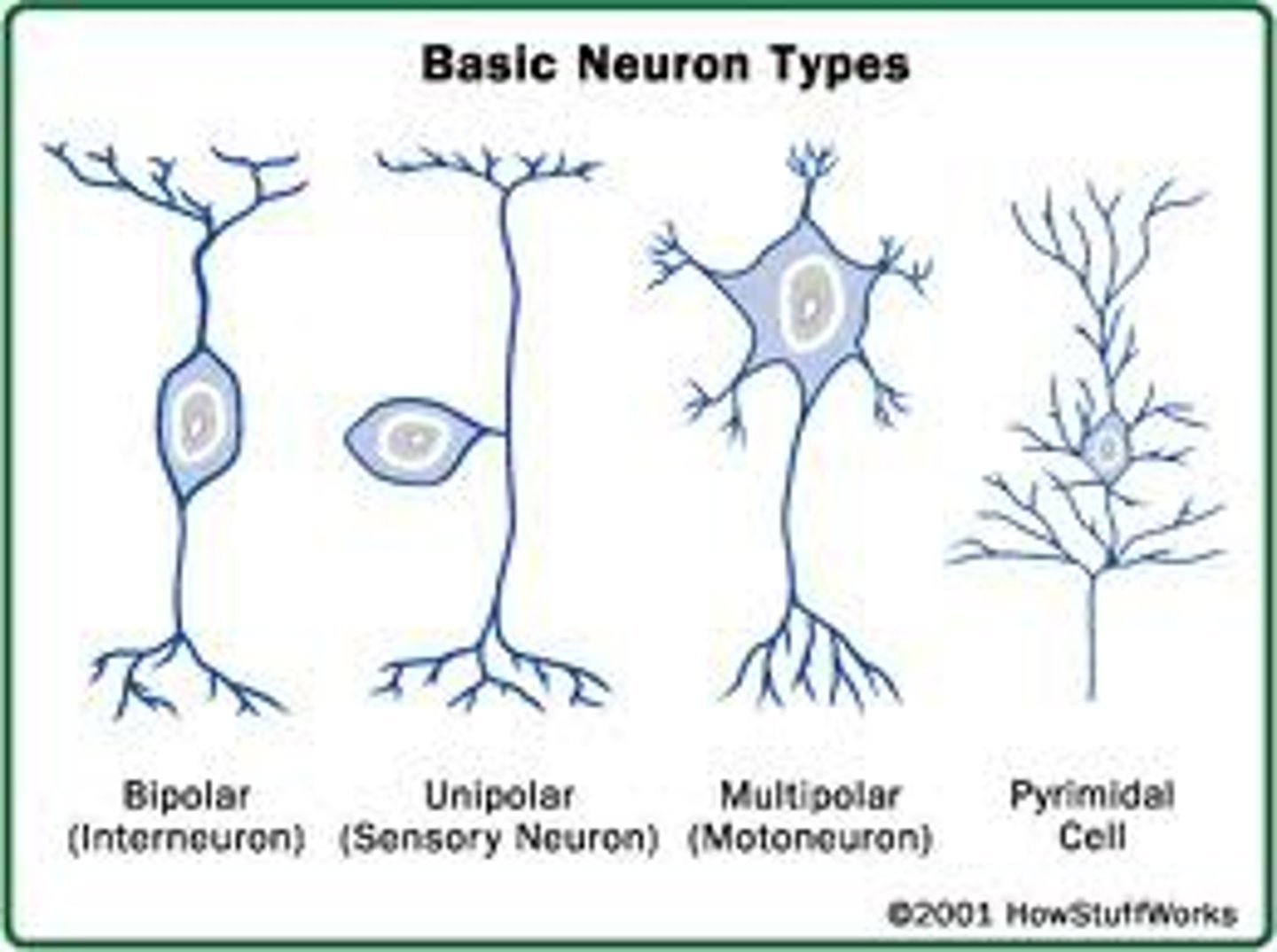
Neuron Types
Multipolar, bipolar, unipolar
At Which part of Neuron are the various excitatory and inhibitory signals summed together.
Axon Hillock
Connections between Neuron
Dendrites - beginning of a Neuron
Axon Terminal is end of old Neuron
Synapses
Dendrites - beginning of a Neuron
Axon Terminal is end of old Neuron
When Dendrites and axon hillock come together it's synapses
Synaptic Cleft
The space between when two Neurons coming together
presynaptic neuron and Post synaptic
Signal Termination
1. Degradation - Degrades neurotransmitter
2. Reuptake - back to presynaptic neuron
3. Diffusion -
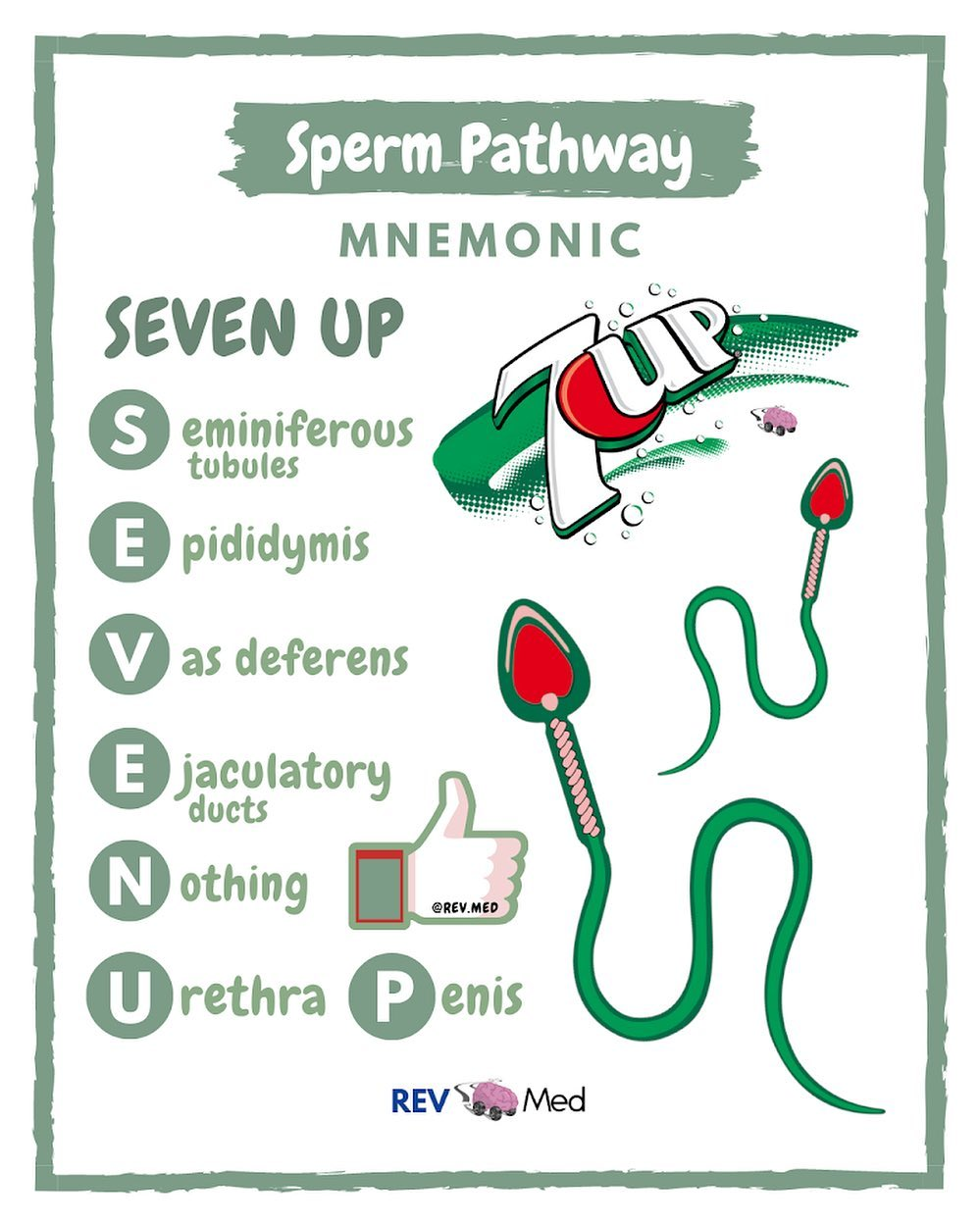
Pathway of Sperm
Mnemonics: SEVEN UP
Seminiferous tubules —> Epididymis —> Vas deferens —> Ejaculatory duct —> Nothing —> Urethra, Penis
Female: Vagina —>cervix —> uterus —>fallopian tube.
Fertilization in women occurs in Fallopian tube.
When muscles in the skin contract and cause the hair of an animal to “stand on end,” the skin could be functioning as a regulator of:
Body temperature.
Albumin is the major blood osmoregulatory protein. The most likely effect of a sharp rise in the level of serum albumin is:
An influx of interstitial fluid into the bloodstream.
Chromosomal Duplication
Study of Meiosis
During prokaryotic protein synthesis, translation begins as soon as the newly synthesized mRNA strand begins to extend from the DNA strand. This situation differs from that in eukaryotes, because eukaryotes:
Localize the processes of transcription and translation in the nucleus and cytoplasm, respectively.
DNA Replication
Poly A tail - help mRNA travel from nucleolus to Cytoplasm without getting degraded
5 cap - is where translation begins. Ribosome recognizes this site. attaches and looks for AUG start Codon.
For Prokaryotes
The shine dalgarno sequence - same thing as 5cap. Ribosome attaches and does its translation
After the gall bladder is removed from a patient, the patient will most likely have reduced ability to digest: Fat
The gall bladder stores bile produced by the liver and secretes it into the small intestine as needed. Bile acts as an emulsifier, facilitating fat digestion. When the gall bladder is removed, a patient will have reduced ability to digest fats.
In the human "knee-jerk" reflex, the knee is struck and the lower leg jerks forward. Which of the following represents the complete pathway that the nerve impulse travels in effecting this response?
Sensory neuron and Motor Neuron The knee-jerk reflex is a simple monosynaptic stretch reflex. A tap to the tendon that connects the quadriceps to the patella activates a sensory neuron that directly synapses with a motor neuron in the spinal cord, causing the quadriceps to contract.
Reflex Arc
Super fast
Sensory Neuron, Motor neuron Uturn
Doesn’t reach Brain
Synthesis of antibody proteins in eukaryotic cells is associated with what organelle?
As secreted proteins, antibodies are translated by ribosomes attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Actin filaments within cells can be identified experimentally by the use of a labeled molecule that binds specifically to actin and not to other cell substances. Which of the following would be best to use as the labeled molecule?
Myosin binds to actin during contraction and will remain bound until phosphorylated by ATP. Actin filaments can be “decorated” with portions of the myosin molecule. Although ATP provides energy for muscle contraction, it provides energy for many other cell activities as well and would therefore be nonspecific. In addition, ATP binds to myosin, not to actin, in the contraction cycle. Albumin is a protein found in blood plasma. Myoglobin is the oxygen-binding pigment in muscle. Neither of these molecules is likely to have any specific affinity for actin.
Myosin
Myosin binds to Actin in order to contract muscle
Hardy Weinberg Equations
A set of equations used to calculate allele and genotype frequencies in a population under certain conditions, assuming no evolution occurs.
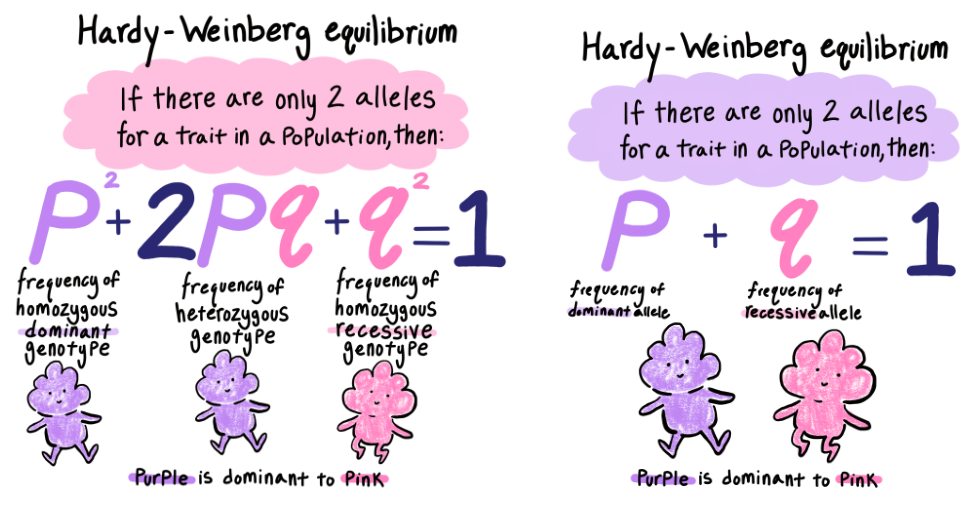
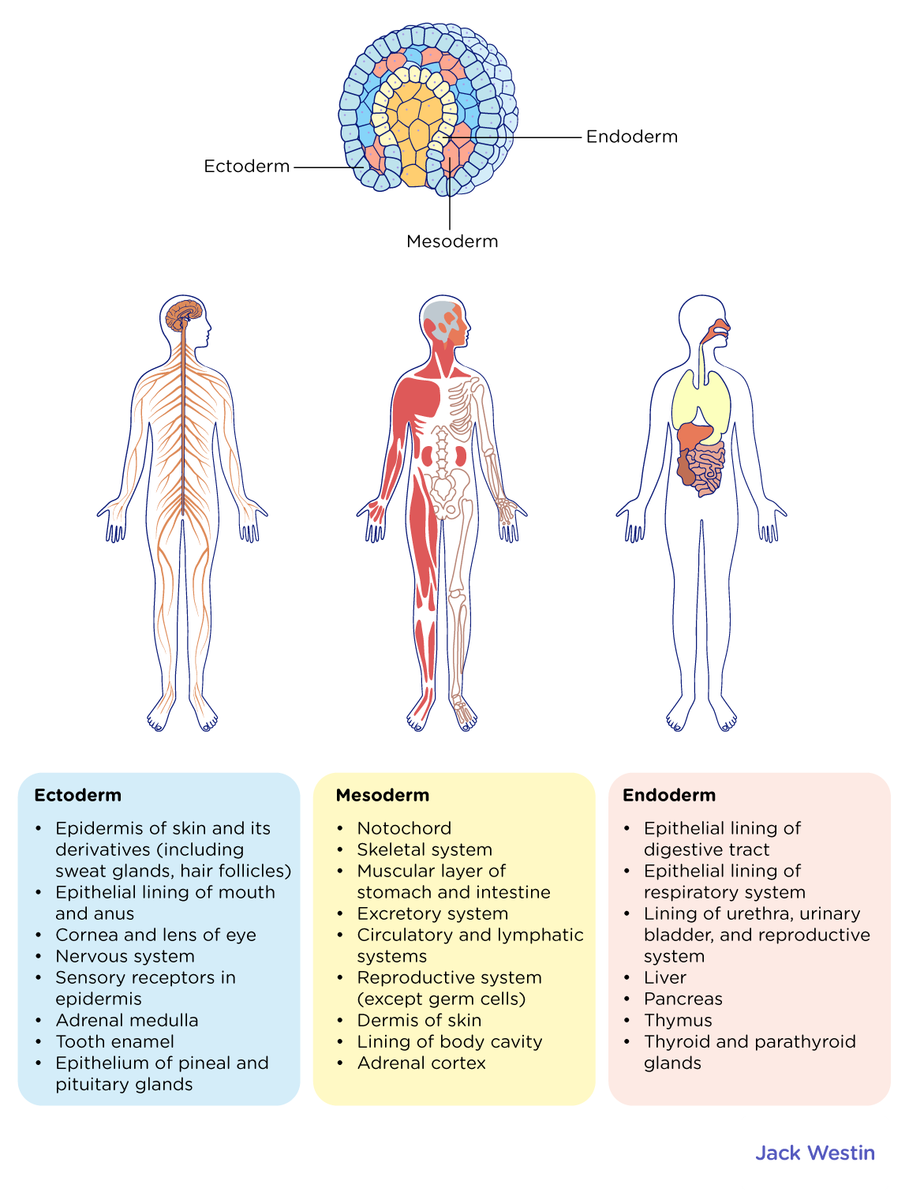
Germ Layers
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
Ectoderm

Mesoderm

Endoderm
Bacteria
Viruses reproduce by replicating within a host cell and thus cannot be said to reproduce by fission, as bacteria do. Many bacteria do have rigid cell walls, but many viruses have rigid capsids, so the presence of a rigid outer covering does not distinguish the two. Neither bacteria nor viruses have a nuclear membrane and both bacteria and viruses can contain RNA and protein. Thus, the best distinction between a bacterium and a virus is reproduction by fission, answer choice A.
Viruses
Viruses reproduce by replicating within a host cell and thus cannot be said to reproduce by fission, as bacteria do. Many bacteria do have rigid cell walls, but many viruses have rigid capsids, so the presence of a rigid outer covering does not distinguish the two. Neither bacteria nor viruses have a nuclear membrane and both bacteria and viruses can contain RNA and protein. Thus, the best distinction between a bacterium and a virus is reproduction by fission, answer choice A.
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
is a retrovirus, an RNA virus that can insert itself into the human genome. This virus can reproduce in host cells because it contains
The question states that HIV is a retrovirus. For the virus to reproduce itself in host cells, its RNA must be converted to DNA, which requires the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
Lung Airway Pathway
Air travels through the nose and mouth through the pharynx. It then flows through the larynx and the trachea before entering the bronchi. The bronchi branch into the bronchioles and finally terminate into the alveoli, where gas exchange can take place between the lungs and the blood stream.
Alveoli
Red blood cells
Do not have organelles, because of they carry Oxygen
Macrophage
Erythrocyte
Osteoblast
Osteoclast
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Translation of antibody proteins in eukaryotic cells is associated with what organelle?
The stem asks which of the organelles listed is associated with the translation of antibody proteins. Of the organelles listed, only the endoplasmic reticulum is associated with translation of proteins. Synthesis is accomplished by the ribosomes, which are associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. The nucleus contains the genetic information, the mitochondria are involved in cellular respiration, and the Golgi apparatus is involved in the processing and/or export of proteins. Therefore, the key is C.
Antidirutic Hormnes