BIS 2B Midterm 2 studying
1/54
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Aristotle Scala Naturae
350 BCE god, angles, demons, heavens, heavens, humans, animals, plants, minerals (static species)
Zhuang Zhou
369-286 BCE all life comes from one species and depending on location becomes different things. Species change over time even into other species.
Ibn Khaldun's Muqaddimah
1377 mans relationship to the world “descent though mo“
Linneas System *names*
famous for taxonomy he loved categorizing things … problematic
Alexander Von Humbolt
“scientific geography “ Biomes fundamental and realized niche very anti slavery
George Cuvier
catastrophism famous for craneomety (measuring skulls) bad
Charles Lyell
Gradualism , in geology but not in biology [grand canyon] . he thought species didnt change
jean baptiste lamark
believed organisms passed on traits acquired through use/ disuse (giraffe neck thing)
John edmonstone Darwins mentor
really really good at takidermy cause he learned in a really humid environment taught at uni of edinburgh
Darwin
pigeons - selective breeding on the origin of species “decent though modefication“
Wallace
same ideas as darwin but no credit ☹
catastrophism
earth and life on it and are primarly shaped by major , sudden events
gradualism
earth and life on it are shaped by long slow processes
by mid 1800’s
gradual change is important in earths history , earth is old , extinction occurs
evolution
genetic change over time
adaptation
type of evolution that occurs though natural selection
micro evolution
small across generation
macro evolution
accumulation of micro evolution changes that a new group arises large scale across species change
necessary conditions for natural selection
variation
heritability (0-1)
differential success - fitness
Phenotype
is the traits it
exhibits (its physical appearance)
Genotype
Genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism
relative fitness
absolute fitness / pop mean fitness
sexual selection
Alturism
a behavior that reduces individual fitness and increases the fitness of other individuals
kin selection
selection that favors the increase the success of relatives
Negative Frequency dependent selection
the rarer phenotype have highest fitness , phenotypes ocelots
Deleterious
decrease fitness
Breeders equation
R=h²S
R is how much the phenotype shifts after selection
H is the heritability
S is the strength of selection in one generation . Og mean - new mean
Patterns of natural selection
Directional
Stabilizing
Diversifying / disruptive
Transcription
DNA → RNA
RNA polymerase
Translation
RNA → Proteins
Ribosome
DNA base pairs
C-G
T-A
In RNA the T is swapped for U
Codon
3 base pairs
Types of mutations
Substitution
Insertion
Deletion
Silent / synonymous
Law of segregation
I’m production of gametes , the two copies of a gene separate so that each gamete contains 1 copy
Law of independent assortment
Alleles of different genes sort independently of one another during gamete formation
Recombination
When meiosis happens the chromosomes Wind and switch genetic material
Considering multiple genes & probability
P(Y&R) = P(Y) * P(R)
& means multiply or means add so two expressions and add
Single / complete dominance
A single dominant allele produces the dominant phenotype. Rr same as RR in phenotype ❤
Incomplete dominance
The heterozygote phenotype is an intermediate between the homogeneous phenotypes Rr 🩷
Codominant
The heterozygote phenotype is both homogeneous phenotypes expressed fully ❤&🤍
Linkage
Genes on the same chromosome and are close together are more likely to get inheriated together
Pleiotrophy
When one gene affects multiple characteristics
Polygenic inheritance
One trait is additivley controlled by many genes (darker shards of something)
❤🧡💛
Epistasis
When multiple genes interact to determine phenotype 🐶🐕🦺🐶🦮
Hardy -Weinberg equilibrium
No mutations
No natural selection
No gene flow
No genetic drift
YES random mating
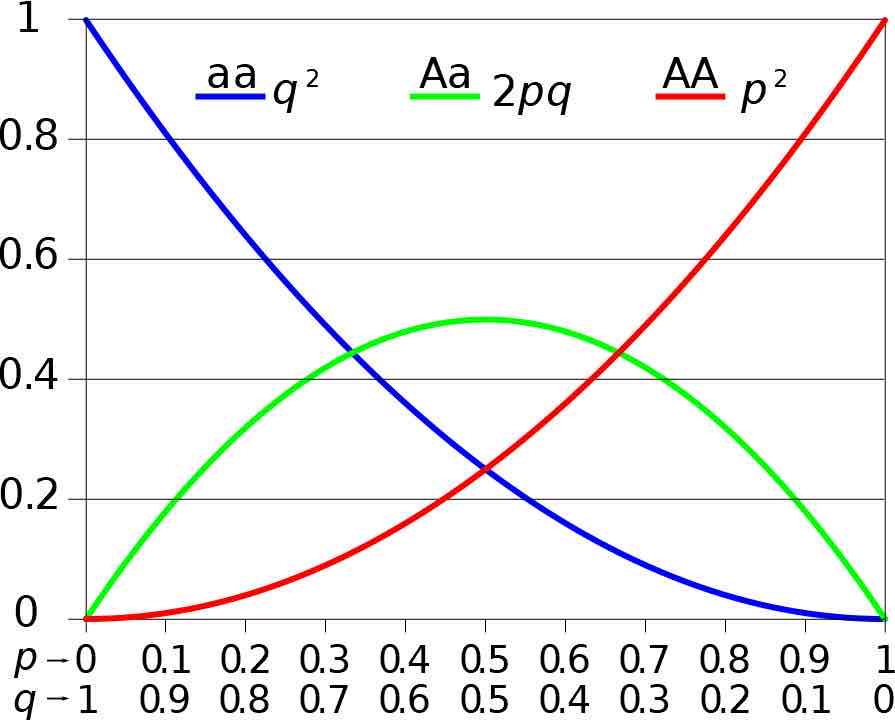
H-W pq shit
Frequency :
P. A1
q. A2.
Frequency of getting a A1A1 = p²
Frequency of getting a A1A2 = 2pq
Frequency of getting A2A2 = q²
Frequency of one allele
F(A) = F(AA) + ½ F(Aa)
Genetic drift
Chance events that cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from one generation to the next. “Marbles”
Smaller pop size = stronger drift
If there is no random mating
Inbreeding 🩷x🩷
Outbreeding 🩷x💜
this reduces heterogeneity until I’m extreme cases there are no hetero left
*so much fewer Aa than we EXPECT in HW — compare to itself not others
This is why deleterious traits show up more think royal 🫅 👸 family
Reproductive barriers
Pre zygotic barriers:
Habitat isolation
Temporal isolation (time)
Behavioral 🔥🪰
Mechanical isolation
Gamete isolation
Post zygote barriers : (prevent zygote from being viable)
Reduced hybrid viability - non complete development
Reduced hybrid fertility - hybrid offspring are viable but can’t reproduce themselves
Hybrid breakdown → viable → viable → infertile
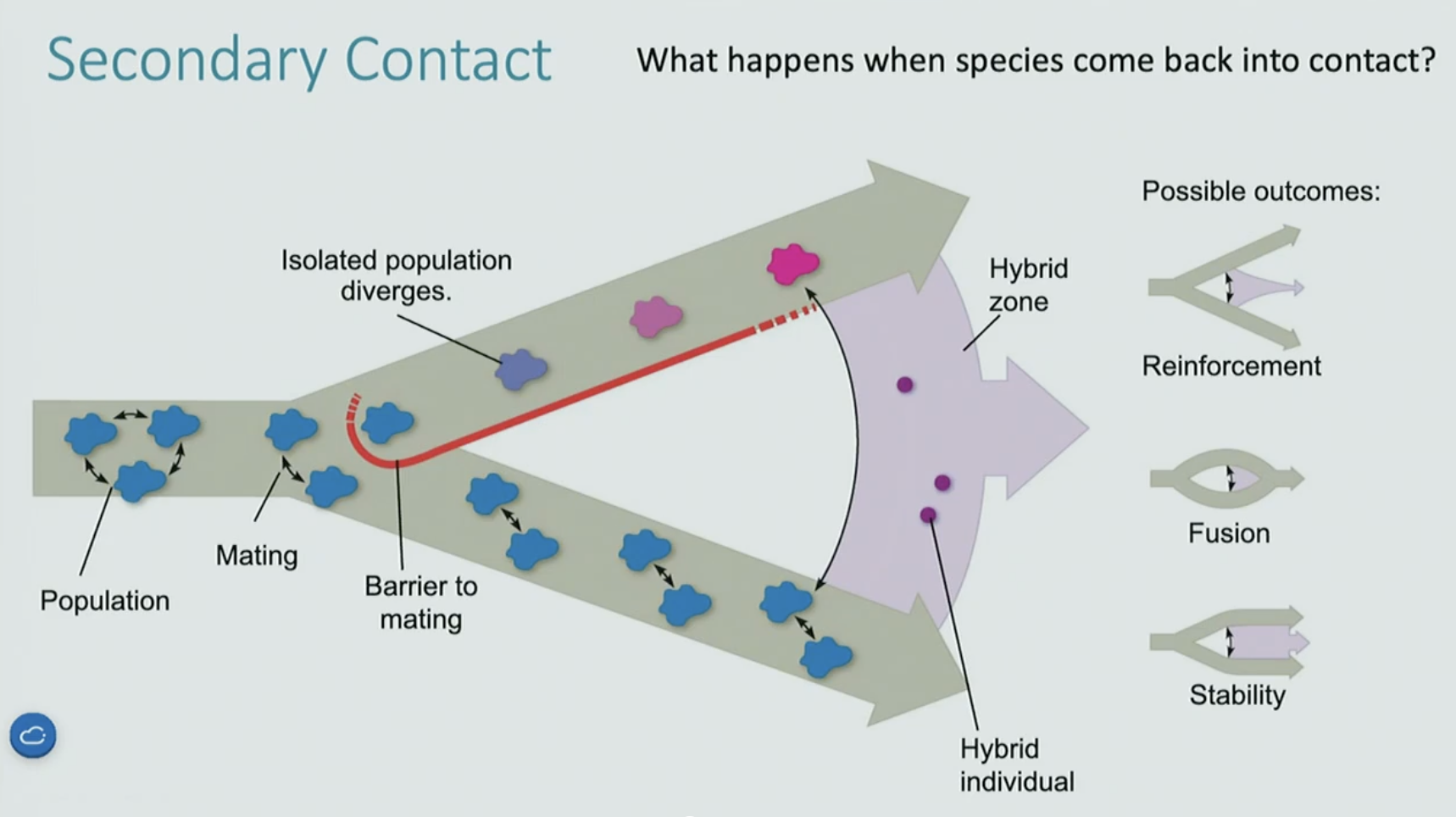
Secondary Contact
reinforcement
fusion
Stability
descent with modification
this is what causes homologous traits. the organisms are very similar because they all descended from one common ancestor
Convergent Evolution
this is what causes Analogous traits which are similar in different organisms because of similar SELECTIVE PRESSURES