Level Up RN and Book- Exam 1, Week 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is automaticity?
Pacing Function
What is Excitability?
Response of Non-Pacemaker Cells
What is Conductivity?
Sends stimuli from cell to cell
What is Contractility?
Muscles response to stimuli
What is the SA Node?
P-Wave
What is the AV Junction?
PR Segment
What is continuous electrocardiography?
Close proximity to the monitoring system
What is telemetry echocardiography?
Allows client to ambulate
How big is a SMALL box on an EKG?
0.04 seconds
How big is a LARGE box on an EKG?
0.2 seconds
How many small boxes make up a large box?
5 boxes
How many large boxes in one minute?
300
How many large boxes in a 6 second strip?
30 boxes
What does the P-Wave represent?
Atrial Depolarization (Contract)
What is a normal PR Interval?
0.12-0.20
What is a normal QRS complex?
0.04-0.10
What happens in the QRS?
Ventricular Depolarization (Contract)
What happens in the ST Segment?
Ventricular Repolarization (Relax)
What happens in the T-Wave?
Ventricular Repolarization (Relax/Filling)
What happens in the QT Interval?
Ventricle Depolarization/Repolarization (BOTH)
How to calculate HR?
Count R to R
1500 divided by # of small boxes
What causes no P-Wave?
Heart Block
Junctional
Atrial Arrythmia
Ventricular Arrythmia
What are the 3 Irregularly Irregular rhythms?
A-Fib
Paced Beats
Premature Beats
Who is a cardioversion given to?
Atrial Dysrhythmias (A-Fib+A-Flutter)
SVT
Ventricular Tachycardia (V-Tach)
Who is defibrillation given to?
V-Tach and V-Fib
What must A-fib patients be on before a cardioversion?
Anticoagulation 4-6 weeks
How long before a cardioversion is digoxin held?
48 hours
What is the treatment for Bradycardia?
Atropine
Epinephrine
Pacemaker
What is the treatment for A-Fib, SVT, V-Tach
Amiodarone
Adenosine
Cardioversion
What is the treatment for V-Tach and V-Fib?
Amiodarone
Lidocaine
Defibrillation
What must be performed for asystole?
CPR
What is Normal Sinus Rhythm?
Rate: 60-100 BPM
Rhythm: Regular
P-Wave: Present and Consistent
PR: 0.12-0.20
QRS: 0.06-0.10
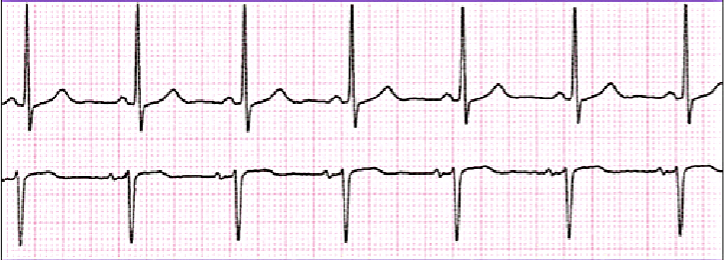
What is sinus tachycardia?
Rate: 100-160 BPM
Rhythm: Regular
P-Wave: Present and Consistent
PR: 0.12-0.20
QRS: 0.06-0.10
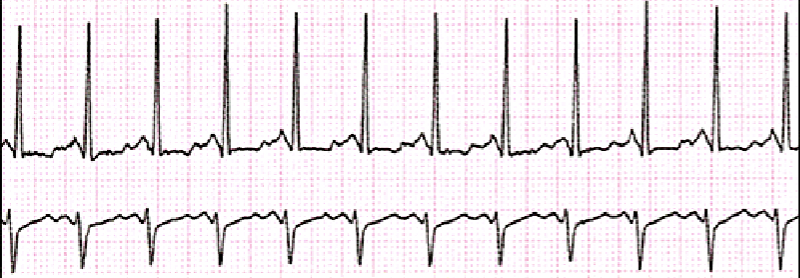
What is sinus bradycardia?
Rate: Less than 60 BPM
Rhythm: Regular
P-Wave: Clear and Consistent
PR: 0.12-0.20
QRS: 0.06-0.10
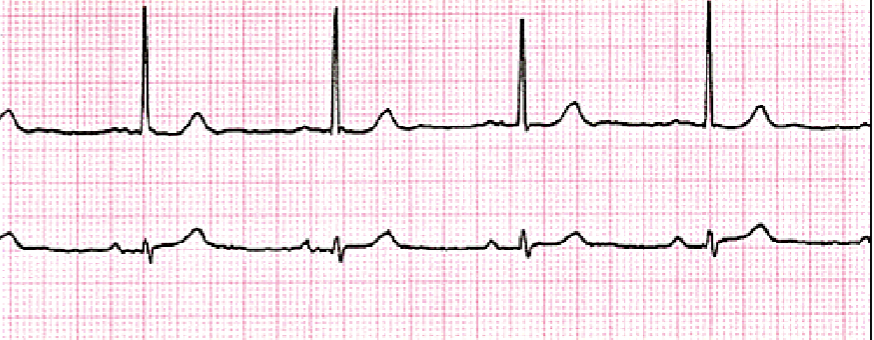
What is a premature atrial complex?
Fire an impulse before it’s due
Stress, Fatigue, Anxiety, Inflammation, Caffeine, Nicotine, Alcohol, Infection, Certain Drugs
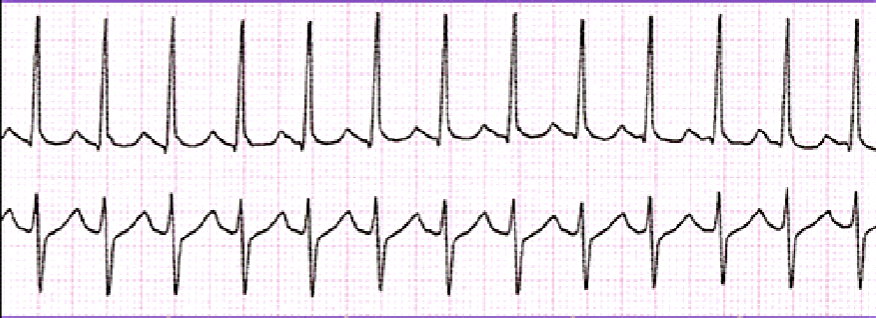
What is SVT?
Rate: 100-280 BPM
Rhythm: Regular
P-Wave: May not see due to fast rate
PR: Varies
QRS: 0.06-0.10
How much does cardiac output decrease with A-Fib?
20-30%
What are A-Fib patients at a high risk for?
Blood Clots and Strokes
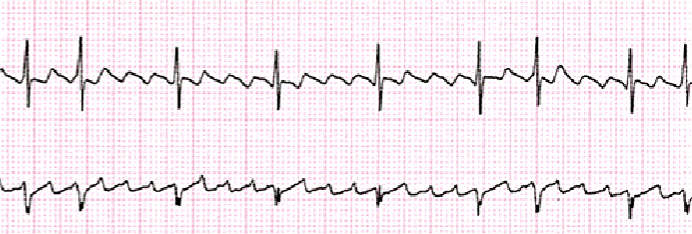
What is A-Fib?
Rate: 120+ BPM
Rhythm: Irregular
P-Wave: None or Fib Wave
PR: None
QRS: 0.06-0.10
What is digoxin’s therapeutic range?
0.5-2
What is the antidote for digoxin?
Digiband
When should digoxin be held?
Under 60 BPM
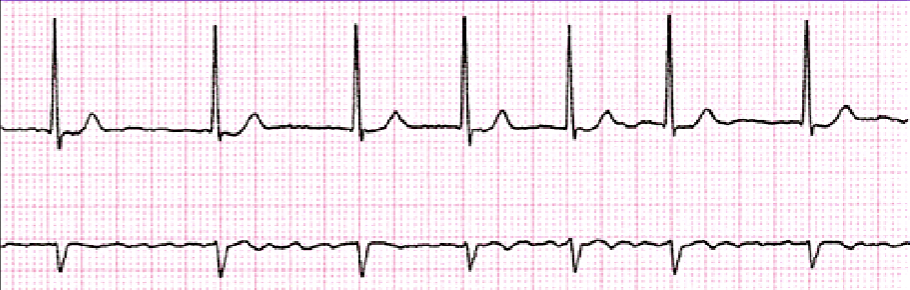
What is A-Flutter?
Rate: 120+ BPM
Rhythm: Irregular or Regular
P-Wave: Sawtooth
PR: None
QRS: 0.06-0.10
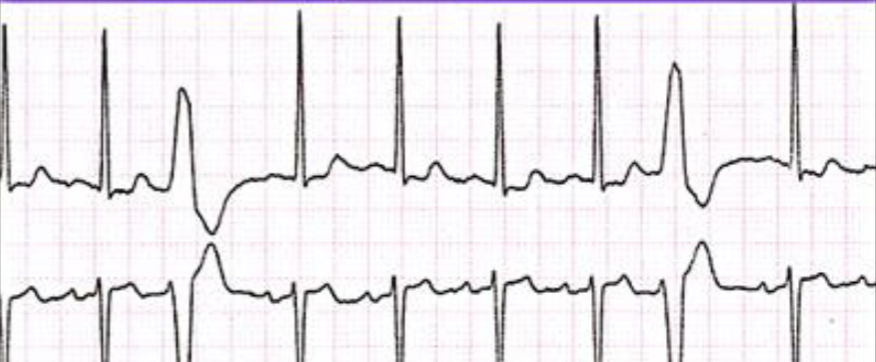
What is premature ventricular complex?
Increased irritability of ventricular cells
Early complex followed by a pause
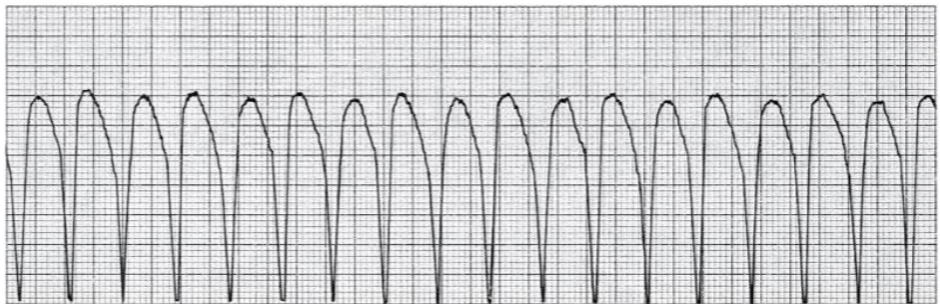
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Rate: 140-180 BPM
Rhythm: Regular
P-Wave: None or Buried
PR: None
QRS: Wide
Why does checking a pulse matter for ventricular tachycardia?
Pulse= Amiodarone, Adenosine, Cardioversion
NO Pulse= Amiodarone, Epinephrine, Defibrillation
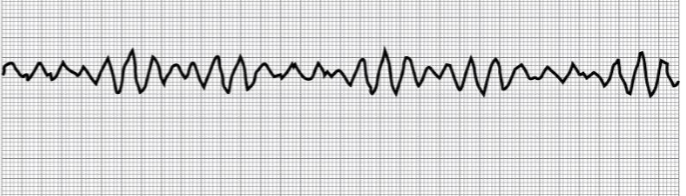
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Rate: None
Rhythm: Irregular
P-Wave: None
PR: None
QRS: Ventricular Chaos
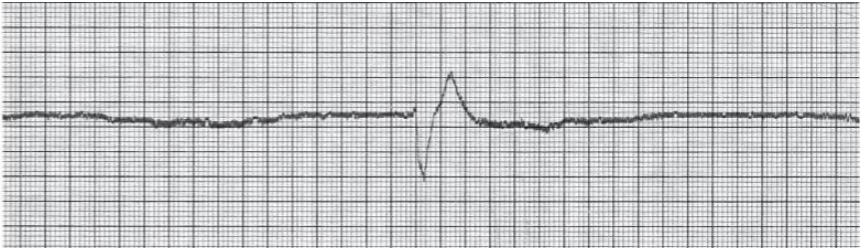
What is ventricular asystole?
Absence of anything
What is a transcutaneous pacemaker?
From defibrillator pads (Bradycardia)
What is epicardial pacemakers?
Attach directly to heart (CABG)
What is endocardial pacemaker?
Permanent
What needs to be reported immediately with a pacemaker?
Hiccups and Cool/Clammy Skin
What is an asynchronous pacemaker?
Fires at a consistent rate
What is a synchronous pacemaker?
Fire when under a preset threshold
What is important teaching with a pacemaker?
Take HR and Temp everyday
Avoid magnetic fields
Carry ID
What is a first degree heart block?
QRS comes home late
What is second degree type 1 heart block?
QRS comes home later and later and then doesn’t show
What is second degree type 2 heart block?
QRS is regular and then suddenly doesn’t show up
What is third degree heart block?
No communication between P and QRS
What is the COOL CHICKEN for Adenosine?
In den of sin, Mom sees, Gets Tachycardia, Needs to slow HR
What is the COOL CHICKEN for atropine?
Atropine on trampoline= Increase HR
What is the COOL CHICKEN for V-Fib?
V-Fib=D-Fib