Pharmacology 4
1/70
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
too small to be seen without a microscope
microorganism
4 types of microorganisms
bacteria
viruses
protozoa
fungi
when microorganisms are dangerous, they are called
pathogens
what fights bacteria
antibiotics
spherical, rod shaped, spiral shaped
bacteria
how fast can bacteria reproduce
20 minutes
bacteria are unicellular or multicellular
unicellular
viruses can or cannot live outside of a living cell
can’t
uses a host to produce new virus
viral
a viral microorganism needs a compatible _______ _____
receptor site
limited pharmacotherapeutic drugs and the ability to mutate are medical concerns for
viruses
strep, TB, pneumonia, gonorrhea, syphilis, sinus infection, diphtheria, and whooping cough are examples of
bacterial infections
flu, mumps, genital herpes, fever blisters, measles, AIDS, and COVID are all examples of
viruses
bacteria
virus
protazoa
fungus
unicellular and colonial organisms
protazoa
which microorganism has characteristics of animal life
protazoa
protozoa are transmitted by (3)
contaminated feces, insect bites, person-person
can protozoa survive outside the host organism
yes
amebic dysentery, giardiasis, and vaginitis are examples of
protazoa
lichen, mushrooms, toadstools, puffballs, mold, and yeast are examples of
fungi
what does a fungus need to live
moist area and O2
do fungi live on living or dead things
dead
antibiotics, cheese, bread, beer, and wine are ___________ examples of fungi
industrial
thrush, ringworm, and athlete’s foot are examples of
fungi
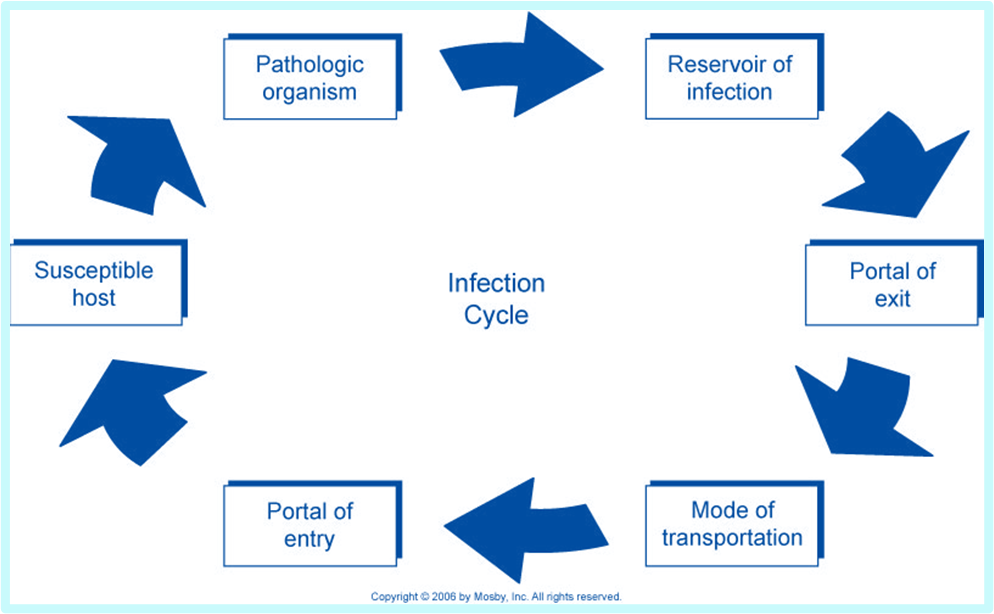
chain of infection
what is the purpose of soap when washing hands
friction
what the pathogen can get in
resovoir
what can the infection cycle be broken by
washing hands
prevention is ______ _____
common sense
refers to the treatment of blood and body fluid, requiring them to be treated the same, regardless of patient’s apparent infectious state
universal precautions
barrier techniques are
PPE
clean from ______ contaminated to most _______
least, most
clean from ___ to ______
top, bottom
unpleasant state of tension forewarning danger
anxiety
sudden, unexpected, intense attack of apprehension
panic disorder
_______ _________ manifests though physical symptoms and feelings of impending doom
panic disorder
psychological condition that consists of irrational fear leading to avoidance
phobia
_____ manifests through physical symptoms, and does not need a psychiatric diagnosis
phobia
T or F: of severe enough an already compromised organ can fail due to anxiety
True
drug induced relaxation for unpleasant procedures
conscious sedation
what is the difference between conscious sedation and general anesthesia?
dosage
patient history, physical exam, heart and lung assessment, all known medications, all known allergies, last oral intake and abnormalities of the organ must beknown before
conscious sedation
what medications can be used for conscious sedation
analgesic and antianxiety
two types of antianxiety medications
barbiturate and benzos
what do antianxiety meds act on
limbic system
antianxiety medications block stimulation or increase it
block
antianxiety medications increase
GABA
type of analgesic medication
narcotics
thiopental, methohexital, and phenobarbital are all types of
barbiurates
thiopental induces ____ anesthesia
full
the onset f thiopental is ___ minutes, with sleep duration of about __ minutes
30, 45
pediatric conscious sedation before MRI could be a use for
thiopental
methohexital has ___ onset and _____ duration
rapid, short
which barbiturate is used for brief procedures
methohexital
which barbiturate is used for pediatric CT studies
methohexital
which barbiturate is given to an adult patient the night before and morning of an study to keep them calm
phenobarbital
what reverses the effects of antianxiety drugs
flumazenil
midazolam is an example of a
benzodiazepine
midazolam has a onset of ___ to ___ minutes and a duration of __ minutes
2 to 15, 90
which is more likely to have hangover/amnesia effects benzos or barbiturates
benzos
morphine, meperidine, fentanyl, and dilaudid are expamples of
opiates
______ ______ decrease the perception of pain
opiate analgesics
T or F: midazolam is a barbiurate
false
T or F: methohexital is a benzo
false
T or F: opiate-induced respiratory depression can be treated with naloxone
true
T or F: flumazenil is the antidote for midazolam overdose
true
T or F: benzos can cause drowsiness, hallucinations, and amnesia
true
T or F: combining opiates with benzos may produce synergistsic effects
true