Cross Sectional Lower Extremity Anatomy
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
lower extremity function
responsible for bearing weight of upper body and accommodating demands of movement placed on this system
lower extremity consists of
hip/hip jt, femur, patella, knee/knee jt, tib/fib, ankle/ankle jt, foot (tarsal bones/metatarsals/phalanges)
hip function
provides strength to carry the weight of the body in an erect position
hip joint type/articulation of
synnvial ball and socket- wide range of motion
created by articulation of femoral head with acetabulum of pelvis
femur
longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in body
proximal end= head, neck, 2 processes (greater and lesser trochanters)
distal portion of femur broadens into ____ covered in
medial and lateral condyles covered in articular cartilage
knee jt
distal femur, proximal tibia, patella, proximal fibula
patella is
largest sesamoid bone in body with a flat, triangular shape and distal pointed apex
patella location
embedded in quadriceps tendon
tibia has
widened proximal end with two cartilage covered projections called medial and lateral condyles
superior articular surface of tibia
condyles has flattened surface called tibial plateaus that articulate with femoral condyles
intercondylar eminence
separate condyles of tibia and end in two points called medial and lateral intercondylar tubercles
attachment sites for ACL and meniscus
intercondylar tubercles and roughened areas around them
Type 1 tibial plateau fx looks like
wedge shaped fx of lateral tibial plateau w/ displacement or depression <4mm
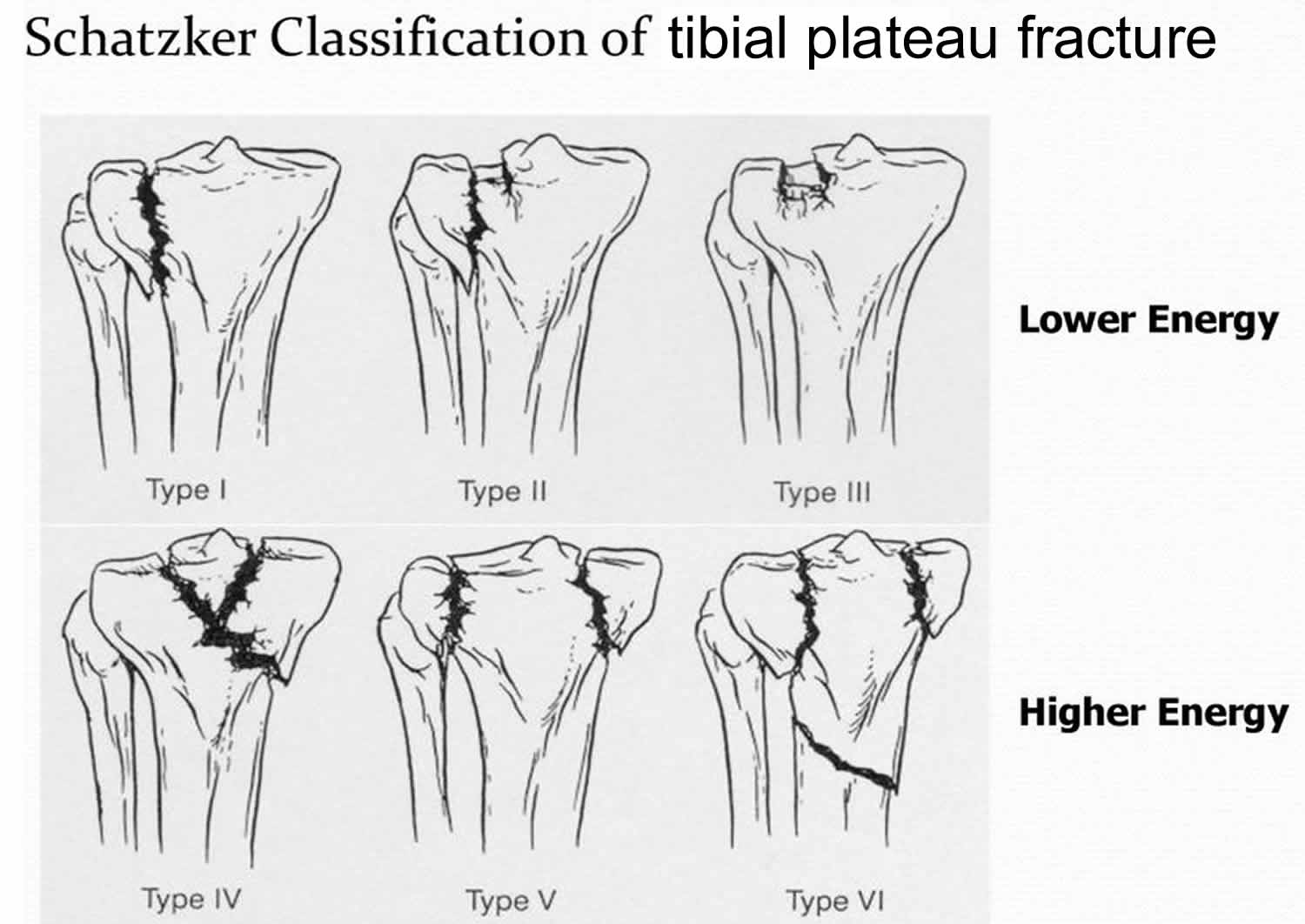
Type 1 tibial plateau fx caused by
lateral femoral condyles being driven into articular surface of tibial plateau
Type 2 tibial plateau fx looks like
fx with compression of lateral tibial plateau (type 1 fx w/ depressed component) > 4mm
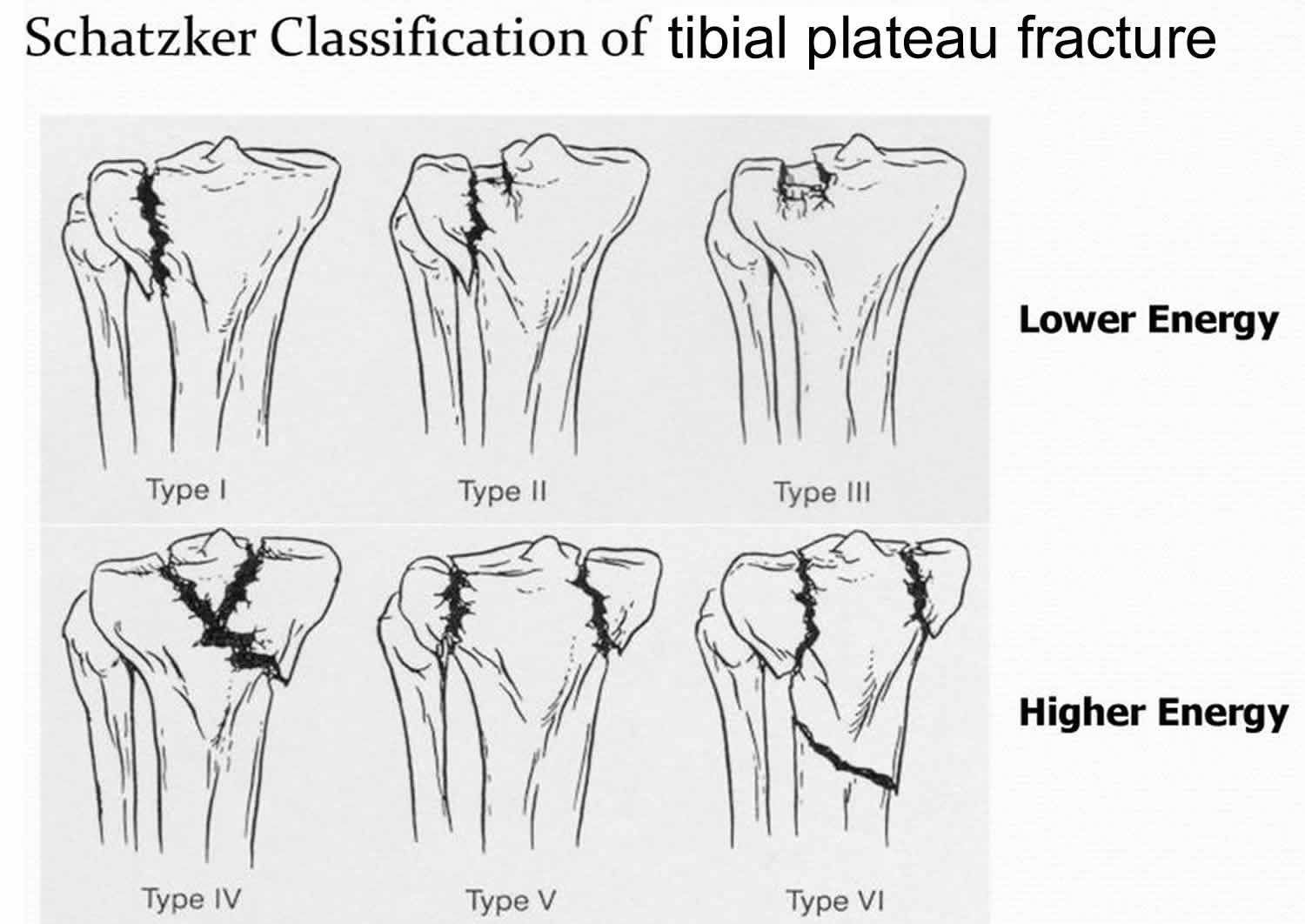
Type 3 tibial plateau fx looks like
compression fx of lateral tibial plateau in which the articular surface is depressed and driven into the lateral tibial metaphysis
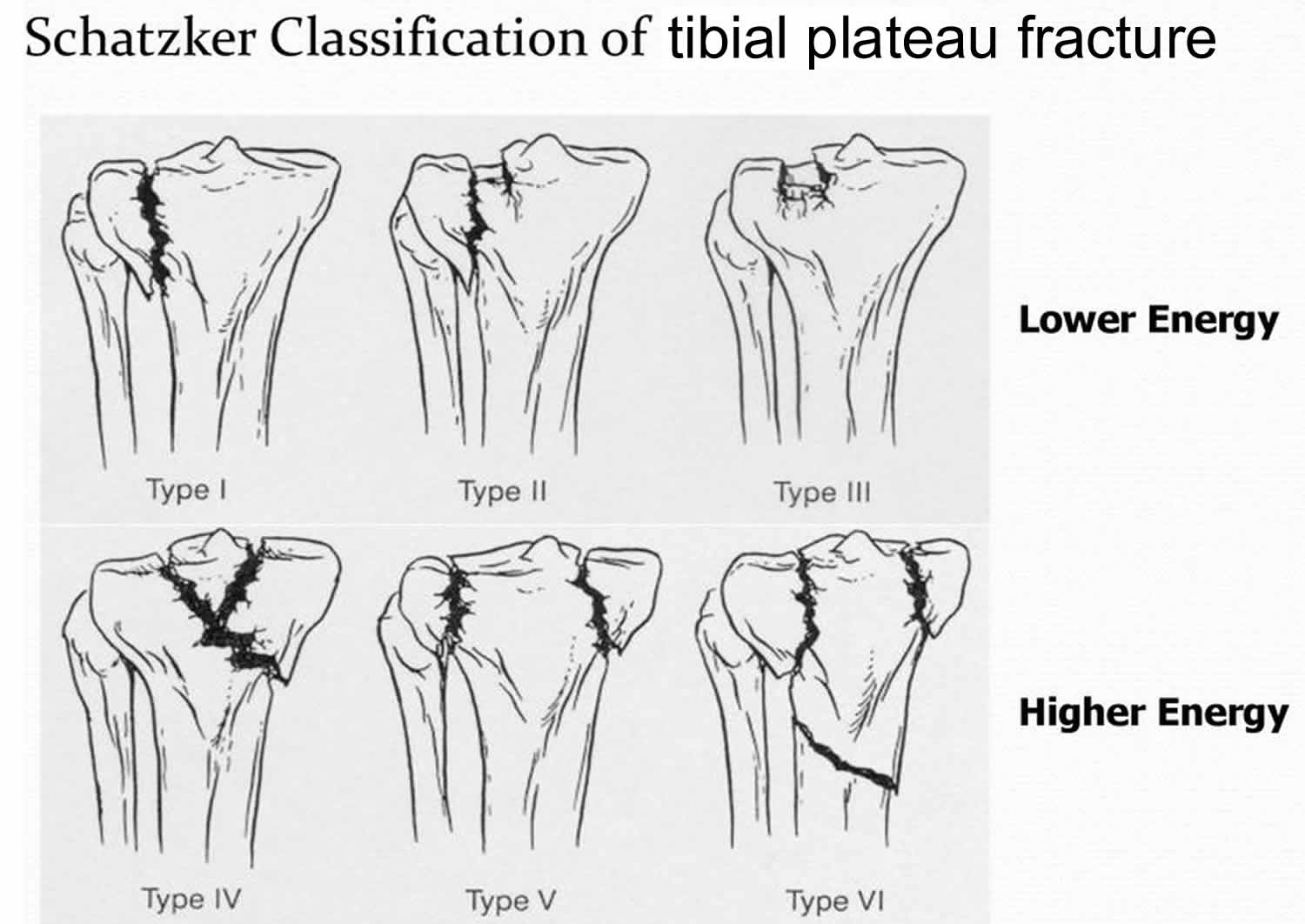
Type 3 tibial plateau fx caused by
axial forces
Type 4 tibial plateau fx looks like
medial tibial plateau fx w/. asplit or depressed component
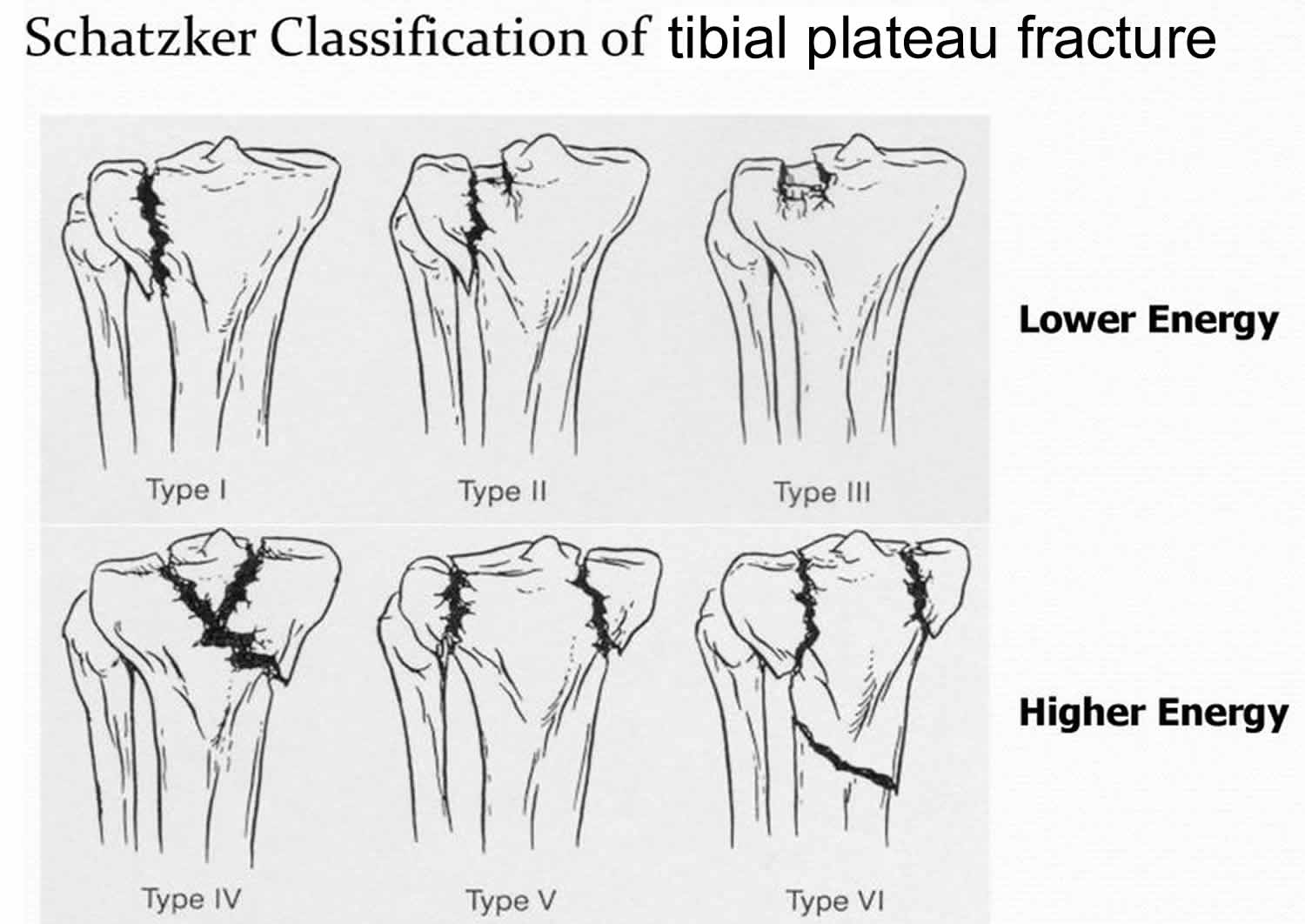
Type 4 tibial plateau fx caused by
forces combined with axial loading in a hyperflexed knee
worst prognosis tibia fx
type 4
Type 5 tibial plateau fx looks like
wedge fx of medial and lateral tibial plateau w/ an inverted Y appearance. Articular depression typically seen in lateral plateau and might be associated with a fx of the intercondylar eminence
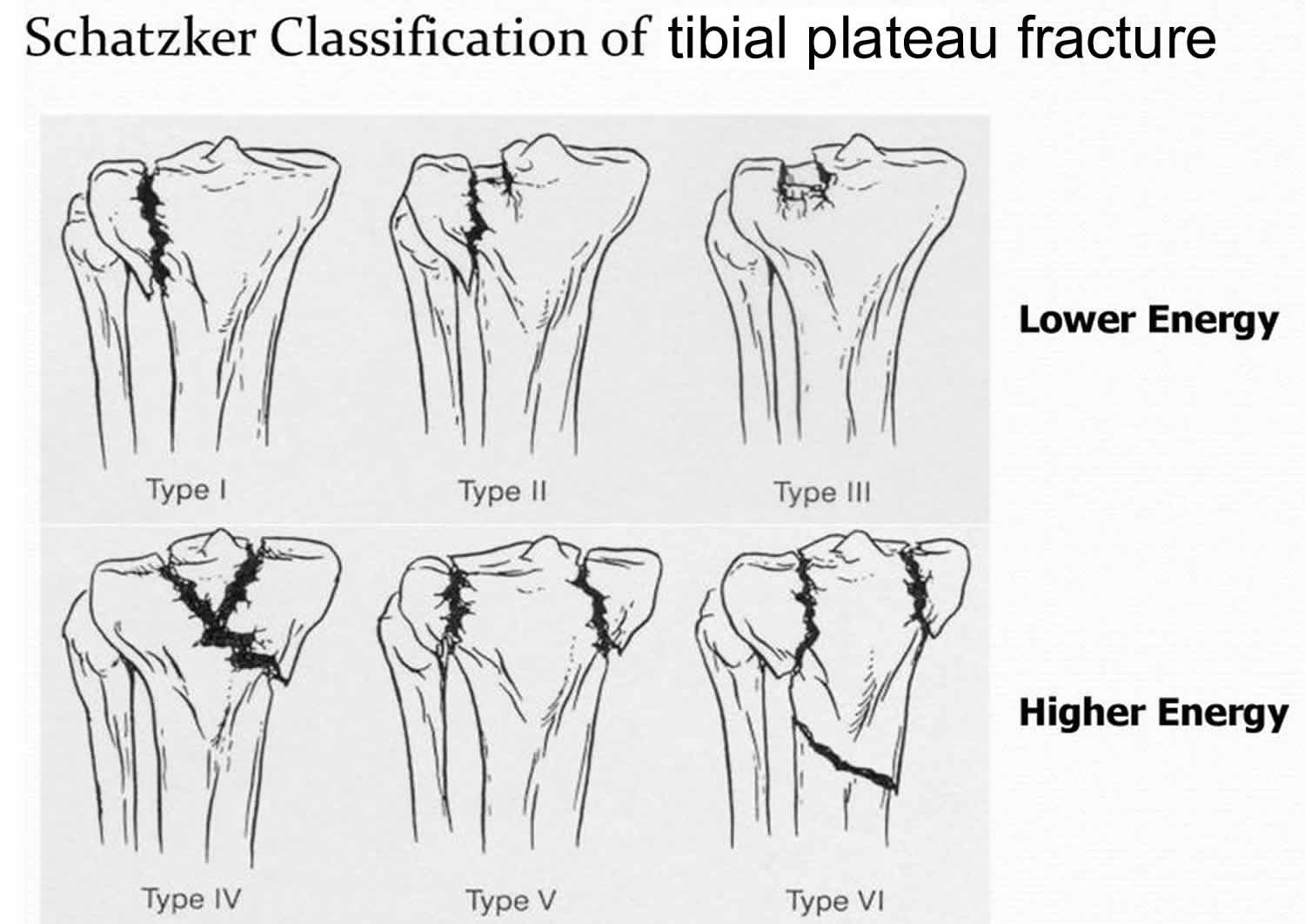
Type 5 tibial plateau fx caused by
MVA or motorcycle accident
Type 6 tibial plateau fx looks like
bicondylar fx w/ a dislocation of the metaphysis from the diaphysis
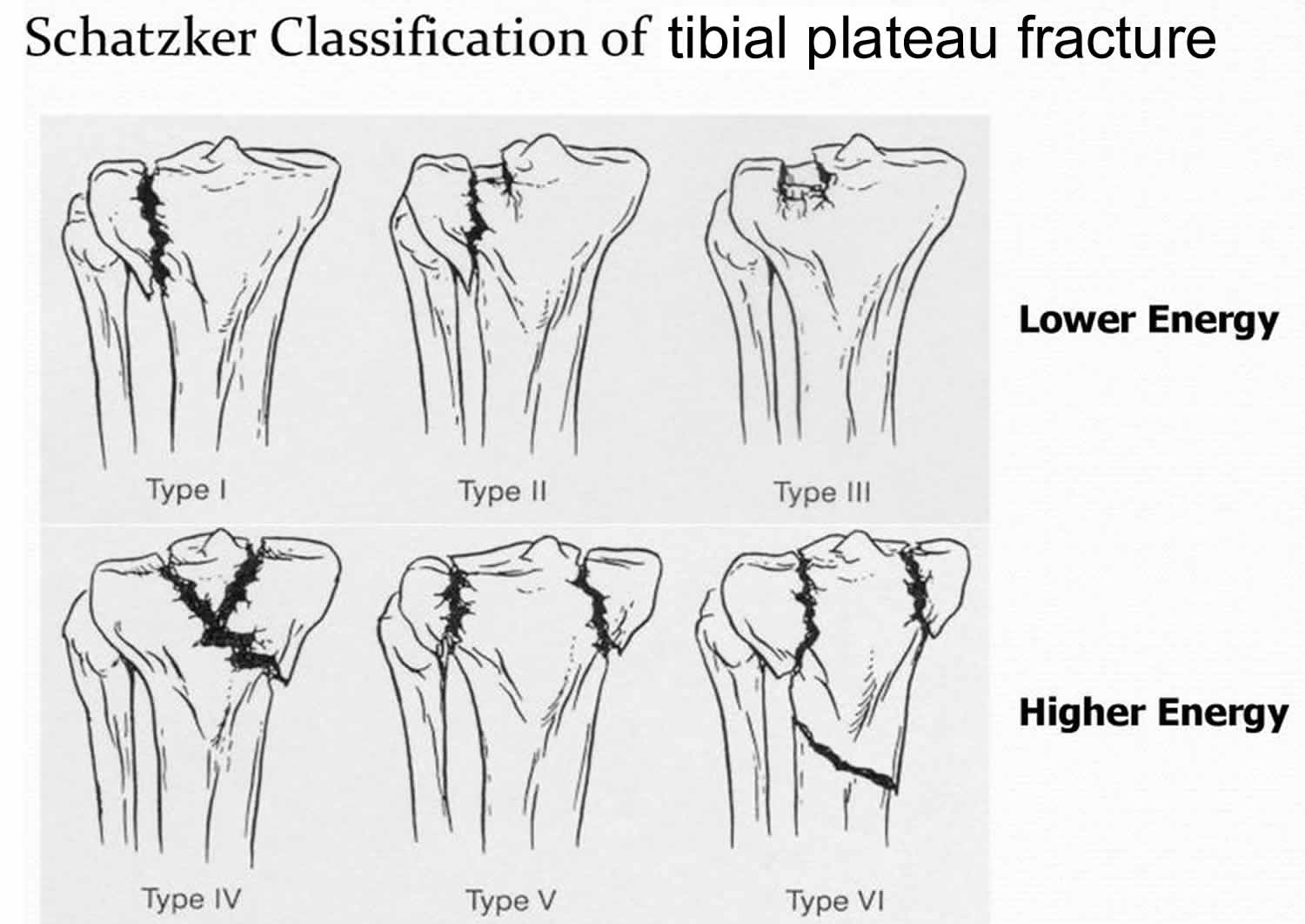
Type 6 tibial plateau fx caused by
high energy trauma and diverse combinations of forces
tarsal bones
talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid, medial cuneiform, intermediat cuneiform, lateral cuneiform
talus
2nd largest tarsal bone responsible for transmitting entire weight of body to foot
what transmits entire weight of body to foot
talus
talus anatomy
head- articulates with navicular bone
neck- short and broad extends anteriorly to head
body- wedge shaped w/ upper articular surface wider in front than back (trochlea)
calcaneus shape
largest tarsal bone
elongated shape with posterior surface comprising prominence of heel
calcaneus medial surface
shelf-like process called sustentaculum tali which supports the talus
calcaneus posterior plantar surface
calcaneal tuberosity which is large and is insertion for ligaments and tendons (Achilles Tendon)
cuboid location
lateral and anterior to calcaneus
cuboid articulation
anteriorly with bases. of4th and 5th metatarsal bones
navicular articulation
posteriorly with talus and anteriorly with cuneiform bones on medial side of foot
cuneiform articulations
1st-3rd metatarsal bases
metatarsal bone shape
long and slender
each have distal head, proximal base, shaft
metatarsal articulations
heads with proximal phalanges of toes
bases with tarsal bones
1st metatarsal has
2 sesamoid bones on medial and lateral surface of metatarsal head
how many phalanges in each foot
14
3 on each toe (proximal, middle, distal)
2 on great toe (proximal, distal)
phalanges of toes compared to fingers
shorter and stoutier than finger phalanges and each have body, base, head
common studies for bad fx of lower extremity
CTA lower extremity