Anatomy Lecture Final (Exams 1-3 + Lecture 10 SG)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy
the study of body structure
2
New cards
Physiology
examines how the body functions
3
New cards
What are the 2 major body cavities?
dorsal cavity (posterior aspect)
ventral cavity
ventral cavity
4
New cards
Positive feedback
the outcome amplifies the stimulus
5
New cards
Negative feedback
the outcome negates the stimulus
6
New cards
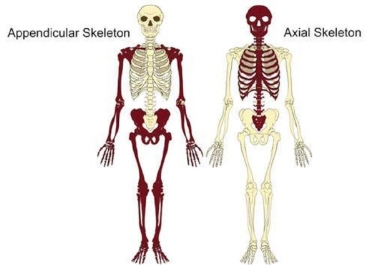
The main division of bones
axial and appendicular skeleton
7
New cards
Superior
above
8
New cards
Inferior
below
9
New cards
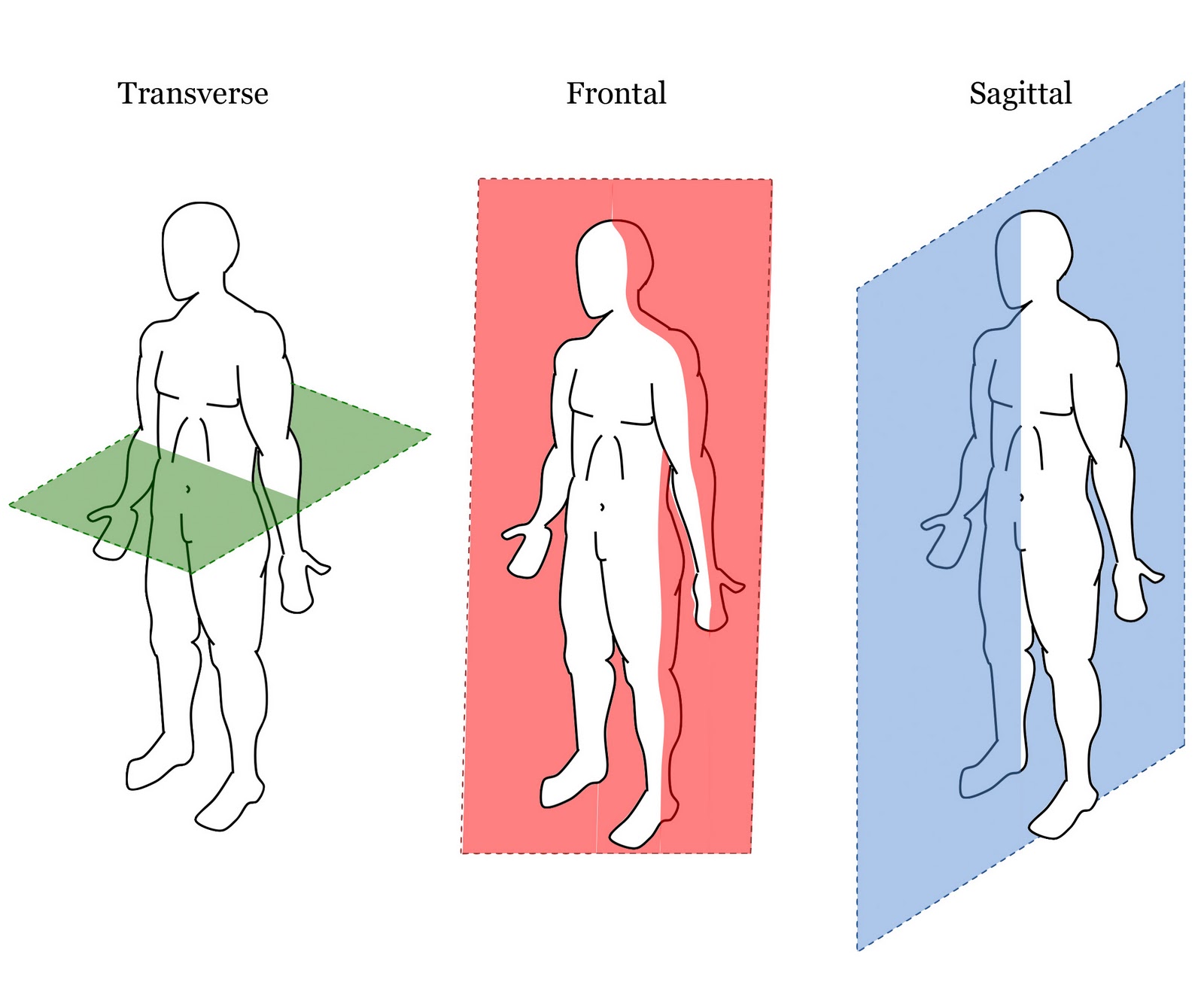
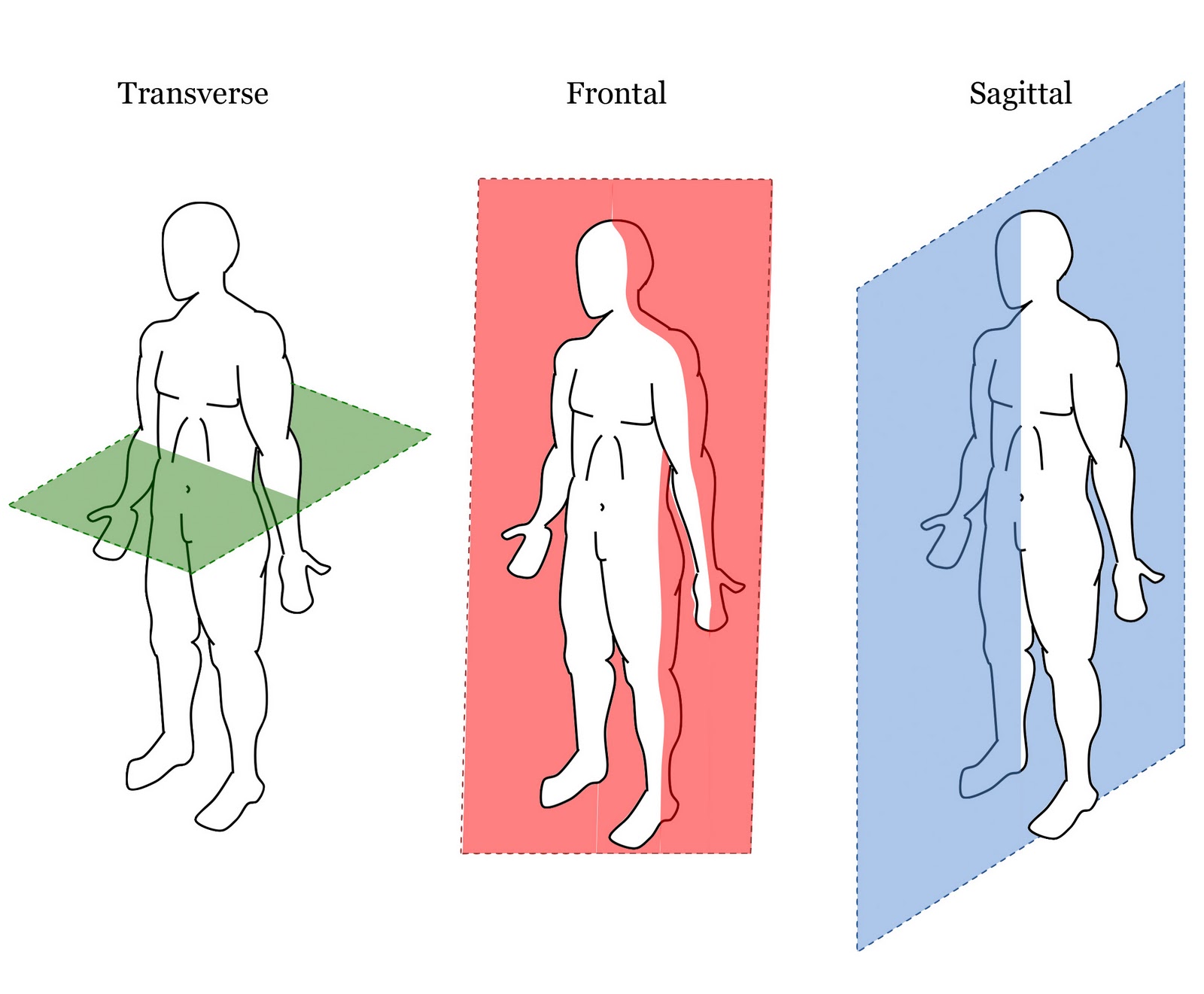
Body planes
transverse
frontal
sagittal
frontal
sagittal
10
New cards
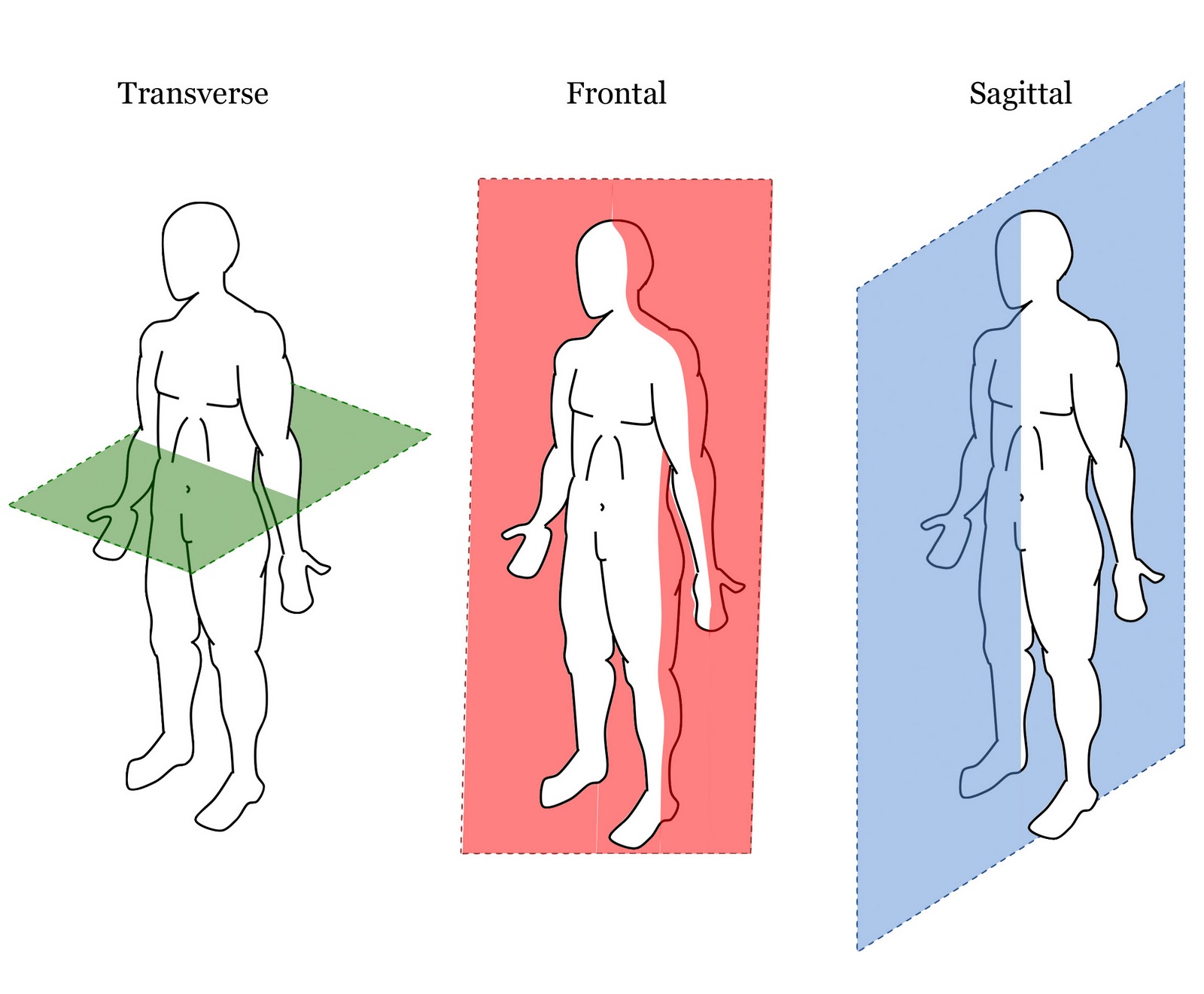
Transverse plane
horizontal
11
New cards
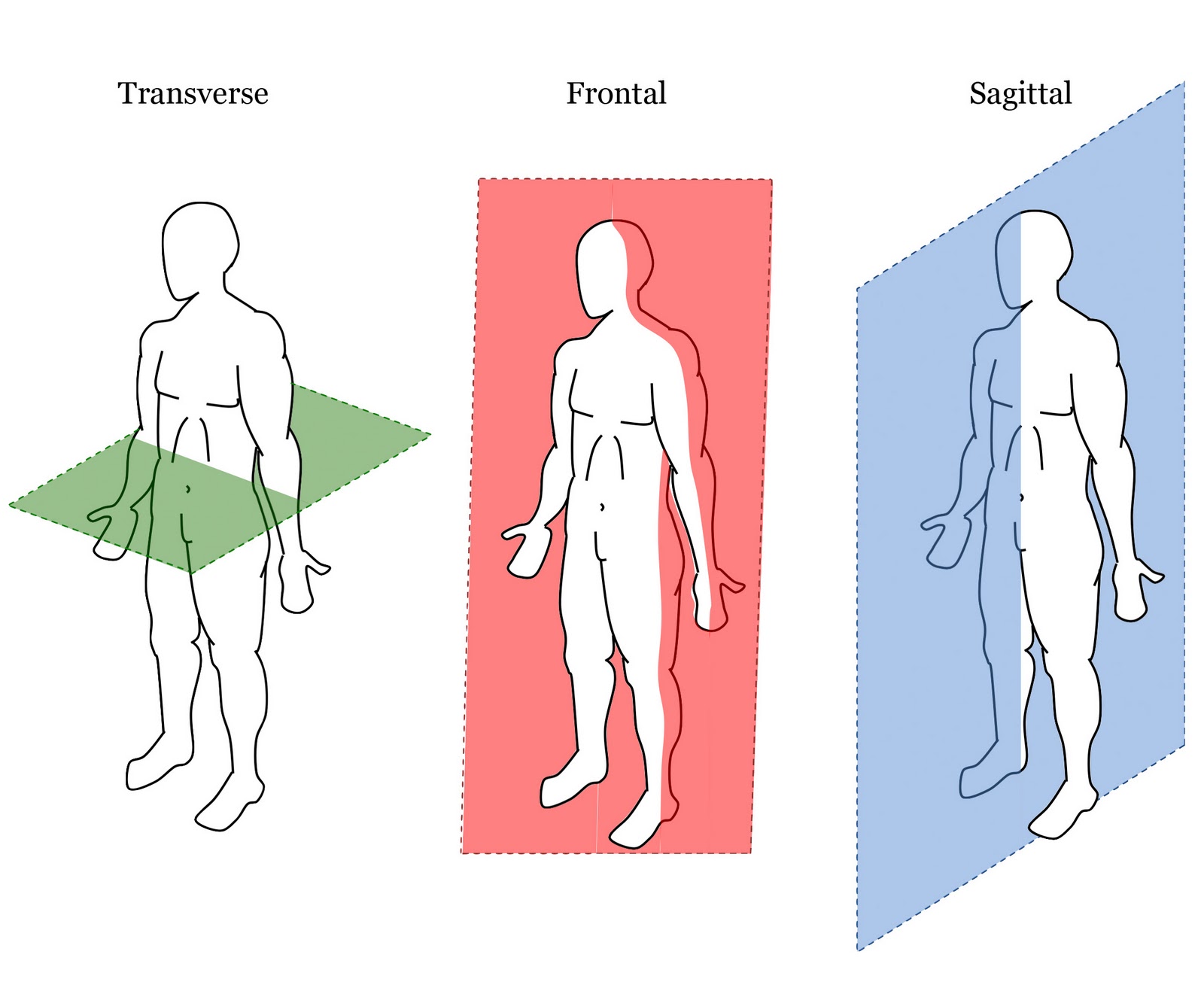
Frontal plane
aka coronal plane
vertical plane divides body into anterior and posterior sections.
vertical plane divides body into anterior and posterior sections.
12
New cards
Sagittal
vertical line dividing the body into left and right sections.
13
New cards
The visceral pleura is the inner layer covering the
lungs
14
New cards
The study of developmental changes (from conception to birth) is known as
embryologic anatomy
15
New cards
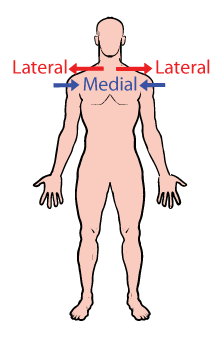
Lateral vs. medial
lateral: away from midline
medial: towards midline
medial: towards midline
16
New cards
Body membranes
thin sheet of tissues lining the body cavities
17
New cards
3 layers of meninges
dura mater
arachnoid
pia mater
arachnoid
pia mater
18
New cards
3 serous membranes
pleura
pericardium
peritoneum
pericardium
peritoneum
19
New cards
Visceral layer
covers external surface of organs
20
New cards
Parietal layer
lines internal surface of body wall
21
New cards
pleura
serous membrane lining lungs
22
New cards
Pericardium
two layered serous membrane associated with the heart
23
New cards
Peritoneum
two layered serous membrane lining the abdominopelvic cavity
24
New cards
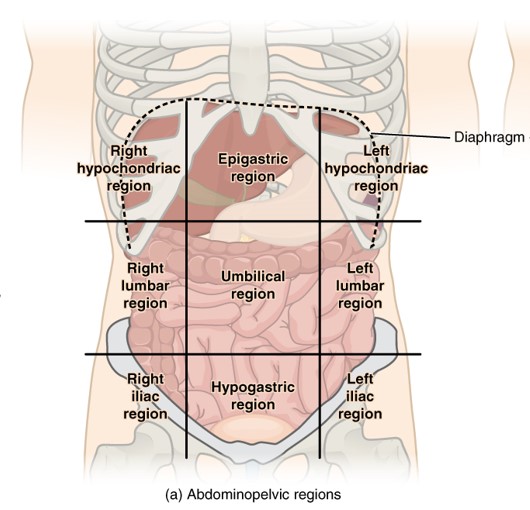
Abdominopelvic cavity has how many compartments?
9
25
New cards
Abdominopelvic regions
umbilical region
epigastric region
hypogastric region
right/ left hypochondriac regions
right/ left lumbar
right/ left iliac
epigastric region
hypogastric region
right/ left hypochondriac regions
right/ left lumbar
right/ left iliac
26
New cards
The body's largest and heaviest organ
the skin
27
New cards
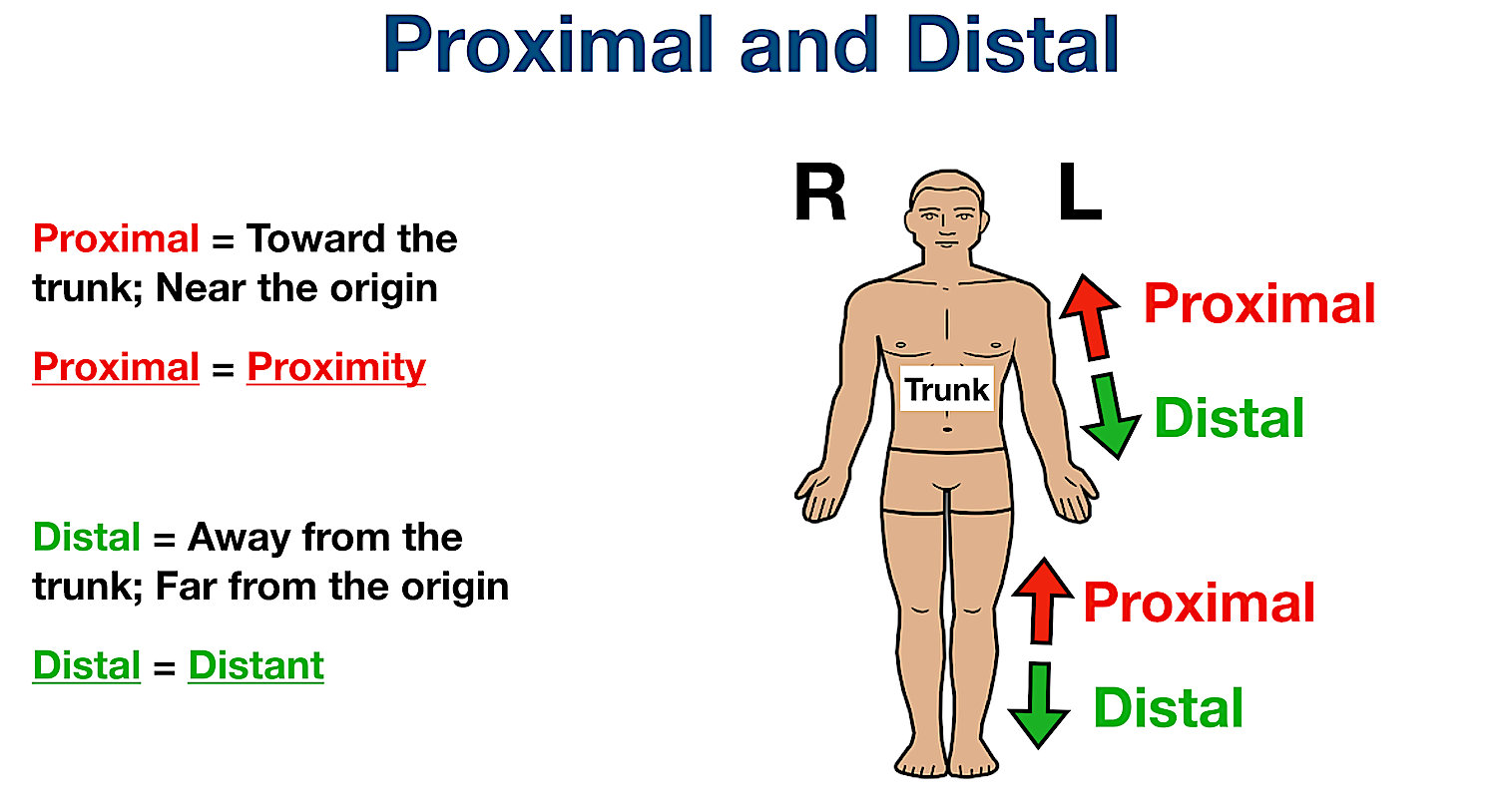
Proximal vs distal
proximal: towards trunk *proximity
distal: away from trunk *distant
distal: away from trunk *distant
28
New cards
Proximal
nearest point of attachment to limb or structure
29
New cards
Contents of ventral cavity
thoracic cavity
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
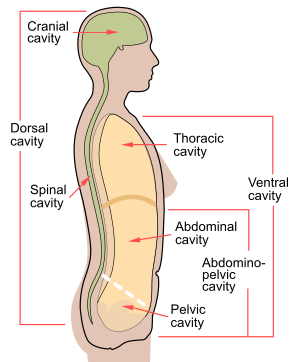
30
New cards
Contents of dorsal cavity
the brain and the vertebral cavity that contains the spinal cord
CNS
CNS
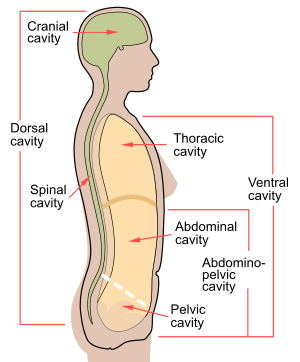
31
New cards
3 types of cartilage
hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
32
New cards
4 types of tissues
epithelial tissue
nervous tissue
muscle tissue
connective tissue
nervous tissue
muscle tissue
connective tissue
33
New cards
3 categories of dense CT
dense regular CT
dense irregular CT
elastic CT
dense irregular CT
elastic CT
34
New cards
The skin's first line of defense is
epithelial tissue
35
New cards
Functions of epithelium
protection
secretion
absorption
lining of cavities
secretion
absorption
lining of cavities
36
New cards
Simple epithelium
single layer of cells with each cell in contact with the basement membrane
37
New cards
Epithelial tissue lines
cavities and surfaces of organs
38
New cards
When epithelium is lining the internal surface of blood vessels it is called
endothelium
39
New cards
At any entrance or exit in the body you can find
epithelial tissue
40
New cards
Diaphragm
separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity
41
New cards
Prognosis of epithelial injury is
good because epithelium is highly regenerative and heals well.
42
New cards
Meninges cover the
dorsal cavity
43
New cards
Where can you find simple squamous epithelium?
inside blood vessels
44
New cards
Where can you find simple cuboidal epithelium?
kidneys, ovaries, some endocrine
45
New cards
Simple columnar epithelium lines
fallopian tubes, GI tract, respiratory tract, stomach, intestine
46
New cards
Simple ciliated columnar epithelium is found on
trachea and lining airway
47
New cards
Stratified squamous epithelium lines
mouth, esophagus, vagina, hands, feet, eye
48
New cards
Stratified cuboidal epithelium lines
salivary glands, sweat glands, mammary glands
49
New cards
Nonkeratinized stratified epithelium is found on
conjunctiva of the eye, external female genitalia, and some parts of the oral cavity
50
New cards
Transitional epithelium
is designed to allow epithelium to stretch/expand/ transition
51
New cards
Transitional epithelium lines
preterm urethra, and bladder
52
New cards
Epithelium is vascular or avascular?
avascular
53
New cards
Epithelium is innervated
true
54
New cards
CT is always found underneath
epithelial tissue
55
New cards
Connective tissue arises from
mesoderm/ mesenchyme
56
New cards
Synovial membrane (synovium)
CT lining inner surface of capsule of synovial joint.
Secretes synovial fluid as a lubricating function, allowing for joint surfaces to move smoothly across each other
Secretes synovial fluid as a lubricating function, allowing for joint surfaces to move smoothly across each other
57
New cards
Reticular fibers
much thinner but similar to collagen fibers.
58
New cards
Reticular fibers are
abundant in spleen, liver, and lymph nodes
59
New cards
Elastic fibers
contain elastin and stretch and recoil easily
60
New cards
Elastic fibers are found in
arteries, veins, lungs, and skin
61
New cards
Collagen fibers are
the most common
strong, cable-like, flexible, and very resistant to stretching
strong, cable-like, flexible, and very resistant to stretching
62
New cards
Collagen fibers are found in
tendons and ligaments
63
New cards
CT properties
Composed mostly of non-living extracellular matrix that separates the cells of the tissue.
Can be found between different tissue and organs.
Range from avascular to highly vascular
Can be found between different tissue and organs.
Range from avascular to highly vascular
64
New cards
Stratum basale
the bottom layer of cells with some cells containing melanin protein: melanocytes
65
New cards
Which layer of the integument is thicker?
dermis
66
New cards
The epidermis arises from the
ectoderm
67
New cards
Dermis is
dense irregular CT
68
New cards
Dermis arises from
mesoderm
69
New cards
Calciferol hormone
steroid hormone that increases absorption of calcium in the small intestine
70
New cards
Layers of skin in order from top to bottom
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous layer, hypodermis
dermis
subcutaneous layer, hypodermis
71
New cards
Thick skin
Contains all 5 layers of epidermis strata
Contains sweat glands, but NO hair follicles or sebaceous glands
Contains sweat glands, but NO hair follicles or sebaceous glands
72
New cards
Adipose CT
Highly vascularized loose CT composed mostly of adipocytes.
Provides insulation, energy, protection, cushion and protects organs.
Provides insulation, energy, protection, cushion and protects organs.
73
New cards
Loose CT (Areolar CT)
Contains relatively fewer cells and protein fibers than dense CT.
Protein fibers are sparse and irregularly arranged.
Protein fibers are sparse and irregularly arranged.
74
New cards
Loose CT contains
fibroblast cells
macrophage cells
mast cells
macrophage cells
mast cells
75
New cards
Mature cartilage
Avascular
Provides more flexibility than bone.
Chrondocyte cells
Provides more flexibility than bone.
Chrondocyte cells
76
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
Most common
Most of fetal skeleton
Functions in support
Most of fetal skeleton
Functions in support
77
New cards
Hyaline cartilage is found in
nose, bronchi, larynx
78
New cards
Elastic cartilage
elastic fibers ensuring resilience and flexibility
79
New cards
Elastic cartilage is found in
external ear and epiglottis
80
New cards
Fibrocartilage
good shock absorber and resists compression
81
New cards
Fibrocartilage is found on
intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, knee joint
82
New cards
Cardiac muscle tissue (myocardium)
1 or 2 central located nuclei
Minimal capacity of regeneration
Intercalated discs
Involuntary
Minimal capacity of regeneration
Intercalated discs
Involuntary
83
New cards
Smooth muscle tissue is
involuntary
84
New cards
The integumentary system is
A visual indictor of our physiology and health.
Covers the body and consists of skin and accessory tissues.
Covers the body and consists of skin and accessory tissues.
85
New cards
Aponeurosis attaches muscle to
bone, ligament, or fascia
86
New cards
Tendons attach
muscle to bone
87
New cards
Ligaments attach
bone to bone
88
New cards
3 layers of CT of skeletal muscles in order from top to bottom layer
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
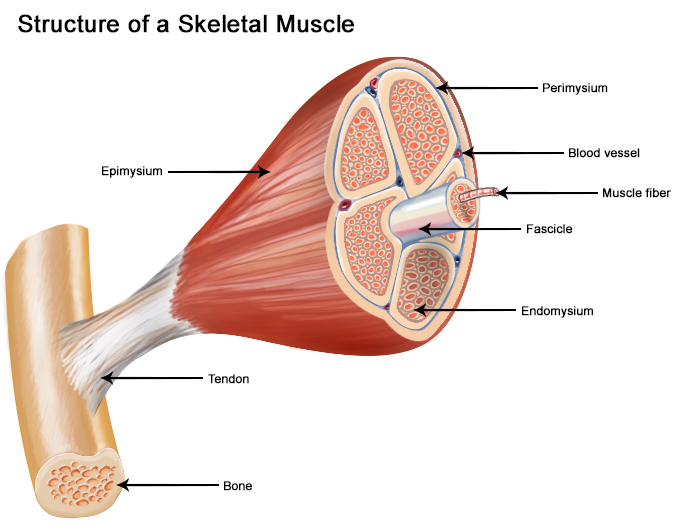
89
New cards
Smooth muscle is
involuntary
90
New cards
Smooth muscle is found in
intestine, urinary tract
91
New cards
Cardiac muscle is
involuntary and only found in the heart
92
New cards
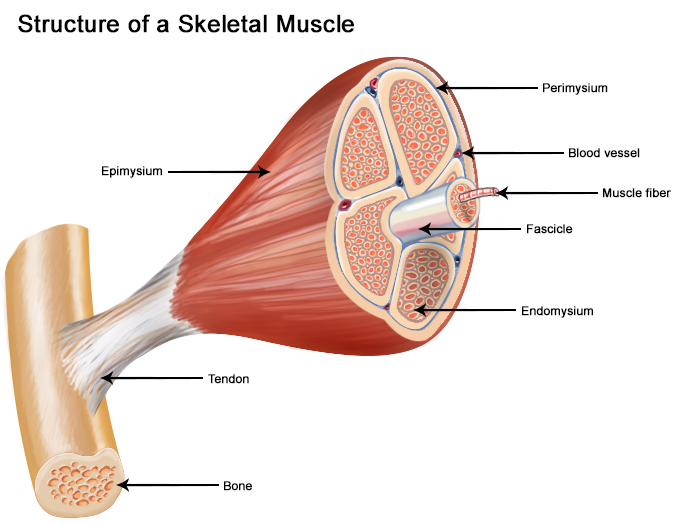
Fascicle is
a bundle of several skeletal muscle fibers and is surrounded by PERIMYSIUM
93
New cards
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber located UNDER ENDOMYSIUM
94
New cards
Endomysium
areolar CT that surrounds each muscle fiber
95
New cards
Perimysium
layer of dense irregular CT surrounding each fascicle
96
New cards
Primary function of smooth muscle is
contraction
97
New cards
The prevalence and risk factor of osteoporosis (reduced bone mass) is what in women than in men?
higher
98
New cards
Women gain or lose more skeletal mass each decade
loss
99
New cards
When would yellow bone marrow convert back to red bone marrow?
during severe anemia
100
New cards
As children mature into adulthood,
yellow bone marrow is produced as a product of red bone marrow degeneration