pregnancy and human development
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
han 202
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
pregnancy
events that occur from fertilization until birth
○ Divided into 3-month intervals called trimesters
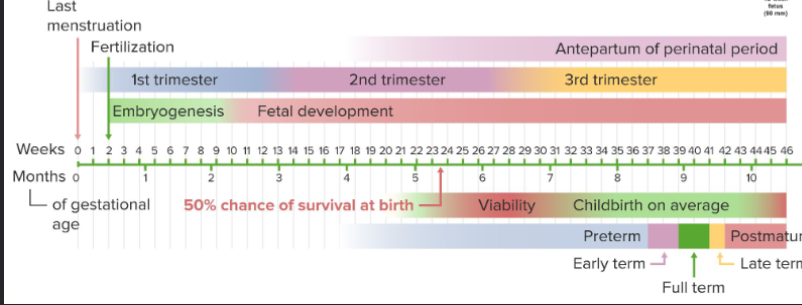
gestation period
time from the last menstrual period (LMP) until birth (~280 days)
○ Average 266 days from conception to childbirth
conceptus
the products of conception
○ Pre-embryonic stage: from fertilization through first 16 days
○ Embryo: conceptus from day 16 through week 8
○ Fetus: conceptus from week 9 through birth
gamete migration
The oocyte is viable for 12-24 hours
● Sperm is viable 24-48 hours after ejaculation
● For fertilization to occur, coitus must occur no more than ...
○ Two days before ovulation
○ 24 hours after ovulation
○ Fertilization: when the sperm’s chromosomes combine with those of a secondary oocyte (immature egg) to form a fertilized egg (zygote)
sperm transport
Propelled by...
○ Whiplike tail movements of their flagella
○ Endometrial cilia & forceful uterine contractions which disperse them throughout uterine cavity
ejaculated sperm (40-500 million)
○ Leak out of the vagina immediately after deposition
○ Are destroyed by the acidic vaginal environment
○ Fail to make it through the cervical mucus
○ Are dispersed in the uterine cavity or destroyed by
phagocytes
○ Few (100 - few thousand) reach the uterine tubes
○ Total trip = 5 inches
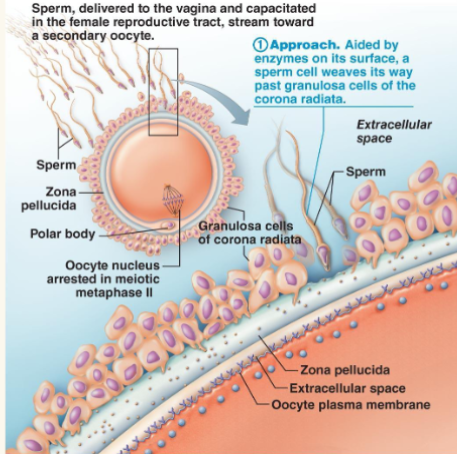
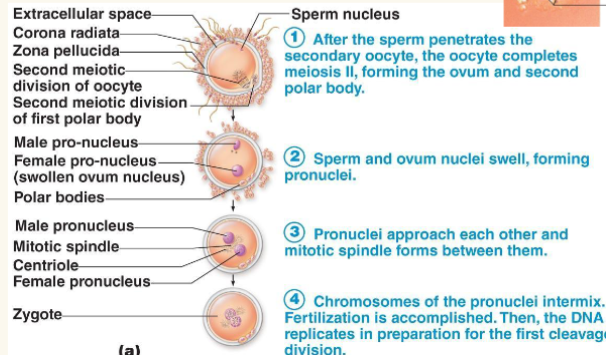
fertilization
● Sperm need to pass 2 layers to reach the oocyte
○ Corona radiata & zona pellucida
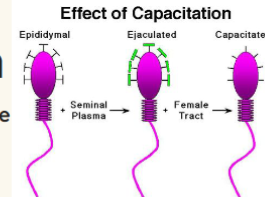
● Sperm must be capacitated before they can penetrate the oocyte
○ Secretions of the female tract weaken the acrosome membrane
fertilization: capacitation
sperm membranes become fragile so hydrolytic enzymes can be released
■ Make sperm membrane more permeable to calcium
■ Activate receptors for chemical attractants
sperm penetration
An acrosomal process forms
and binds to receptors on the
oocyte’s plasma membrane
● Sperm and oocyte membranes fuse
● Nucleus is pulled into oocyte cytoplasm
● Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate the oocyte (monospermy)
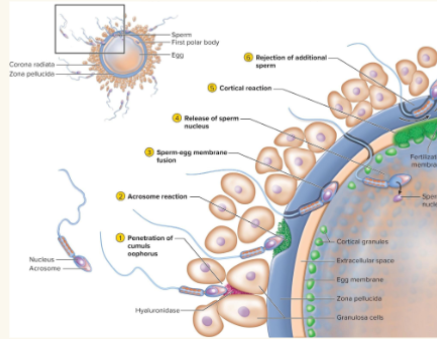
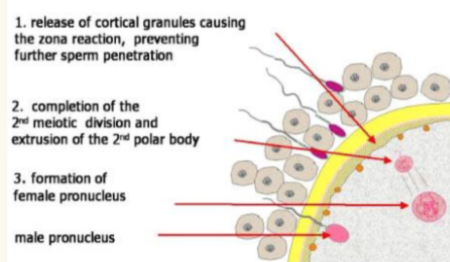
sperm penetration: once sperm enters oocyte:
Waves of Ca+ are released into oocyte’s cytoplasm. This activates:
○ Oocyte to prepare for 2nd meiotic division
○ Cortical reaction: Zonal Inhibiting Proteins (ZIPS) are released; this blocks other sperm from entering
fertilization explained image
pre-embryonic stage
First 16 days of development, culminating in an embryo
● Involves three major processes:
○ Cleavage
○ Implantation
○ Embryogenesis
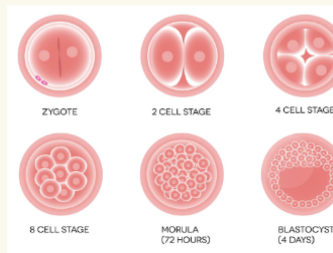
cleavage
Rapid mitotic divisions of zygote without increase in size
○ This increases surface area, increases # of cells
○ Easier for uptake in nutrients, O2 , and removal of wastes
zygote
Blastomeres (36 hours): 2 to 8 cells →
○ Morula (72 hours): 16 or more cells →
○ Blastocyst (4-5 days): fluid filled hollow sphere; reaches the uterus
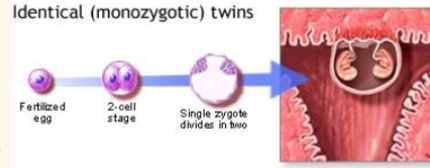
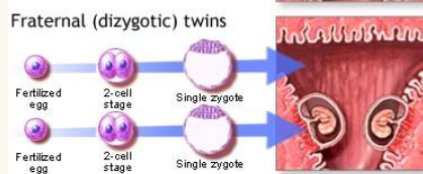
identical twins (monozygotic)
○ One egg/ one sperm = one zygote
○ Embryoblast divides into two within 2 weeks of fertilization
fraternal twins(dizygotic)
○ Two eggs/ two sperm = two zygotes
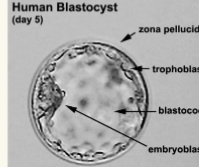
pre-embryonic stage: blastocyst
○ Trophoblast cells: single layer of flat cells
■ Participate in placenta formation
○ Inner cell mass:
■ Becomes the embryonic disc
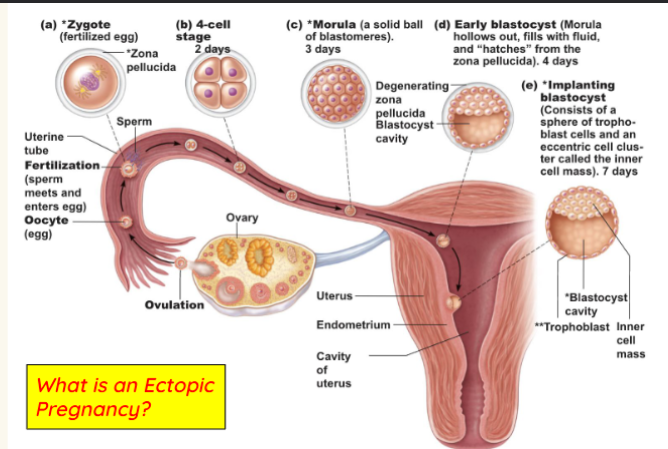
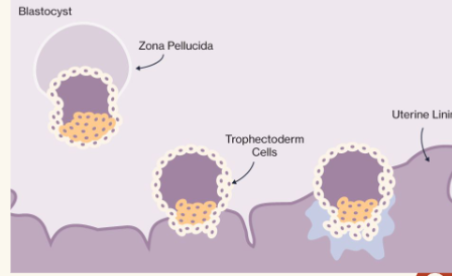
implantation
Blastocyst floats for 2-3 days
○ Nourished by uterine secretions
● Implantation begins 6-7 days after ovulation
○ Trophoblast adheres to the endometrium
○ Secretes enzymes which irritate the endometrium
If implantation fails, the blastocyst is aborted.
hromones of pregnancy
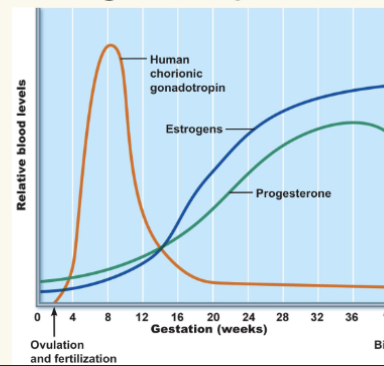
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG):
○ Secreted by trophoblast cells, later the chorion
○ Prompts corpus luteum to continue secretion of progesterone and estrogen
○ hCG levels rise until the end of the second month, then decline as the placenta begins to secrete progesterone and estrogen
hCG levels are used in pregnancy tests
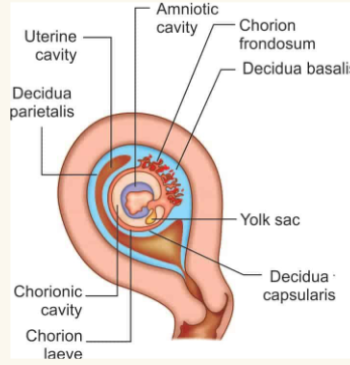
placentation
Formation of the placenta from embryonic and maternal tissues
○ Embryonic tissues:
■ The chorion (develops from the inner cell mass)
○ Maternal tissue:
■ Decidua basalis
Mother & baby’s blood supply lie close but do not intermix
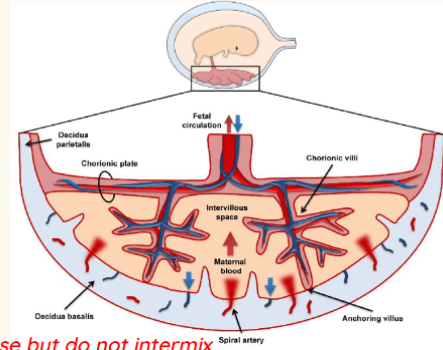
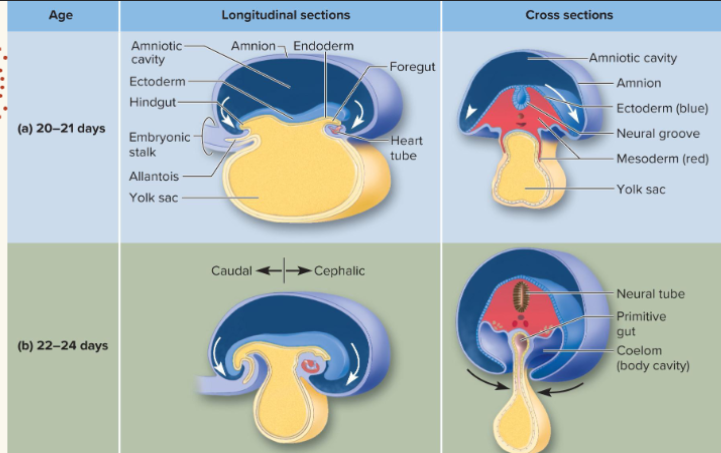
development of circulation
First blood cells arise in the yolk sac
● By the end of the third week:
○ Embryo has a system of paired vessels
○ Can hear a baby’s heartbeat
● Unique vascular modifications:
○ Umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood
○ Umbilical veins carry oxygenated blood
teratogens
Harmful substances that can cross placental barriers and enter the fetal blood which may cause congenital abnormalities or even death.
● Examples:
○ Alcohol: “fetal alcohol syndrome”
○ Nicotine: hinders O2 delivery
○ Medications: sedatives
■ Thalidomide
thalidomide
sedative of 1960’s to prevent morning sickness
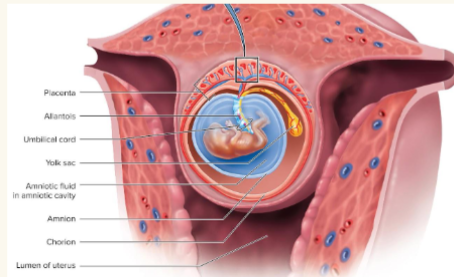
extraembryonic membranes
Amnion: forms amniotic sac
● Yolk sac: forms part of digestive tube
● Allantois: umbilical cord
● Chorion: helps form the placenta
All formed within first 2-3 weeks of development
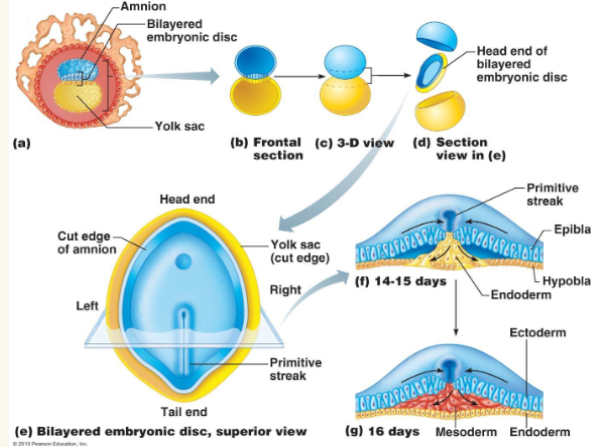
embryogenesis
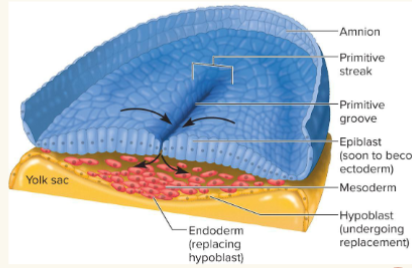
Gastrula → Fetus = Gastrulation:
● During implantation, the blastocyst starts to convert to a gastrula
● Inner cell mass develops into the embryonic disc (subdivides into epiblast and hypoblast)
● The three primary germ layers and the extraembryonic membranes develop (week 3)
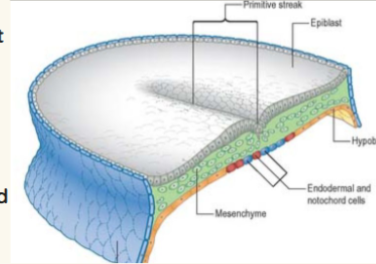
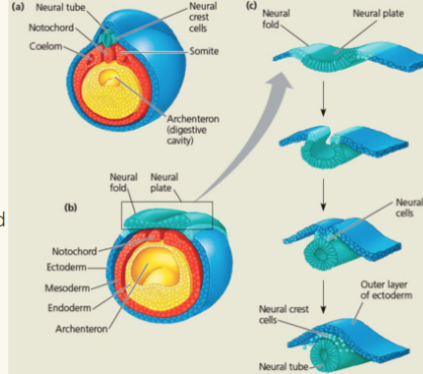
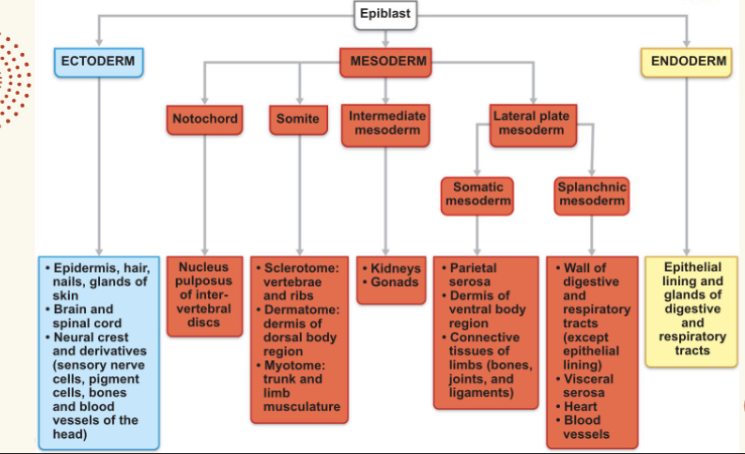
gastrulation
Embryonic disc (2 layer) becomes a 3-layered embryo (endoderm, mesoderm, & ectoderm)
● Appearance of primitive streak (dorsal groove)
● Notochord:
○ Mesodermal cells
○ Form axial support
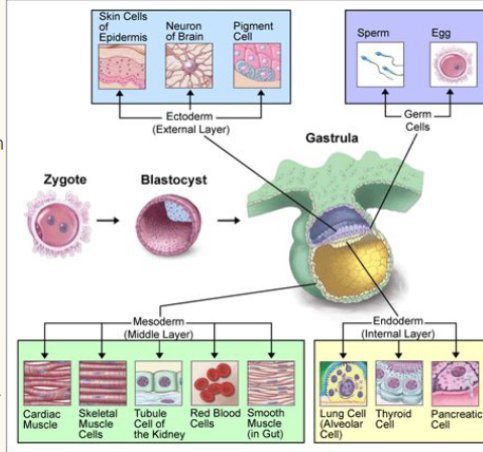
germ layers
Ectoderm → nervous system and skin epidermis
● Endoderm → epithelial linings of the digestive, respiratory, and urogenital systems
○ Endoderm & ectoderm are considered epithelia
● Mesoderm → forms all other tissues, i.e.: muscles
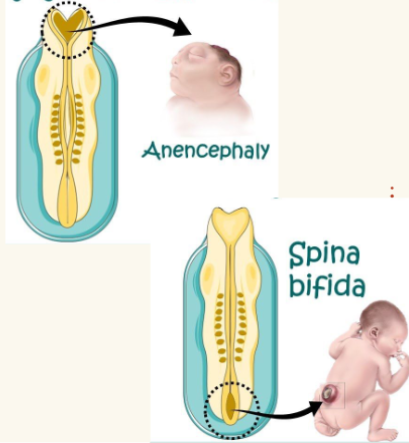
germ layers: specialization of Ectoderm
Neurulation:
○ First major event of organogenesis
○ Gives rise to the brain and spinal cord
○ Neural plate folds inward as a neural groove & fuses into the neural tube
○ Neural crest cells → cranial, spinal, and sympathetic ganglia, and adrenal medulla
longitudinal and cross sections
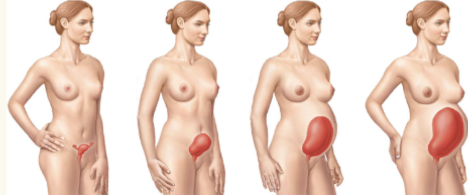
adjustments to pregnancy
Relaxin (placenta) causes pelvic ligaments and the pubic symphysis to relax to ease birth passage
● Reproductive organs become engorged with blood
● Increase in lordosis
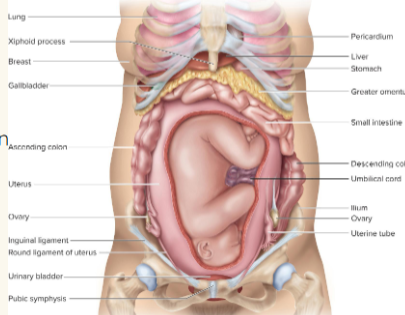
● The uterus expands, occupying most of the abdominal cavity
organogenesis
● Formation of body organs and systems
● At eighth week:
○ All organ systems are present, but not fully functional
○ End of the embryonic period; embryo becomes a fetus
● Fetal development: time of rapid growth of body structures established in the embryo; occurs from week 9 through birth
adjustments to pregnancy: systems
GI tract: Morning sickness due to elevated levels of estrogen and progesterone
Urinary system: Increased urine production due to increased metabolism and fetal wastes, stress incontinence
Respiratory system: Tidal volume increases; dyspnea may occur later in pregnancy. Why?
CV system: Blood volume increases 25-40%; blood pressure and pulse rise venous return from lower limbs may be impaired. Why?
initiation of labor: during the last few weeks of pregnancy
● Fetal secretion of cortisol stimulates the placenta to secrete more estrogen
○ Causes production of oxytocin receptors
○ Antagonizes calming effects of progesterone, leading to Braxton Hicks contractions (weak irregular contractions) in uterus - false labor
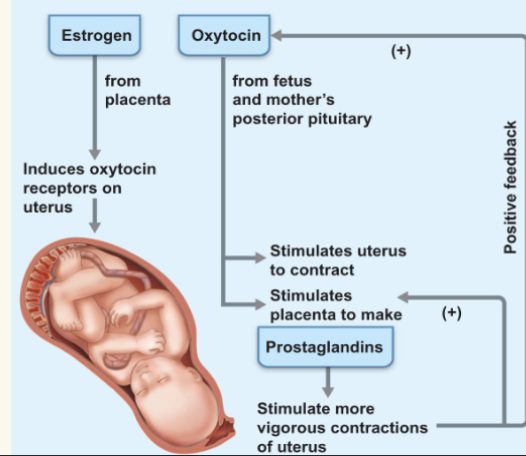
initiation of labor: positive feedback occurs
● Surfactant Protein A:
○ From fetal lungs, causes softening of the cervix
● Fetal Oxytocin:
○ Causes the placenta to produce prostaglandins
● Maternal emotional and physical stress:
○ Activates the hypothalamus, causing oxytocin release causing powerful uterine contractions
parturition
the act of giving birth; Labor events that expel the infant from the uterus
stages of labor
1. Dilation: longest stage; can last 6-12+ hours
2. Expulsion: lasts about 30 min
3. Placental: afterbirth; occurs about 30 min later
dilation stage
Initial weak contractions:
○ 15-30 minutes apart, 10-30 seconds long
○ Become more vigorous and rapid
● Cervix dilates fully to 10 cm
● Amnion ruptures, releasing amniotic fluid → “water breaking”
● Engagement occurs: head enters the true pelvis
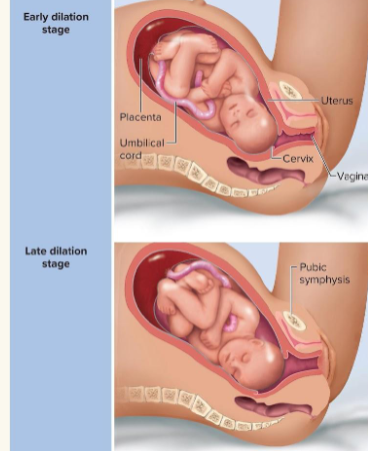
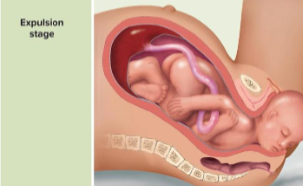
expulsion stage
Strong contractions every 2-3 minutes, about 1 minute long
● Urge to push increases (in the absence of local anesthesia)
● Crowning occurs when the largest dimension of the head distends the vulva
● Lasts about 30-50 min
● Ends with the delivery of infant
placental stage
● Strong contractions continue, causing detachment of the placenta
● Delivery of the afterbirth (placenta & membranes) occurs ~30
minutes after birth
● All placenta fragments must be removed to prevent postpartum
bleeding
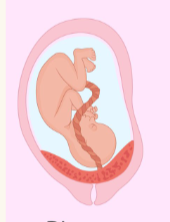
placenta previa:
Placenta formation low in the uterus, adjacent to and/ or covering the cervix
placental abruption
Placenta separates from uterus wall prior to birth
firstkh
↑ CO2 → central acidosis → stimulates respiratory control centers
to trigger the first inspiration
○ Surfactant in alveolar fluid helps reduce surface tension
● Respiratory rate: ~ 45 breaths per minute for first two weeks, then declines
○ Premise usually put on respirators, lungs still immature
extratrauterine life
Neonatal period: four-week period immediately after birth
● Physical status is assessed 1 & 5 minutes after birth
○ APGAR score: 0-2 points each for...
○ Score of 8-10: healthy
lactation
Production of milk by the mammary glands
○ Anterior pituitary releases prolactin
● Oxytocin causes the letdown reflex → Actual ejection of milk from mammary glands
● Colostrum: yellowish secretion rich in vitamin A, protein, minerals, and IgA antibodies
○ Released the first 2-3 days
methods contraception
