Biodiversity and Ecosystem Function
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on lecture notes about biodiversity, ecosystem function, and related concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Biodiversity
The variability of all living organisms from all sources
Willis and Gillson, 2007
Alpha diversity
The number of species in a specific location.
Dornealas et al., 2014
Beta diversity
How different communities are between places.
often over a small distance, between habitats
Dornealas et al. 2014
Gamma diversity
the total species richness of a large geographic area - from ecological communities to entire biomes/ continents
reflects combined influences of alpha and beta diversity
Lomolino et al., 2017
Why is biodiversity important ?
Ecosystem stability
Without biodiversity humans struggle
Lomolino et al., 2017
number of green spaces are related to mental health
the more species in park the less hospitalisations due to mental health
Methrost et al., 2021
Ecosystem function
The result of interactions between organisms.
biodiversity increases ecosystem function
more species - the better the species get in growing
becoming more efficient in using the resources in Niches
becoming more complementary
efficiency increases - redundancy decrease
Reich et al., 2012
Biodiversity does not always increase plant productivity
Biodiversity loss at regional scales may effect ecosystem functioning
ecosystem functioning was higher in patches with the lowest realised diversity
There is a point which all species will die out
Hagan et al., 2021
Why is ecological complexity important ?
more taxa present that support the same function = increased redundancy
higher diversity of taxa that support different functions = increased functional uniqueness
Wagg et al., 2019
Microbiome diversity and microbial network complexity positively influenced several ecosystem functions
greater microbial richness = greater complexity + greater association among taxa that support several functions
we loose complexity, we loose functions
Wagg et al., 2019
Case study for complexity over time
recovering meadows in the Netherlands
complexity and function increase through time
soil networks had more and stronger interactions = more efficient carbon use
Morriën et al. 2017
Pulse disturbance
A disturbance that happens once and then disappears
Lomolino et al., 2017
Press disturbance
A disturbance that stays through time.
Lomolino et al., 2017
Examples of disturbance
wildfires, storms, floods, volcanic eruptions
Begon and Townsend, 2021
Impact of disturbances
Can open up gaps for new species to colonise and thrive
some cases it prevents one species from dominating - maintains a diverse range of species - allows inferior species to colonise
after a disturbance pioneer species arrive
Begon and Townsend, 2021
E.g. Atlantic forest in Brazil was flooded
Resistance
Ability to withstand disturbance.
most disturbance combination of press and pulse
Lomolino et al., 2017
Robustness
How much a species changes after a disturbance
Lomolino et al., 2017
Biodiversity increases ecosystem stability, but not resilience
Ecosystems with better diversity are able to overcome disturbance better
Greater chance of having species with traits that are able to adapt to change
Biodiversity stabilises ecosystem productivity to things such as climate events
over time - ecosystems more stable
McCann, 2000
Latitude and climate
increase in species from the poles to the tropics
temperatures are higher and precipitation is greater at lower latitudes
needed for species growth + survival - more energy here
e.g. troical diversity among mammals die to higher levels of fruit-eating lifestyle
Cox and Moore, 2019
Diagram from Rahbek et al., 2019
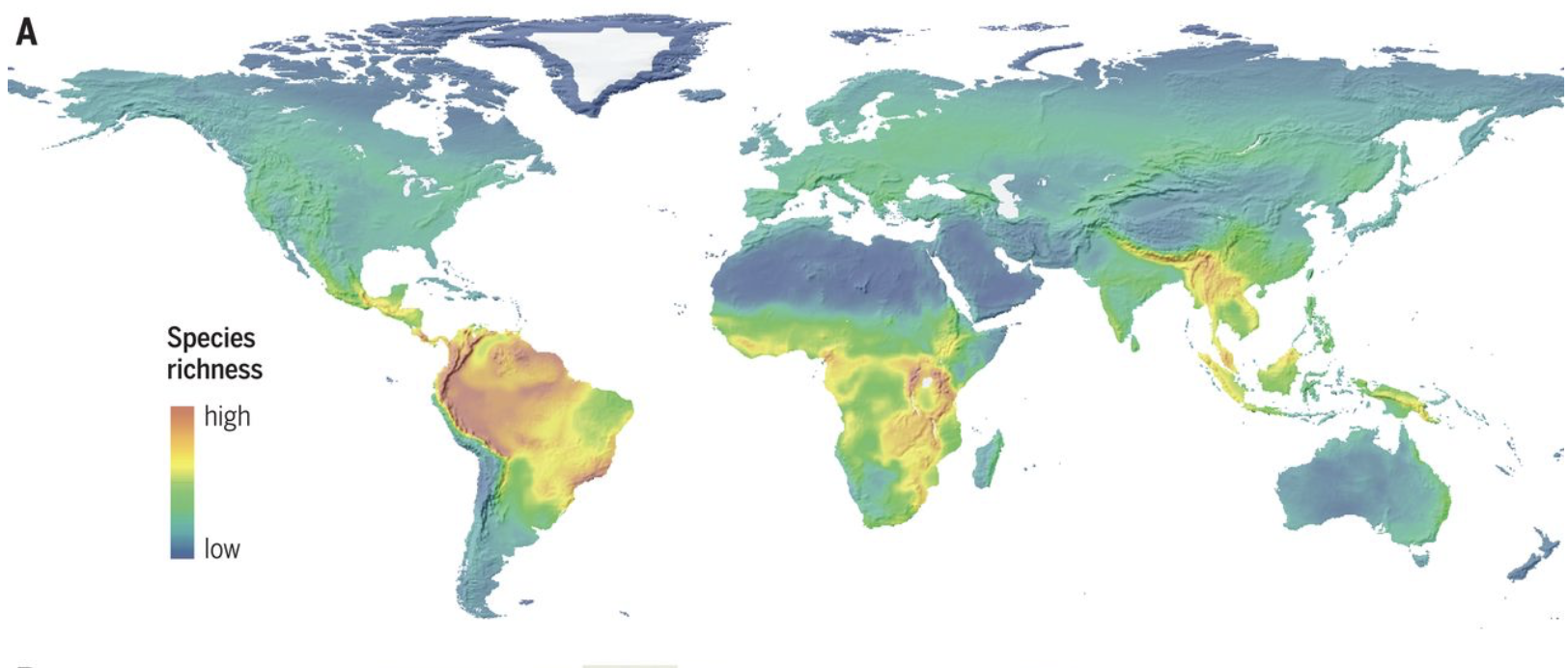
Elevation and climate
decrease of species richness with elevation
high elevation communities occupy small areas
declining temperatures - less energy - harder for growth
high elevations - moisture os frozen + unavailable
diversity increases as altitude increases, reaches a peak - then decreases
e.g. Mount Kinabalu - distance peak
Begon and Townsend, 2021
Biodiversity hotspots
areas that are extremely rich in species
E.g. tropical rainforests, coral reefs and islands
25 hotspots
land surface area = 1.4 %
Low-latitude concentration of hotspots
Diversity not evenly spread over globe
Lomolino et al., 2017
Factor influencing biodiversity - Productivity
species locate where conditions and resources are appropriate
plants - productivity depends on nutrients or conditions + solar radiation
higher productivity is linked to wider resources
there are occasions of high productivity and low species richness
high productivity —> high pop growth —> extinction of some species present
species richness lower in extreme environments
Begon and Townsend, 2021
Factor influencing biodiversity - Area / Physical barriers
environments that are heterogeneous can accommodate new species
as wider variety of microhabitats + microclimates
Environmental temperature regimes - serve as barriers
physical barriers - prevent spread of an organism e.g. mountains etc
climatic and biological barriers e.g. geology and soil chemistry + competition
Cox and Moore, 2019
Factor influencing biodiversity - Competition
Biotic interactions can constrain distributions within a range
organisms that share the same resource compete with each other can suffer from reduced growth, survival and reproduction
exploitative competition - individuals use up resources and make them unavailable to others
interference competition - individuals use aggressive dominance to deny others access to resources
predation - when one organism kills another
Lomolino et al., 2017
Spatial scale
Local scale - species interactions - big importance
Landscape scale - landscape configuration e.g. connected corridors etc
Global scale - climate, biogeography etc
diagram - Willis and Whittaker, 2002
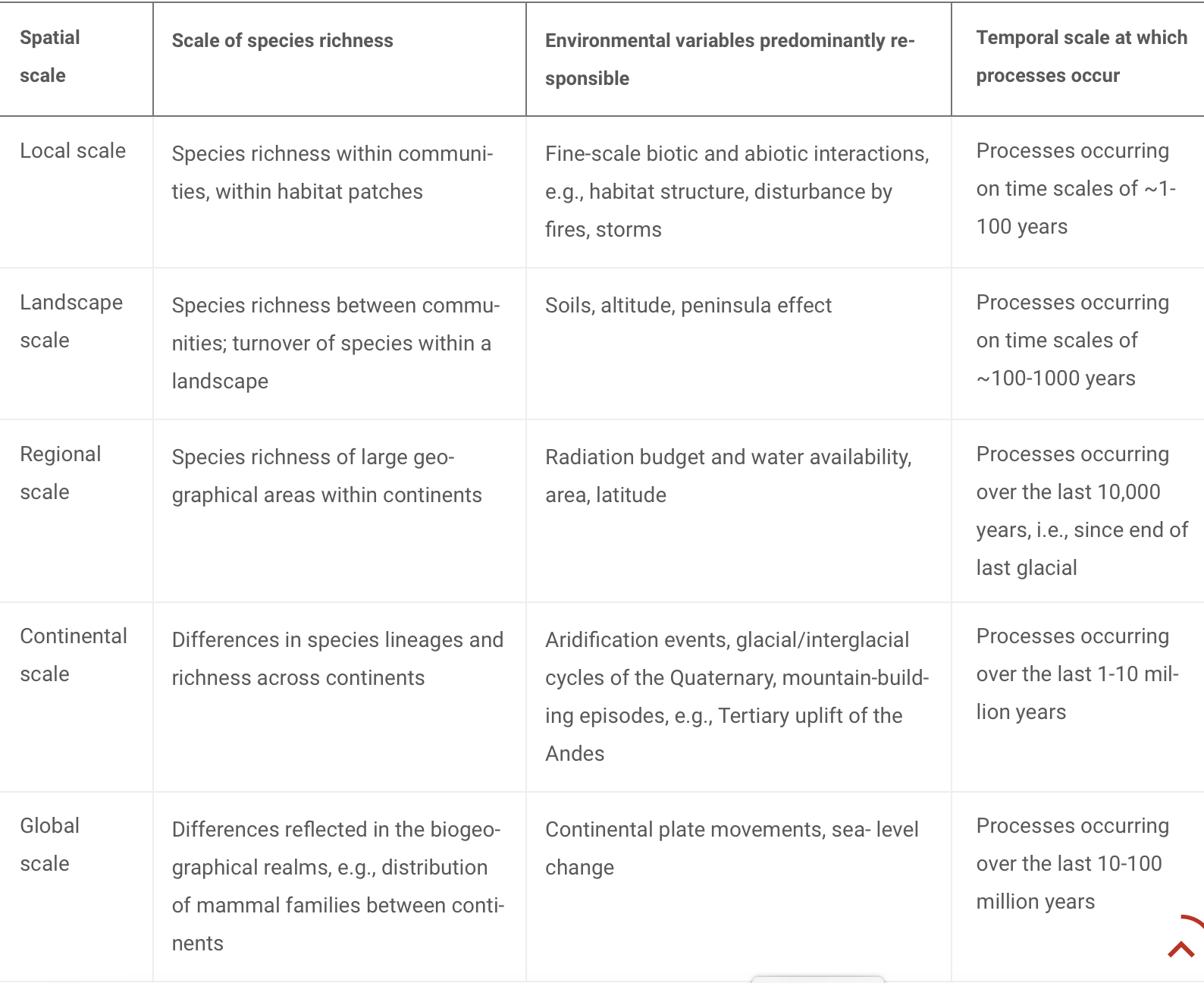
Temporal scales
may be predictable and unpredictable
predictable - allows specialised adaptation
unpredictable changes = disturbance
communities are disturbed in extended timescales
Begon and Townsend, 2021