Stages of mieosis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Interphase
The same as mitotic interphase
G1
The cell grows and develops mRNA and proteins for DNA synthesis
S
Chromosomes are copied
G2
The cell grows and checks for any mistakes and such
2n, 46 chromosomes, 92 chromatids (Diploid)
Prophase 1
The nuclear membrane breaks down
The DNA (Chromatin) condenses into chromosomes
The chromosomes then pair with their homologous pair (same size and placing of genes)
They create a tetrad shape
Crossing over occurs (parts of each chromosome switching sides)
Centrosomes begin to appear at different ends of the cell
Metaphase 1
The homologous chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell (Metaphase plate)
The Spindle fibres then attach to the centromeres
The way they align is also random which introduces more genetic variation
How is genetic variation introduced in meiosis
By crossing over which is the homologous chromosomes switching parts of their genetic code to each other while they are paired up
By the order the chromosomes are aligned during metaphase since it is random
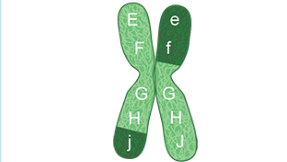
what is an Allele
A version of genes that could be inherited. Like

Anaphase 1
The spindle fibers pull the homologous chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell
The sister chromatids are still attached at the centromere
Telophase 1
A new nuclear membrane forms around to 2 groups of DNA
The chromosomes then decondense into chromatin again
Spindle fibers disappear
2 nucleus are at opposite poles
Cytokinese 1
A bunch of proteins called a contractile ring form around the equator of the cell and pinches the cytoplasm, creating a cleavage furrow until the cell divides
n, 23 chromosomes, 46 chromatids (haploid)
Prophase 2
The nuclear membrane dissolves and the chromatin reforms into chromosomes and spread out
Centrosomes form and move to opposite poles of the cell
Metaphase 2
The chromosomes move to the metaphase plate of the cell
Spindle fibers attach to each sister chromatid of the chromosome
Anaphase 2
The sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers and are moved to the opposite poles
Telophase 2
The nuclear membrane reforms around the chromosomes
The sister chromatids unravel back into chromatin
Cytokinesis 2
A bunch of proteins called a contractile ring form around the equator of the cell and pinches the cytoplasm, creating a cleavage furrow until the cell divides
n, 23 chromosomes, 23 chromatids, (haploid)
Difference between males and females in meiosis
The males create 4 equal size sperm cells
The females create 1 large egg cell and 3 smaller cells
The large cell is called the Ovum and the smaller ones are called polar bodies (They are byproducts and just die)
What would happen if mieosis occured without DNA replication
2 of the 4 cells created would have no genetic material
But the good thing is that this wouldn’t happen because the G2 phase checks for mistakes like this
What would happen if the spindle fibers never attached during metaphase 1
This would cause the cells to miss out on some genetic information
This is because only some chromosomes would be on either side (whole homologous chromosomes would be on each side)
What would happen if sister chromatids were not pulled apart at anaphase 2
This would cause the chance of both sister chromatids ending up in a cell
This would cause some cells miss out on a full set of chromosomes
What would happen if cytokinesis 2 didn’t occur
The cell would have 2 amounts of DNA in 1 cell
Why is the egg cell the biggest cell in the human body and the sperm cell the smallest
So that the whole sperm cell can fit inside the egg cell and create a zygote