APHuG Final exam
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Agglomeration
when industries are clumped together for mutual advantage.
Antecedent boundary
a boundary made before people were there
Break-of-Bulk points
when the forms of transport change
Bulk-gaining industry
when the product weighs more than the raw materials
Cartogram map
A map in which the shape or size is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as travel, population or economic production
Central Place theory
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on how far people are willing to ttravel for that service
circulation
short term repetitive stuff
ex: kid going to school, then practice, then home every day
combine
a machine used for harvesting crops, especially grain

commercial agriculture
large scale farming used primarily for profit
core countries
According to world systems theory, the most advanced countries
cottage industry
Manufacturing based in homes rather than in a factory, commonly found before the Industrial Revolution
cumulative causation
a self-reinforcing process where initial changes within a system lead to increasingly stronger and sustained effects, often without a clear end point
deglomeration
when industries that formerly existed in an established agglomeration disperse
denomination
religious subgroup
ex: baptist in christianity
Devolution
when a central government breaks down into smaller, more dispersed groups of power
distribution
way things are dispersed
ethnic religion
-a religion that is particular to one culturally distinct group of people
-hard to adopt
ex: Hinduism, Judaism, and Shintoism
EEZ (Exclusive Economic Zone)
The 200 miles from a nation's shoreline where they can use it for its materials and resources
Feedlot
-an area or building where livestock are fed and fattened up
-not much room
-commercial agri
Fordist production
-Form of mass production in which each worker is assigned one specific task to perform over and over
-by Henry Ford
formal region
An area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics
functional region
-An area organized around a node or focal point and the reach it has
geopolitics
the study of how geography influences politics and international relations
GMO's
genetically modified organisms
Gravity model
the interaction between two places can be determined by the product of the population of both places, divided by the square of their distance from one another
heartland theory
Hypothesis proposed by Halford MacKinder that held that any political power based in the heart of Eurasia is key to power
Hinduism
-A religion native to India, featuring belief in many dietys and reincarnation
- holy book is The Vedas
-temple is place of worship

infrastructure
the basic framework of a building or a system
intervening obstacles
Any forces or factors that may limit human migration.
intraregional migration
Permanent movement within one region of a country.
landlocked state
A state that does not have a direct access to the sea.
international law of the sea
adopted in 1983, it says that foreign countries could not have their military or other ships travel within 12 miles of the coast of any country, and countries have exclusive economic zones (meaning that they have the right to explore for resources up to 200 miles off their shores.)
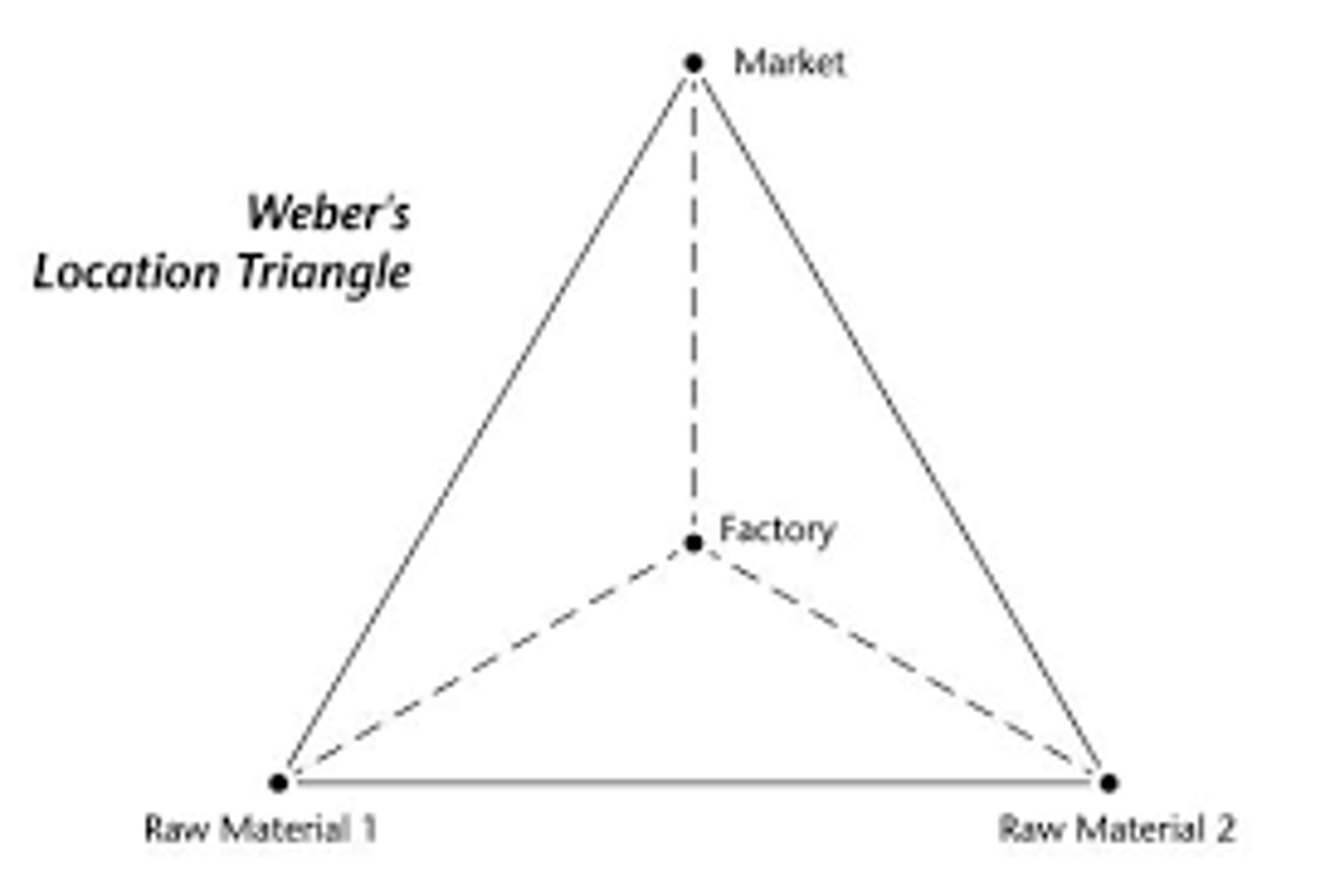
least cost theory
a concept developed by Alfred Weber to describe the optimal location of a manufacturing establishment in relation to the costs of transport and labor, and the relative advantages of agglomeration or deglomeration
Maquiladores
Companies located in Mexico but owned by American firms
median-line principle
an approach to dividing and creating boundaries at the mid-point between two places.
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people
mental maps
image or picture of the way space is organized as determined by an individual's perception, impression, and knowledge of that space
metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
missionary
An individual who helps to diffuse a universalizing religion.
Monotheism
Belief in one God
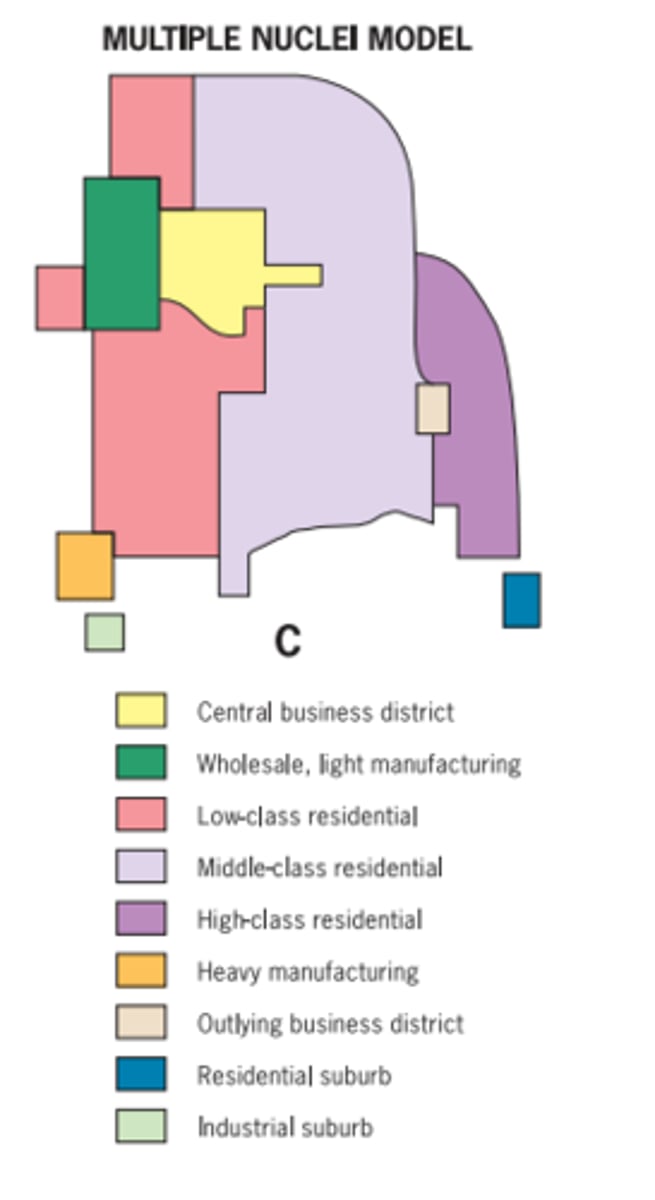
multiple nuclei model
NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement; allows open trade with US, Mexico, and Canada.
New international division of labor
Transfer of some types of jobs, especially those requiring low-paid less skilled workers, from more developed to less developed countries.
Operational boundary dispute
Conflict over the way a boundary should operate or function, such as the conflict over allowing migration across the border
Outsourcing
-A decision by a corporation to turn over much of the responsibility for production to independent suppliers.
-cheaper labor
Perceptual Region (Vernacular)
how people think about or percieve a region
physical boundary
boundary defined by a physical land mark like a river or a lake
Polytheism
Belief in many gods
pull factor
a factor that makes people to move to a new location
push factor
a factor that makes people to leave old residences
Refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
region
An area distinguished by a unique combination of trends or features.
relic boundary
A boundary no longer observed but that still affects the present-day area (ex: berlin wall)
Rimland Theory
the belief of Nicholas Spykman that domination of the coastal fringes of Eurasia is key for power
scale
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole
scale of analysis
how zoomed in or out you are when looking at geographic data
Site factors
the physical characteristics of a location itself
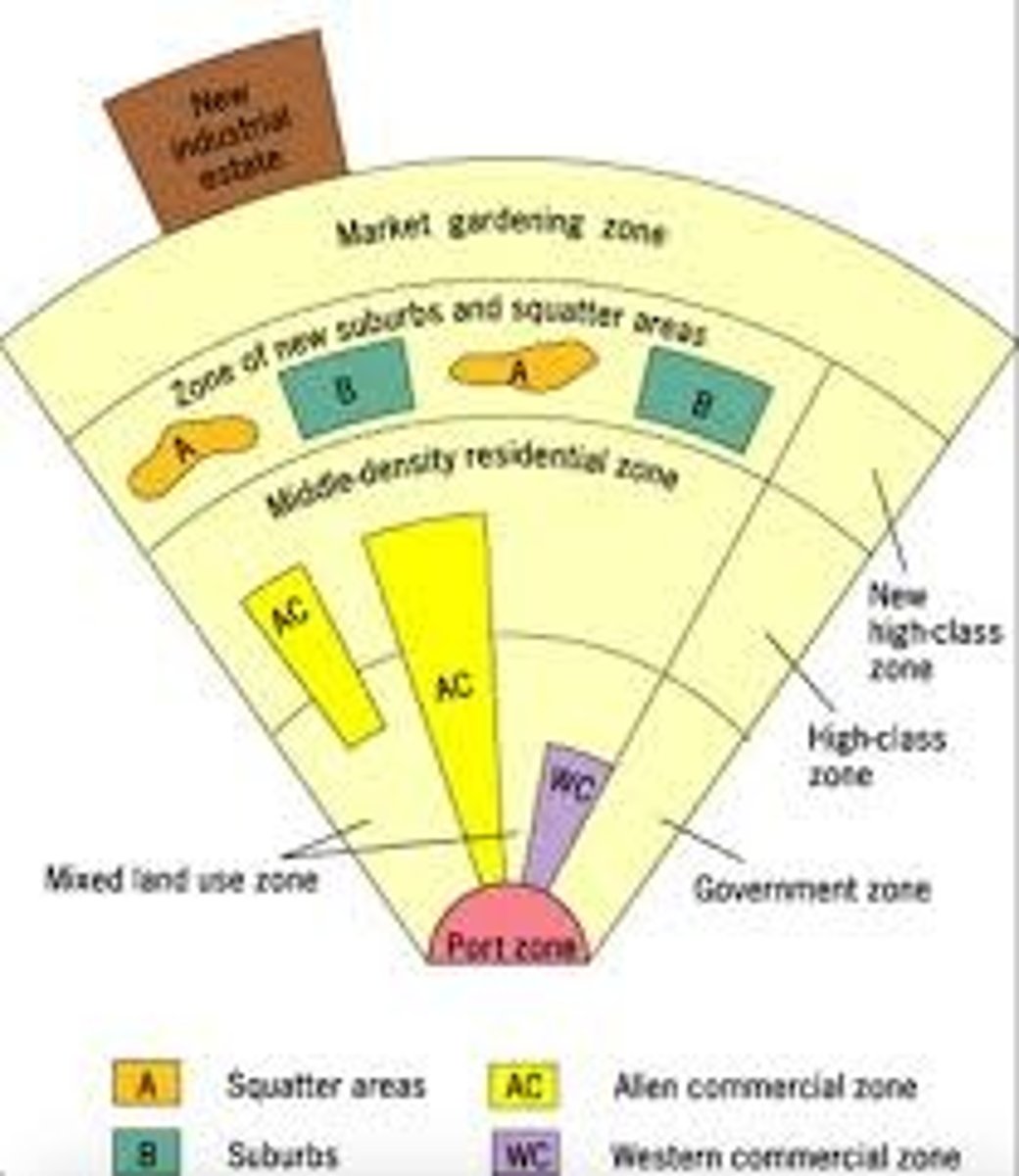
Southeast Asian City Model
Sovereignty
states right to have power over their state
states
a country
Supranationalism
three or more countries agree to give up a degree of autonomy in order to pursue common goals. (ex. European Union)
sustainable agriculture
farming for family and close community
syncretic
blending cultural or religious beliefs
Tertiary Sector
the part of the economy that involves services rather than goods
Themes of Geography
location, place, region, movement, human-environment interaction
time-space comprerssion
shorter time for things to get to others
Unitary State
places most power in the hands of central government officials
Universalizing Religion
-A religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location.
-easy to adopt in everyday life
Voluntary Migration
wanting to migrate
Von Thunen's Model
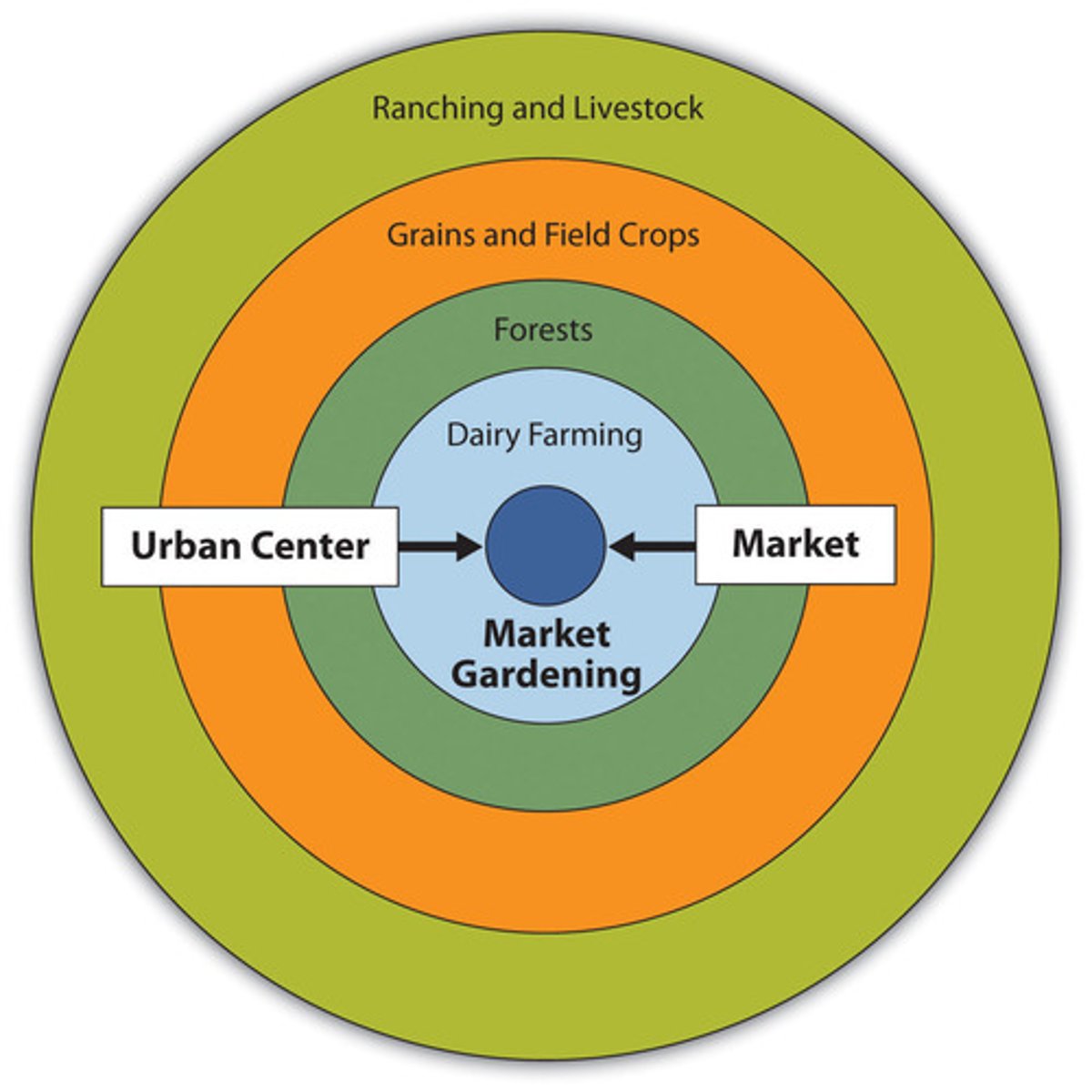
world city
Centers of economic, culture, and political activity that are strongly interconnected and together control the global systems of finance and commerce.
World Systems Theory
Theory originated by Immanuel Wallerstein and illuminated by his three-tier structure, proposing that social change in the developing world is inextricably linked to the economic activities of the developed world.
international law of the sea
foreign countries cannot have ships/military within 12 miles of the coast of another country