Biochemistry - Chapter 4: Levels of Protein Structure
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
protein structure: parts 1 and 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
native conformations
3D shapes of proteins with biological activity
levels of protein structure
1) primary
2) secondary
3) tertiary
4) quaternary
primary structure (1o)
order in which amino acids are covalently linked together
secondary structure (2o)
ordered 3D arrangement of the backbone atoms in a polypeptide chain
tertiary structure (3o)
3D arrangement of all atoms in a protein, including those in side chains and prosthetic groups
prosthetic groups
non-peptide compounds that mostly attach to proteins and assist them in different ways
configuration of prosthetic groups
usually trans to each other, but sometimes cis
quaternary structure (4o)
arrangement of subunits with respect to one another in more than one polypeptide chain
primary structure is always written from ___________
amino terminal to carboxyl terminal, from left to right
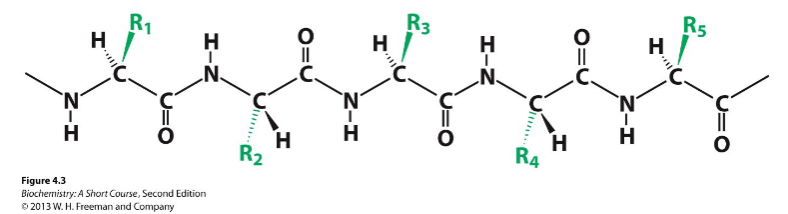
components of a polypeptide chain
constant backbone and variable side chains
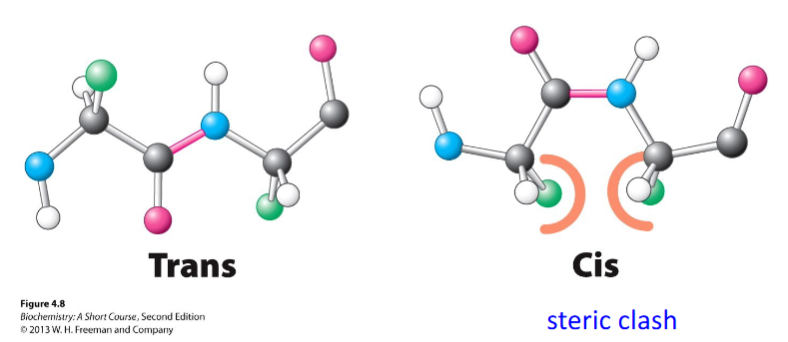
benefit of trans configuration in peptide bonds
minimizing steric clashes between neighboring R groups
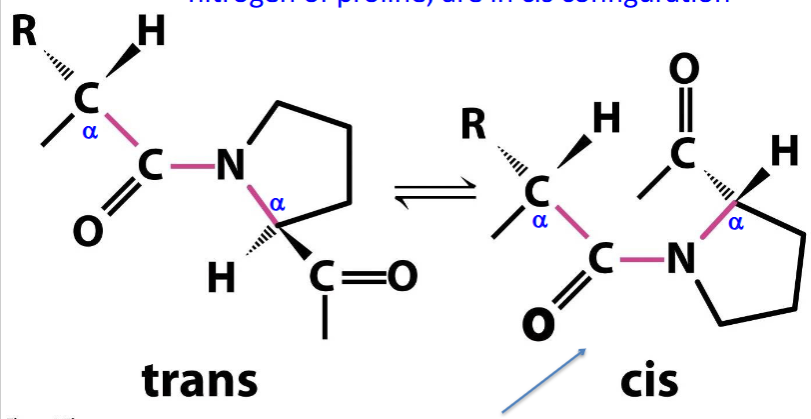
peptide bonds in cis configuration
those involving the imino nitrogen of proline
residue
each amino acid in a protein
what the amino acid sequence helps determine
the 3D conformation of a protein
what the conformation of a protein determines
its properties
hemoglobin S (HbS)
sickle cell hemoglobin
sickle cell hemoglobin is caused by _________
substitution of valine instead of glutamate at position 6 of β chains
CFTR protein
cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
CFTR protein function
a channel across the membrane of cells that produce mucus
delta 508
most common mutation in CFTR protein, deleting one amino acid at position 508
effect of delta 508
resulting abnormal cell membrane channel prevents the normal transport of chloride ions and water into and out of cells, causing abnormally thick, sticky mucus production in the cells that line the passageways of the lungs and other organs, obstructing airways
planar configuration of peptide bonds restricts ____________
rotation around the bond
card and swivel analogy
peptide chains (cards) linked at opposite corners by swivels
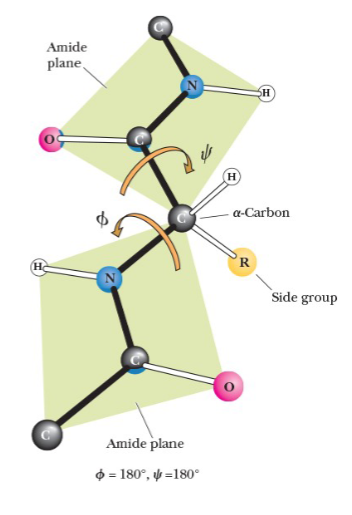
secondary structure and angles
secondary structure can be described by the two angles at which the two bonds coming from an α-carbon can rotate
phi (Φ)
angle between the α-carbon and amino nitrogen
psi (ψ)
angle between the α-carbon and carboxyl carbon
when two amide planes are parallel, both angles are assigned the value of _______
180o
secondary structure
3D structure formed by hydrogen bonds between peptide NH and CO groups of amino acids near one another in the primary structure
prominent examples of secondary structure
α-helix and β-sheets
α-helix
stabilized by hydrogen bonds that are parallel to the helix axis within the backbone of a single polypeptide chain
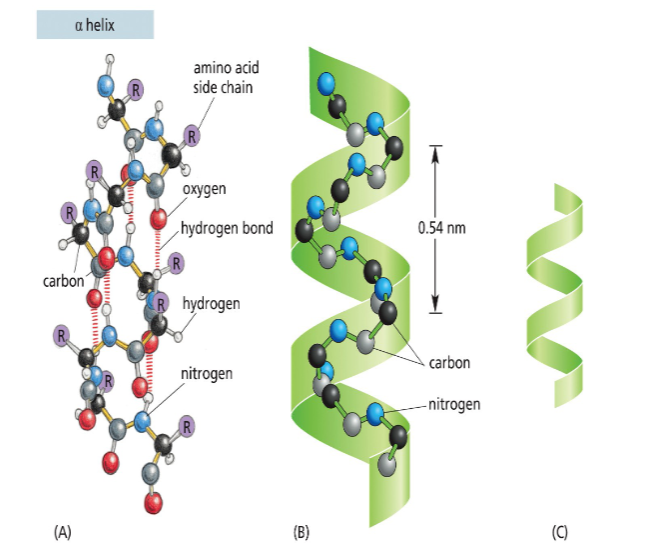
features of an α-helix
clockwise or right-handed coil
3.6 amino acid residues for each turn of the helix
linear distance between corresponding points on successive turns (pitch = 5.4 Angstroms)
1.5 Angstroms per amino acid residue
1 Angstrom =
10-10 m
features of hydrogen bonds in β-sheets
occur between peptide chains as interchain or intrachain
perpendicular to the direction of the protein chain
give rise to the zigzag structure
parallel β-sheets occur when _______________
the adjacent chains run in the same direction as one another
antiparallel β-sheets occur when _____________
adjacent chains run in opposite directions of each other
position of the R groups of β-sheets
alternate between being above and below the plane
β-strand structure
fully extended polypeptide
3.5 Angstroms between amino acid residues
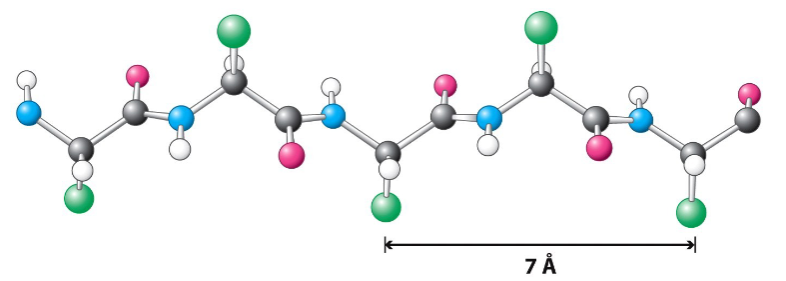
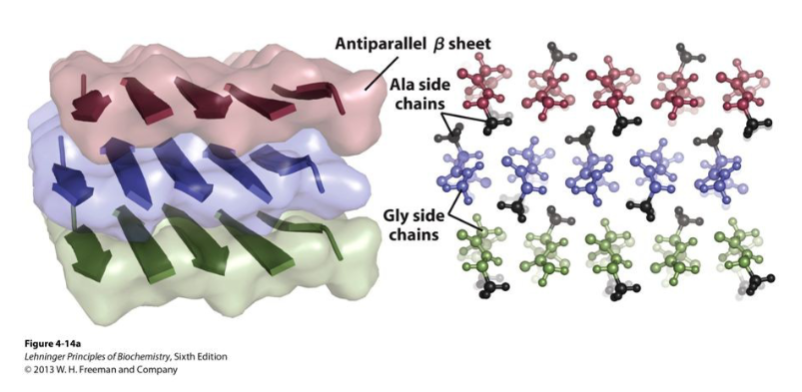
antiparallel β-pleated sheets
hydrogen bonds between strands are more straight
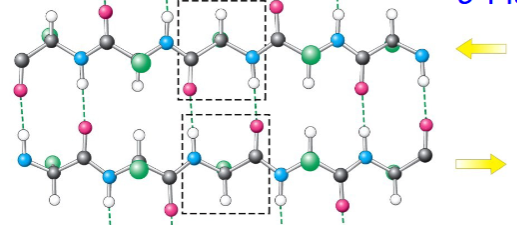
parallel β-pleated sheets
hydrogen bonds between strands are more diagonal
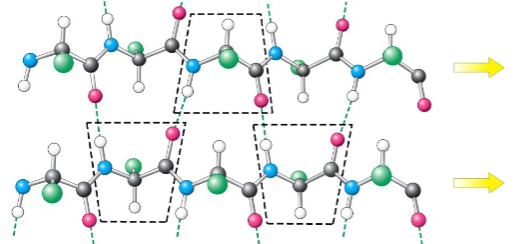
antiparallel β-pleated sheet arrangement
hydrogen bonds are perpendicular to the direction of the polypeptide
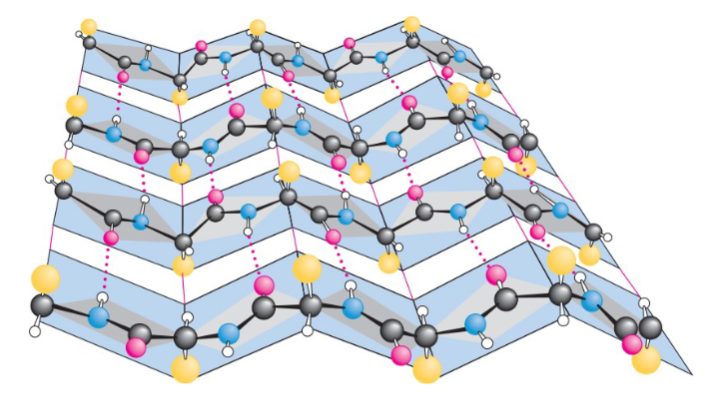
benefits of antiparallel orientation
allows for maximum hydrogen bonding because the oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen atoms are in a straight line
supersecondary structures result from ___________
combination of α- and β-strands
βαβ unit
the most common supersecondary structure in which two parallel strands of β-sheets are connected by a stretch of α-helix
reverse turn
type of non-regular secondary structure that changes the direction of a polypeptide chain
reverse turn with proline
addition of proline puts a kink in the chain that sets up the reverse turn
benefit of R-group in glycine being H in a reverse turn
H is a small atom, allowing glycine to fit inside the reverse turn
fibroin
protein of silk produced by insects and spiders; composed almost entirely of β-sheets
fibroin structure
layers of antiparallel beta sheets rich in alanine and glycine residues with small side chains interdigitated, allowing close packing of sheets
noncovalent interactions tertiary structures depend on
1) hydrogen bonding
2) hydrophobic interaction
3) electrostatic attraction
4) complexing several side chains to a single metal ion
hydrogen bonds in tertiary structures occur between _________
polar side chains of amino acids
hydrophobic interactions in tertiary structures occur between ____________
nonpolar side chains
electrostatic attraction in tertiary structures occur between ____________
side chains of opposite charge
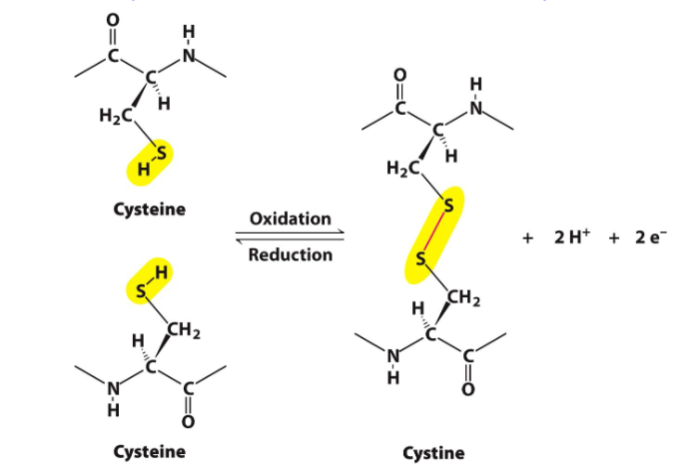
covalent interactions tertiary structures depend on
disulfide bonds between side chains of cysteines
function of disulfide bonds in tertiary structures
restrict folding patterns available to polypeptide chains
disulfide bonds are absent in ______ and ______ but present in ______ and ______
myoglobin, hemoglobin; chymotrypsin, trypsin
in some proteins, polypeptide chains can be cross-linked by ______________ through oxidation and reduction mechanisms
disulfide bonds between cysteine residues
conformation of polypeptide backbones constrains ________
the possible arrangement of side chains
structural features of myoglobin
eight α-helical regions
no β-pleated sheet regions
exterior containing mostly polar side chains
interior containing nonpolar side chains and two histidine residues
myoglobin
single polypeptide chain with one oxygen-binding site
stabilization of α-helical regions in myoglobin occurs by ______________
hydrogen bonding in the polypeptide backbone
features of myoglobin chain
single polypeptide chain of 153 amino acid residues
heme prosthetic group in a hydrophobic pocket
heme
iron-containing cyclic compound
subunit
each chain in a quaternary structure
oligomers
molecules made up of a number of smaller subunits
methods by which chains interact with one another noncovalently in quaternary structures
electrostatic attractions
hydrogen bonds
hydrophobic interactions
allosteric
property of multisubunit proteins in which a conformational change in one subunit induces a drastic change in another subunit
tetramer overall structure with two α-chains and two β-chains
α2β2
homologous
when the same amino acid residues in the same positions
examples of polypeptide chains that are homologous
α-chain, β-chain, and myoglobin
denatured proteins can only recover their natural shapes when ____________
their primary structures are left intact
conformation of a protein is determined solely by ___________
its amino acid sequence
shape of myoglobin
globular
features of fibrous proteins
contain polypeptide chains organized approximately parallel along a single axis
consist of long fibers or large sheets
tendency to be mechanically strong
insoluble in water
play important structural roles in nature
examples of fibrous proteins
keratin and collagen
globular proteins
proteins in which the polypeptide backbone folds on itself to produce a more spherical shape
features of globular proteins
most of their polar side chains are on the outside
most of their nonpolar side chains are buried on the inside
substantial sections of α-helices and β-sheets
tend to be soluble in aqueous solutions
have compact structures
collagen
fibrous protein organized in water-insoluble fibers of great strength
collagen fibers (tropocollagen)
consist of three polypeptide chains wrapped around each other in a triple helix
repeating sequence of amino acid residues in collagen
X-Pro-Gly or X-Hyp-Gly
Hyp
hydroxyproline
hydroxyproline
formed in posttranslational modification from proline by a specific hydroxylating enzyme after the amino acids are linked together
three collagen strands
each a helix; held together by hydrogen bonds involving hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine to make a superhelical cable structure
protein folding in fibrous proteins
overall shape is a long rod
the backbone of the protein doesn’t fold back on itself
the only important aspect of tertiary structure that is not specified by secondary structure is the arrangement of atoms in the side chains
info needed for protein folding in globular proteins
how helical and pleated sheet sections fold back on each other
positions of side-chain atoms
positions of any prosthetic groups
folding patterns in tertiary structures often _________________
bring residues that are separated in the primary amino acid sequence into proximity to one another
denaturation
the unraveling of the 3D structure of a macromolecule caused by the breakdown of noncovalent interactions
factors that can cause denaturation
heat
large pH changes
detergents
urea and guanidine hydrochloride
effect of detergents on hydrophobic interactions
disrupts them
sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
detergent and protein disruptor
effect of urea and guanidine hydrochloride on proteins
disrupts their hydrogen bonding
reduction of covalent disulfide bonds
leads to more unraveling of the 3D structure of a macromolecule
double-headed arrow
denotes when a native conformation can be recovered when denaturing conditions are removed
β-mercaptoethanol’s role in the denaturation of ribonuclease
used to reduce disulfide bridges to two sulfhydryl groups
urea is added to a reaction mixture of β-mercaptoethanol and ribonuclease to ______________
facilitate unfolding and increase the accessibility of the disulfides to the reducing agent
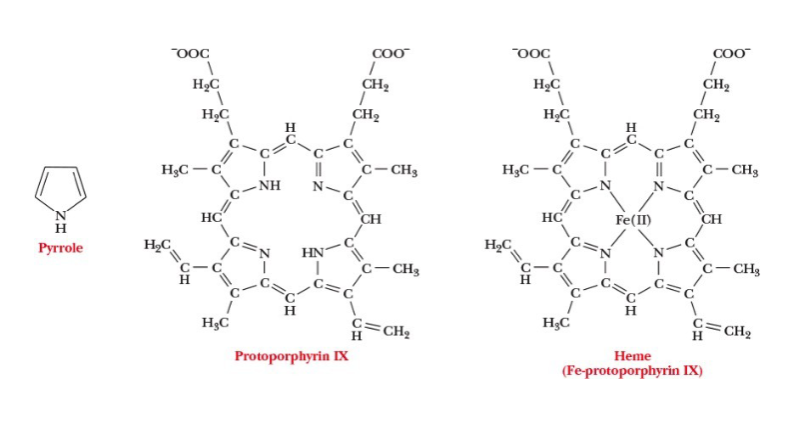
heme group consists of
a metal ion Fe(II) and an organic part protoporphyrin IX
features of the metal ion of heme group
has six coordination sites and forms six metal-ion complexation bonds
four sites are occupied by the N atoms of the four pyrrole-type rings in porphyrin
fifth coordination site is occupied by one of the N atoms of the imidazole side chain in histidine residue F8
O2 is bound at the sixth coordination site
protoporphyrin IX in a heme group
consists of four five-membered rings that are linked by methine (-CH=) groups; based on pyrrole structure
pyrroles
five-membered rings with the formula C4H4NH that can form metal complexes
heme group structure
presence of His E7 _______ affinity of free heme for carbon monoxide by ____
reduces,100x