Blood vessels study guide
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
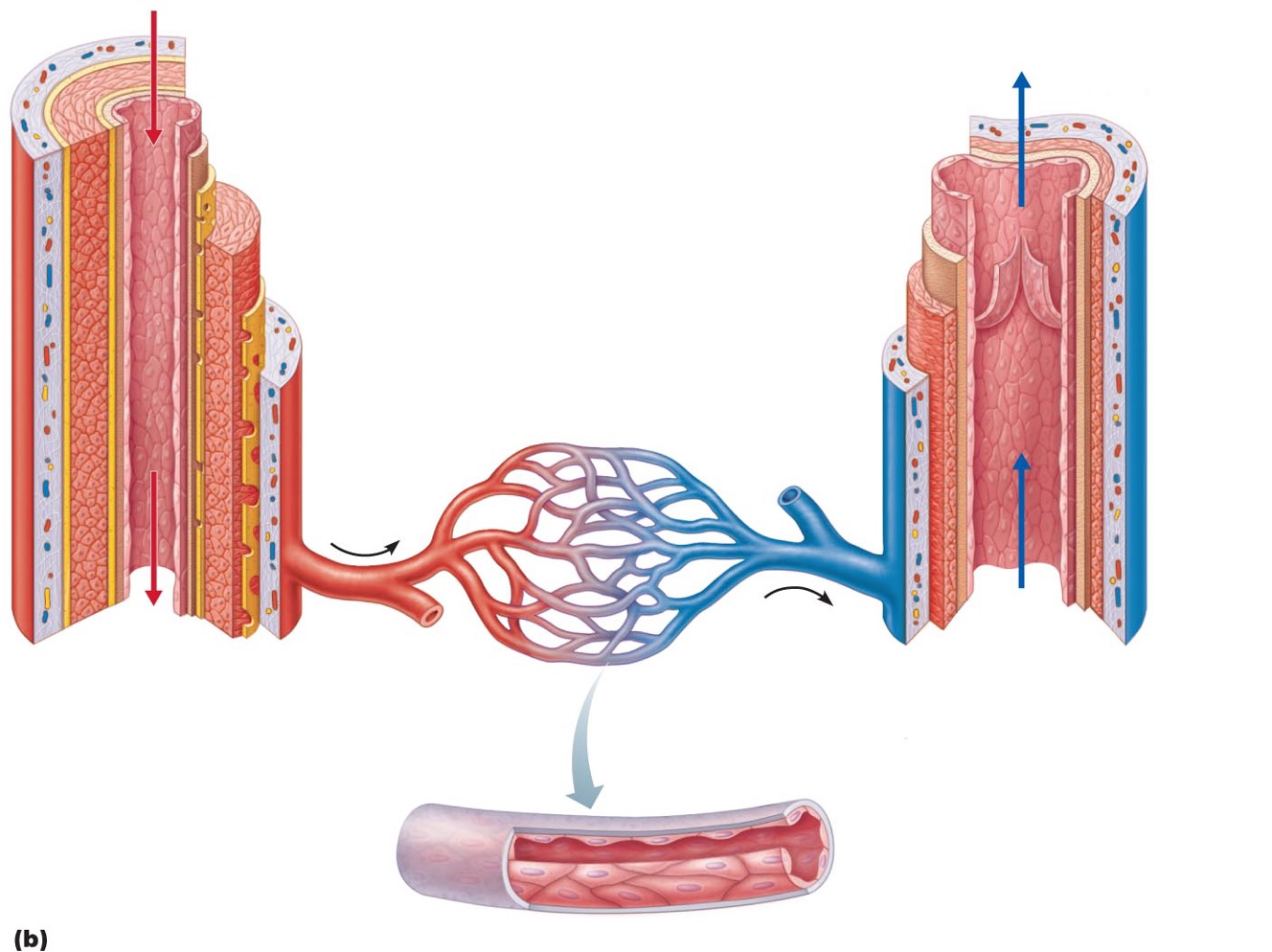
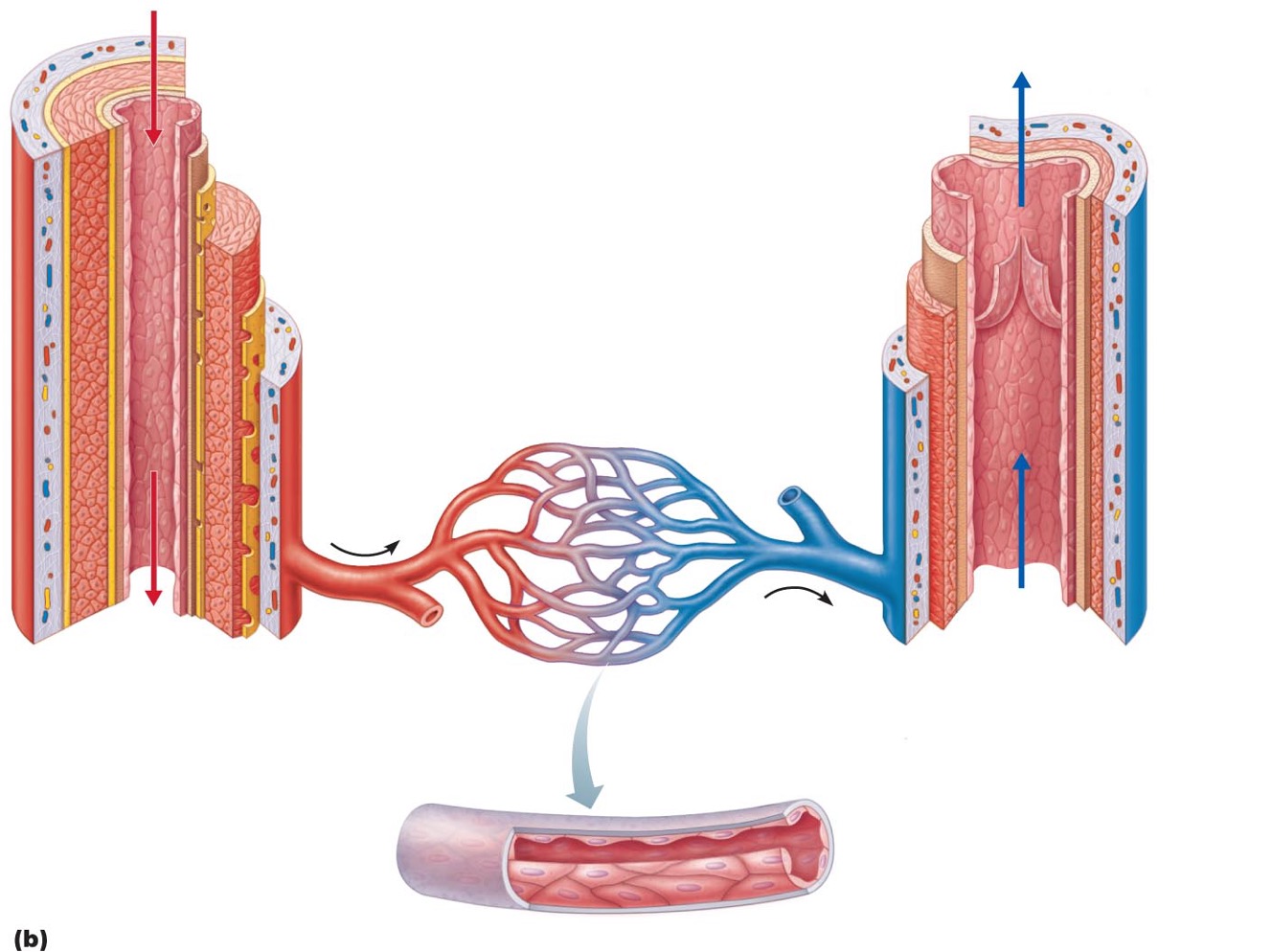
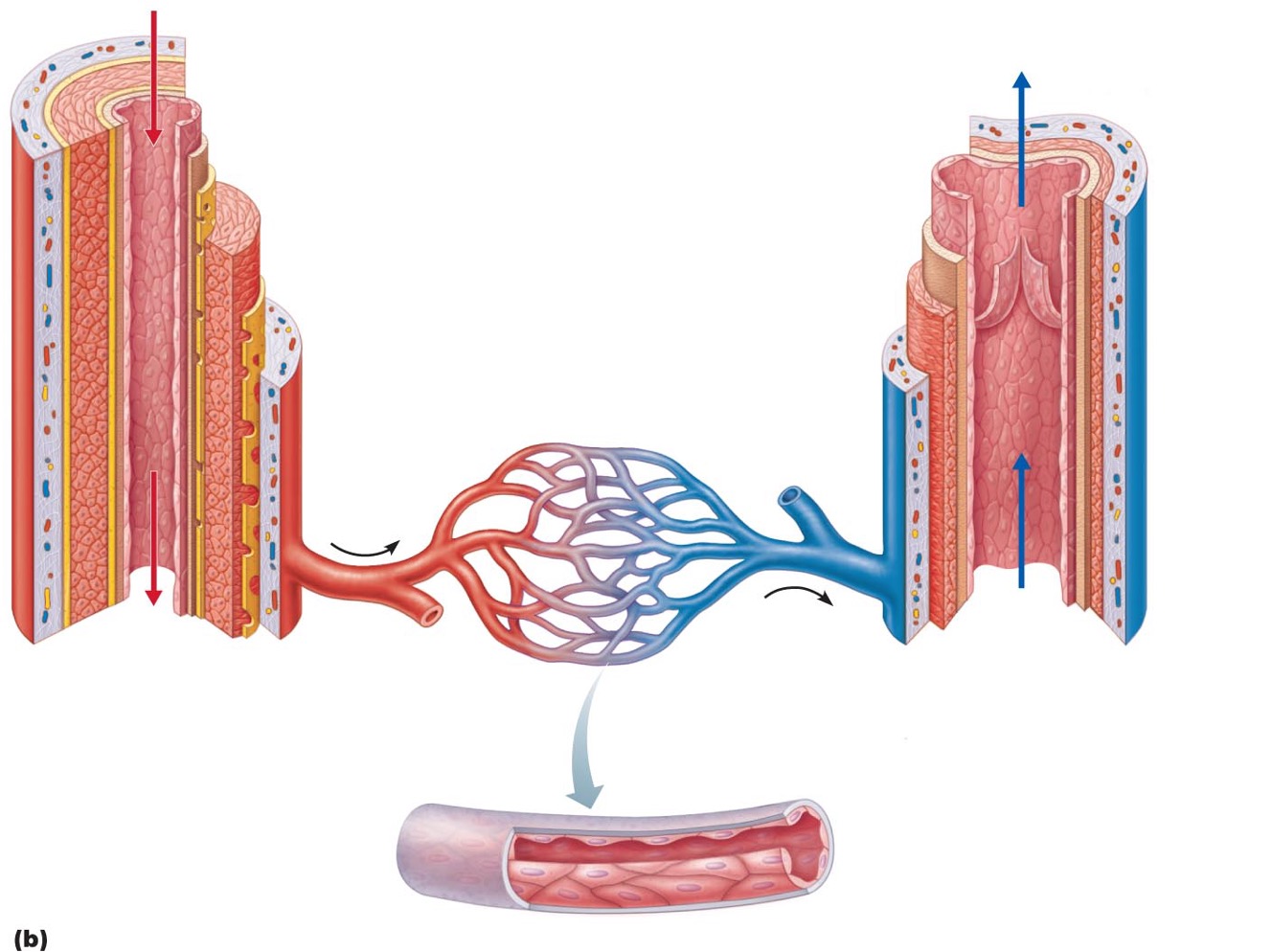
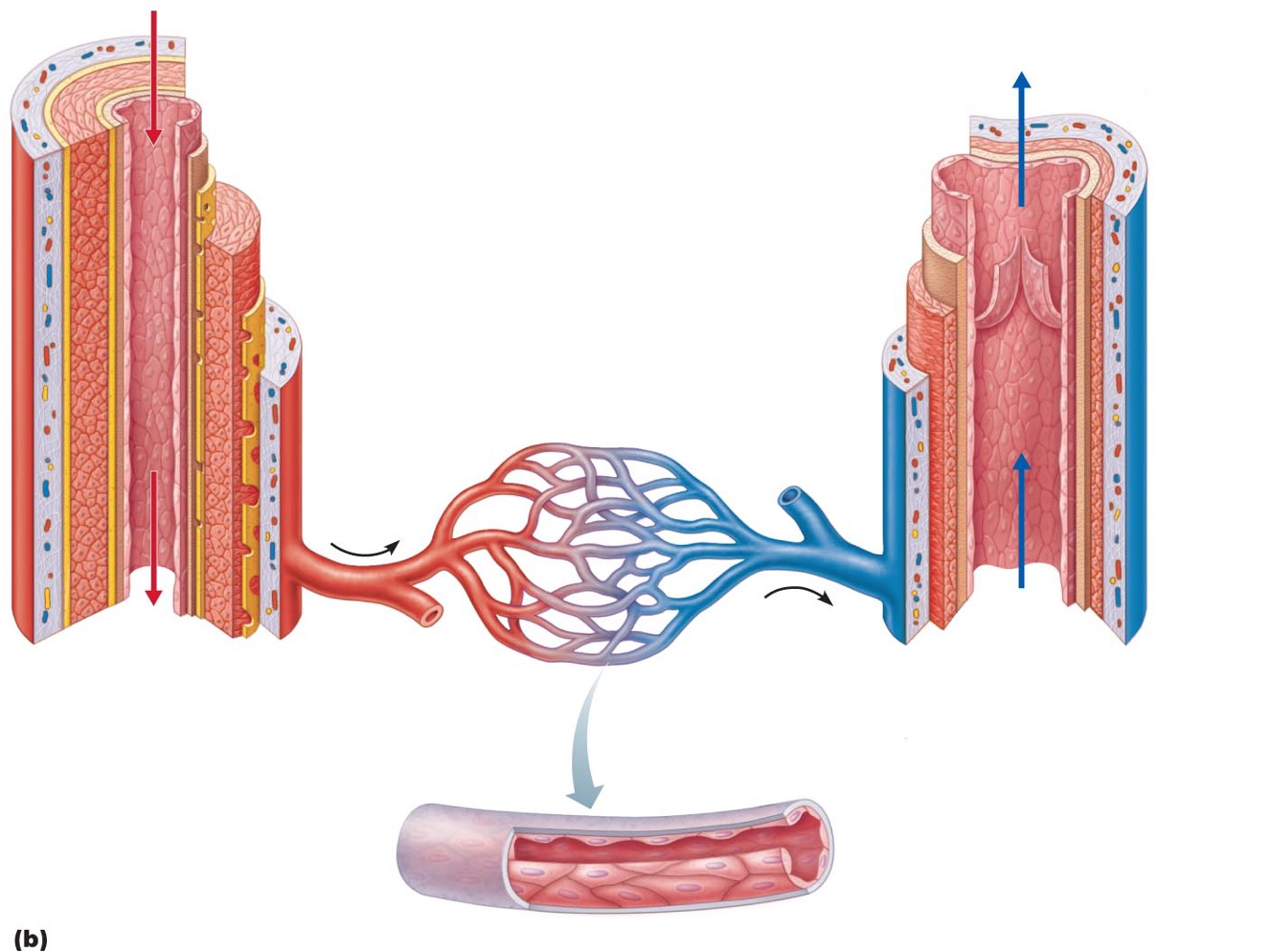
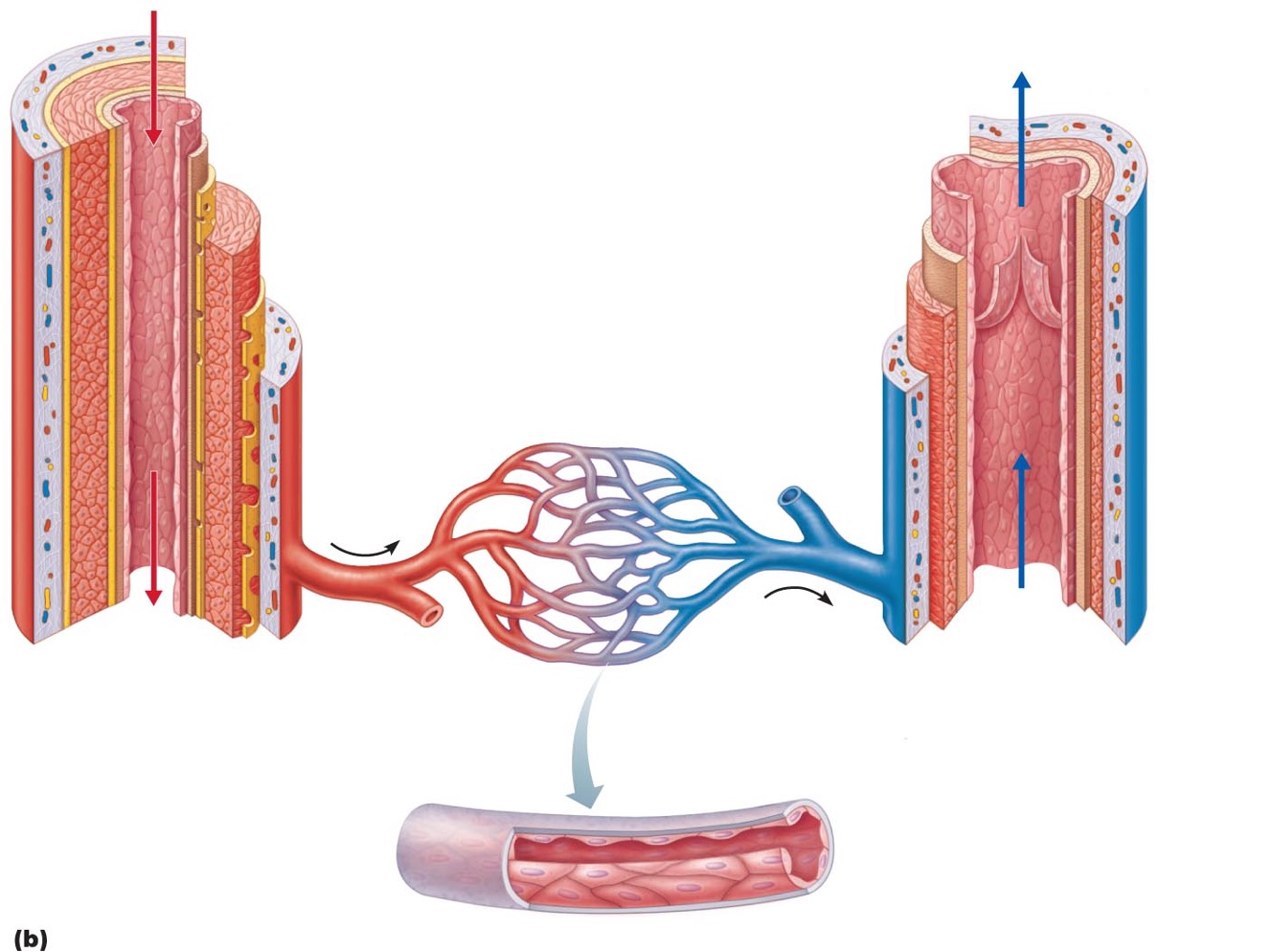
Arteries
•: carry blood away from heart
•Systemic – carry oxygenated blood
•Pulmonary – carry oxygen low blood
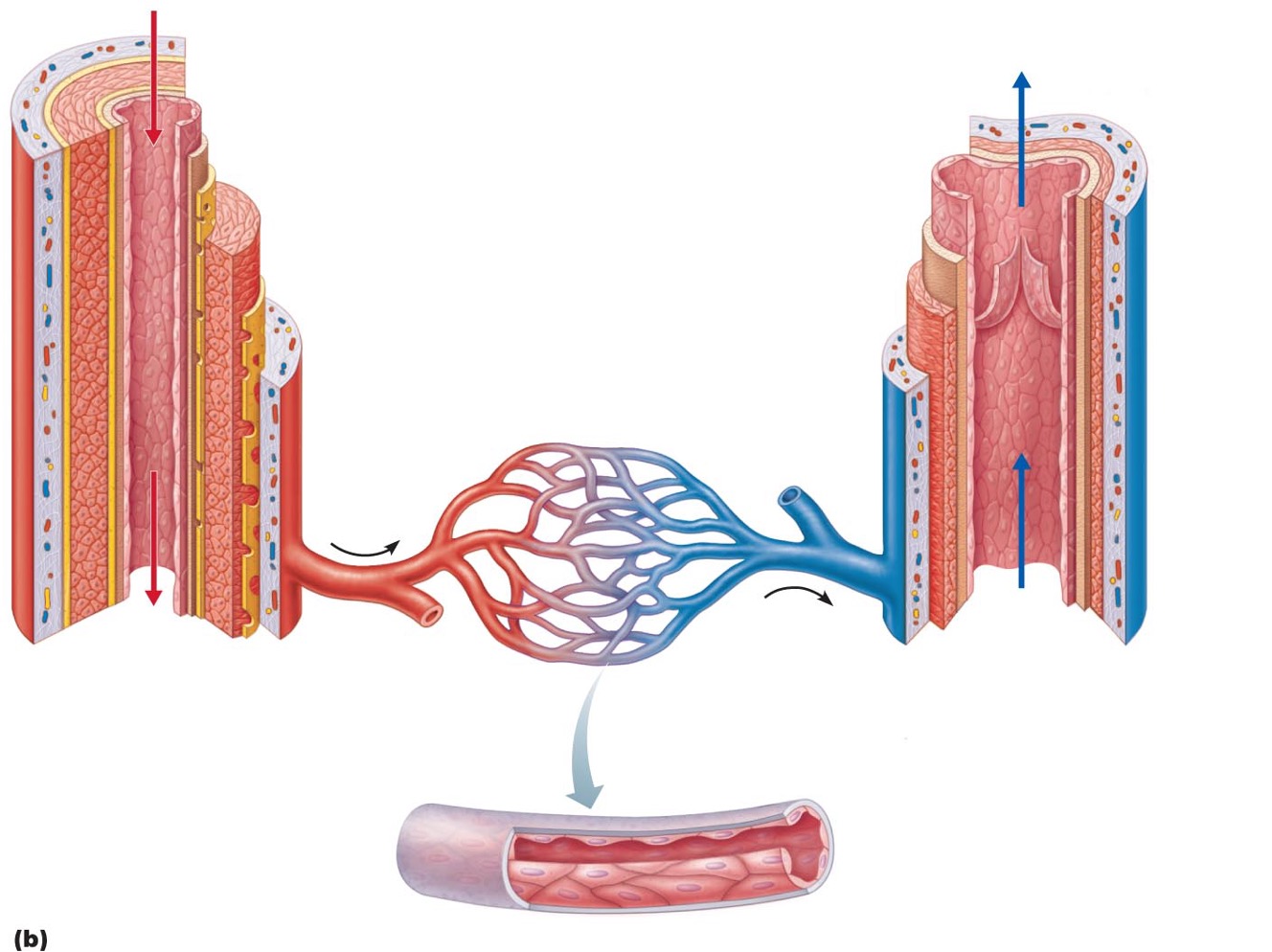
Veins
•carry blood toward heart
•Systemic – carry oxygen poor blood
•Pulmonary – carry oxygenated blood
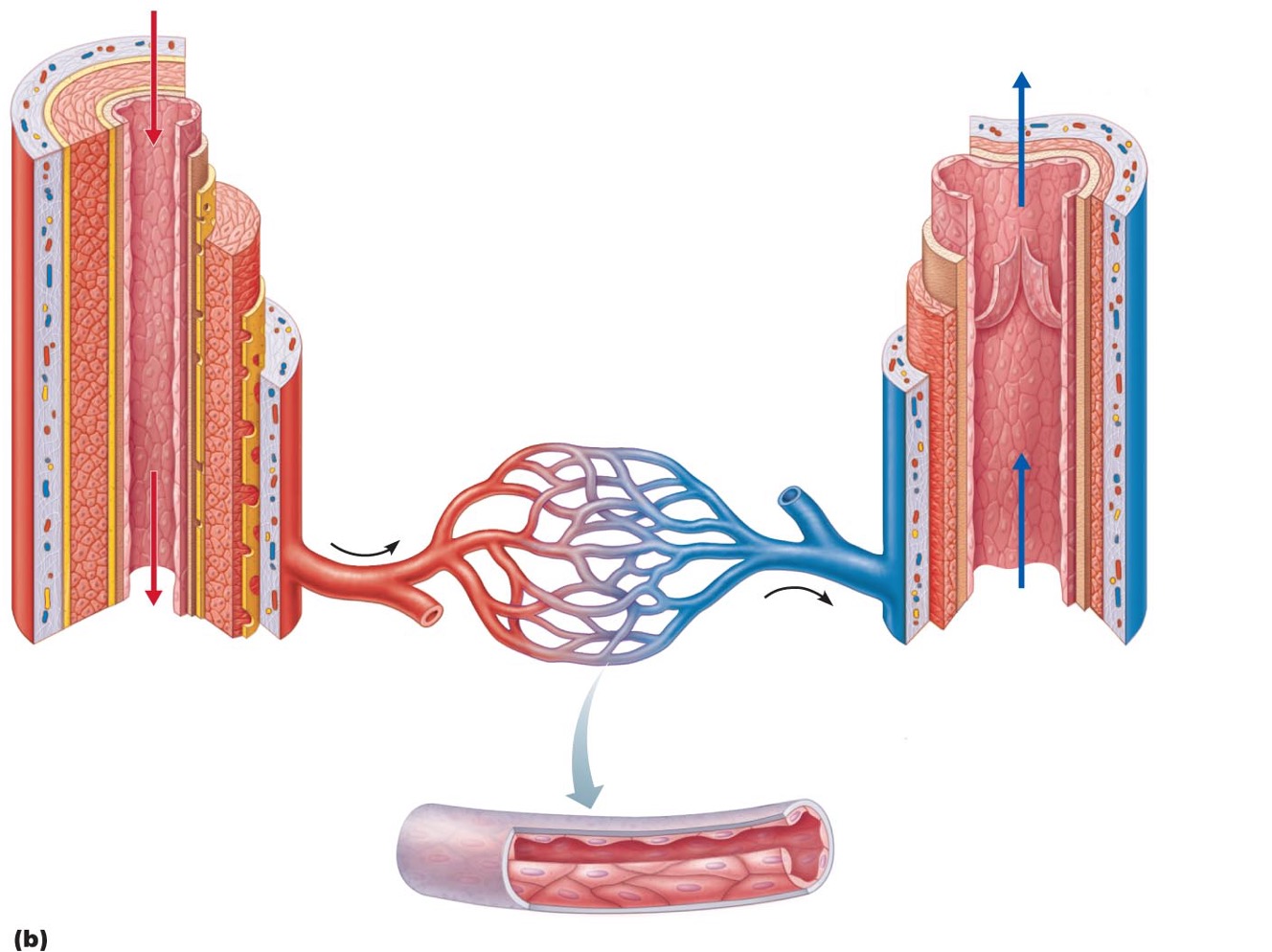
Capillaries
only vessels to contact tissue cells; directly serve cellular needs
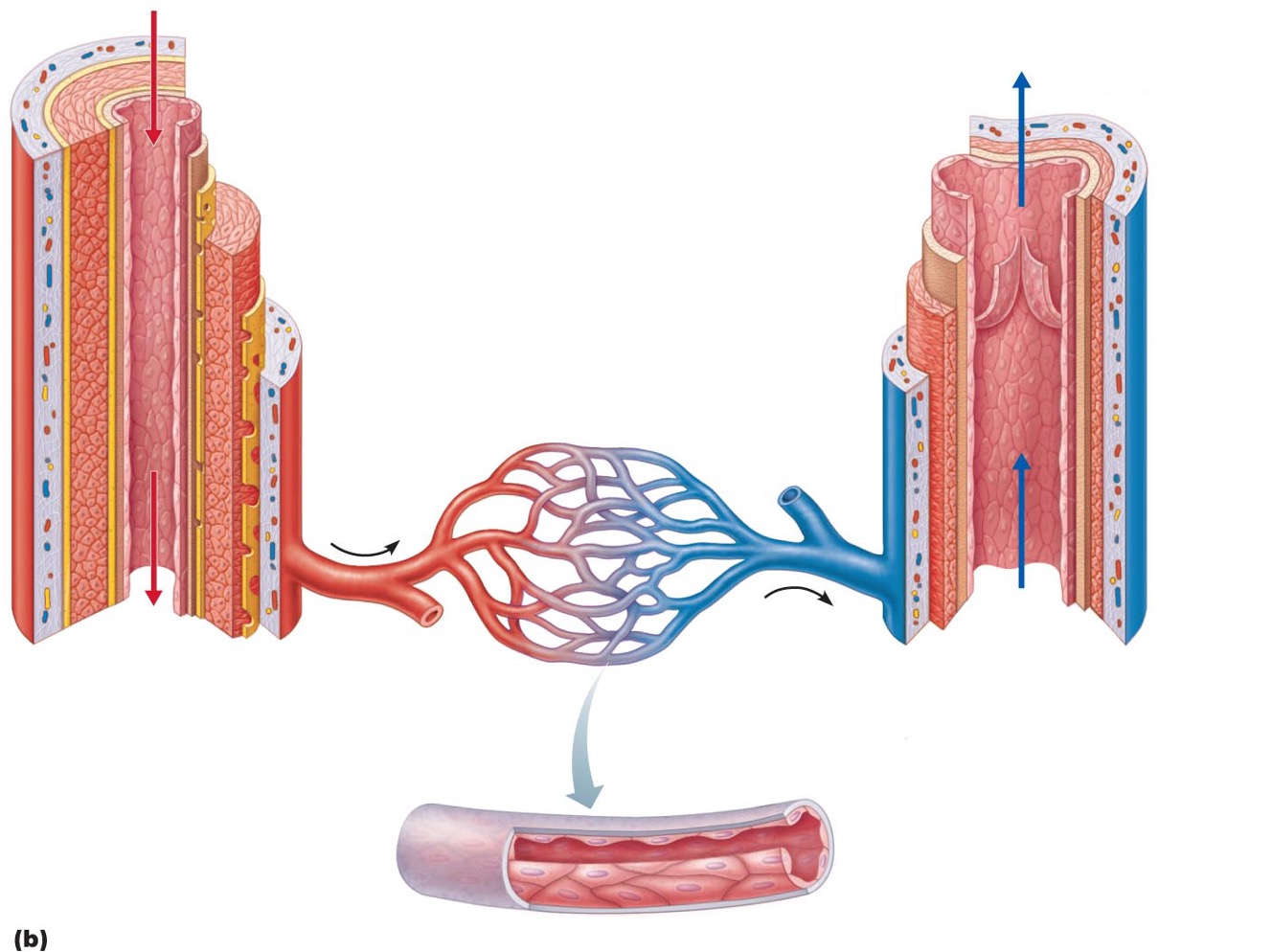
•Tunica intima (intimate contact with blood)
•Endothelium lines lumen of all vessels
•The endothelium is continuous with endocardium
•Forms a slick surface that reduces friction as blood moves via the lumen
Subendothelial layer
•in vessels larger than 1 mm
•Has connective tissue basement membrane supporting the endothelium
Tunica media
•middle tunic
•Composed of smooth muscle cells (SMC) and sheets of elastin
•The activity of the smc is regulated by the sympathetic vasomotor nerve fibers and chemicals
Vasoconstriction
- lumen diameter decreases as the smc contract
Vasodilation
•lumen diameter increases as the smc relaxes
•Influence blood flow and blood pressure
Tunica externa
•(outer layer)
•Made up of collagen fibers protect, reinforce, and anchors the vessel to the surrounding structures
•Contains nerve fibers, lymphatic vessels
•Vasa vasorum
system of smaller blood vessels in larger vessels
•Functions to nourishes external layer
Pericytes
smc that help stabilize their walls and control permeability
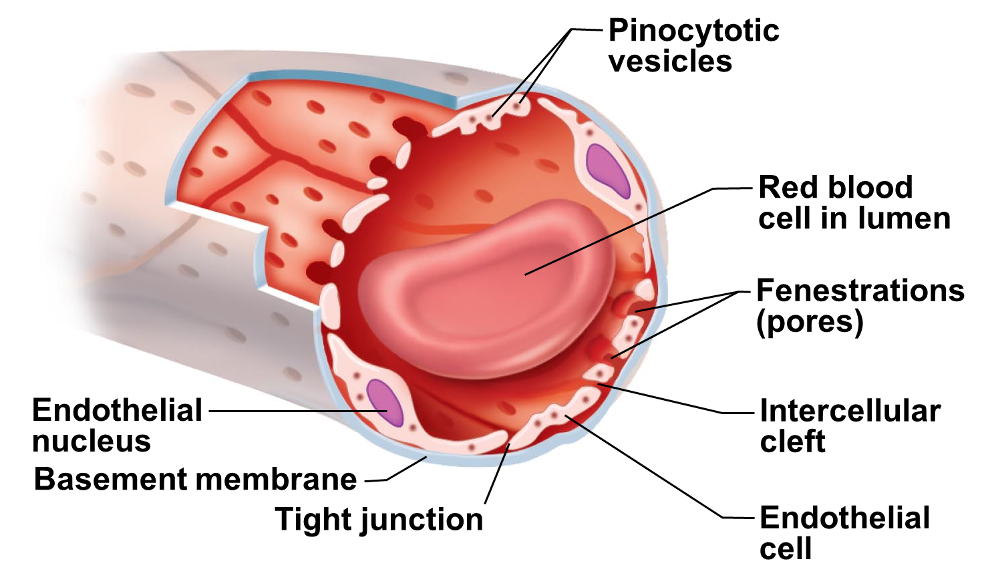
Continuous Capillaries
•Most common and are abundant in skin and muscles
•Joined together with tight junctions that connect endothelial cells
intercellular clefts
gaps that are found in continuous capillaries and allow passage of smaller solutes and fluids
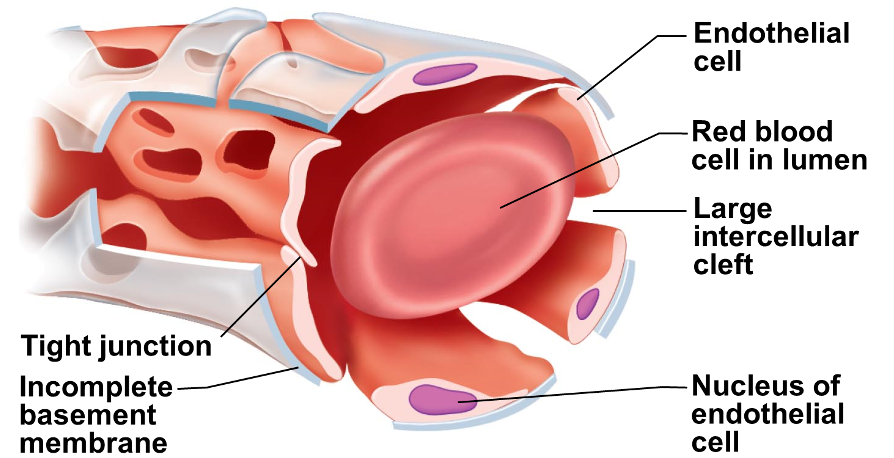
Fenestrated Capillaries
•Like continuous but have endothelial cells with pores or fenestrations
•More permeable than continuous capillaries
•Function in absorption or filtrate formation
•small intestines- nutrients absorption
•endocrine gland- hormones quickly enter the blood stream
•Kidneys- rapid filtration of blood plasma
Sinusoid Capillaries
•Highly modified with slow blood flow
•fewer tight junctions
•usually fenestrated
•larger intercellular clefts
•large irregularly shaped lumens
•Large molecules and blood cells pass between blood and surrounding tissues
•Found only in the liver, bone marrow, spleen, adrenal medulla
•Macrophages in lining to destroy bacteria
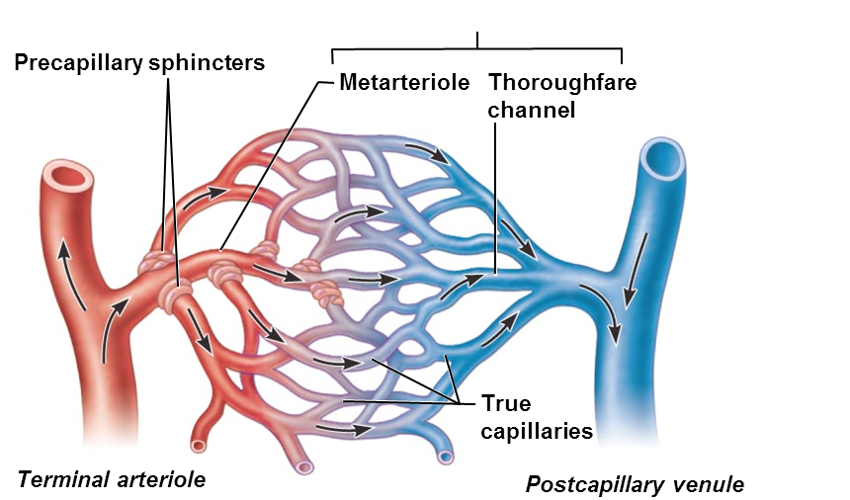
Capillary bed
•interwoven network of capillaries between arterioles and venules
Microcirculation
blood flow from between arterioles and venules
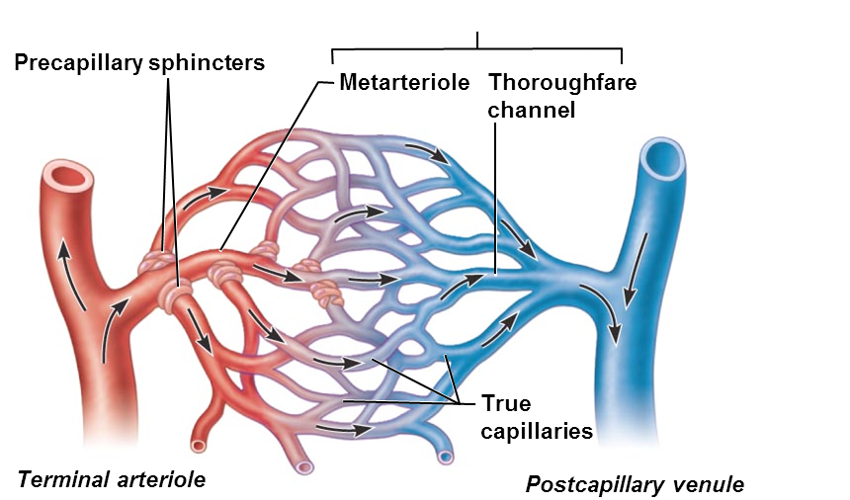
Terminal arteriole > ________
metarteriole
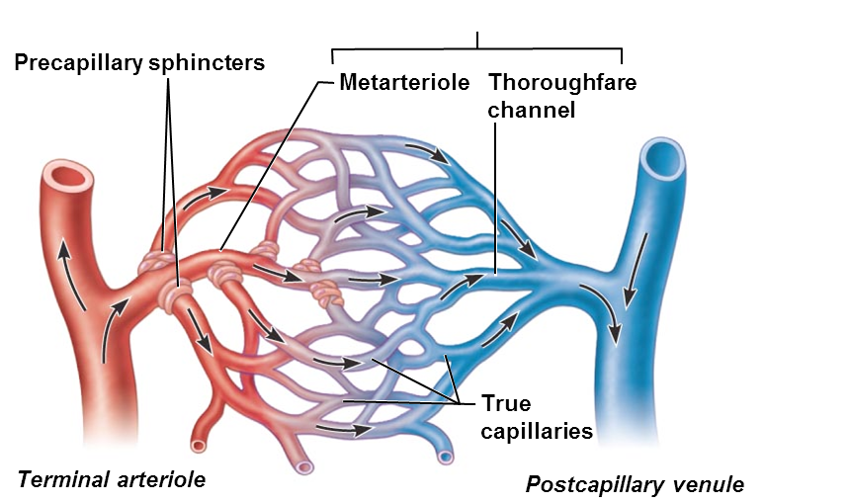
Metarteriole continuous with
thoroughfare channel (intermediate between capillary and venule)
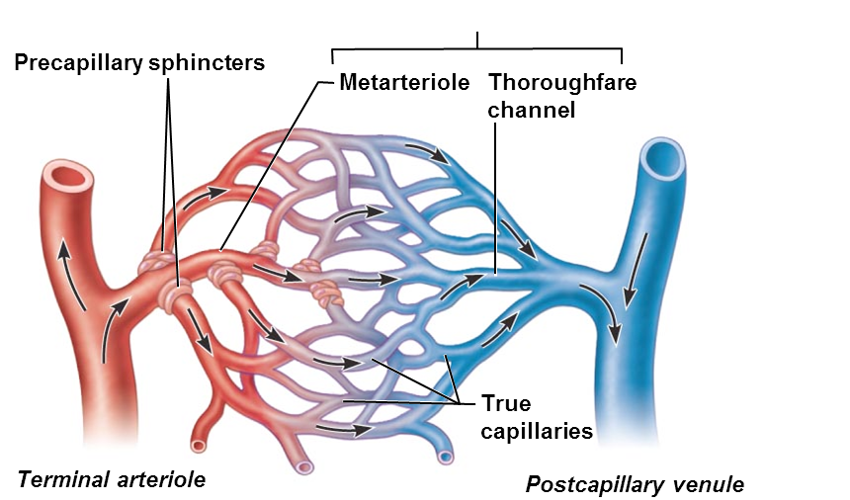
thoroughfare channel > _______ that drains bed
postcapillary venue
Vascular shunt
•(metarteriole—thoroughfare channel)
•Directly connects terminal arteriole and postcapillary venule
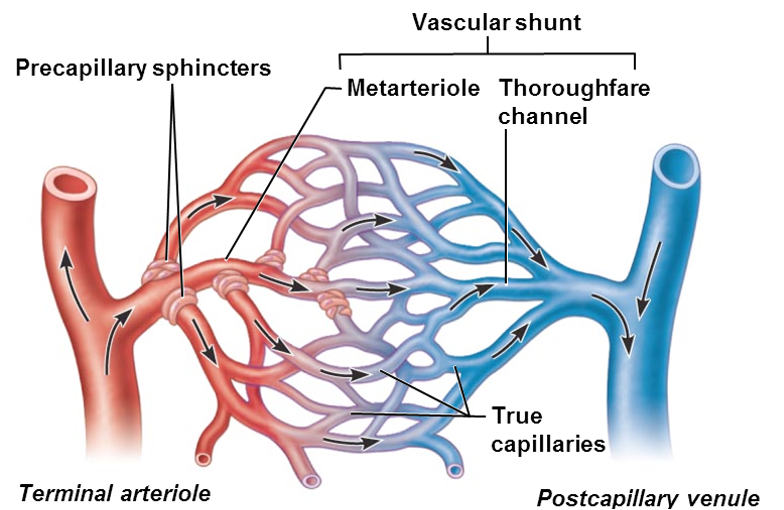
•True capillaries
•10 to 100 exchange vessels per capillary bed
•Branch off metarteriole or terminal arteriole
Precapillary sphincters
•regulate blood flow into true capillaries
•Surround the root or each true capillary at the metarteriole
•Regulates blood flow into the capillary
Vennules
•- formed when capillary beds unite
•Smallest - postcapillary venules
•Composed endothelium and pericytes
•Very porous; allow fluids and WBCs into tissues
Veins form when _____
venules converge
veins are called ________
capacitance vessels (blood reservoirs); contain up to 65% of blood supply
Venous valves
•prevent backflow of blood
•Most abundant in veins of limbs
Venous sinuses
•flattened veins with extremely thin walls
•Supported by the tissues that surrounds them (e.g., coronary sinus of the heart and dural sinuses of the brain)
______ helps circulation
Exercise (because muscles contract and squeeze blood back to heart)
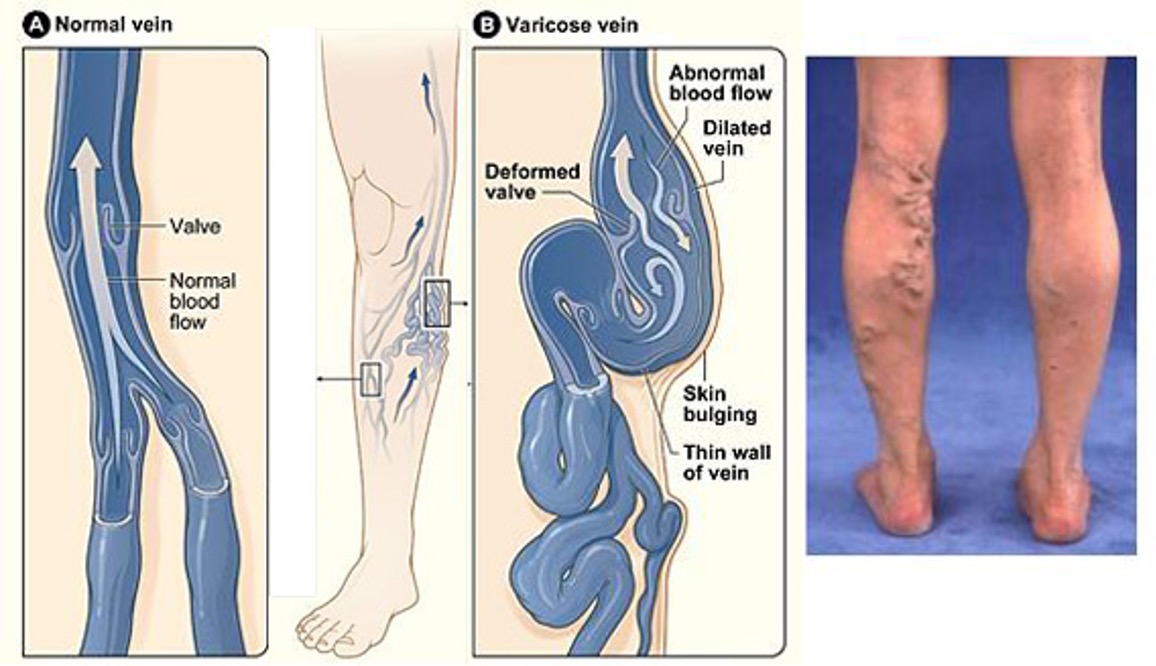
Varicose veins
- veins that have become enlarged and twisted due to leaky valves
Arterial anastomoses provides alternates pathways (______) to given body region
collateral channels
Venous anastomoses are
Common
Blood flow
Volume of blood flowing through vessel, organ, or entire circulation in given period
•Measured as ml/min
•Equivalent to cardiac output for entire vascular system
•Relatively constant when at rest but can vary widely through individual organs, based on needs
Blood pressure (BP)
Force per unit area exerted on wall of blood vessel by blood
•Expressed in millimeters of Mercury (mm Hg)
•Typically measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near heart
•Pressure gradient – Difference in the BP in the entire system
•Provides the force that keeps blood moving from higher to lower pressure areas
Resistance
•opposition of flow
•Measures of amount of friction blood encounters with vessel walls, generally in peripheral (systemic) circulation
Blood viscosity
- thickness
•Increased viscosity = increased resistance
•Constant but polycythemia (high RBC’s) can increase the viscosity
Blood vessel length
•Longer vessel = greater resistance encountered
Blood vessel diameter
greatest influence on resistance
Blood pressure near heart is ______
Pulsatile (goes up and down)
Systolic pressure
•pressure exerted in aorta during ventricular contraction
•Averages 120 mm Hg in normal adult
Diastolic pressure (lowest)
lowest level of aortic pressure
Pulse pressure
•difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
•Throbbing of arteries (pulse)
Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
pressure that propels blood to tissues
•MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3 pulse pressure
•Pulse pressure and MAP both decline with increasing distance from heart
•Ex. BP = 120/80; MAP = 93.3 mm Hg
Low capillary pressure is _____
Desirable
•High BP would rupture fragile, thin-walled capillaries
•Most very permeable, so low pressure forces filtrate into interstitial spaces
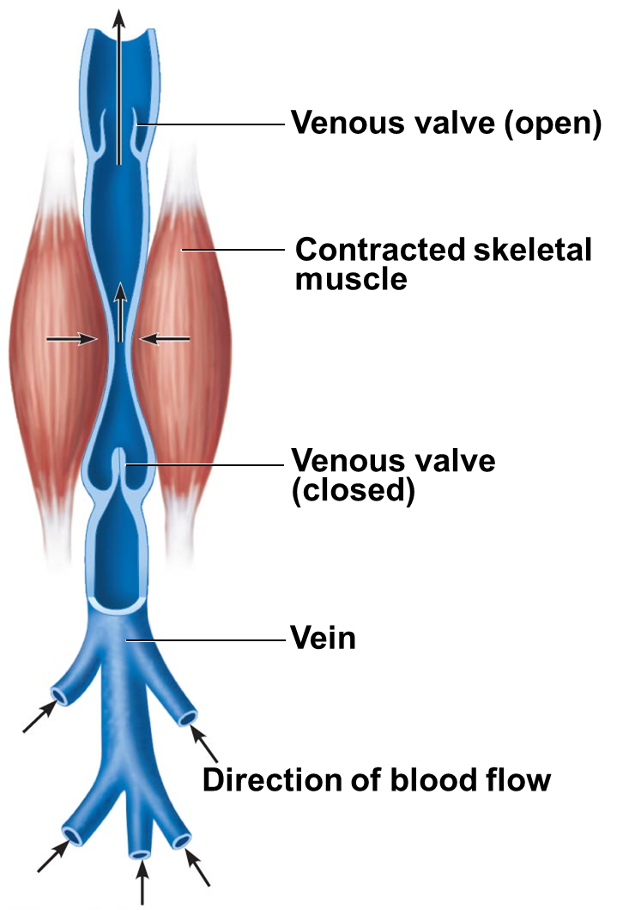
Muscular pump
1.contraction of skeletal muscles "milks" blood toward heart; valves prevent backflow
•Long periods of standing can cause edema in ankles
Respiratory pump
.pressure changes during breathing move blood toward heart by squeezing abdominal veins as thoracic veins expand
•Inhale abdominal pressure increases squeezing the veins and forces blood to the heart
•The pressure in the chest decreases and thoracic veins expand sending blood to the right atrium
______ under sympathetic control pushes blood toward heart
Venoconstriction
maintaining blood pressure
Requires
Cooperation of heart, blood vessels, and kidneys
Super vision by brain
Factors influencing BP
Cardiac output
peripheral resistance
blood volume
•Short-term neural and hormonal controls
•Counteract fluctuations in blood pressure by altering peripheral resistance and heart output
•Long-term renal regulation
•Counteracts fluctuations in blood pressure by altering blood volume with the kidneys
•Neural controls of peripheral resistance
•Maintain MAP by altering blood vessel diameter
• if low blood volume all vessels constricted except those to heart and brain
•Alter blood distribution to organs in response to specific demands
•During exercise, blood is diverted from the digestive organs to the skeletal muscles
Neural controls operate via _____
Baroreceptors
Stretch receptors found in the carotid body, aortic body and the wall of all large arteries of the neck
•Vasomotor center sends steady impulses via sympathetic efferents to blood vessels à moderate constriction called _____
vasomotor tone
Monitoring circulatory efficiency Vital signs
•pulse and blood pressure, along with respiratory rate and body temperature
Pulse
•pressure wave caused by expansion and recoil of arteries
•Can detect a pulse from any artery that is close to the surface
Radial pulse
•(taken at the wrist) routinely used
Pressure points
•where arteries close to body surface
•Can be compressed to stop blood flow
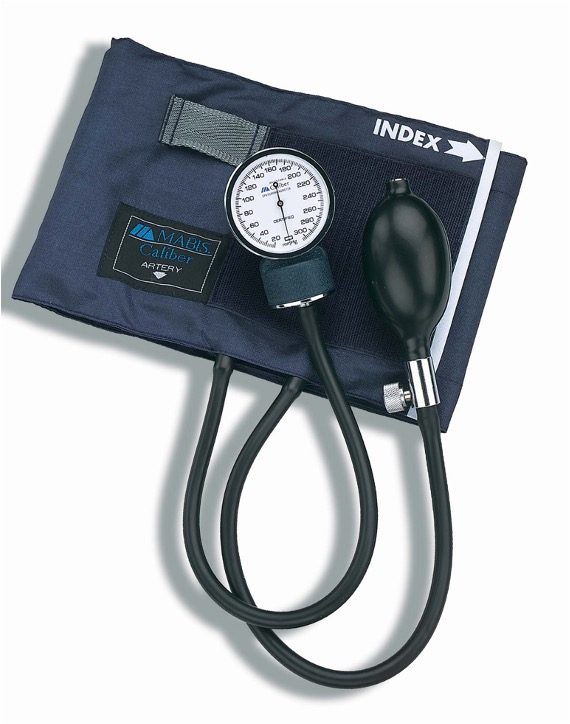
sphygmomanometer
measures systemic material BP
•Pressure increased in cuff until it exceeds systolic pressure in brachial artery
•Pressure released slowly and examiner listens for sounds of Korotkoff with a stethoscope
Systolic pressure
normally less than 120 mm Hg, is pressure when sounds first occur as blood starts to spurt through artery
Diastolic pressure
normally less than 80 mm Hg, is pressure when sounds disappear because artery no longer constricted; blood flowing freely
Hypertension
•high blood pressure
•Sustained elevated arterial pressure of 140/90 or higher
Prehypertension
•if values elevated but not yet in hypertension range
•May be transient adaptations during fever, physical exertion, and emotional upset
Often persistent in obese people
Prolonged high BP is major cause of
•heart failure, vascular disease, renal failure, and stroke
•Heart must work harder à myocardium enlarges, weakens, becomes flabby
Also accelerates atherosclerosis
Secondary hypertension
•less common
•Due to identifiable disorders including obstructed renal arteries, kidney disease, and endocrine disorders such as hyperthyroidism and Cushing's syndrome (high cortisol)
Treatment focuses on correcting underlying cause
Hypotension
•low blood pressure
•Blood pressure below 90/60 mm Hg
•Usually not a concern
•Only if leads to inadequate blood flow to tissues
Often associated with long life and lack of cardiovascular illness
Orthostatic hypotension
•temporary low BP and dizziness when suddenly rising from sitting or reclining position
Chronic hypotension
•can be due to severe malnutrition and warning sign for Addison's disease (adrenal cortex) or hypothyroidism
Acute hypotension
important sign of circulatory shock; threat for surgical patients and those in ICU
•Tissue perfusion involved in
•Delivery of O2 and nutrients to, and removal of wastes from, tissue cells
•Gas exchange (lungs)
•Absorption of nutrients (digestive tract)
•Urine formation (kidneys)
MAP below 60 mm Hg can cause
•syncope (fainting)
MAP above 160 can result in
•cerebral edema
As temperature rises
•Hypothalamic signals reduce vasomotor stimulation of skin vessels à
•Warm blood flushes into capillary beds à
•Heat radiates from skin
Sweat causes vasodilation via ____ in perspiration
bradykinin
•Bradykinin stimulates NO release
Hypovolemic shock
•: results from large-scale blood loss
•Acute hemorrhage, serve vomiting, diarrhea or extensive burns
Vascular shock
results from extreme vasodilation and decreased peripheral resistance
Cardiogenic shock
results when an inefficient heart cannot sustain adequate circulation