Gas Exchange
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
2 Places where gas exchange occurs
External respiration: Alveoli
O2 to blood, CO2 to lungs
Internal respiration: Blood vessels (capillaries)
CO2 to blood, O2 to tissues
Do gases travel down a concentration gradient?
No, gases travel down a pressure gradient, and each have their own partial pressure, not concentration
Dalton’s Law
Total air pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of each component gas added together.
Air pressure
Air pressure (total) at sea level = 760mmHg
pO2 = 160 mmHg
pCO2 = 0.3 mmHg
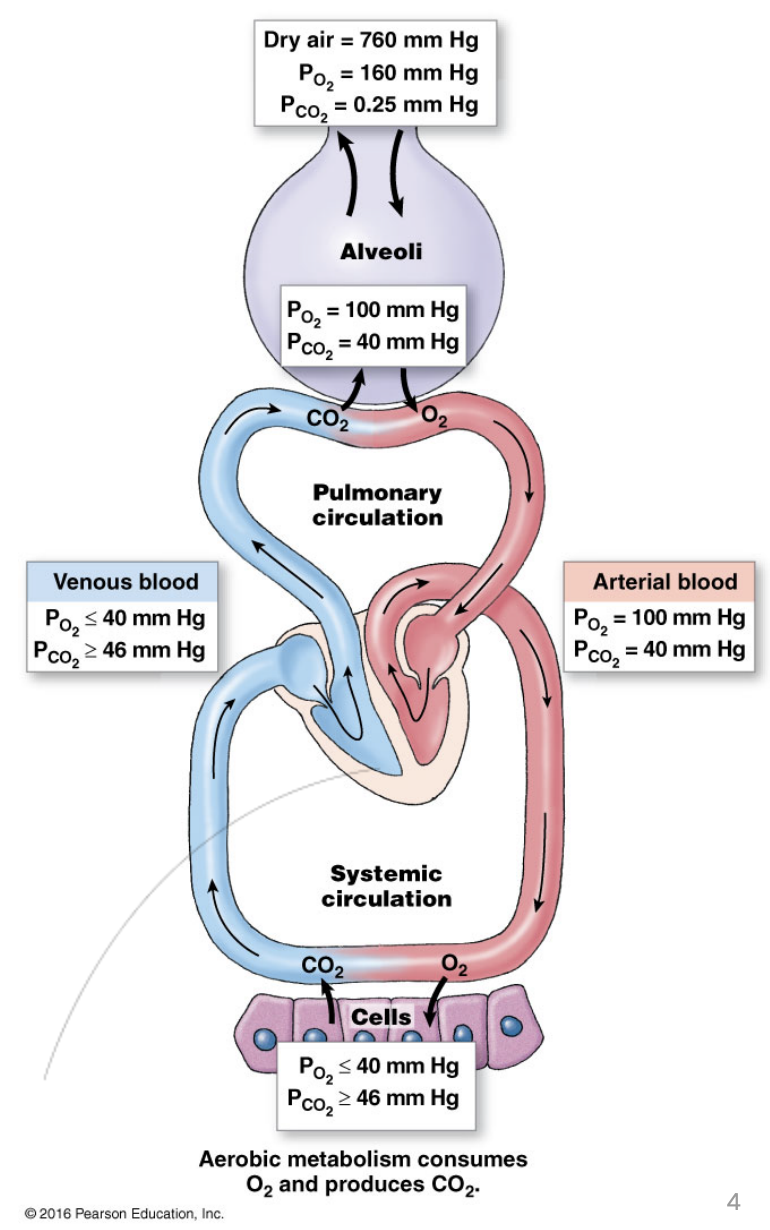
O2 & CO2 is outside at normal air pressure
Air travels through the conducting zones, becomes humidified and warmed up, mixes with the stale air (residual volume in lungs) and arrives at the alveoli.
Venous blood in the veinules wrapping the alveoli, has a specific partial pressure to prompt O2 into the blood and CO2 out of the blood
Pressure of the blood changes as it becomes arterial blood (same O2 & CO2 partial pressure as in the alveolus.
Capillaries arrive at tissue sites and gas exchange occurs again, has a specific partial pressure to prompt CO2 into the blood and O2 into the tissues.
The deoxygenated blood that enters the capillaries has the same pressure as the venous blood.