Lecture 15 Impulse transmission 2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Postsynaptic Potentials
Neurotransmitters can activate different ion channels in the post synaptic membrane
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP
Na+ channel activation (depolarization), nonspecific ion channels activation
More Na+ than K+, (Depolarization), Ca2+ channel activation (Depolarization)
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
K+ channels activation (hyperpolarizing)
Cl- channel activation (hyperpolarizing)
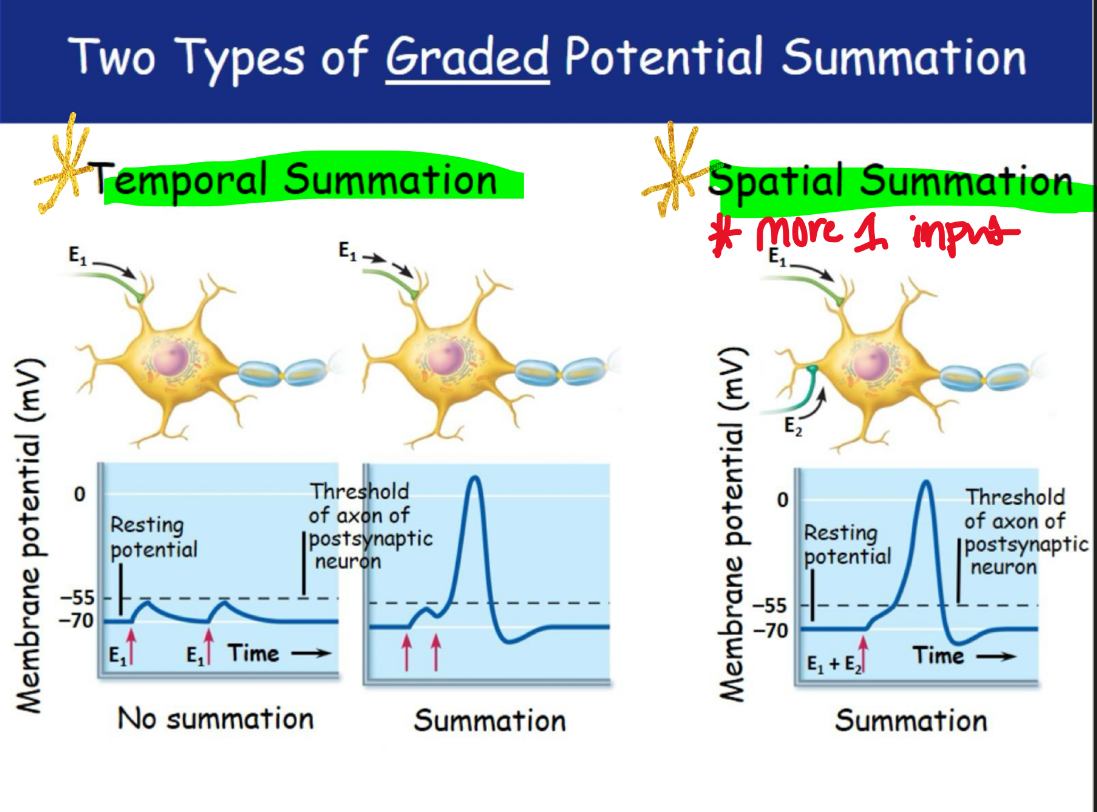
Synaptic Integration: Summation
A single EPSP cannot induce Action Potential
EPSPs can add together to influence postsynaptic neuron
IPSPs can also add together
Most neurons receive both EXCITATORY and INHIBITORY inputs from thousands of other neurons
Action potentials are started ONLY if SPSP’s dominate and bring membrane potential to threshold
2 types of graded potential summation
Spatial summation of opposing stimuli
changes in membrane potential can cancel each other out
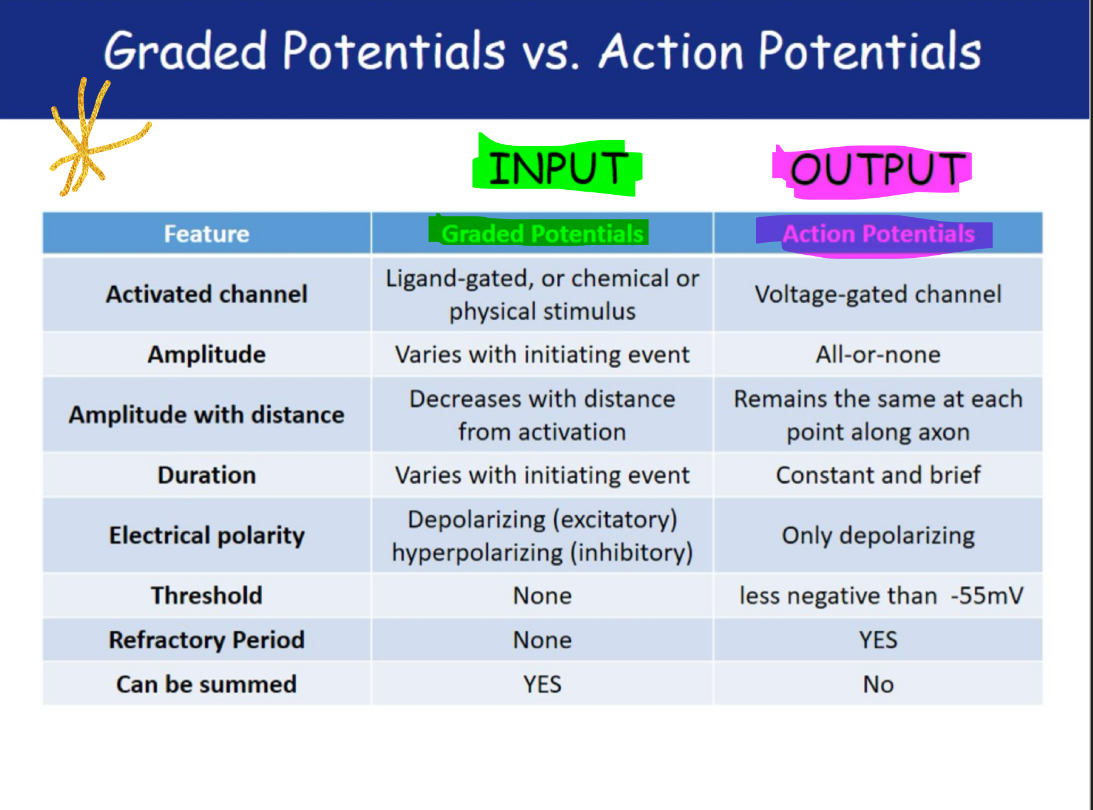
Graded potentials vs Action potentials
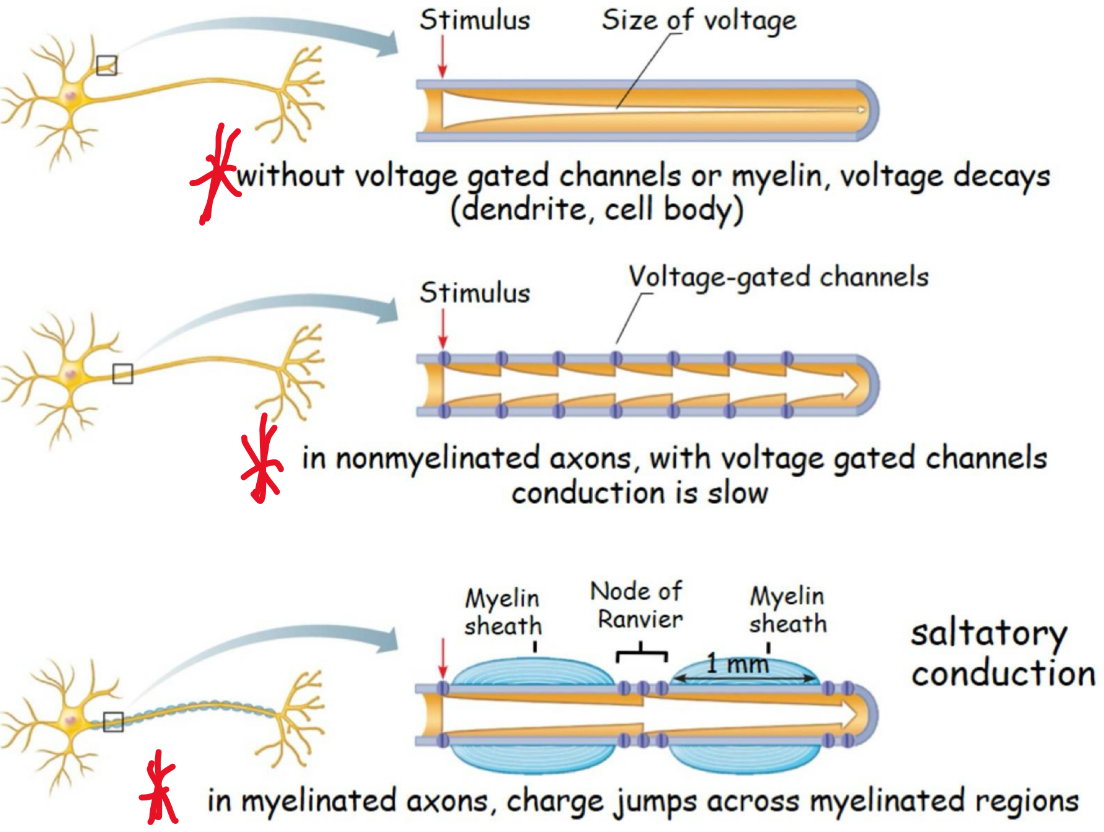
Conduction velocity - Speed
Speed of electrical propagation depends on:
Axon diameter: larger diameter: FASTER (less resistance) ex. Squid giant axon
Degree of myelination
Myelin insulate and prevents leakage of charge
action potentials traveling though myelinated neurons propagate about 30 times faster than unmyelinated neurons
Conductivity
Multiple sclerosis (MS) - demyelination
Autoimmune disease primarily affects young adults
Myelin sheaths in CNS destroyed through inflammation and scarring
Immune system attacks myelin and turns it to hardened lesions called scleroses
Impulse conduction slows and eventually ceases
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis
visual and speech disturbances
Weakness and loss of muscular control
Urinary incontinence