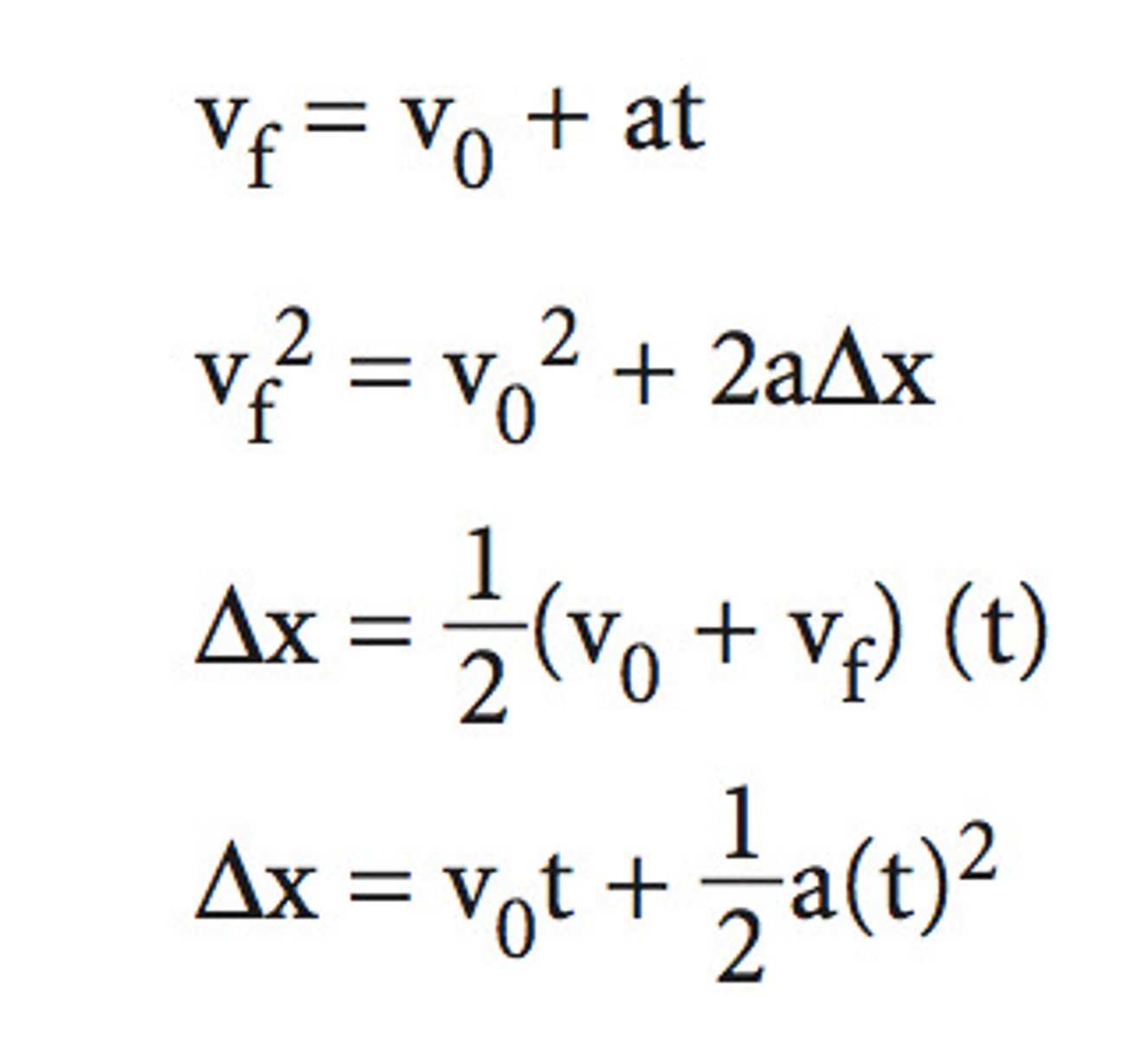AP Physics 1 Unit #1 – 1D Kinematics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Line of best fit
A line that follows the trend of a set of data and is drawn such that there is an equal number of points above and below the line.
Linearization
The creation of a linear representation of non-linear data.
How is a rational equation linearized?
Plot y vs. 1/x or x vs. 1/y
How is a quadratic equation linearized?
Plot y vs. x² or √y vs. x
How is a square root equation linearized?
Plot y vs. √x or y² vs. x
Model
An analogy or interpretation of phenomena in terms of what can be seen or understood.
Theory
A broad, detailed explanation of phenomena that provides quantitatively testable predictions
Law
Concise but general statements about nature
Principle
Usually refers to a more specific law.
Estimated uncertainty
The range of values in which the true value of a measurement is believed to be; generally, estimated uncertainty is ± the place of the last significant digit.
Percent uncertainty
(estimated uncertainty ÷ measured value) × 100%
Significant figures
The reliably known digits in a measured value.
Significant figure rules
→ all non-zero digits are significant.
→ zeros between non-zero digits are significant.
→ trailing zeros in a number with a decimal point (either before or after the decimal point) are significant.
→ leading zeros, or trailing zeros in a number without a decimal point, are insignificant.
→ the uncertain digit in a measurement is generally the last digit measured by the tool.
→ when multiplying or dividing numbers, the final result should have the same number of significant figures as the numerical value used with the fewest significant figures.
→ when adding or subtracting numbers, the final result should have the same number of decimal places as the numerical value used with the fewest decimal places.
Scientific notation
A method of writing numbers using powers of ten, which clearly expresses the amount of significant figures in a number.
Accuracy
The proximity of a measurement to its true value.
Precision
The repeatability of a measurement using a given instrument.
Unit
A standard quantity in terms of which other quantities may be expressed.
Standard
A consistent definition for a given thing.
Base quantity
One of seven chosen standards that represents all measurements in the natural world.
What are the base quantities?
→ length (meter, m)
→ time (second, s)
→ mass (kilogram, kg)
→ electric current (ampere, A)
→ temperature (Kelvin, K)
→ quantity (mole, mol)
→ luminous intensity (candela, cd)
Derived quantity
A quantity derived from one or more base quantities.
Operational definition
The procedure used to define any quantity.
Conversion factor
A ratio of equivalent measurements, equal to 1.
Order-of-magnitude estimate
An estimate that rounds all numbers used in a calculation to one significant figure and its power of 10 to make a general approximation of the answer.
Dimension
A measurable extent.
Dimensional analysis
Analysis that uses conversion factors to convert between equivalent measurements
Scalar
A quantity that has only magnitude.
Vector
A quantity that has magnitude and direction.
Average speed
|v|; the total distance traveled by an object divided by the time it takes to travel this distance.
Velocity
The displacement of an object divided by the time it took to displace this distance; a vector that measures both magnitude and direction.
Average velocity
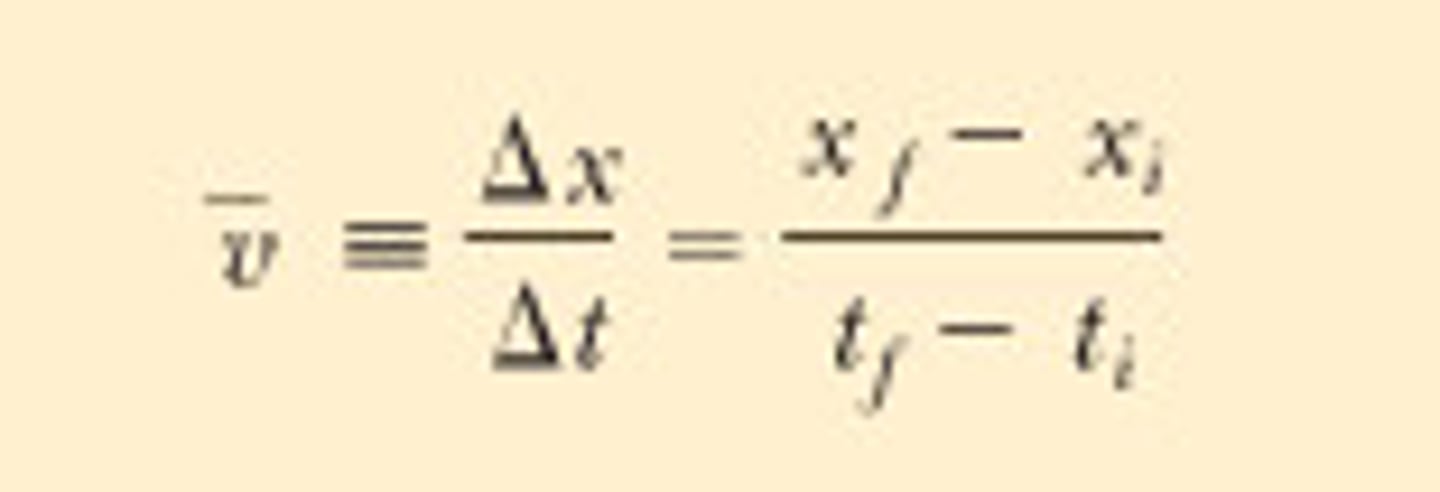
Instantaneous velocity
The average velocity of an object over an infinitesimally short time interval.
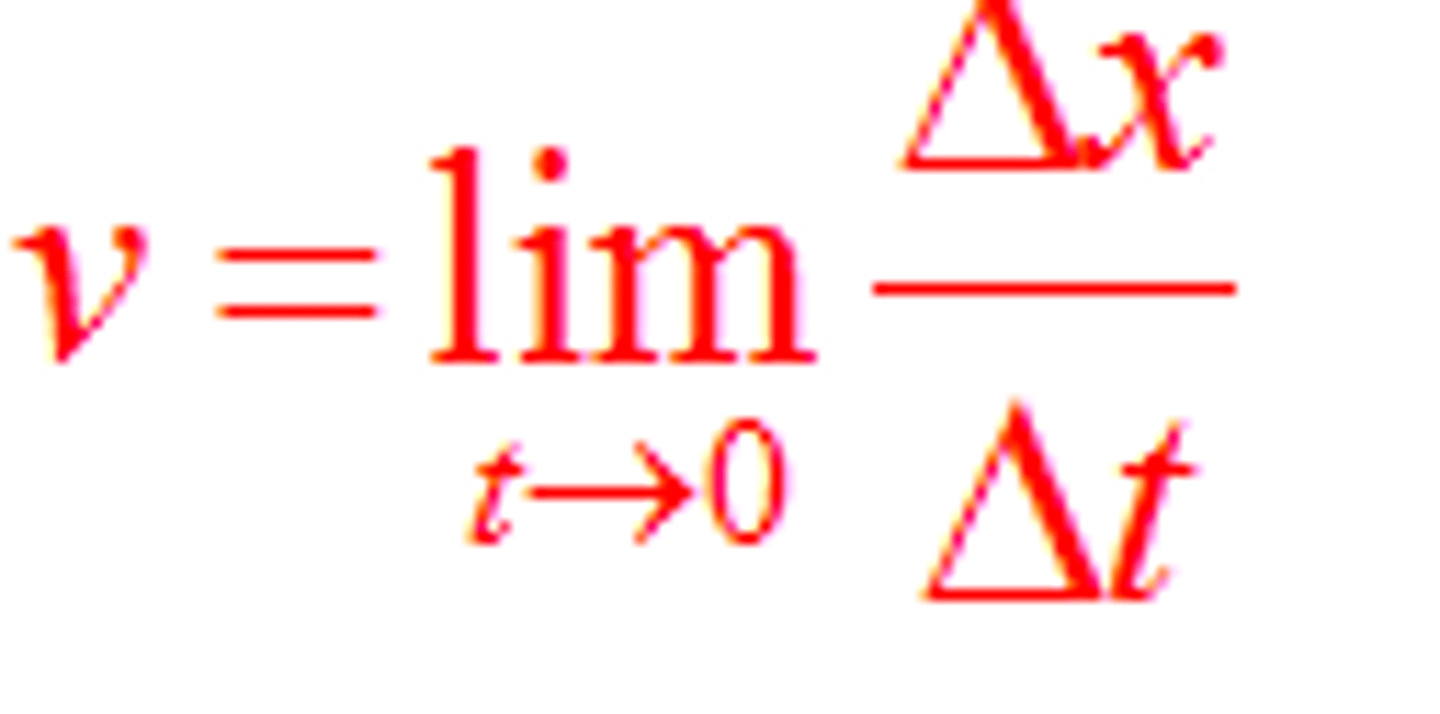
If an object moves at a constant velocity...
...then its instantaneous velocity at any point in time equals its average velocity.
Acceleration
The rate of change in velocity.
Average acceleration
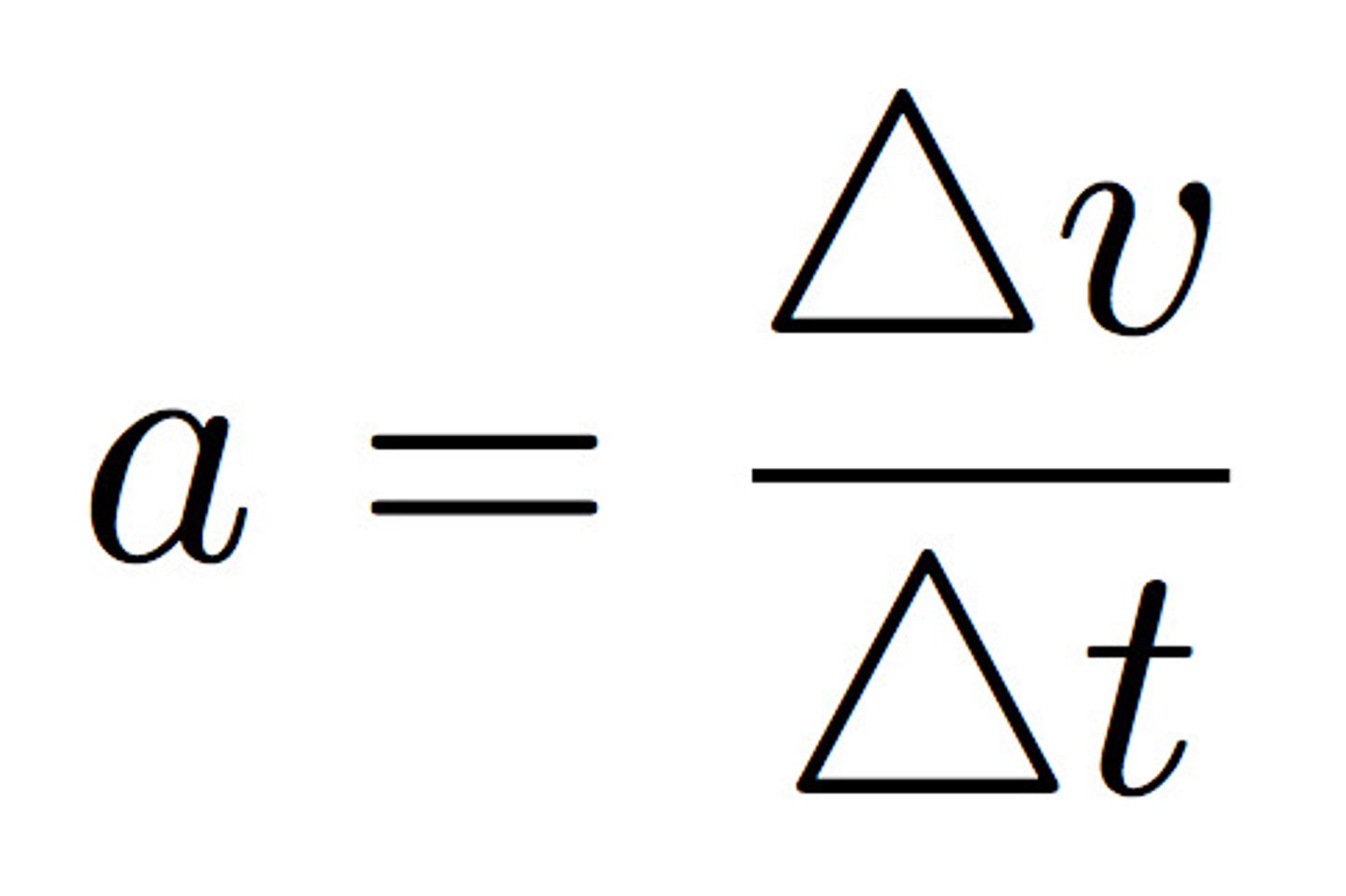
Instantaneous acceleration
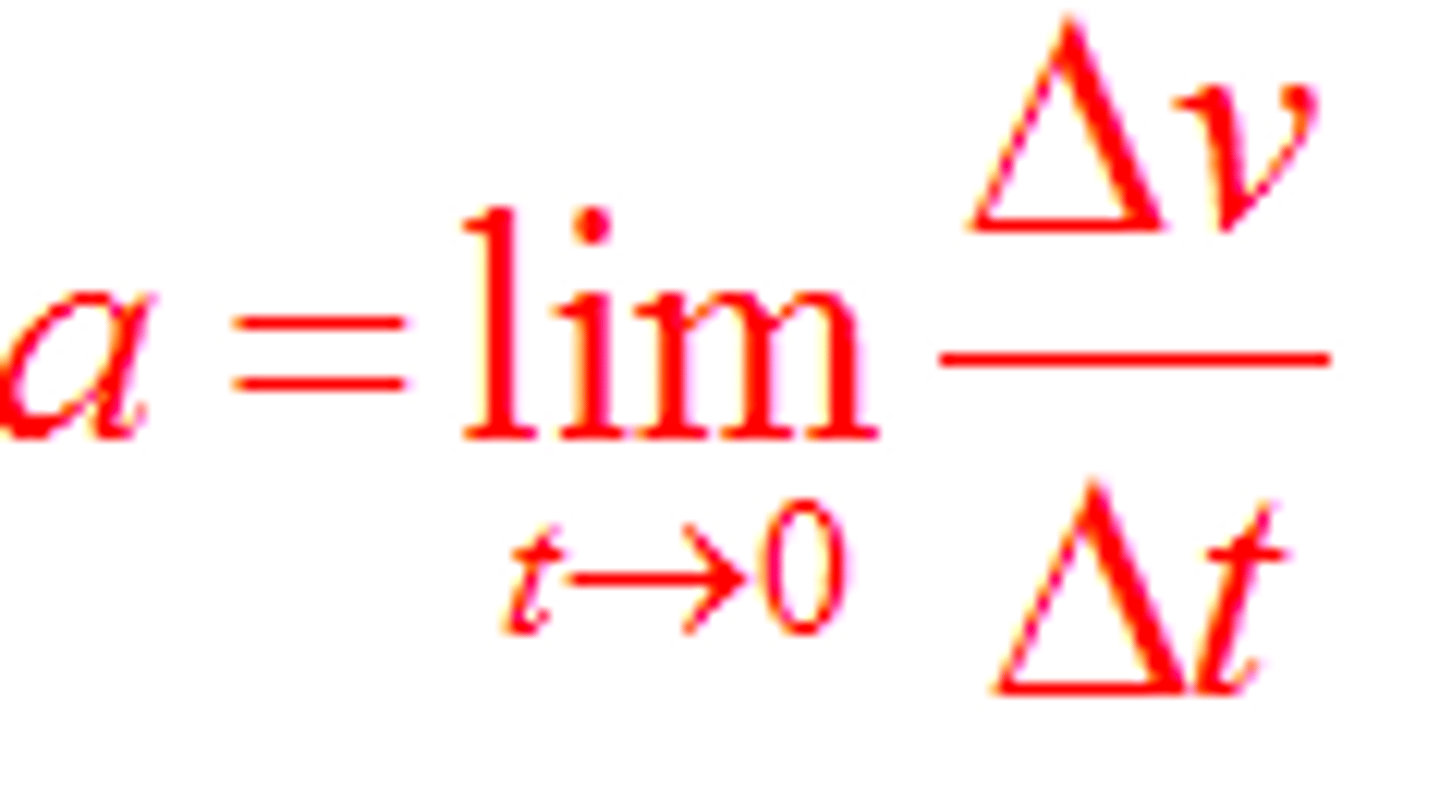
What are the units of acceleration?
meters per second squared (ms⁻²)
Deceleration
The slowing down of an object.
As an object decelerates, does its acceleration necessarily become more negative?
Not necessarily; an object moving to the left and decelerating has its acceleration moving towards the right (in the positive direction.)
The area under a velocity-time graph is equivalent to...
...the total displacement up to the given time.
The area under a speed-time graph is equivalent to...
...the total distance travelled up to the given time.
The area under an acceleration-time graph is equivalent to...
...the change in velocity up to the given time.
Kinematic equations for constant acceleration
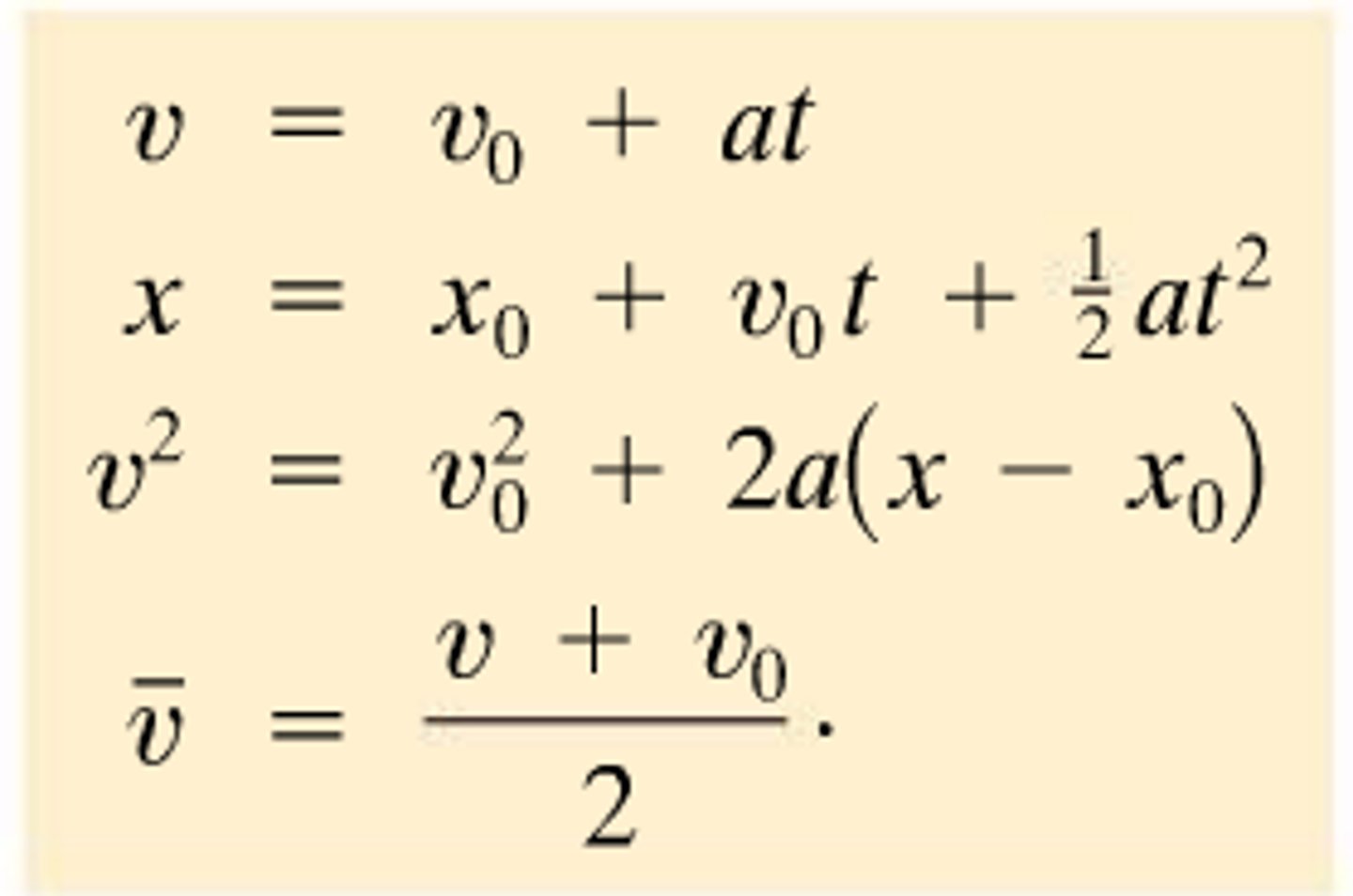
Under the influence of gravity...
...all objects fall at the same rate, neglecting air resistance.
Freefall
An object that is moving only due to the influence of gravity.
Kinematic equations