Plant Biology Test Review
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
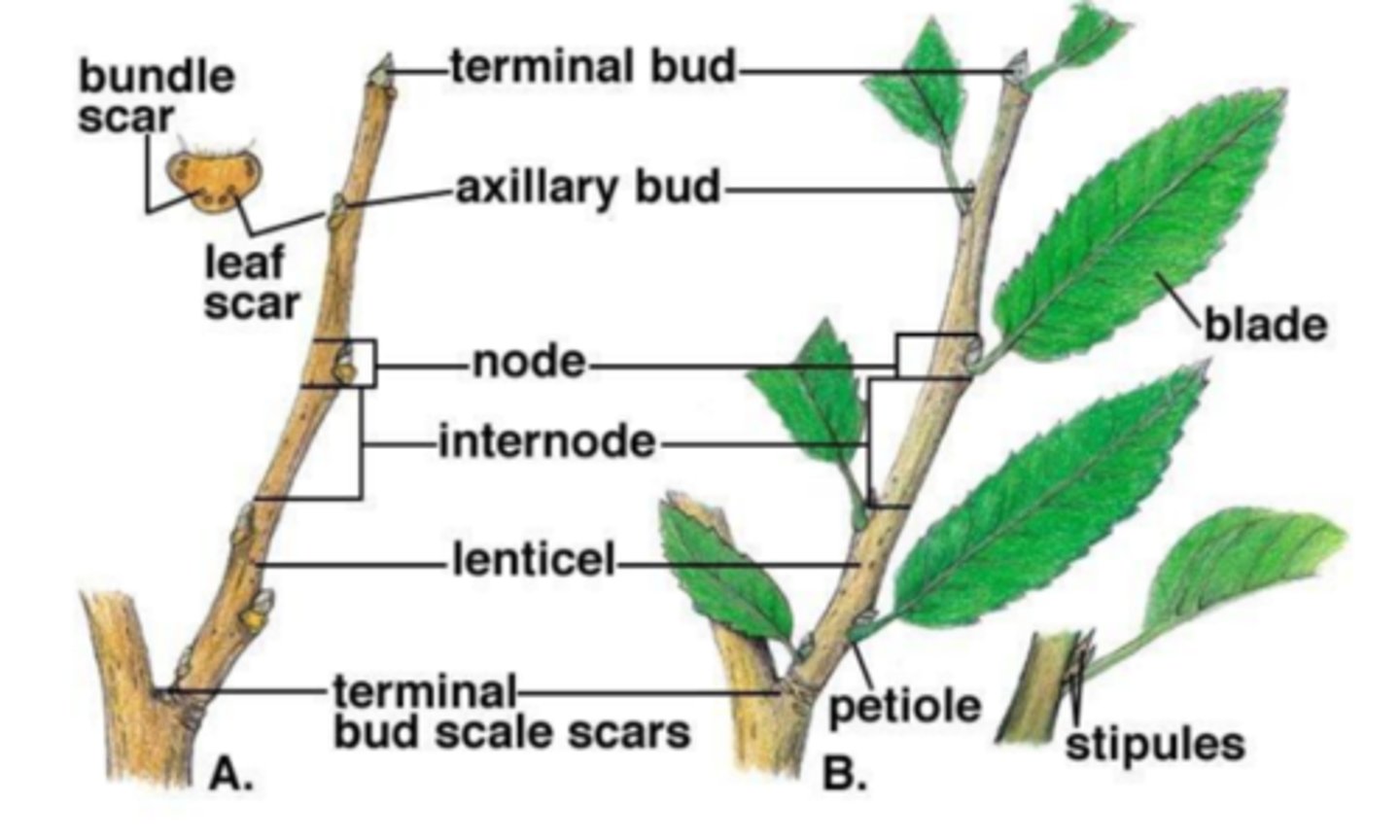
Axil
angle between a stem and a leaf/structure occurring at the node
the root cap
What region of the root is an amyoplast located?
Collenchyma
Simple tissue that provides support for developing organs and lies under the epidermis
Pericycle
Area of the root inside the endodermis that functions to continuously divide after maturity to create vascular cambium and lateral roots
Primordia
Any organ at its earliest stage of development
Saprophyte
Organism that lacks chlorophyll and obtains nutrients from organic matter via parasitic roots
How do you properly write a scientific name?
1) underline or italicize genus and species
2) capitalize Genus, leave species lowercase
Protoderm, Procambium, Ground Meristem
What are the 3 primary meristematic tissues (produced by apical meristem)
Carl Linnaeus
Created binomial nomenclature
-ales
Botanical suffix for Order
Nodes, Internodes, Axillary buds
Stems have what structures that roots and leaves do not?
Ferdinand Lindheimer
Father of Texas Botany
Intercalary Meristem
Adds vertical length in monocot plants
-aceae
Botanical suffix for Family
Parenchyma
Simple tissue most common in all plants, serves multiple roles
Spine
Modified leaf
Thorn
Modified stem
Prickle
Modified epidermal layer
4 common traits of all plants
1) chlorophyll a&b
2) carotenoids
3) starch as primary food source
4) cellulose in cell walls
4 reasons we use Latin in Taxonomy
1) Historical
2) Dead language
3) Internationally known
4) Precise & accurate
Monocots
- 1 cotyledon
- parallel venation
- fibrous roots
- vascular bundles scattered
- floral parts in 3s
Dicots
- 2 cotyledons
- netted venatian
- taproots
- vascular bundles in ring
- floral parts in 4-5s
Lignin
Polymer that forms the chief constituent of wood and serves for structural support
Why do woody stems have wider growth rings in spring vs summer?
There are more nutrient and resources available in the spring to create more mass/growth thus producing more wood
Primary xylem
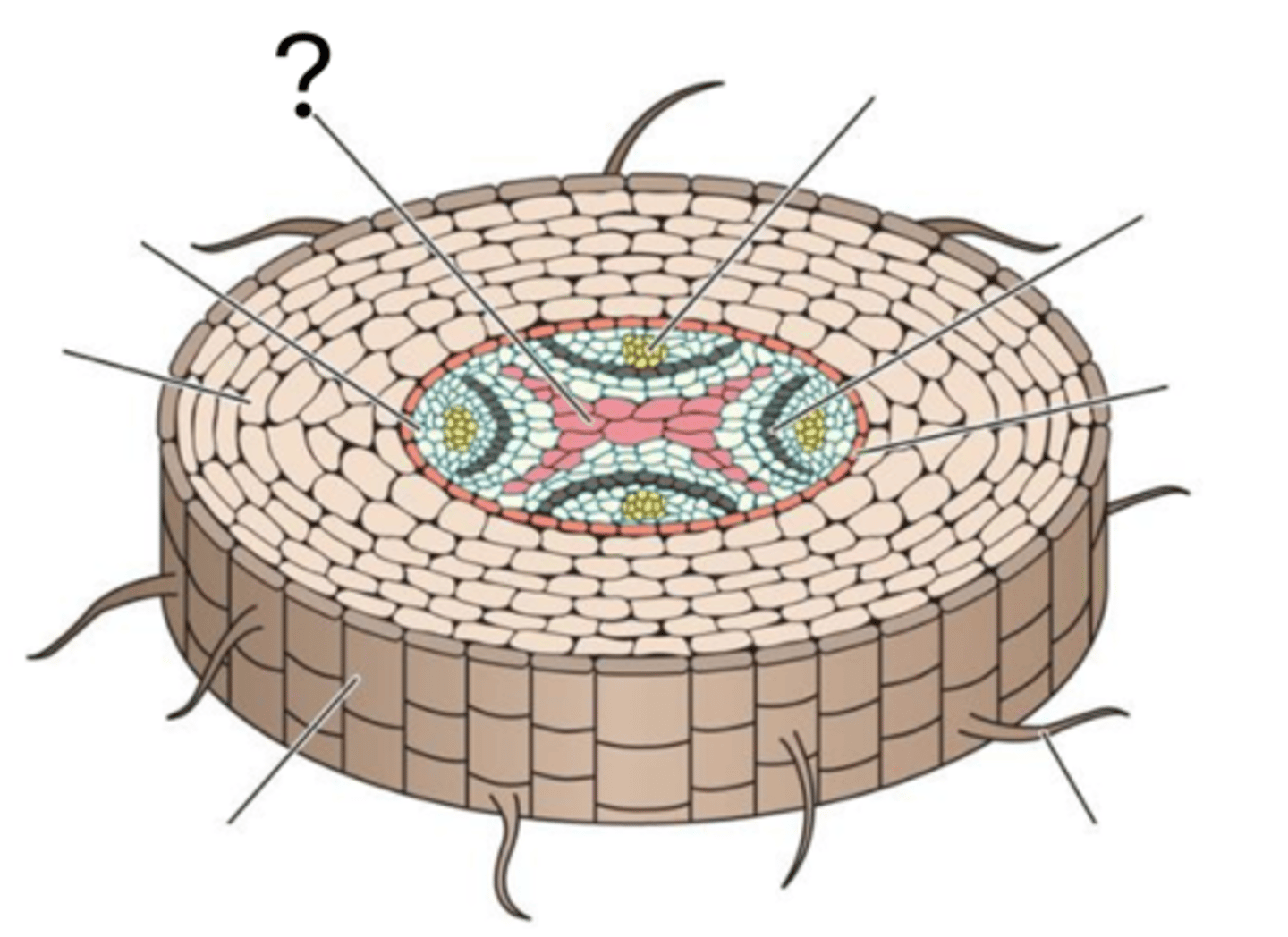
Pericycle
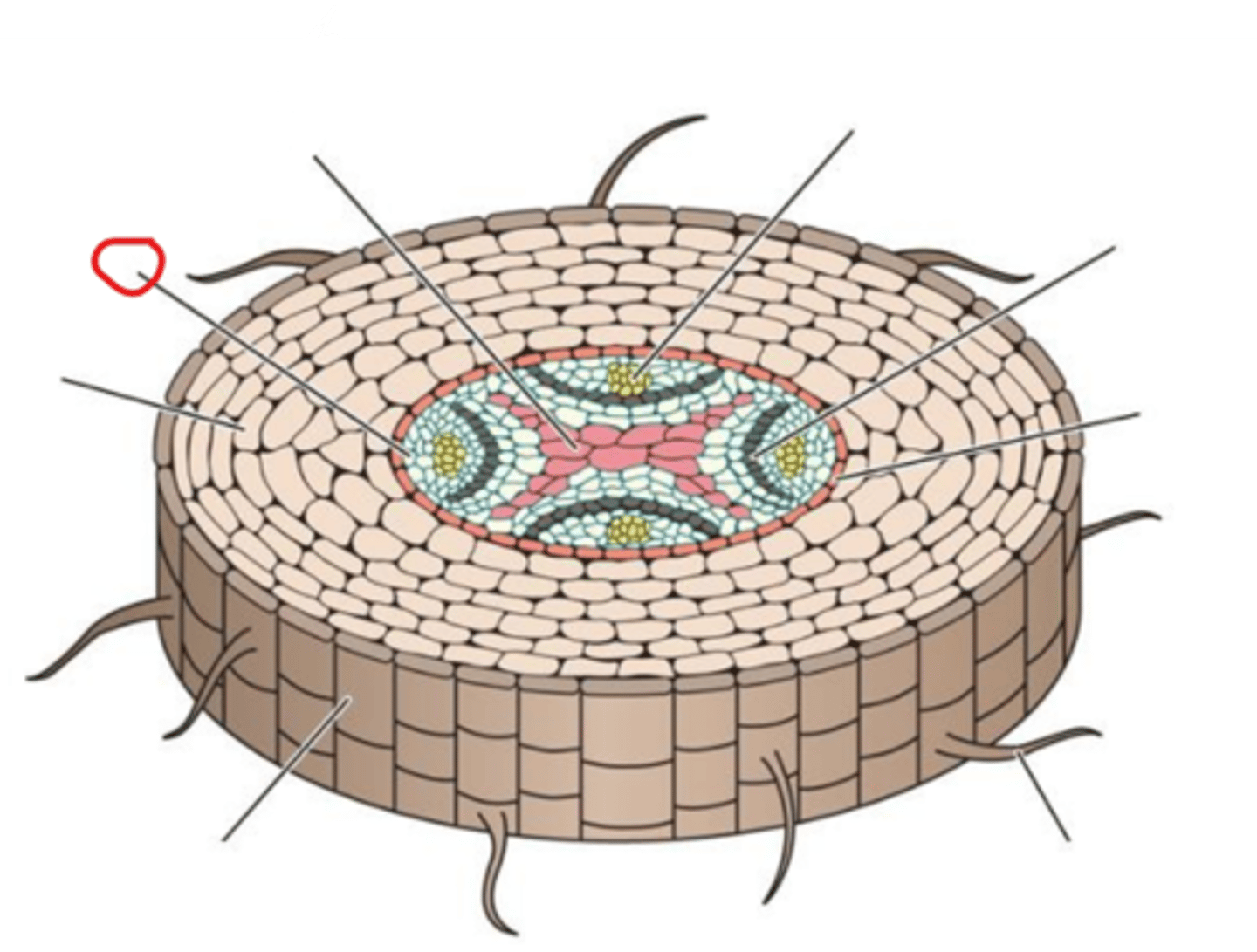
Cortex
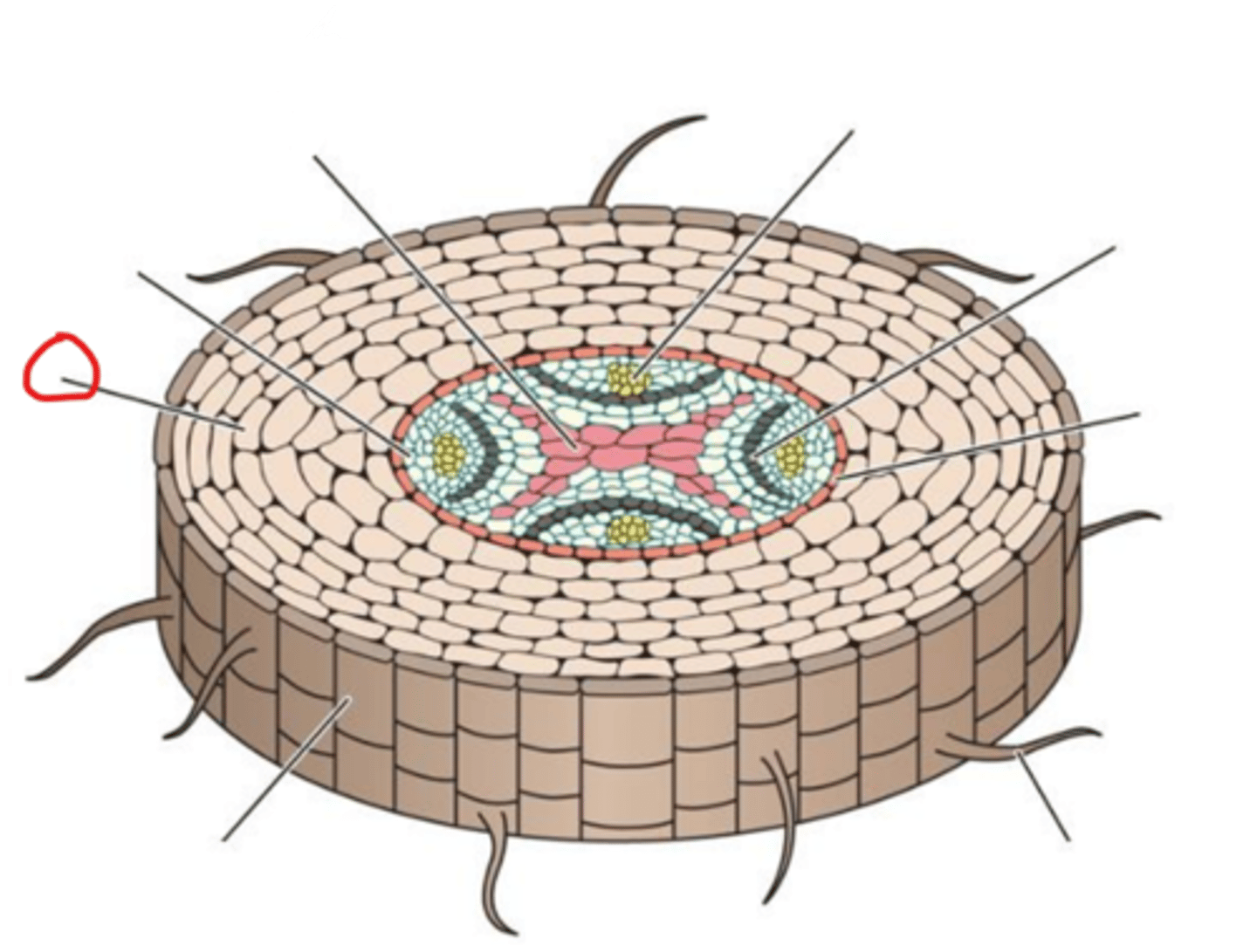
Epidermis
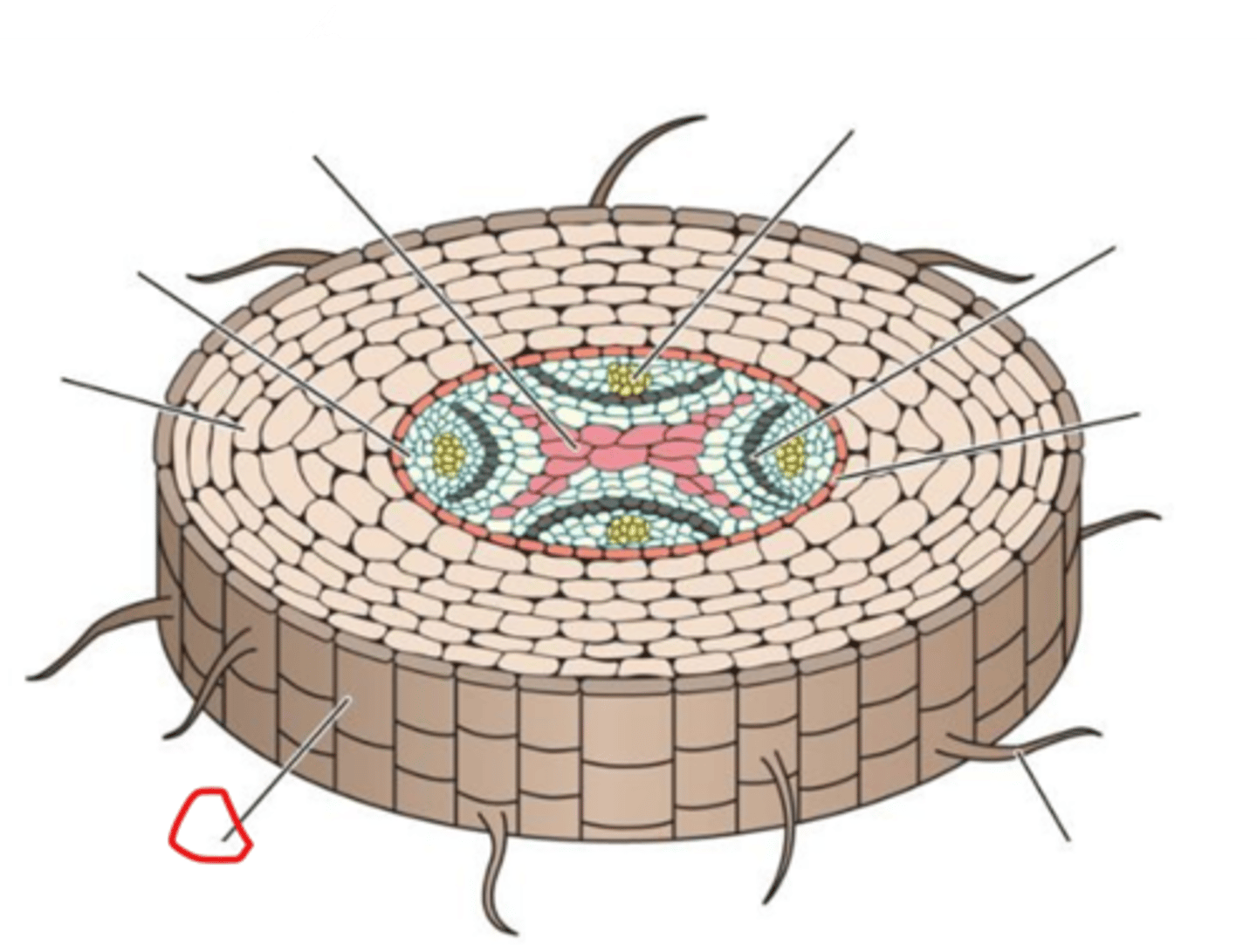
Root hair
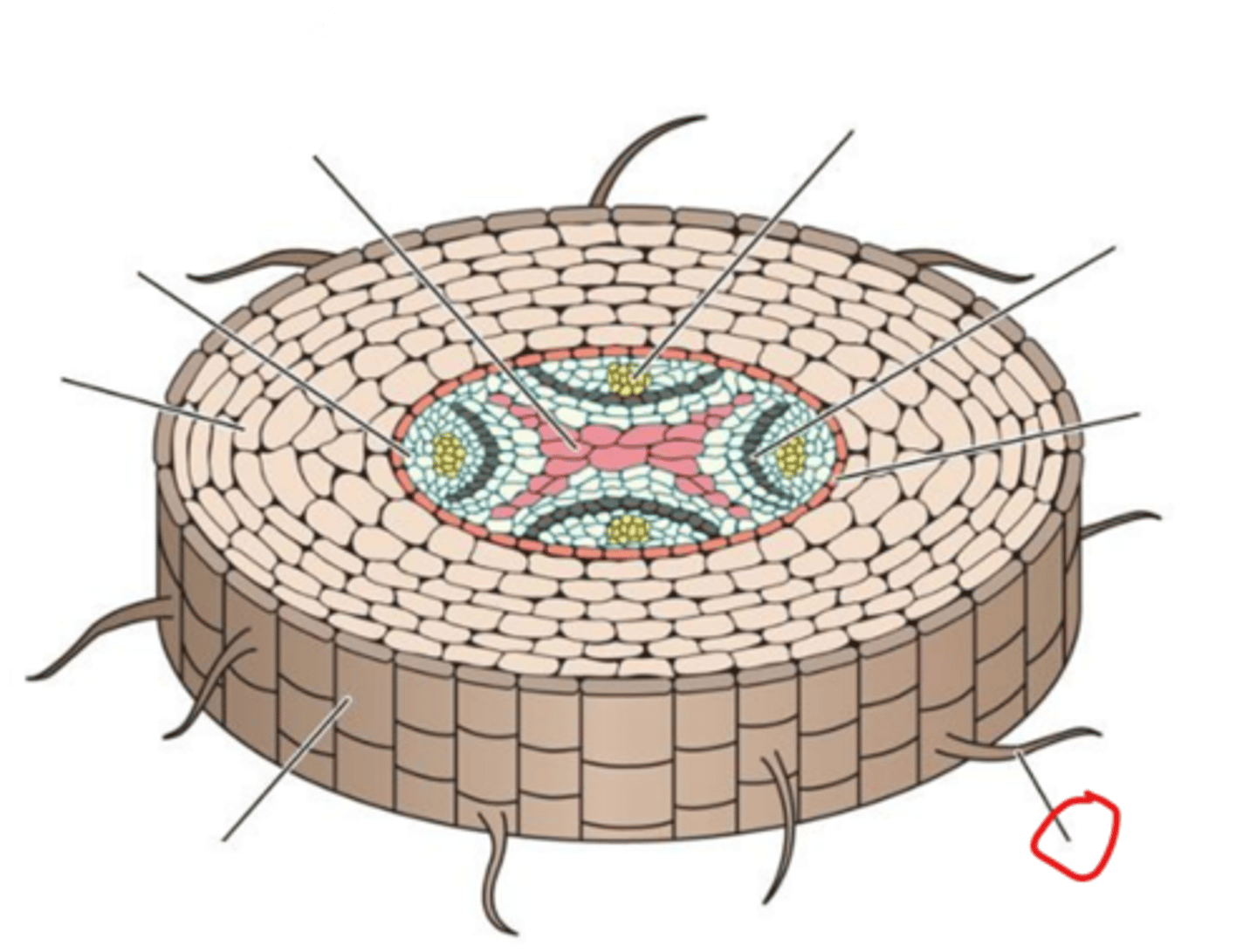
Endodermis
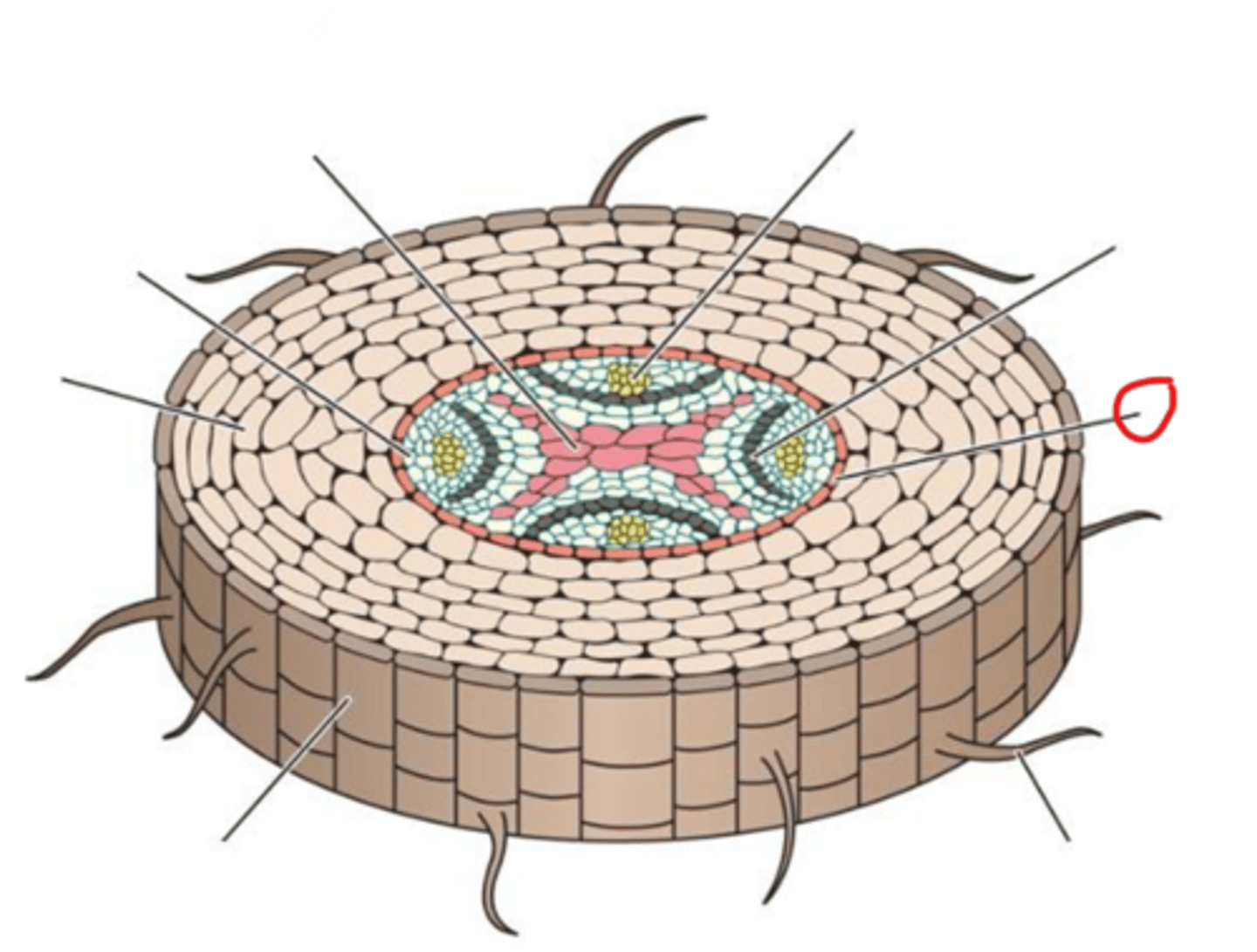
Vascular Cambium
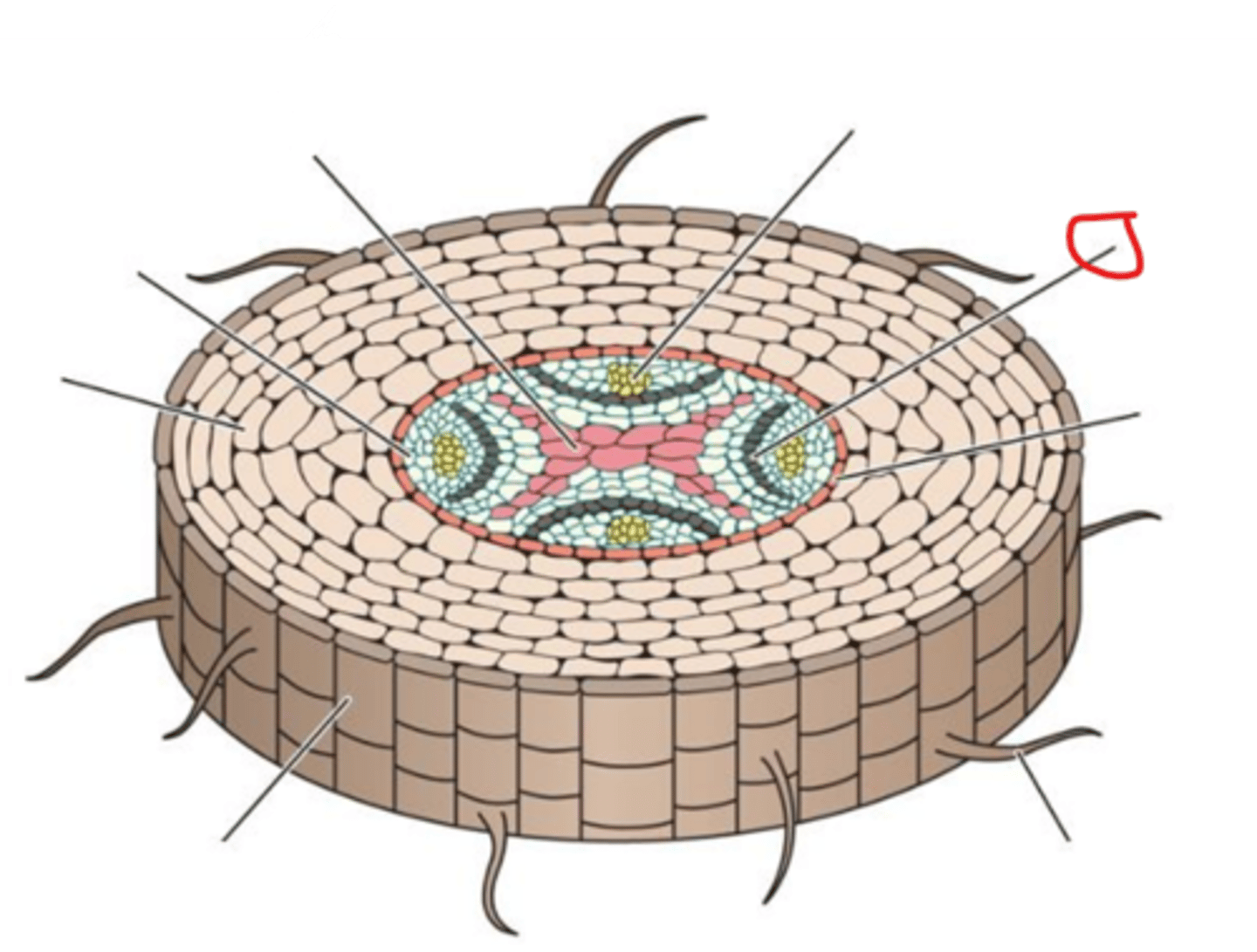
Primary phloem
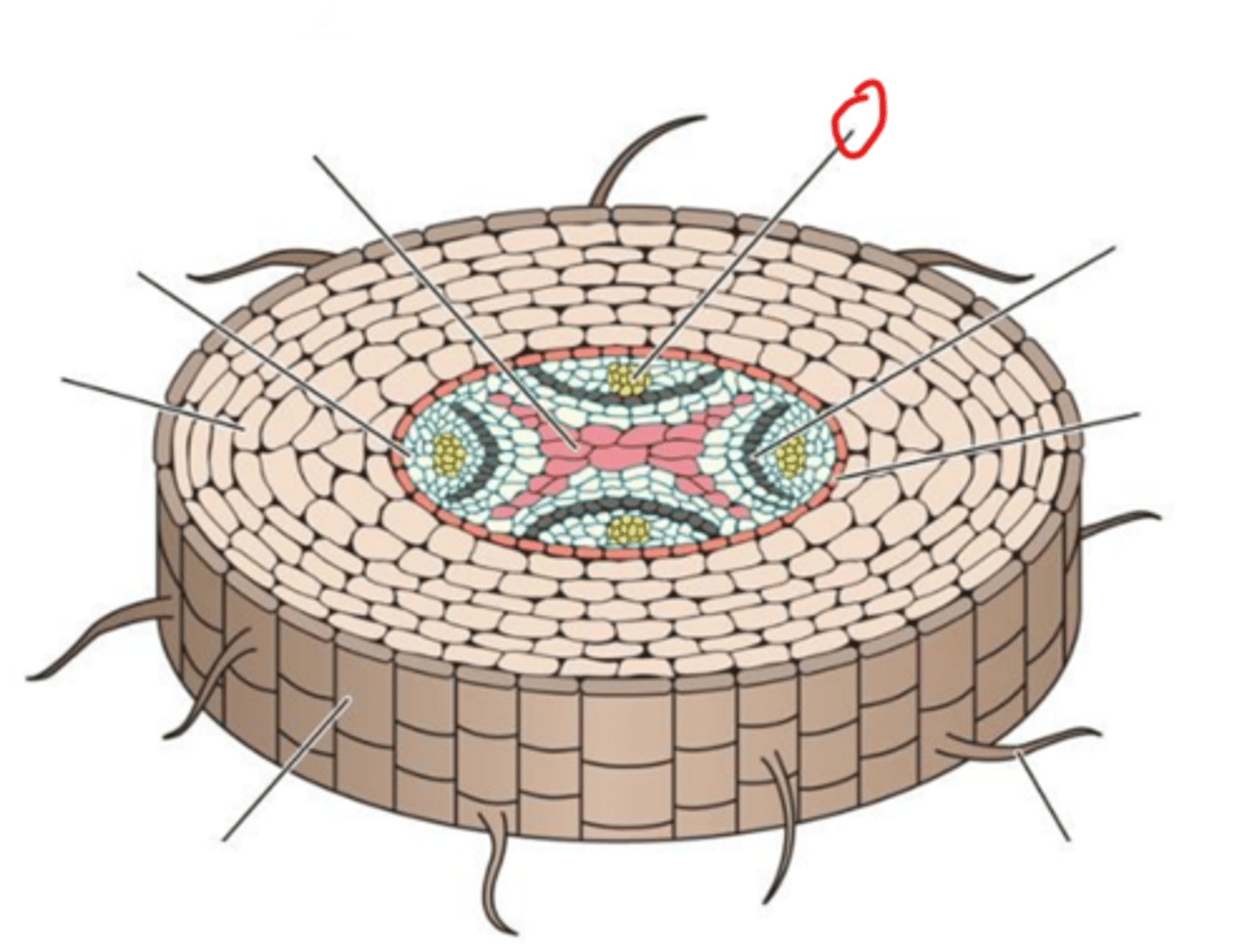
Cork
1
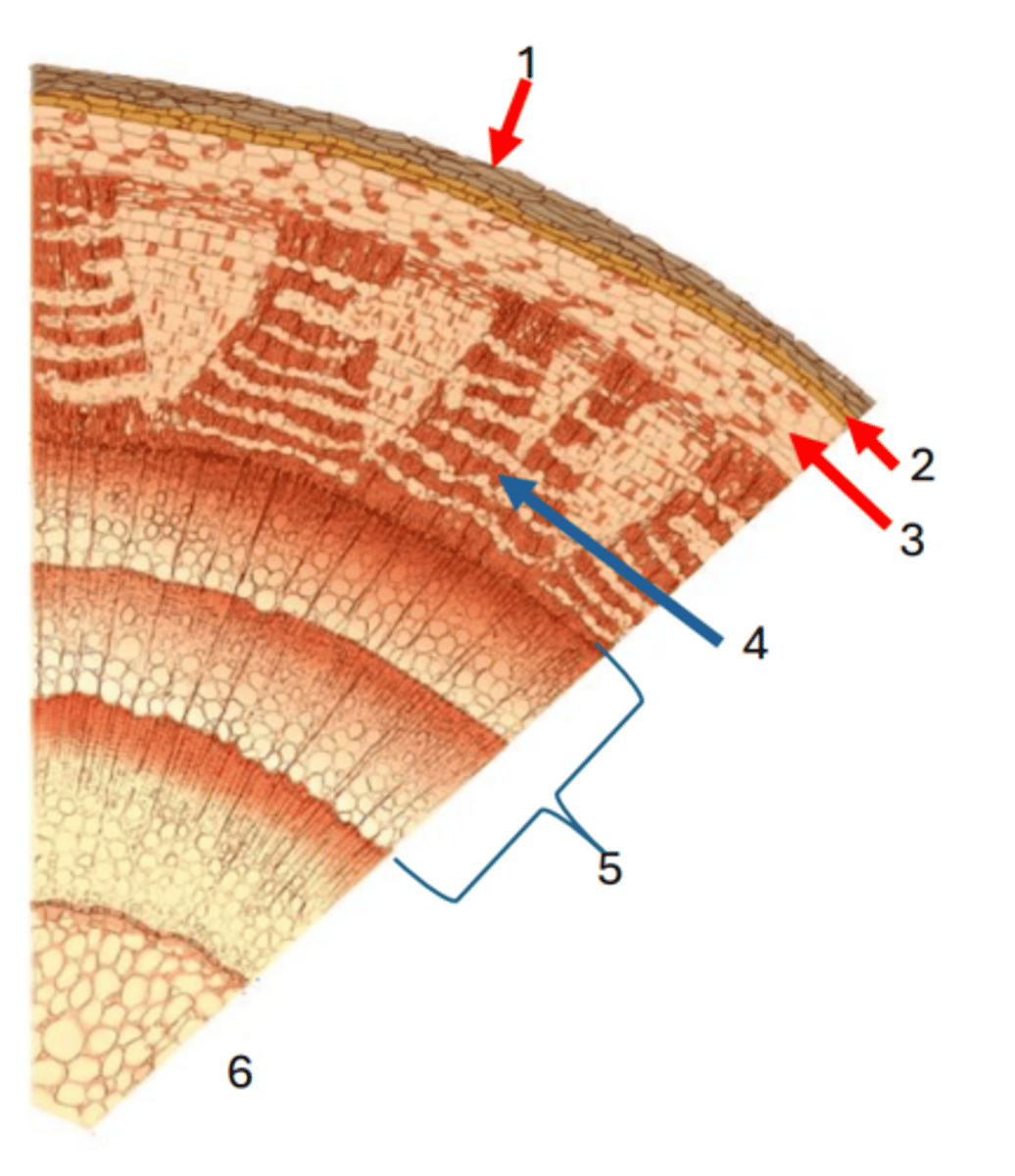
Cork cambium
2
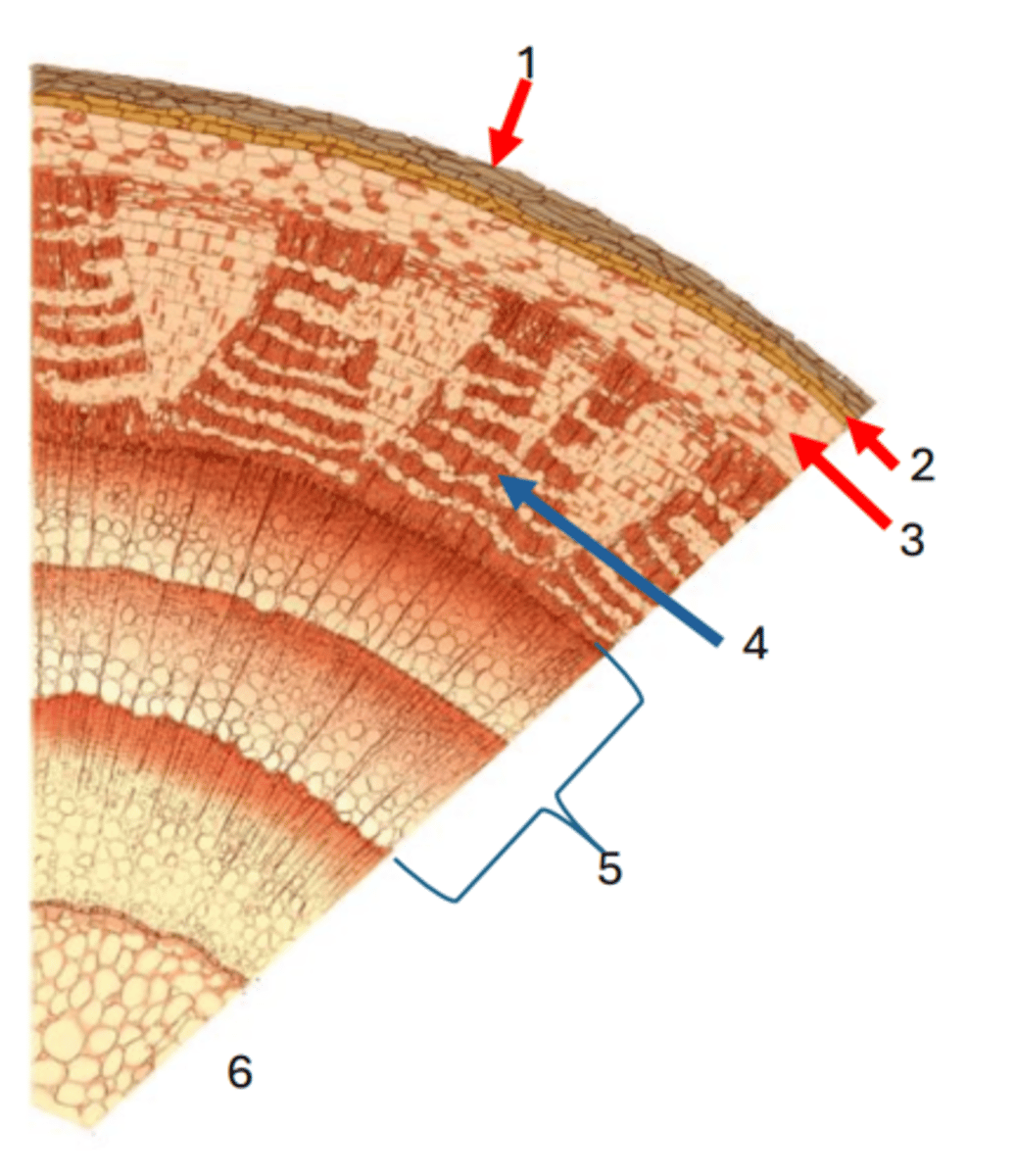
cortex
3
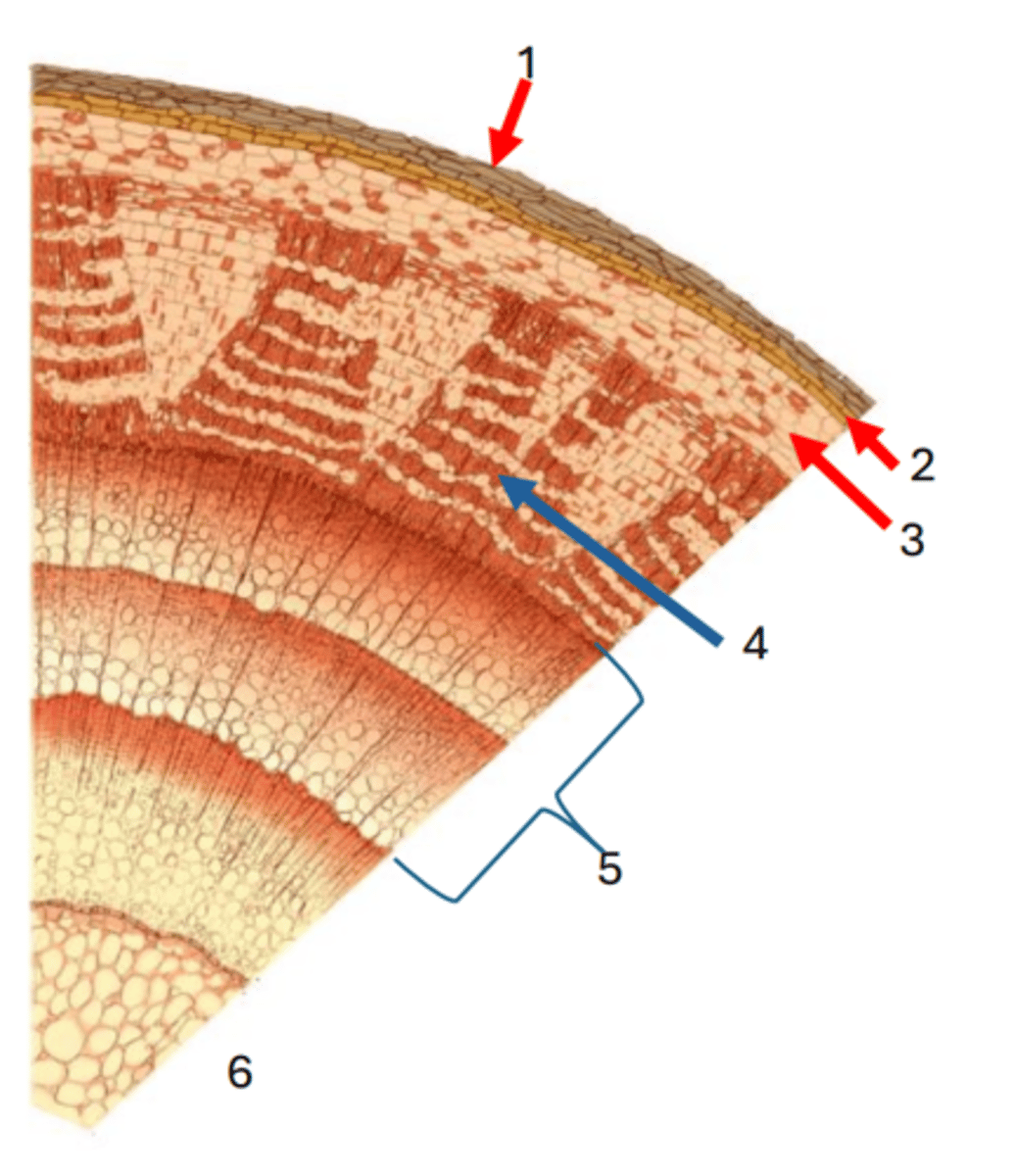
Phloem
4
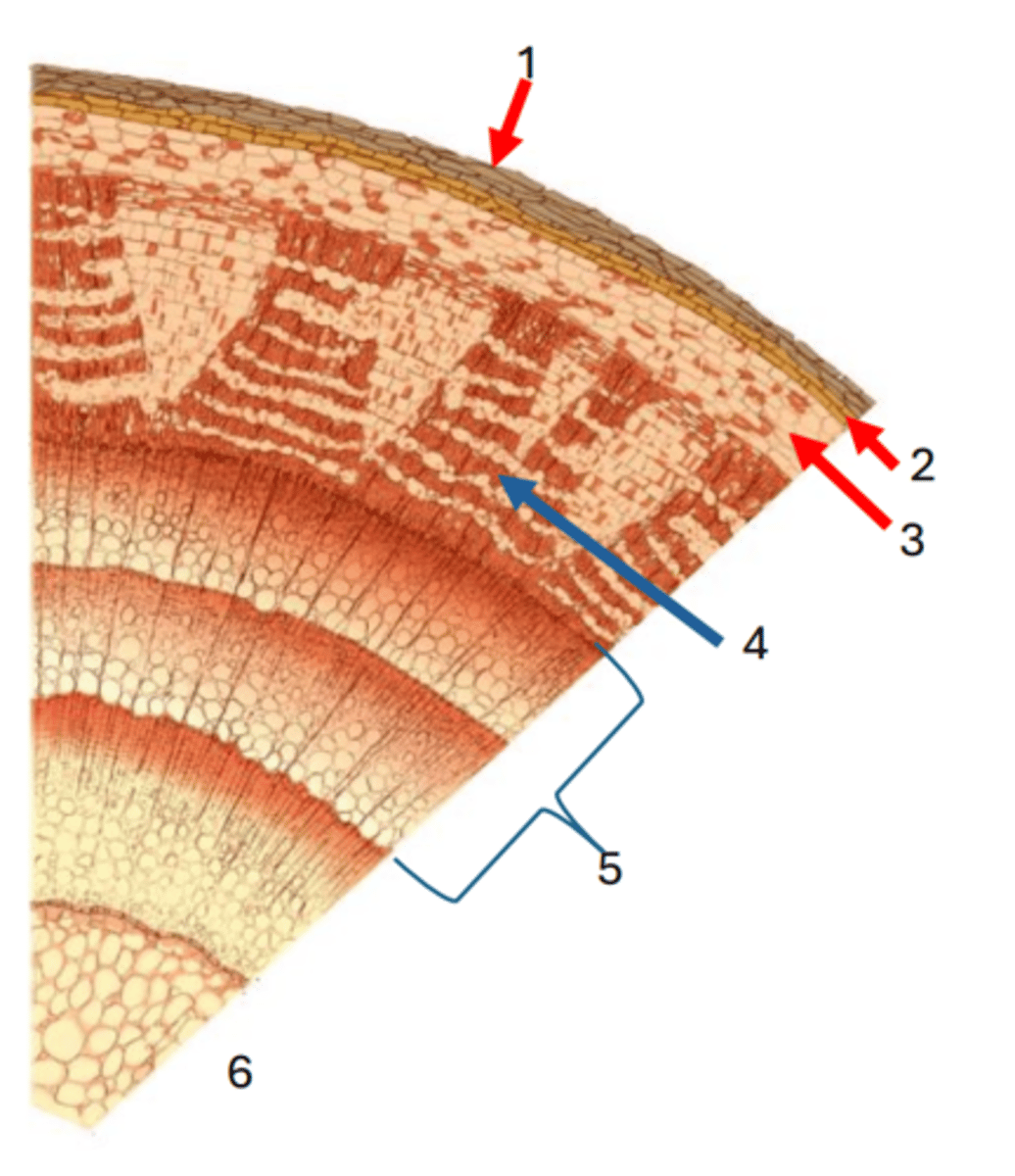
Secondary xylem
5
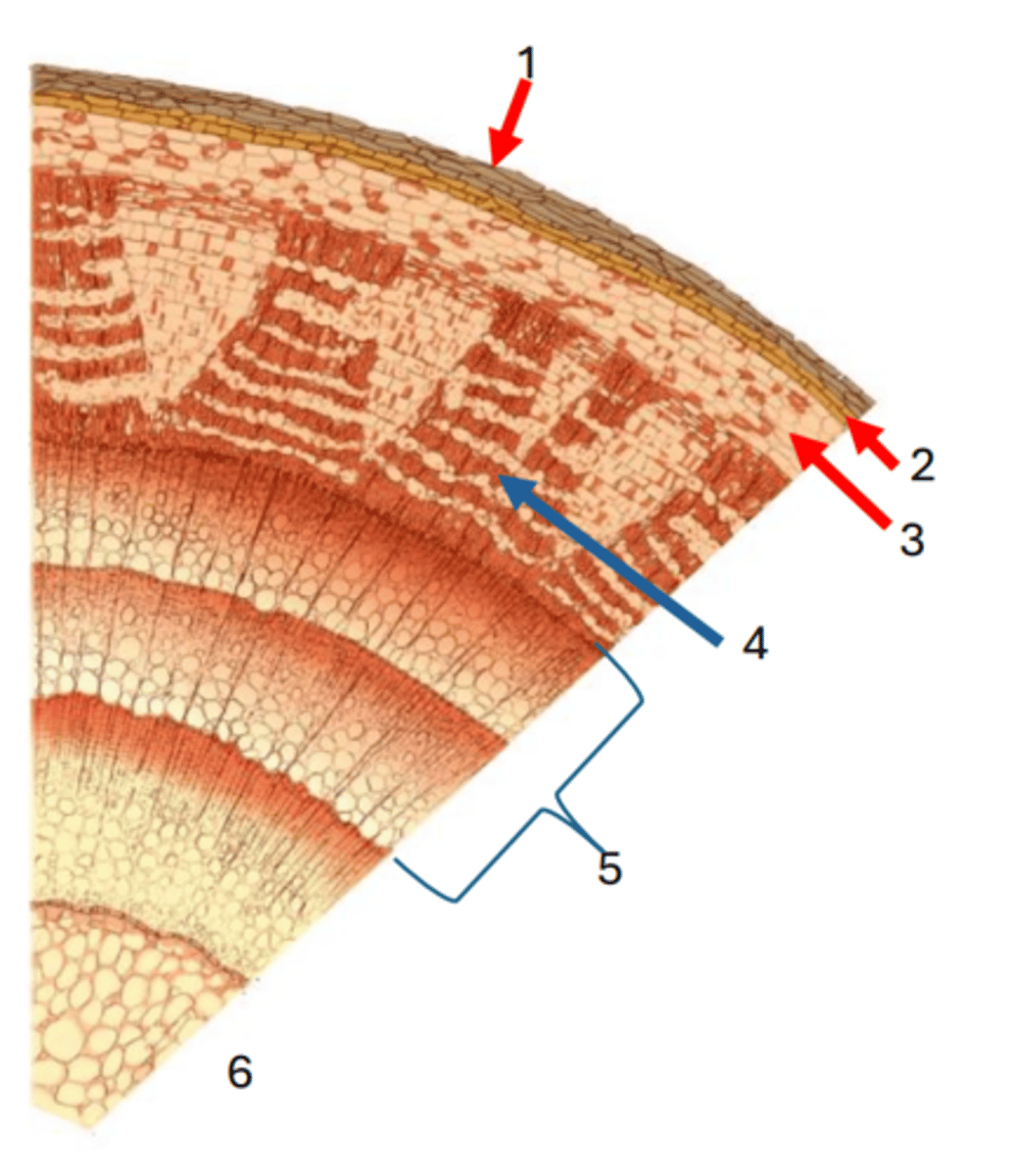
Pith
6
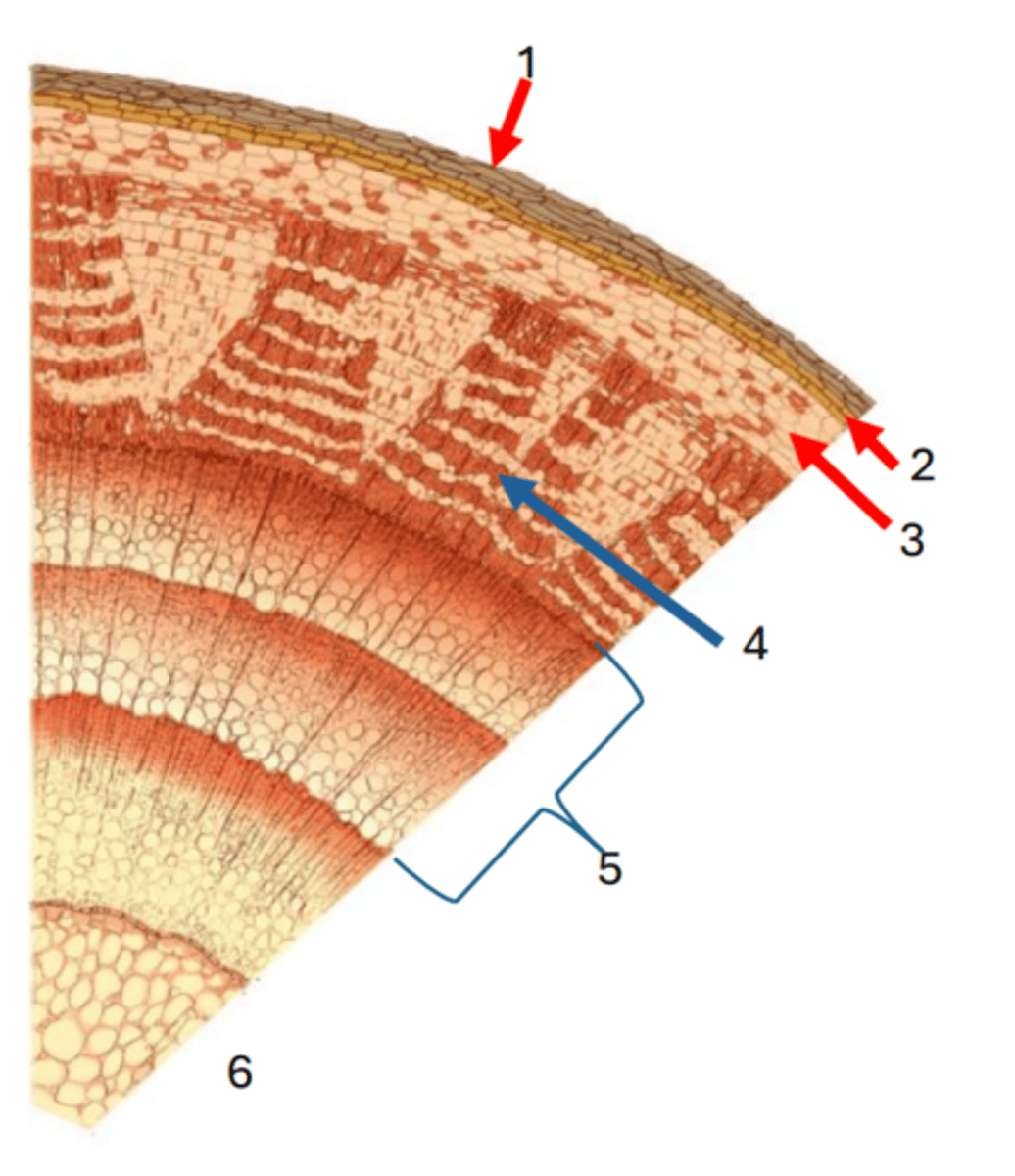
Vascular cambium
Plant systematics
The development of methods to classify groups of plants
Plant physiology
study of plant function and functioning
Plant taxonomy
study of describing, naming, and classifying plants
Plant anatomy
the study of the internal structure of plants
Meristematic tissue
plant tissue found only in the tips of shoots and roots; responsible for plant growth
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
Phloem
distributes nutrients throughout the plant
axillary bud
Root nodules
fabaceae
Casparian band
lignin and superin
Rhizome
below-ground stem
Stolon
above-ground stem
Apical, Lateral, Intercalary
What are the 3 types of meristems?