Trace Evidence
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Why do mammals have hair?
To regulate body temperature
Decrease friction/chafing
Protect against sunlight
Can be sensory organs (like whiskers for cats)
What is the Folicle/Root?
The club-shaped potion embedded in the skin, where blood vessels are connected and where the DNA is found
In a hair, where is the DNA?
Follicle/Root is the bulb part of the hair, it’s where the hair grows from and where the DNA is
What is the Shaft of Hair?
The hair shaft is the non-growing dead portion that portudes from the skin. It’s made of Keratin, which makes it strong and flexible.
What is Keratin and what is it for?
Keratin is the protein that makes the shaft strong and flexible
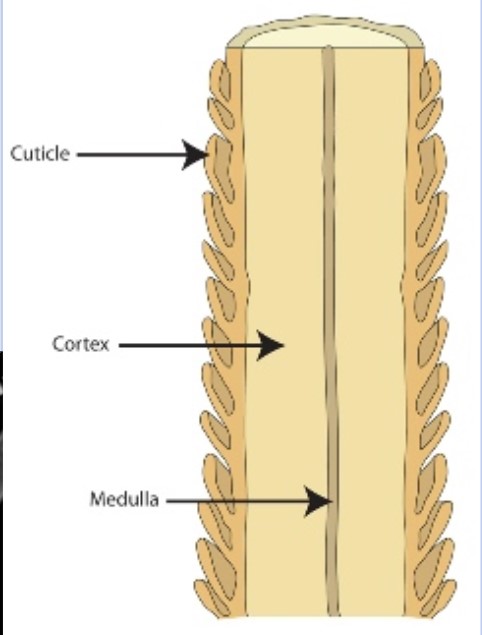
The shaft is composed of what three parts?
Cuticle, the outside part that has a texture
Cortex, the inside part that has pigment
Medulla, the inner string, like pencil led, that can be used to identify if it’s human or not
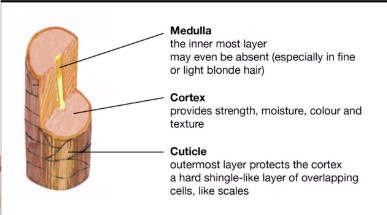
What is the cuticle?
Cuticle is the outside of the hair, it’s the textured outside part. Humans have imbricate pattern (like dogs). Think like nail cuticle, the thin skin layer that goes on top of nails.
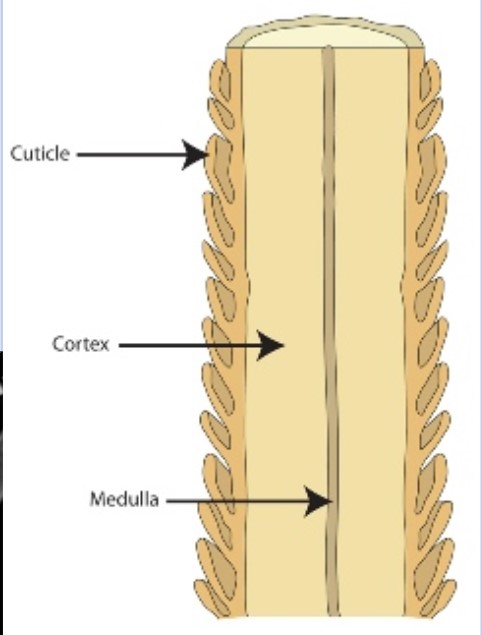
What is the Cortex?
Cortex is the inside part, it contains the pigment
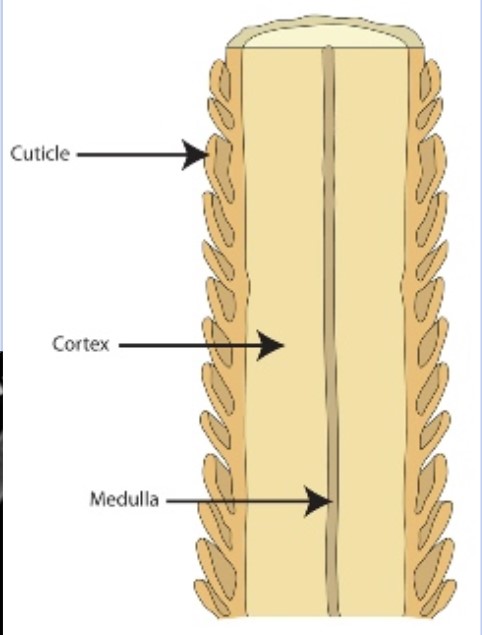
What is the medulla?
The medula is the very inside part of the hair. It can be continuous, interupted, fragmented or segmented, solid, or even no medulla at all.
What pattern of cuticle do humans have?
The cuticle is tranparent and protects the other layers. Humans have imbricate pattern.
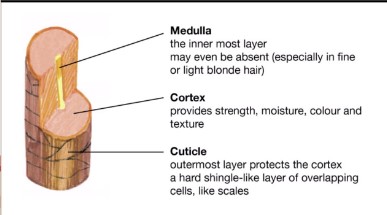
What is the cortex made of? What does it contain?
The cortex is made of Keratin and contains pigment, melanin.
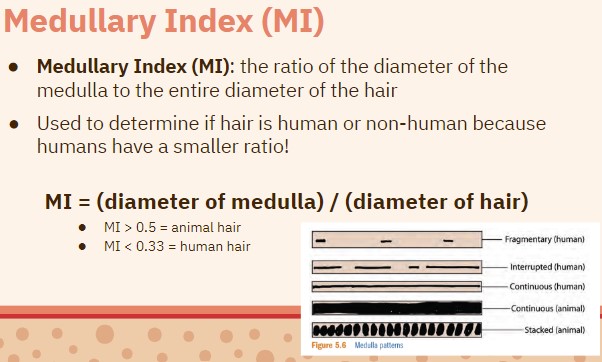
Using the medulla, how can you tell if a hair is human or not?
Human hairs have medullas that are less than 33% medulla
What is the Medullary Index? (MI)
The ratio of the diameter of the medulla to the entire diameter of the hair.
MI = diameter-of-medulla / diameter-of-hair
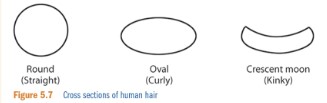
What are the cross section types of hair and what do they mean?
Round (straight hair)
Oval (curly hair)
Crescent moon (kinky or wavy hair)
How thick is the diameter of hair?
Diameter of hair is 15-125 micrometers (mew m)
What is the hair growth cycle?
Anagen (growth phase)
Nourishment of the hair folicle via blood supply enables growth
Catagen (transition phase)
Hair folicle detaches from blood supply
Telogen (resting phase)
Without nourishment, hair dies and falls out
Remember as Anakin grew up to kill cats and fall into lava pits.

What is the anagen state and how long does it last?
Anagen stage is active growth
Hair grows 1.3 cm per month
This stage lasts 2-6 years, and about 80-90% of hair is in this stage.
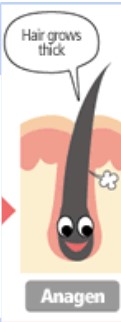

What is the Catagen Stage, and how long does it last?
Catagen stage is transition stage where the follicle starts to degenerate
This lasts 1-2 weeks
2% of hair is in this stage
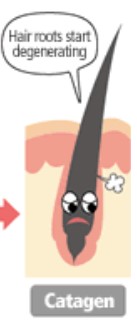

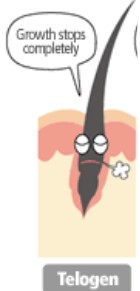
What is the Telogen Stage and how long does it last?
Telogen stage is growth stops completely, the follicle is dormant/resting
It lasts about 2-4 months
10-18% of hair is in this stage
How many hairs do you lose per day?
50-100
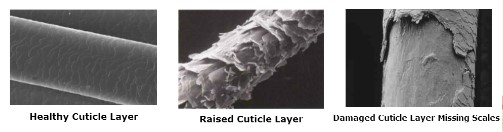
What does bleaching do to hair?
Removes pigment moleculesd from hair
leaves hair yellowish
makes hair brittle
disturbs scales on cuticle
What does dying do to hair?
changes the colour of the hair shaft
Cortex and cuticle affected
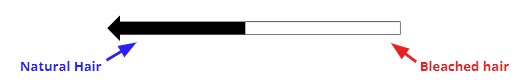
How can you tell how long ago someone changed their hair colour?
Measure length of natural hair roots in cm
divide by growth rate (1.3 cm / month)
Determine number of months since colour change
What is Questioned Hair and what is exemplar hair?
Questioned hair: Comes from crime scene
It’s first checked which speceis, then if it’s human, its charactaristics are compared to the suspect pool
Exemplar hair is from a suspect, for example
What can Hair tell us?
What species
Racial origin (sometimes)
Location on the body
Whether it has been chemically altered (dyed, bleached)
When particular drugs were used over a long period of time
Metal content (can diagnose dietary deficiencies and diseases)
What can hair NOT tell us?
Sex
Age
What is a fiber? Where could fibers come from?
A fiber is the smallest unit of a fabric
It must be at least 100 times longer than wide
it comes from:
carpets
clothing
linens
furniture
insulation
rope
etc
Fibers are spun together to make ______ which is weaved together to make _______
Fibers are spun together to make yarn which are weaved together to make textiles and fabrics

Fibers are used to make:
Textiles (clothes, carpets)
Cordage (rope, string, nets)
brushes
Optical cables
structural materials
What are some examples of natural fibers?
Vegetable
Jute
Hemp
Sisal
Bamboo
Animal (looks like hairs, it is hair)
Wool
Silk
Mohair
Alpaca
Mineral
Asbestos
Fiberglass
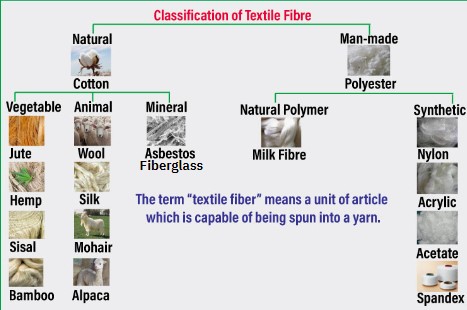
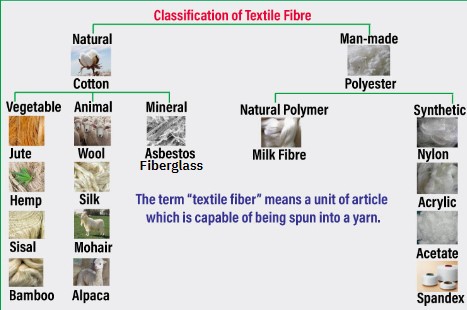
What are some examples of Man-Made fibers?
Natural Polymer
Milk Fibre
Synthetic
Nylon
Acrylic
Acetate
Spandex
Animal fibers are made of _______, while plant fibers are made of _________
Animal fibers are made of protein, while plant fibers are made of cells
Synthetic fibers are either regenerated (_____+______) or Synthetic polymers (________)
Synthetic fibers are either regenerated (Plants+chemicals) or Synthetic polymers (petroleum/plastic)
What is Warp in a textile weave? What is Weft?
Warp is lengthwise, up and down, the stretched set of yarns that the other yarns are weved through. It’s stronger types of fibers.
Weft (remember as “left“) is crosswise. usually weaker fibers
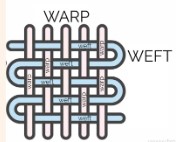
How are fibers gathered?
vacuums, sticky tape, and forceps then put into a bindle
What is an example of a destructive test?
Bleach test
Look for colour change, bubbles, or material dissolving
Burn Test
Does it burn or melt? Shrink from flames? Odors? Residue left?
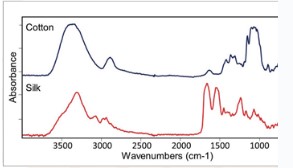
What is Spectroscopy?
Emits a beam of light that bounces off fibers and returns to the instrument
Depending on changes in the beam, the chemical structure can be determined
What is an example of a 2D forensic impression? What about 3D?
2D: Fingerprint (patent or latent)
3D: tool marks, marks bullet caused, creates plastic imprint
What is an example of Pattern Evidence?
Shoe marks
tire marks
Pattern evidence can identify a brand, model, or size
Can identify tread wear, cuts, or nicks
What can shoeprints tell you?
Brand
Model
Size
Foot length
Height
Stride length
Tread wear, cuts, nicks
What are some examples of impression evidence?
Fingerprints
Bite Marks
Footprints
Tire marks/tracks
Tool marks
Is a tool mark a class or individual evidence?
Both.
Tool mark is class becuase it can be traces back to a specific tool
It could become individual through the presence of any minute imperfections or patterns from the life of the tool.
What are the types of tool marks?
Compression/indentation
When a tool is pressed into soft surface (can show size and shape of tool)
Abrasion/Striation
When a tool slides along a surface. (Can narrow down type of tool, or give individual evidence in working edge)
Combination
Pressed and dragged
Cutting marks
Sharp edge cuts something into parts
What is Striation (Abrasion)?
The mark left when a tool slides along a surface. (Can narrow down type of tool, or give individual evidence in working edge)
How do you collect tool mark evidence?
Observe, measure, describe
Photograph perpendicular to toolmark in oblique lighting with ruler
Cast made
if the support where the toolmark was made cant be collected as evidence
How do you collect tool evidence?
Observed and photographed
Working end covered in cloth and boxed and brought back to lab
Comparison tool-marks are made on soft material like clay or lead so extra marks are not created
Comparison microscope is used to compare (one eye in mystery mark, one eye in tool mark, trying to line it up)
If a match is made, common origin is established
How many teeth do adult humans have?
8 different types.
16 on top jaw (maxilla), 16 on bottom jaw (mandible)
What are the 8 types of teeth?
3rd molar (wisdom teeth)
2nd molar
1st molar
2nd premolar
1st premolar
canine
Lateral incisor
central incisor
What is the strongest substance in your body?
Enamel is the strongest substance your body makes. Teeth are made of dentin and enamel.
What are your teeth made of?
Dentin and enamel. Tooth enamel can outlast bone and withstand heat up to 2,000 degrees F.
What are forensics odontologists? What do they do?
Forensic Odontologists identity human remains by their dentition (teeth).
They study dentation of dead people and compare them with dental records. They look at things like location and shapes of fillings, root canals, crowns, tooth positions, and more to find a match.
What are some examples of when teeth can be used to identify bodies?
Mass disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis, plane crashes
Disfigured bodies (drowning, fire, bombs)
Decomposed bodies
Where can bite marks be found?
On a victim that was bitten by suspect
On a suspect that was bitten by victim
On objects suspects or victims have bitten and left at crime scene
Odontologist will study and try to find a match.
What happens when skin is bitten? What are the 3 stages?
Stage 1:
Immediately after a bite
Forms an impression or indentation
Lasts 1-10 minutes
Stage 2:
Area swells with inflammation
Obscures individual tooth marks
Lasts several hours
Stage 3:
Final state
Bruising
What are the bite mark scales? Which are most valuable to forensic odontologists?
Least severe: Level 1
Most Severe: Level 2
Level 3 and 4 are most valuable:
Obvious bite mark
bruising or lacerations
How do you collect bite mark evidence?
Take a photo with rulers and capture much of the mark as possible, different lighting
Make a cast
How do you collect a bite impression?
Obtain warrant to collect bite impression
Bite into soft wax
3D mold
How do you use an overlay in bite mark comparison?
Put sheet of plastic over the bite impression or teeth mold, then trace tooth locations with a marker.
Then, place the overlay on a photo or cast of bite mark to find similarities or difference sin tooth placement and angle.
What are accidental characteristics?
Identifying characteristics made by every day wear and tear, cuts, nicks, dings, and scuff marks.
What is stride length? How do you measure it?
Taller = longer stride length
MEASURE FROM HEEL TO HEEL!