Electrical Energy and the Nervous System Overview
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the formula to calculate Watts in electrical energy?
Watts = Voltage x Amps.

What is the relationship between voltage and potential energy?
Voltage represents potential energy in electrical energy.
What role do elements like sodium and potassium play in electrical energy?
They are used to transfer electrons throughout the body.
What does the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connect?
It connects the Central Nervous System (CNS) to muscles, glands, and sensory receptors.
What is the significance of the PNS being contralateral?
The left side of the brain controls the right side of the body, and vice versa.
What are the three main parts of a neuron?
Axons, cell body (soma), and dendrites.
What is the function of the axon in a neuron?
It serves as the nerve fiber or pathway for transmitting information.
What is the role of the dendrites in a neuron?
They connect the neuron to other cells and body parts.
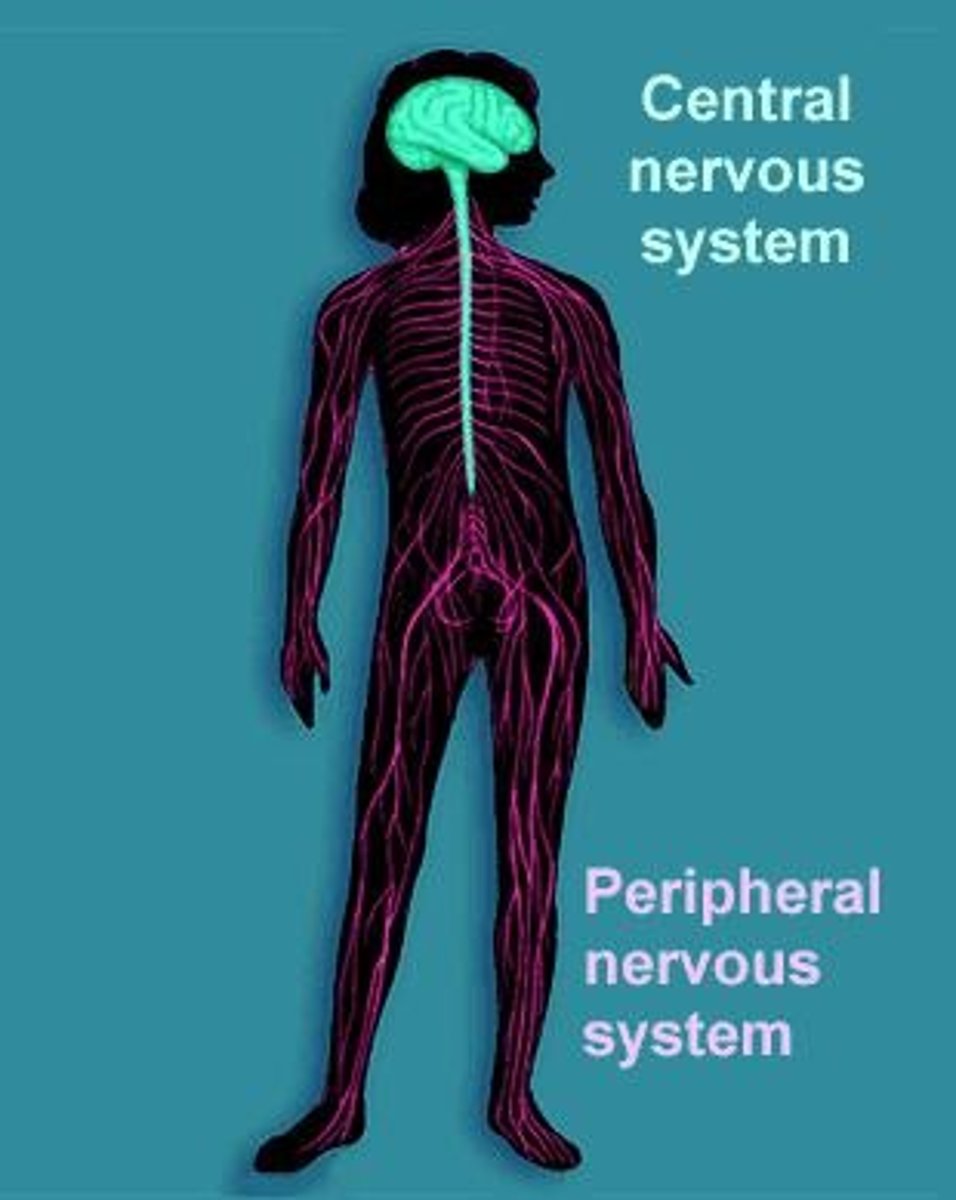
What are the two general systems of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
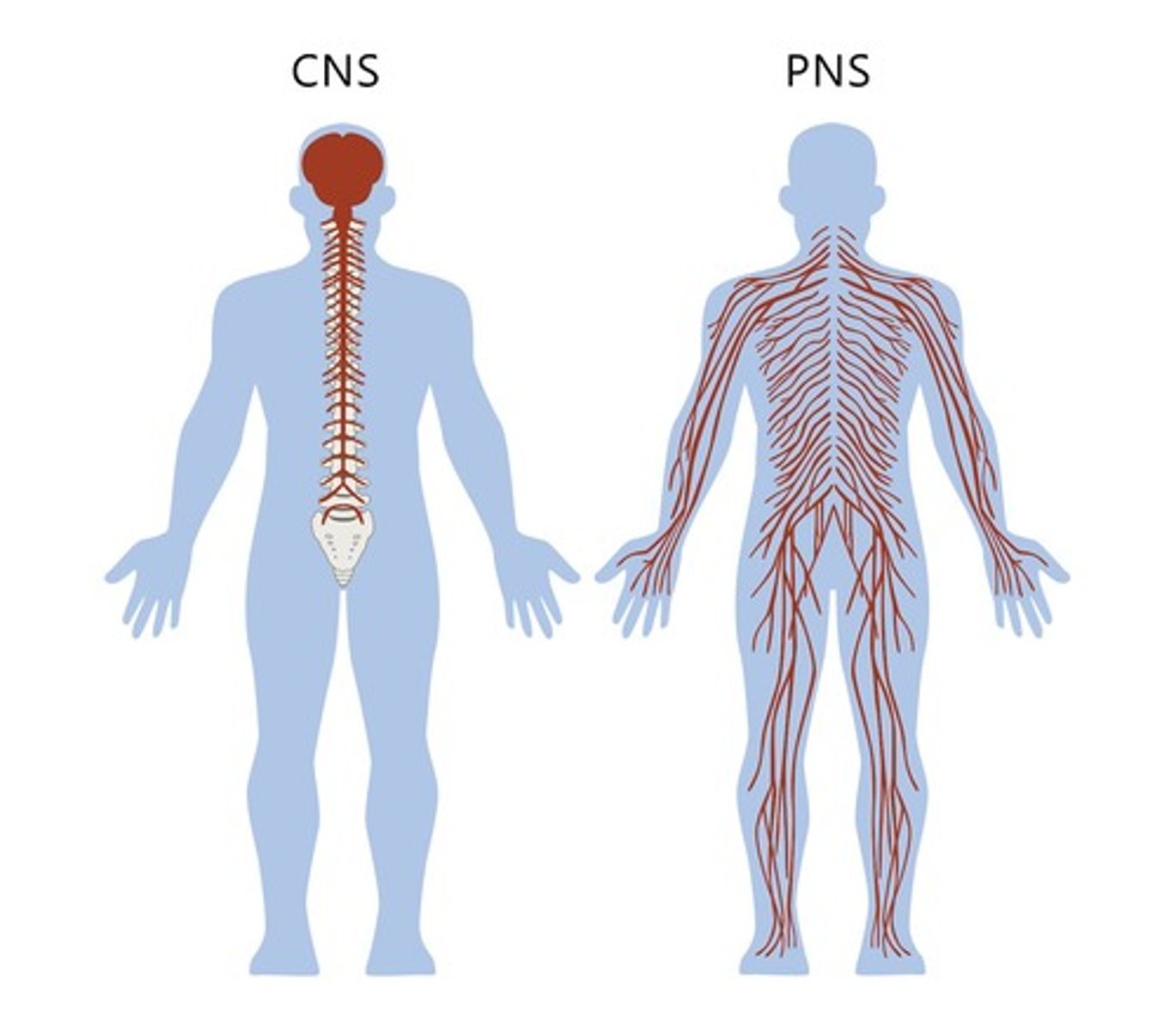
What is the primary function of the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
It acts as the central processing unit for the body, sending and receiving information.
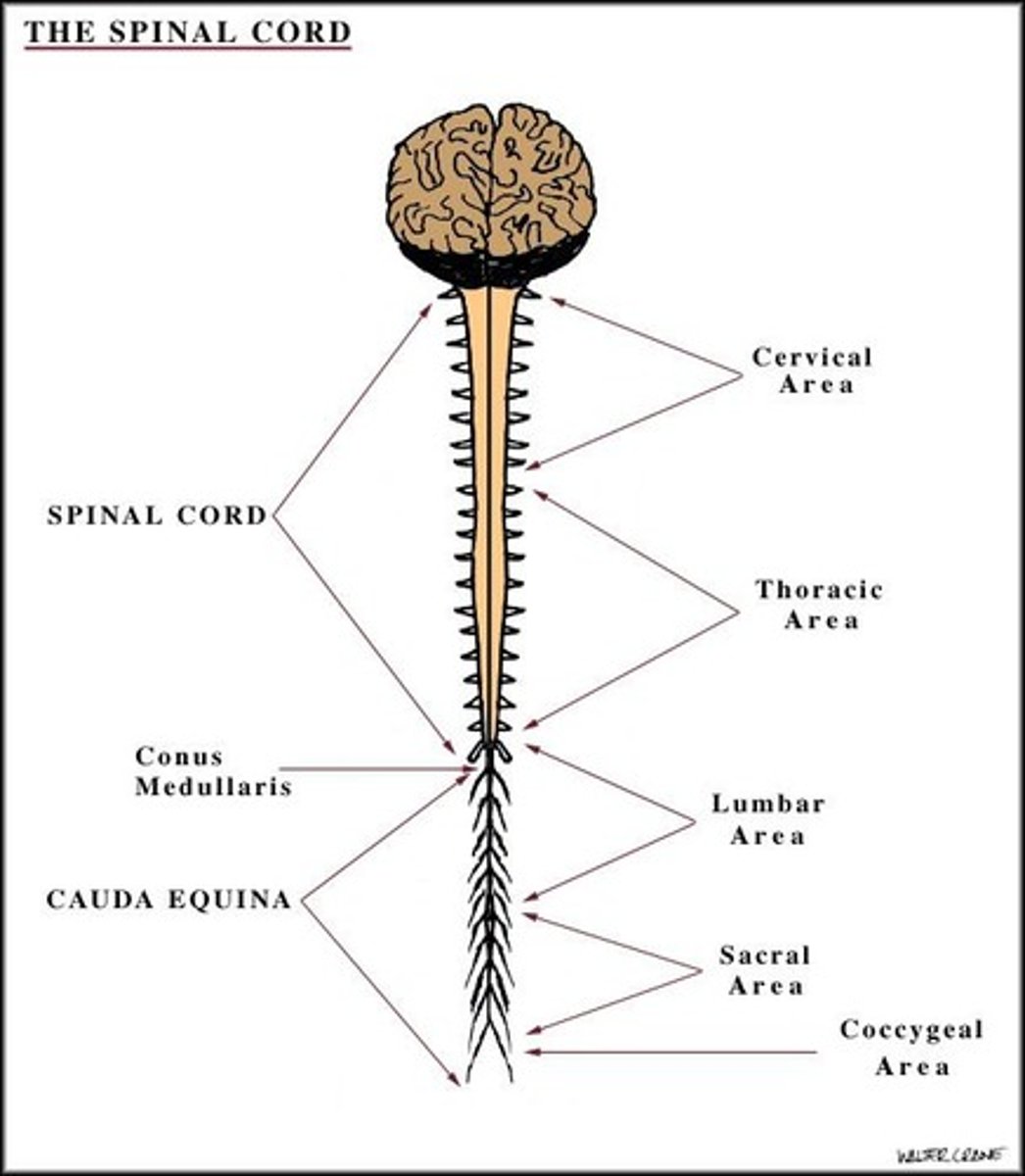
What is the structure and function of the spinal cord?
It provides a connection between the brain and the PNS, running the length of the vertebral column.
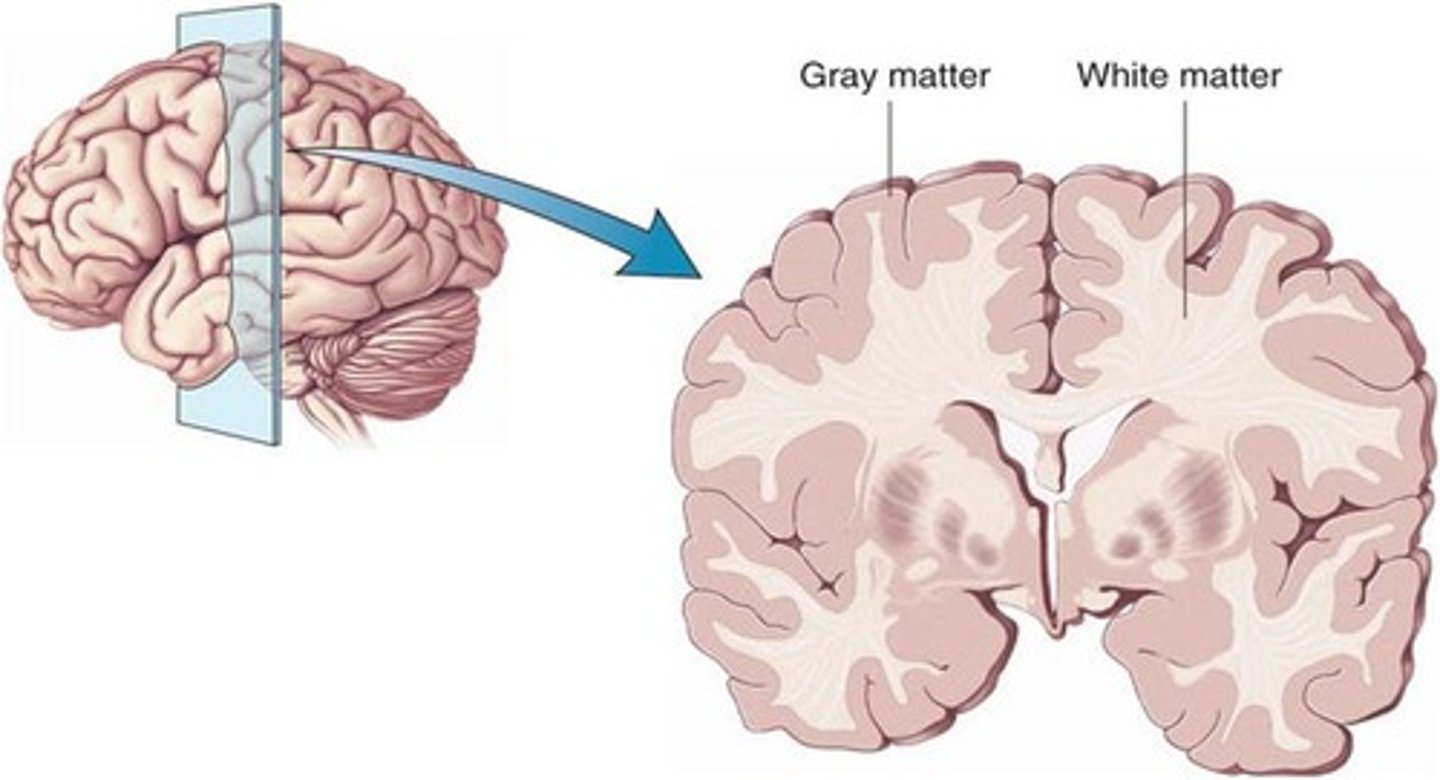
What is gray matter in the brain composed of?
It is comprised of cell bodies of neurons.
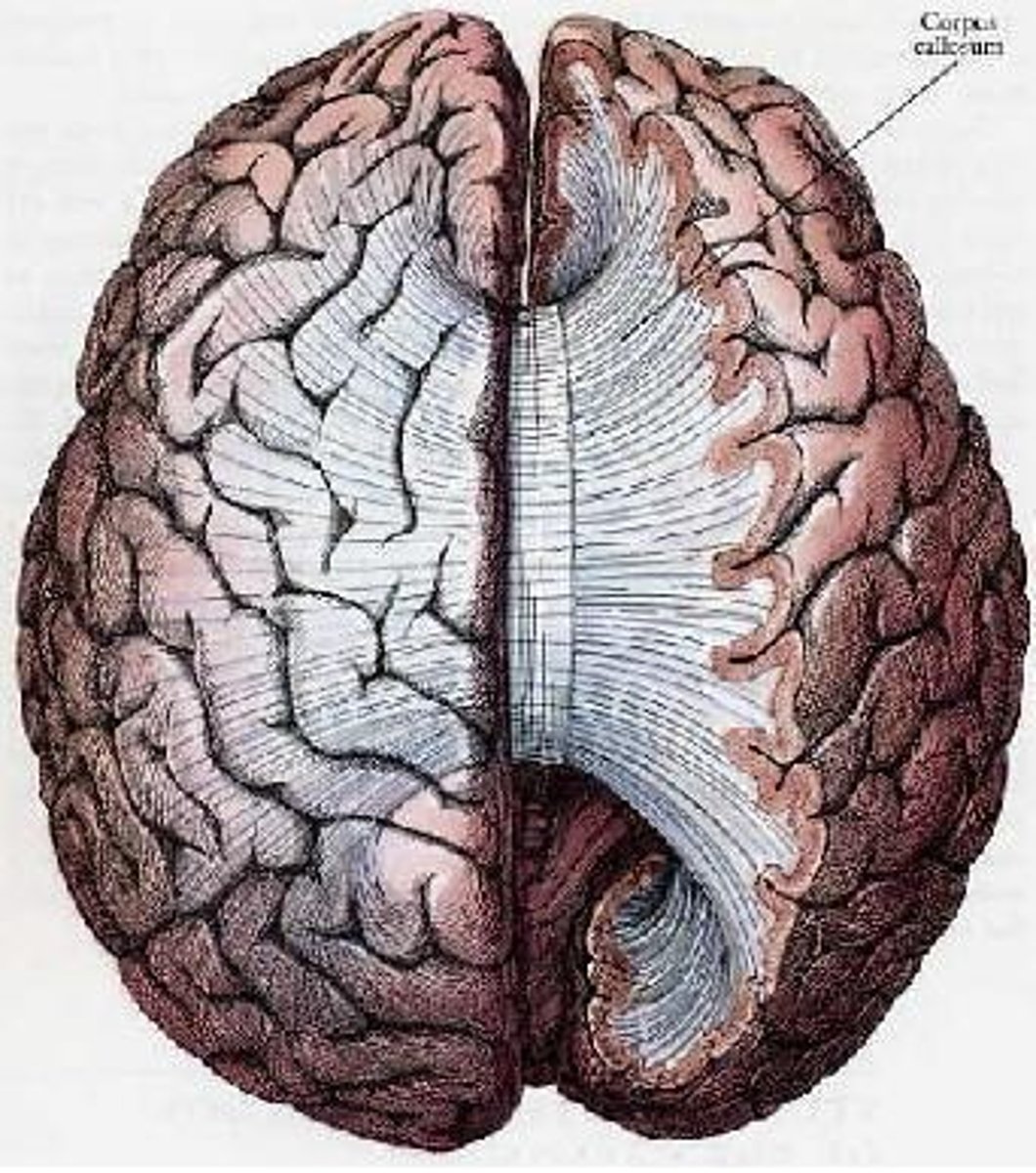
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
It connects the two hemispheres of the brain and facilitates communication between them.
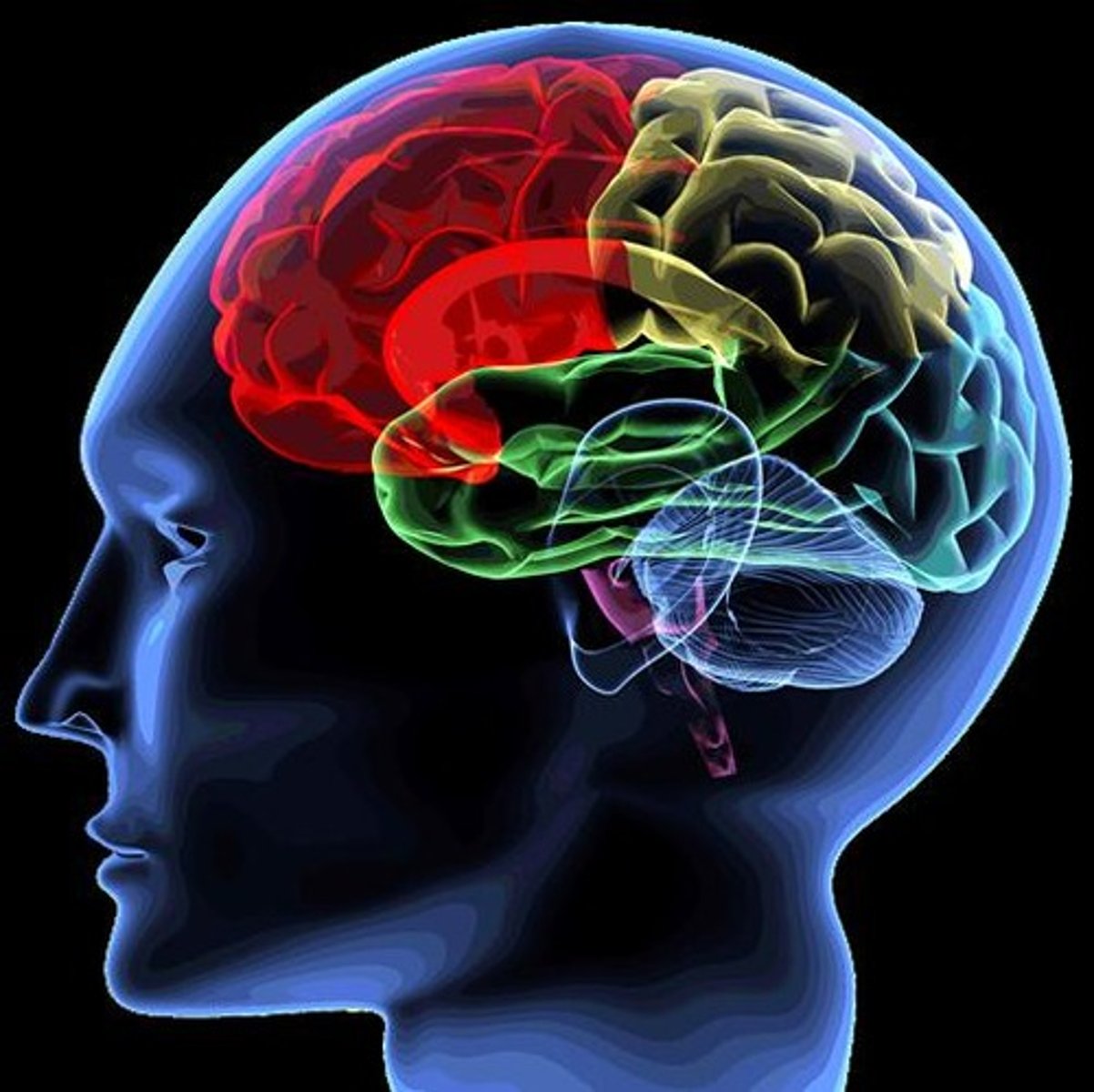
What are the four lobes of the brain and their primary functions?
Parietal (sensory), Frontal (motor), Occipital (vision), Temporal (auditory).
What is the homunculus in relation to the brain?
It represents the motor or sensory locations along the brain, mapping body functions to brain areas.
How many cranial nerves are there, and what is their significance?
There are 12 paired cranial nerves, critical for sensory and movement information, including speech production.
What is the function of the Vagus nerve (CN-X)?
It loops around the aorta and supports movement of the cricothyroid muscle, crucial for vocal fold control.
What is the difference between feedback and feedforward in neuro communication?
Feedback returns output as input to influence future output; feedforward allows prediction of upcoming speech.
What is the McGurk effect?
It is a perceptual phenomenon where visual information influences auditory perception, leading to different interpretations.
What are the steps involved in the speech production process?
1. Cognitive thought is created and language applied; 2. Signals are generated and filtered; 3. Signals sent to cranial nerves; 4. Muscles receive timing and position info; 5. Sensory feedback allows for accuracy checks.
What is aphasia in the context of speech?
It involves linguistic-symbolic planning, organizing linguistic processes according to language rules.
What is apraxia of speech?
It is the transformation of abstract phonological representations into a code readable by the motor speech system, involving motor planning.
What does the limbic system control?
It controls basic emotions such as fear, pleasure, and drives like hunger and care for offspring.
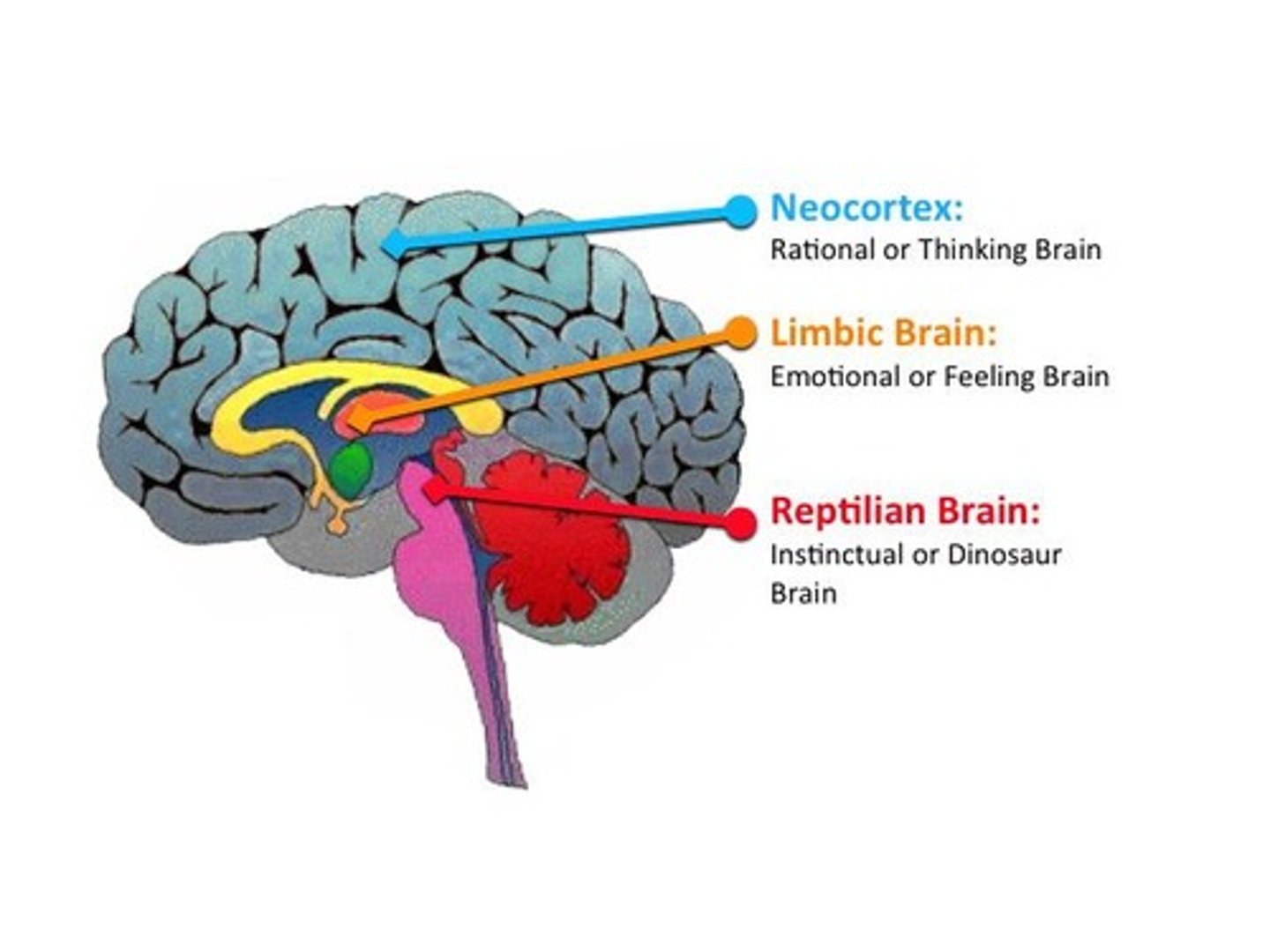
What is the function of the reptilian layer of the brain?
It controls vital non-voluntary functions and regulates voluntary movements for smooth execution.
What is the neocortex responsible for?
It is responsible for higher mental functions like speech, language, and cognition.
What is the significance of the cerebral cortex?
It covers the cerebral hemispheres and is involved in processing sensory and motor information.