Comprehensive Phylogeny, Microbial Diversity, and Eukaryote Evolution
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
What is a phylogeny?
A figure that shows the ancestor-descendant relationships among a group of organisms.
What do nodes represent in a phylogenetic tree?
Nodes represent the splitting events where lineages diverge.
What is a monophyletic group?
A group consisting of a most recent common ancestor (MRCA) and all its descendants.
What distinguishes a paraphyletic group?
It includes the MRCA but excludes one or more descendants.
What is a polyphyletic group?
A group that combines organisms without regard to common ancestry, often formed for convenience.
What is a synapomorphy?
A shared, derived character that is passed down from a common ancestor and distinguishes a group of organisms
What is the difference between homology and homoplasy?
Homology is similarity due to common ancestry, while homoplasy is similarity due to convergent evolution.
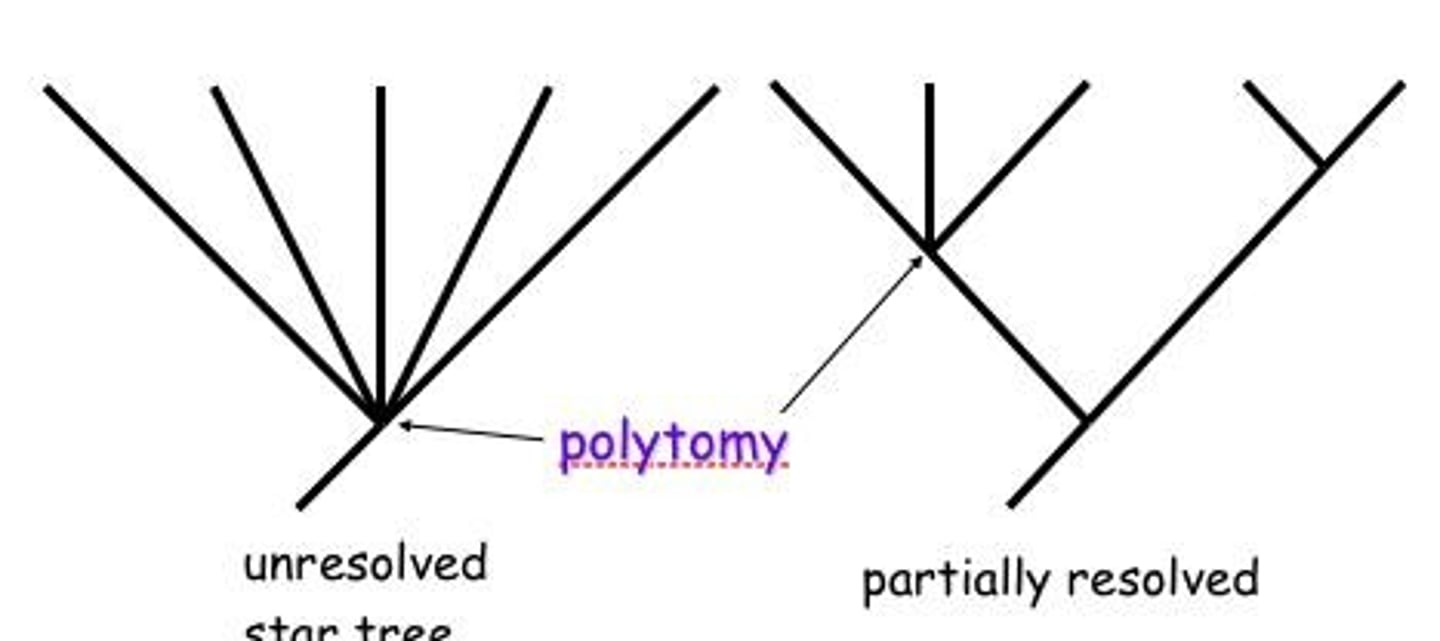
What are polytomies in phylogenetics?
Branches in a phylogenetic tree that indicate uncertainty in the branching pattern.
What is a character in the context of phylogenetics?
A heritable feature of an organism, also known as a character trait.
What is a character state?
The form that a character takes; it can be ancestral or derived.
What is divergence in evolutionary terms?
The process by which species change over time.
What is the significance of sister taxa?
Sister taxa are two descendants that split from the same node, indicating close relatedness.
What is the role of outgroups in building phylogenies?
Outgroups are closely related taxa used to root the tree and provide context for the ingroup.
What is the parsimony method in phylogenetics?
A method to build phylogenies by identifying parsimony-informative characters and calculating the minimum number of changes required.
What are the two types of phylogenetic trees based on time representation?
Chronograms (proportional to absolute time) and phylograms (proportional to genetic change).
What is the purpose of using unrooted trees?
To reduce mathematical complexity when building phylogenies.
What does the root branch of a phylogenetic tree represent?
The root branch leads to the MRCA of all descendant taxa on the phylogeny.
What is a basic model of speciation in phylogenetics?
An ancestral lineage splits into exactly two descendants.
What do phylogenetic trees reflect?
The timing of speciation events and evolutionary relationships.
What is the significance of character states being ancestral or derived?
Ancestral states are the same as the ancestor's, while derived states differ, indicating evolutionary changes (independent changes).
What is the importance of collecting data in building phylogenies?
Data from morphology, genetics, and behavior are used to infer the phylogenetic history of organisms.
What are soft polytomies?
Arise from insufficient data.
What is an unrooted tree?
A tree where the location of the root node is not shown and may be unknown, useful for building phylogenies.
What are the properties of unrooted trees?
They do not specify the order of branching and lack a time component, making sister-group relationships indeterminate.
What is parsimony in phylogenetics?
Selecting the tree with the fewest character changes.
What are parsimony-uninformative characters?
Characters that do not provide useful information for phylogenetic analysis, such as invariant characters or those where one taxon differs from the others.
How do you determine the most parsimonious tree?
By summing the number of changes required for each parsimony-informative character across all trees and selecting the tree with the lowest score.
What is the significance of transitions and transversions in DNA data?
Transitions (substitutions between purines) are more common than transversions (substitutions between pyrimidines), affecting phylogenetic likelihood estimates.
What is maximum likelihood in phylogenetics?
A model-based approach that estimates phylogeny by considering the ratio of transitions to transversions in the data.
What is the binomial system in taxonomy?
A system developed in 1753 where species are given compound names consisting of the genus and specific epithet, italicized or underlined.
What is the problem with polyphyletic groups?
They cannot be defined by features resulting from common ancestry, leading to misleading classifications.
What is the Great Plate Count Anomaly?
The phenomenon where many more microbial cells are present in an environment than can be grown in pure lab cultures due to their reliance on syntrophic communities.
What does LUCA stand for?
Last Universal Common Ancestor, the common ancestor of all life.
What are universal homologies?
Shared features among all living things that provide evidence for a single origin of life.
What is the Central Dogma of molecular biology?
The process by which DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into protein.
What are the three general morphologies of microbes?
1) Sphere (coccus), 2) Rod (bacillus), 3) Helical (spiral).
What is the role of bacteria in ecosystems?
They are key players in processes such as nitrogen fixation and are predominantly beneficial.
What is the significance of the wobble base in genetic code?
The third position in codons is more likely to change due to redundancy in the genetic code.
What is the International Whaling Commission's stance on commercial whaling?
They banned commercial whaling in 1986, but some countries continue to hunt whales for 'scientific' purposes.
What was discovered about giraffes through recent genetic studies?
Giraffes were found to consist of at least four distinct species, contrary to previous beliefs of a single species.
What is the importance of identifying parsimony-informative characters?
They are essential for accurately reconstructing phylogenetic trees by indicating where evolutionary changes have occurred.
What is the role of the outgroup in rooting a phylogenetic tree?
The outgroup helps to determine the direction of evolutionary changes and establish the root of the tree.
What is the biological meaning of a 'step' in DNA nucleotide data?
A character state change, such as the substitution of one nucleotide for another at a specific site in a DNA sequence.
What is the significance of synapomorphies in taxonomy?
They are features that originated in a common ancestor and define monophyletic groups, making classifications more meaningful.
What are the three domains of life according to Woese and Fox?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
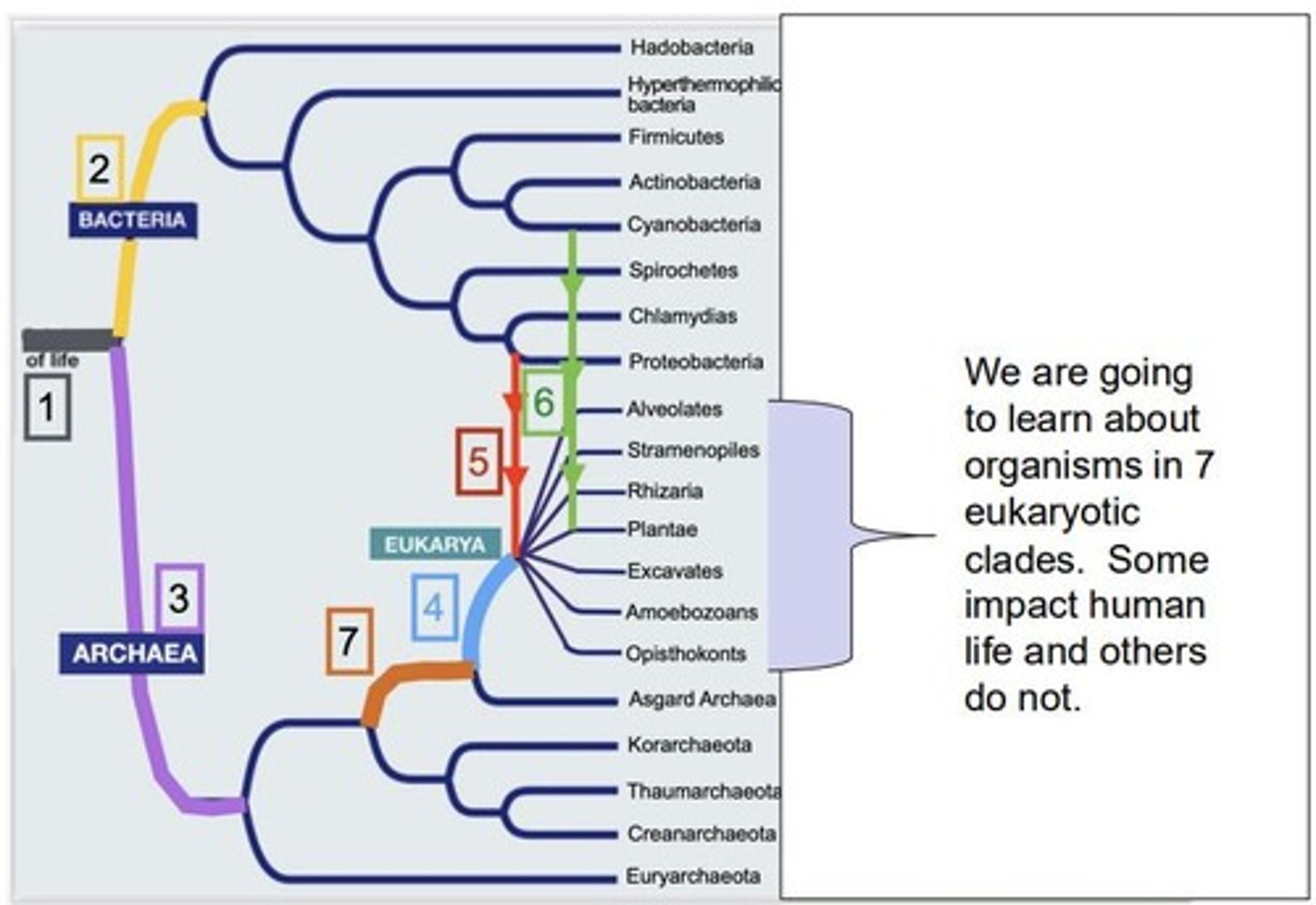
What method allows for the study of organisms without pure cultures?
Culture-independent DNA studies
What is a significant feature of Eukarya?
Eukarya have a nucleus and linear DNA.
What distinguishes Bacteria from Archaea in terms of cell wall composition?
Only Bacteria have peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
What type of DNA do Bacteria possess?
Circular DNA
What is the role of CRISPR-Cas 9 in Bacteria and Archaea?
It acts as a defensive system that protects cells from infection by adapting and disrupting specific DNA.
What is quorum sensing?
A cell-cell communication process that allows bacteria and archaea to share information about cell density and adjust gene expression.
What are extremophiles?
Organisms, often Archaea, that thrive in extreme environments.
What is lateral gene transfer (LGT)?
The process by which bacteria and archaea exchange genetic material across lineages.
What are the three mechanisms of lateral gene transfer?
Conjugation, transformation, and transduction.
What is the significance of Loki's Castle in microbial studies?
It is known for its diversity of extremophiles and has contributed to the discovery of the Lokiarchaeota group of Archaea.
What is the difference between autotrophy and heterotrophy?
Autotrophy refers to organisms that produce their own food, while heterotrophy refers to organisms that consume other organisms for nutrition.
What is the primary concern regarding antibiotics today?
We are facing an antibiotic crisis with very few new antibiotics being developed.
What is the role of plasmids in bacteria?
Plasmids are small, circular chromosomes distinct from the main chromosome that can carry additional genes.
What is the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer, while Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer and an outer membrane.

What is the definition of aerobes?
Organisms that require oxygen for their metabolism.
What is the main characteristic of viruses?
Viruses are intracellular parasites that require a host to replicate.
What is the significance of positive-sense RNA in viruses?
Positive-sense RNA can be directly translated by the host cell's ribosome.
What is the function of autoinducers in quorum sensing?
Autoinducers are chemical signals that bacteria and archaea use to communicate and coordinate their behavior based on population density.
What is the relationship between lateral gene transfer and sexual reproduction?
Lateral gene transfer creates new genetic combinations without reproduction, typically involving only small parts of the genome.
What is the role of the microbiome in an organism?
An organism's phenotype can be influenced by its microbiome.
What is the importance of studying environmental samples in microbial research?
It allows for the discovery of organisms that are not represented in laboratory cultures.
What is the main metabolic limitation of eukaryotes compared to bacteria and archaea?
Eukaryotes are metabolically limited compared to the diverse nutritional strategies of bacteria and archaea.
What is the significance of the term 'trophy' in microbial metabolism?
It refers to how organisms obtain nutrition, derived from the Greek word for nourishment.
What type of membrane lipids are found in Bacteria and Eukarya?
Ester-linked membrane lipids.
Which domains of life contain ribosomes?
All three: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
What type of lipid structure is unique to Archaea?
Lipid monolayer.
What structural component is found only in Bacteria?
Peptidoglycan.
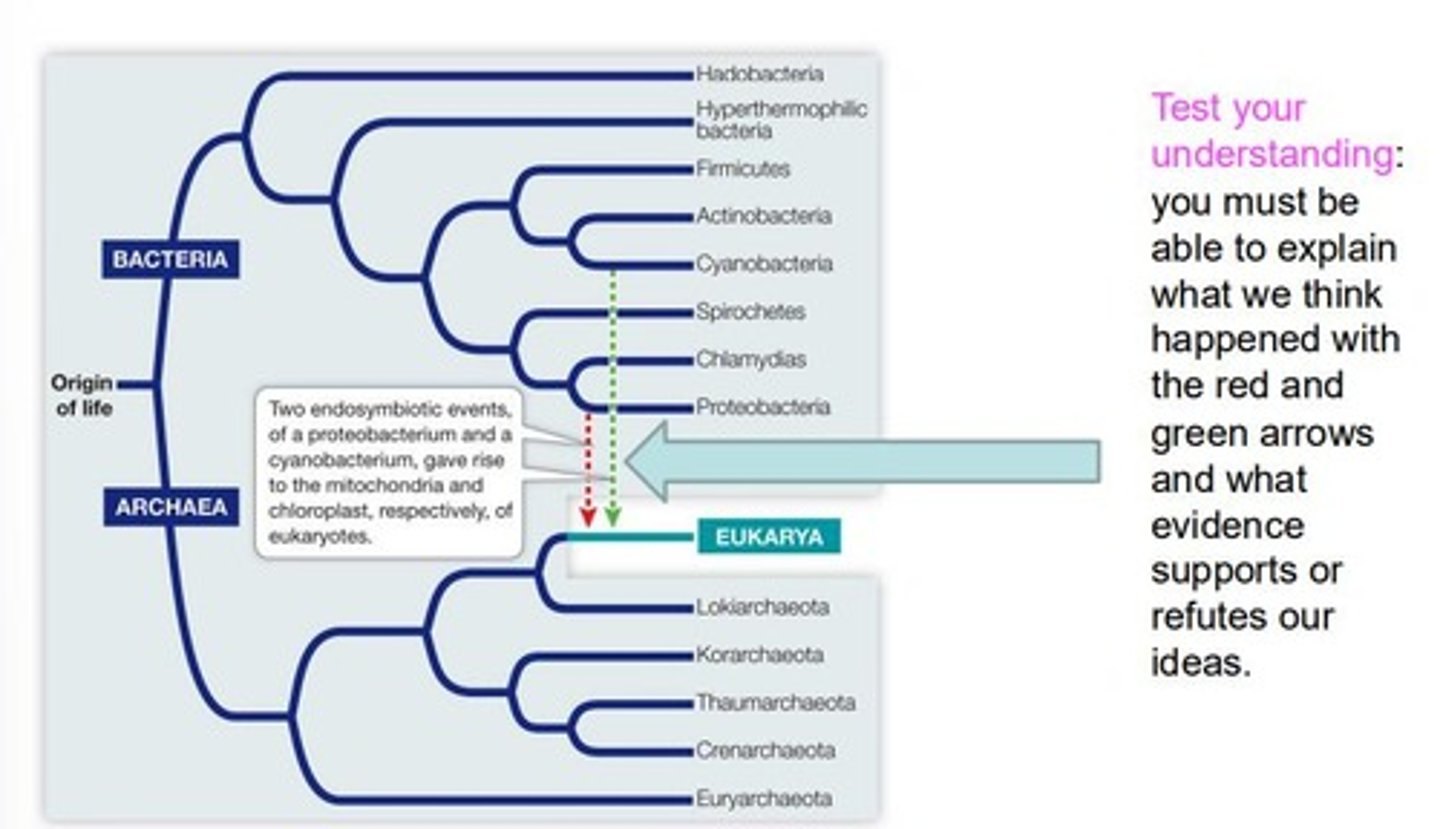
What is a key outcome of lateral gene transfer?
It results in genetically recombinant offspring.
What type of taxon is formed when birds are excluded from the Reptilia phylogeny?
Paraphyletic.
How are tuataras related to lizards and snakes?
Tuataras are equally related to both.
How many root placements are possible on an unrooted tree with 12 taxa?
12.
At which point in the central dogma is RNA translated?
At point D.
If Kim Bergalis contracted HIV from someone other than her dentist, what would be expected?
Patient A would group with LC.
What happens to spacer DNA in the CRISPR system upon infection?
It is transcribed into CRISPR RNA.
What are the two outcomes of the CRISPR process?
Recombination and lateral gene transfer.
What was the composition of Earth's atmosphere when life first appeared?
Oxygen was not part of the atmosphere.
When did life on Earth first appear?
Approximately 3.8 billion years ago.
What process occurred before the existence of plants?
Photosynthesis.
What pigment do algae contain for photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll A.
What is the role of photosynthesis in carbon fixation?
It stores atmospheric carbon (CO2) in carbohydrates like glucose.
What do green and purple sulfur bacteria use as electron donors?
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S).
What is produced when water is used as the electron donor in photosynthesis?
Oxygen.
What evidence supports early oxygen production?
The presence of grey and red bands (iron oxide and jasper) in rock layers from 2.25 billion years ago.
What is the effect of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells?
They can cause genetic degeneration and physiological dysfunction, leading to cell death.
What is the primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
It acts as the terminal electron acceptor.
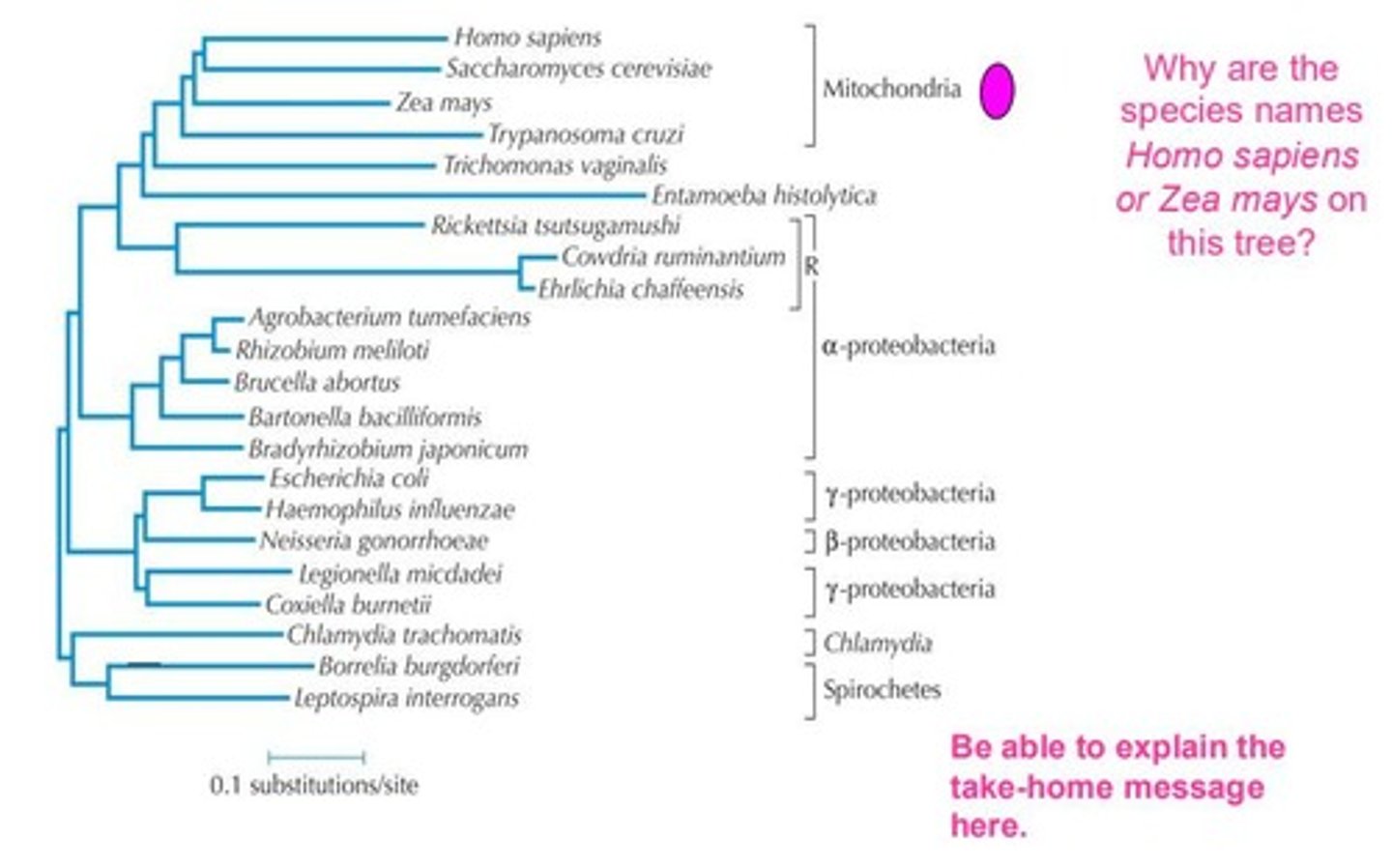
Where did the first eukaryote likely originate?
From a merger between a member of Loki-archaeota and an alpha-proteobacterium.
What is the significance of the actin cytoskeleton in cell engulfment?
It allows the cell membrane to extend and surround another cell.
What theory did Lynn Margulis develop regarding cell evolution?
The serial endosymbiosis theory.
What process allows cells to engulf other cells?
Endocytosis
What organelles are required for engulfing and digesting cells?
Lysosomes
Which archaeon is thought to have contributed to the first eukaryote?
Loki-archaeota
What are the two possible explanations for the origin of eukaryotic cells without mitochondria?
They either originated from a merger with an archaeon or evolved to live in anaerobic environments.
What do hydrogenosomes use as an electron acceptor instead of oxygen?
Pyruvate
Why are hydrogenosomes considered a good drug target?
Their metabolic pathways are distinct from those in mitochondria, reducing effects on host cells.
What unique characteristics do mitochondria and chloroplasts share?
They have double membranes, contain haploid circular DNA, and are thought to be descendants of prokaryotes.