nature and variety of living organism - beginning to food tests
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
movement
respiration
sensitivity
control
growth
reproduction
excretion
nutrition
what does MRS C GREN stand for?
complex and include all animal and plant cells
what are eukaryotic cells?
smaller and simpler like bacteria
what are prokaryotic cells?
nucleas
cell membrane
cytoplasm
mitochondria
ribosomes
what does an animal cell have?
chloroplasts
cell wall
vacuole
and all other animal cells ones
what does a plant cell have?
an organelle containing the genetic material that control’s cell activity
surrounded by its own membrane
what is the function of a nucleas?
this membrane forms the outer surface of the cells and controls the substances that go in and out of the cell
what is the function of the cell membrane?
a gel like substance where most of the cell’s chemical reactions happen.
contain enzymes with control these reactions.
what is the function of cytoplasm?
small organelles where most of the reactions for aerobic respiration happen
what is the function for mitochondria?
small organelles where proteins are made in the cell
what is the function for ribosomes?
the site where photosyntheses happens, makes food for the plants.
chloroplasts contains a green substance called chlorophyll
what is the function for chloroplasts?
a rigid structure made of cellulose, surrounds cell membrane
supports the cell and strengthens it
what is the function for cell wall?
a large organelle that contains cell sap
( a weak solution of sugars and salts) helps support cell
what is the function for vacuole?
a group of similar cells that work together to carry out a particular function.
what is a tissue?
a group of different tissues that work together to perform a function
what is an organ?
organs work together to form organ systems. each system has a different jobs.
what are organs?
they’re specialised to carry out a particular function. so their structures can vary.
different structures for different functions.
why are cells specialised?
can turn into any type of cell
what can embryonic stem cells do?
a process by which a cell changes to become specialised for its Job.
what is cell differentiation?
they develop different organelles and turn into different types of cells.
this allows them to carry out specific functions.
what happens as cells change?
also known as stem cells, can divide to produce lots more undifferentiated cell.s
differentiate into different types of cell, depending on what instructions they’re given.
what are undifferentiated cells and what can they do?
found in the early human embryo.
they have the potential to turn into ant type of cell.
where are stem cells found?
found in certain places like bone marrow.
they can’t turn into any type of cell, only certain ones like blood cells.
where are stem cells in adults found?
grown in a lab to produce clones and made to differentiate into specialised cells to use in medicine and research.
what happens to stem cells from embryos and bone marrow?
cure many diseases.
stem cells transferred from the bone marrow of a healthy person can replace faulty blood cells in the patient who receive them.
what can stem cells also do?
replace faulty cells in sick people- make insulin producing cells for people with diabetes
nerve cells for people with paralysed by spinal injuries.
what can embryonic stem cells also be used to?
stem cells grown in the lab may become contaminated with a virus which could be passed on to the patient and so make them sicker.
what are the risks of using stem cells in medicine?
they feel that human embryos shouldn’t be used for experiments since each one is a potential human life.
others think that curing existing patients who are suffering is more important than the rights of embryos.
why are some people against stem cell research?
argue that the embryos used in the research are usually unwanted ones from fertility clinics, if they weren’t used for research maybe destroyed.
what do they argue about?
plants
animal
fungi
what are examples of eukaryotic organisms?
multicellular
have chloroplasts- photosynthesis
cells have cell walls- made out of cellulose
store carbohydrates as SUCROSE OR STARCH
e.g:
cereals (maize)
herbaceous legumes (peas and beans)
description for plants and e.gs?
multicellular
no chloroplasts- no photosynthesis
no cell wall
nervous coordination- respond to rapid changes of environment
move around from place to place
store carbohydrates as GLYCOGEN
e.gs:
mammals (humans)
insects ( houseflies + mosquitoes)
description for animals and e.gs?
some are single celled
others have a body mycelium made out of hyphae- thread like structure- contains many nuclei
no photosynthesis
cell walls of chitin
feed by saprotrophic nutrition- secrete enzymes absorb nutrition
store carbohydrates as GLYCOGEN
e.gs:
yeast single celled
mucor- multicellular and has a mycelium and hyphae
description for fungi and e.gs?
single celled microscopic
some have chloroplasts
some like animal cell
some like plant cell
e.gs:
chlorella (plant)
amoeba (animal)
description for protoctists and e.gs?
bacteria
what is an example of prokaryotic cells?
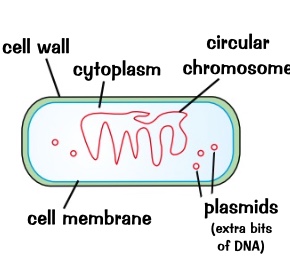
single celled
microscopic
no nucleas
circular chromosome of dna
some can photosynthesis
most bacteria feed off other organisms- both living and dead
e.gs:
lactobacillus bulgaricus ( milk go sour and turn into yoghurt rod shaped)
pneumococcus ( round)
description for bacteria and e.gs?
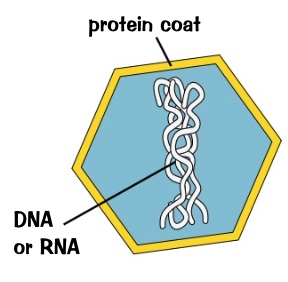
particles smaller than bacteria
only reproduce inside living cells
infects all type of other living organisms
no cellular structure
protein coat around genetic materials
e.g’s:
tobacco mosaic virus- makes the leaves of tobacco plants discoloured stop them form making chloroplasts
HIV
covid
description for viruses and e.gs?
organisms that cause diseases
what are pathogens?
fungi protoctist and bacteria
what are examples of living pathogens?
viruses
what are examples of non living pathogens
plasmodium
what protoctist causes malaria?
pneumococcus
what bacterium causes pneumonia
influenza virus
HIV
what virus causes the flu
what virus cause aids
enzymes are biological catalysts produced by living things. they speed up the useful chemical reactions in the body (metabolic reactions)
what are enzymes?
a substance which increases the speed of the reaction without being changed or used up in the reaction.
what is a catalyst?
a molecule that is changed in a reaction
what is a substrate?
has an active site- the part where a substrate joins on the enzyme
what does every enzyme molecule have?
for an enzyme to work a substrate has to be the correct shape to fit into the active site.
what is the lock and key model?
1) temperature :
temperature increase enzyme and substrate has more energy so it will move about more and more likely to collide and form enzyme-substrate complexes.
if it gets too hot, the enzyme will denature
2) pH.
if too high or too low the ph interferes with the bonds holding the enzyme together. changes the shape of the active site and denatures the enzyme.
optimum temp: 7
what 2 factors affect enzyme function?
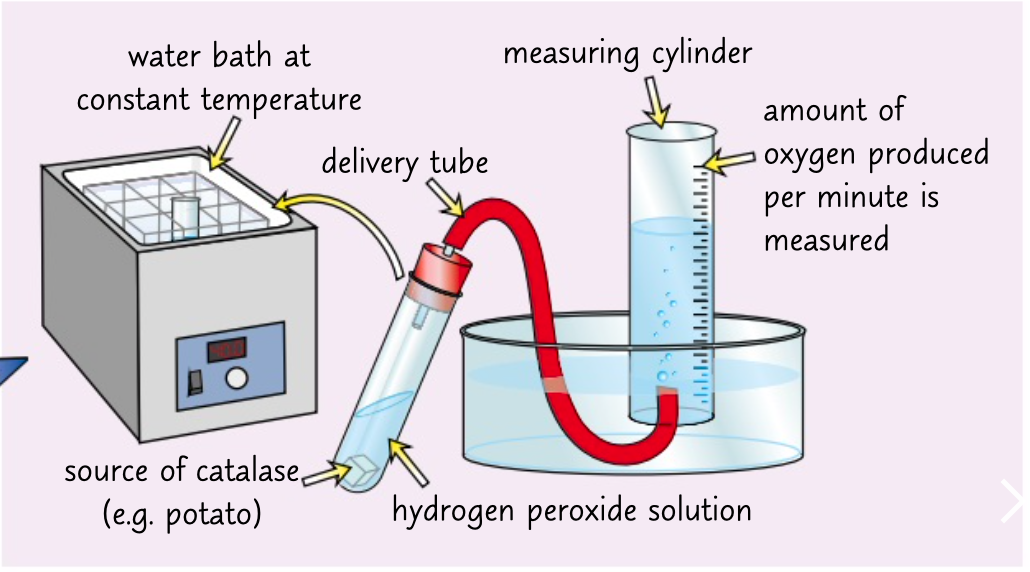
enzyme catalase catalyses breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water to oxygen
collect the oxygen and measure how much is produced in a set time.
use a pipette to add a set amount of hydrogen peroxide to a boiling tube.
put the tube in a water bath at 10 degrees.
add a source of catalyse 1cm3 of potato to the hydrogen peroxide and quickly attach the bung
record how much oxygen is produced in first minute. repeat three times and calculate mean
repeat at different temperature
control any variables to make it a fair test
enzymes hydrogen peroxide practical
to measure how fast a product appears?
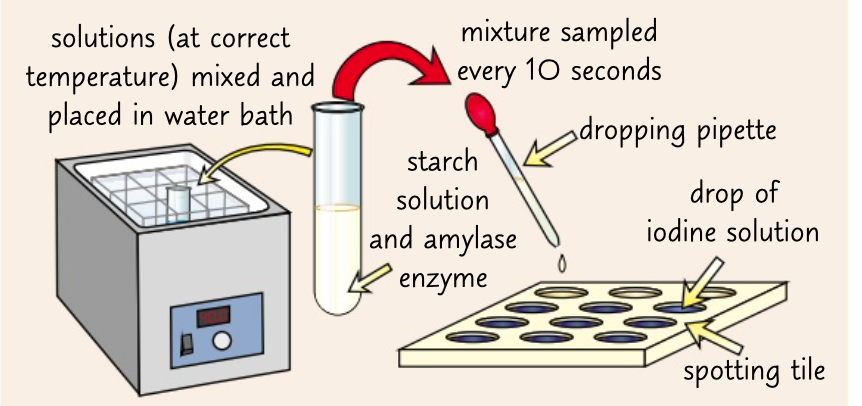
enzyme amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch to maltose
put a drop of iodine solution into each well. every 10 seconds drop a sample of the mixture into a well using a pipette
if it remain brown orange starch it no longer present record total time
repeat with different temp to see how it affects the time taken for starch to be broken down.
enzyme practical to see how fat a substrate disappears?
diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of a lower concentration down a contraption gradient.
what is diffusion?
passive process.
what type of process if diffusion?
glucose, amino acids, water and o2,
big molecule starch and protein
what are examples of small molecules that can pass through the cell membrane ?
osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of a higher water concentration a region of a lower water concentration.
what is osmosis?
will become more concentrated. the solution outside is more dilute so water will move into the cell by osmosis
if a cell is short of water what will happen to the solution?
solution will be more dilute water will be draw out of the cell into the fluid by osmosis
if a cell has lots of water what will happen to the solution?
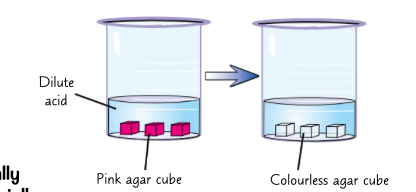
make some agar jelly with phenolphthalein and dilute sodium hydroxide. this will make the jelly pink
put some dilute hydrochloric acid in a beaker. cut out a few cubes from the jelly and put the, in the beaker of acid
cubes will eventually turn colourless as the acid diffuses in agar jelly and neutralises sodium hydroxide
phenolphthalein experiment diffusion?
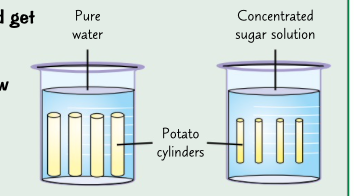
cut up potato into identical cylinder and get some beakers with different sugar solution.
one pure and one very concentrated. others other concentration.
measure the length of cylinder and leave them in beaker.
take them out and measure
if the cylinder has been drawn in water by osmosis they will be longer.
if water has been drawn out they will be shorter
osmosis living system practical
the movement of particles against a concentration gradient from an area of a lower concentration to an area of a higher concentration using energy from respiration.
what is active transport?
used in the digestive system when there is a low concentration of nutrients in the gut but a high concentration of nutrients in the blood
what is active transport used in the digestive system for?
surface area to volume ratio. rate of diffusion osmosis and active transport will be higher in cells with a larger surface area to volume ratio. the smaller the cube the large the surface area
distance- if substance have a short distance to move, then they will move in and out of cells faster
temperature- as the particles in a substance get warmer they have more energy so they move faster. as temperature increases substance move faster
concentration gradient: substances move in and out of cells faster if big difference in concentration.
what are the 4 factors that affect the movement of substances?
contain the elements c,h,o
starch and glycogen are large complex carbohydrates which are made up of many smaller units e.g glucose or maltose molecules joined together in a long chain.
what are carbohydrates?
starch
what does maltose form into?
made up of long chains of amino acids. c,h,o,n
what are proteins?
made up of fatty acids and glycerol
c,h,o
glycerol and fatty acids form lipids
what are lipids?

what is the test for glucose?

what is the test for iodine?

what is the test for proteins?
Add a few drops of ethanol to the food solution. 2 Shake the test tube and leave for one minute. 3 Pour the ethanol into a test tube of water. 4 If the solution turns cloudy, the food contains lipids.
what is the food test for lipids?