RMPRO811: Anatomy Part I and II
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Retention
resistance to vertical displacement away from the bearing surface
Resistance to vertical displacement away from the bearing surface
Retention
Stability
resistance to lateral displacement
Resistance to lateral displacement
Stability
Support
Factors of the bearing surfaces that absorb or resists forces of occlusion
Factors of the bearing surfaces that absorb or resist forces of occlusion
Support
Factors that impact Retention, Stability, and Support
Nature of the Bearing Mucosa
Bone Contours and Retromolar Pad
Muscle Attachments
Saliva
Disease Factors
The Nature of the Bearing Mucosa
-____ vs ___
- degree of ___
attached vs unattached
keratinization
Bone Contours and Retromolar Pad
-___&___ of the alveolar ridge
-presence of ___
-___ patterns
height and contour
tori
resorption
Muscle Attachment
frenum
floor of the mouth, mylohyoid, retromylohyoid space
tongue posture
Saliva
flow rates
palatal glands
posterior palatal seal
effect on retention and comfort of denture
Disease Factors
candida, angular chelitis, epulis fissuratum
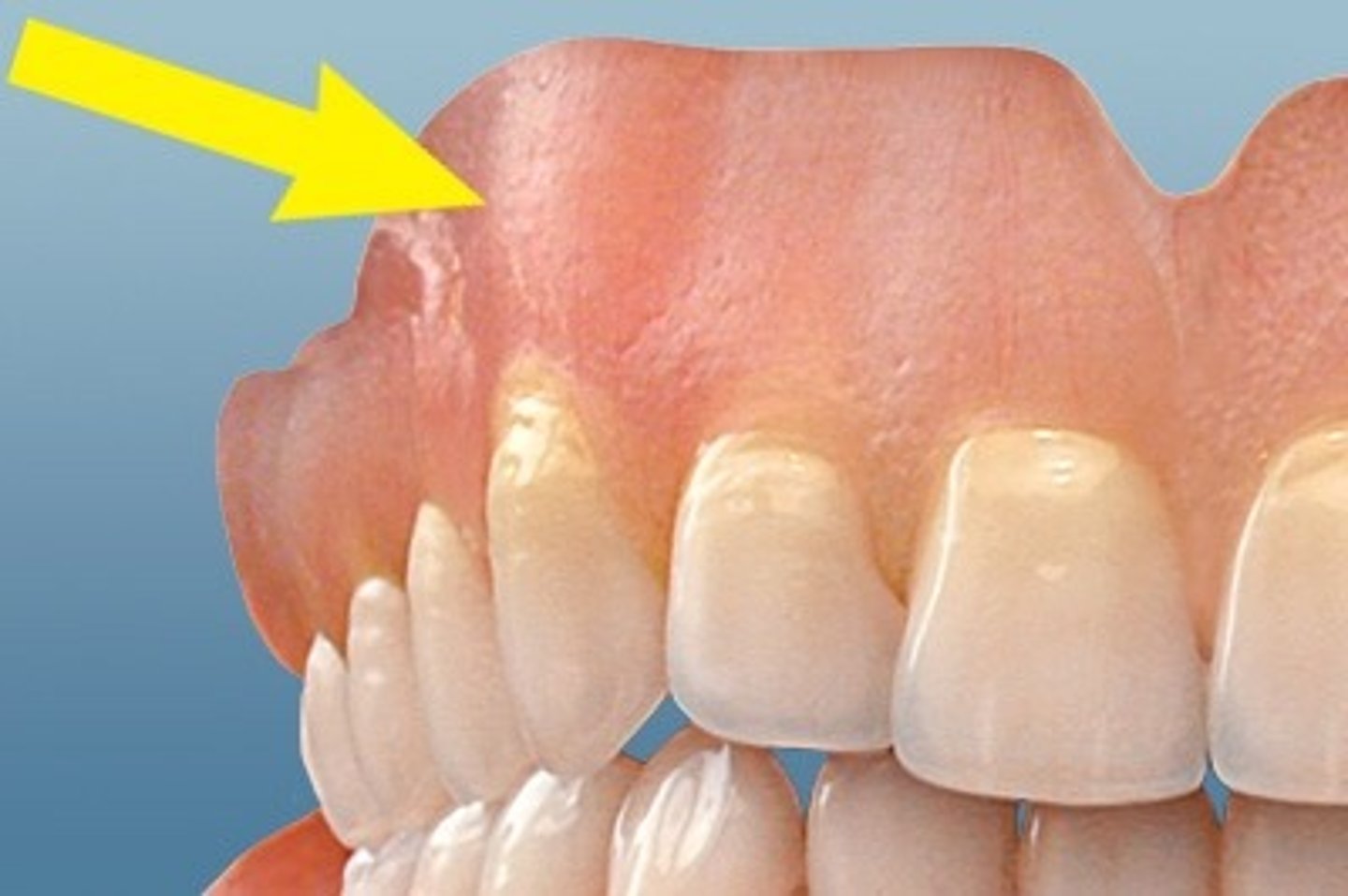
Frenum
folds of mucous membrane and do not contain significant muscle fibers.
Frenum attachments close to the crest of the ridge will _____ denture retention and may require surgical excision.
compromise
What will compromise denture retention and may require a frenectomy?
frenum attachments close to the crest of ridge
Labial Frenum
---
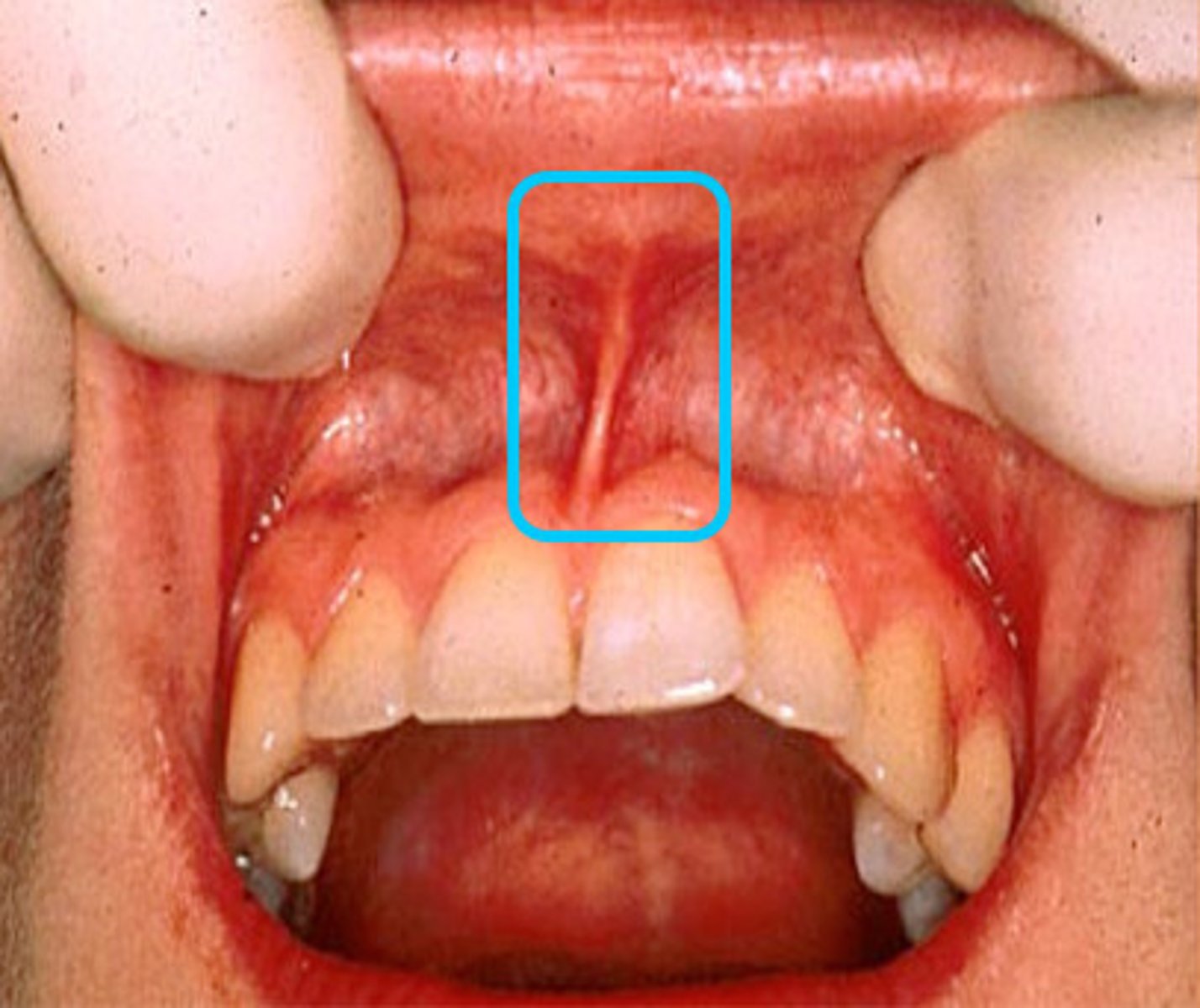
Buccal Vestibule
when the vestibule is properly filled with the denture flange
What greatly enhances stability and retention?
buccal vestibule
Canine Eminence
bony evidence that provides support and presents the denture from rotating and improves denture stability
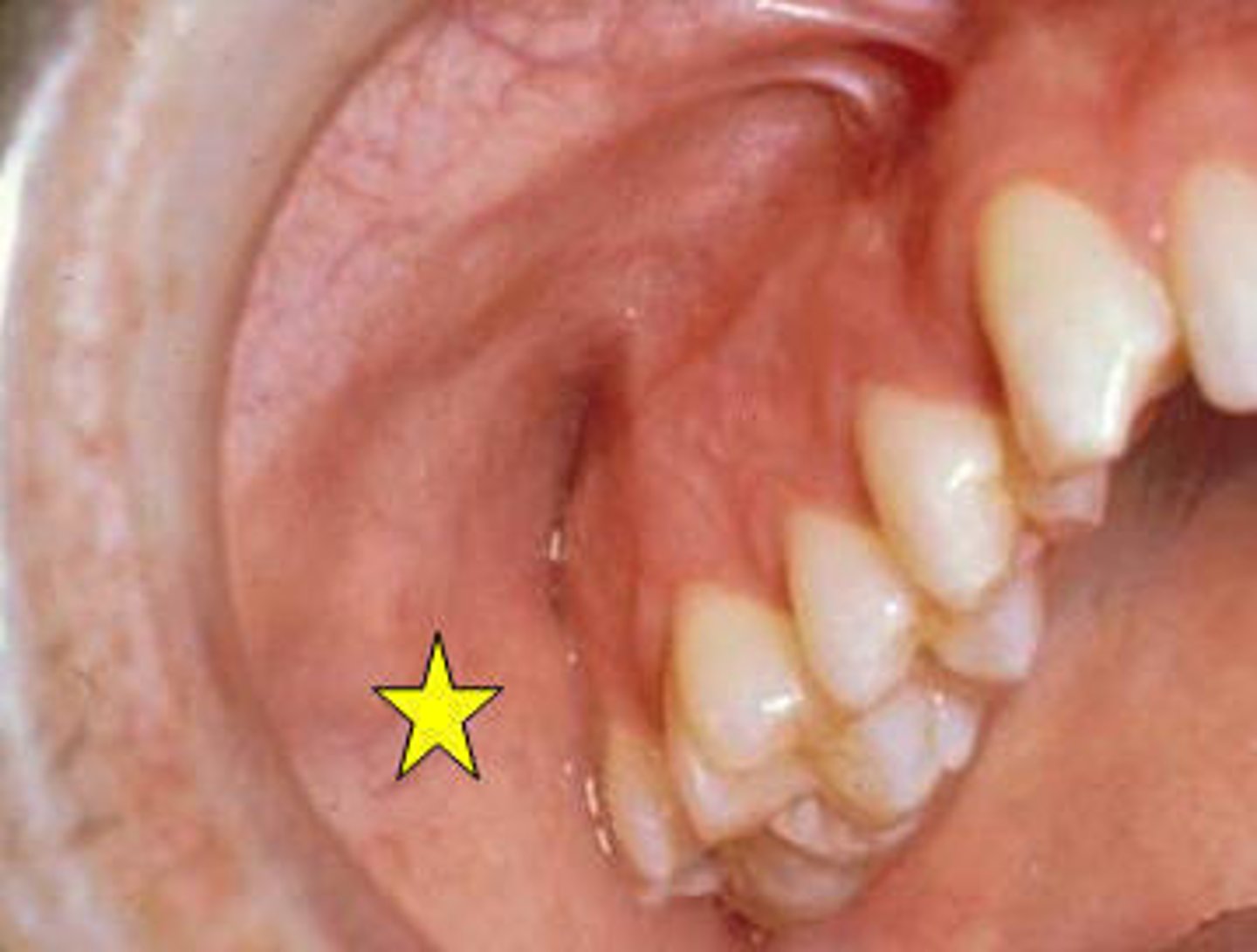
Incisive Papilla
pad of fibrous connective tissue overlying the orifice of the nasopalatine canal.
Pressure in ___ will cause a disruption of blood flow and impingement on the nerve, causing the patient to complain of pain or a burning sensation.
incisive papilla
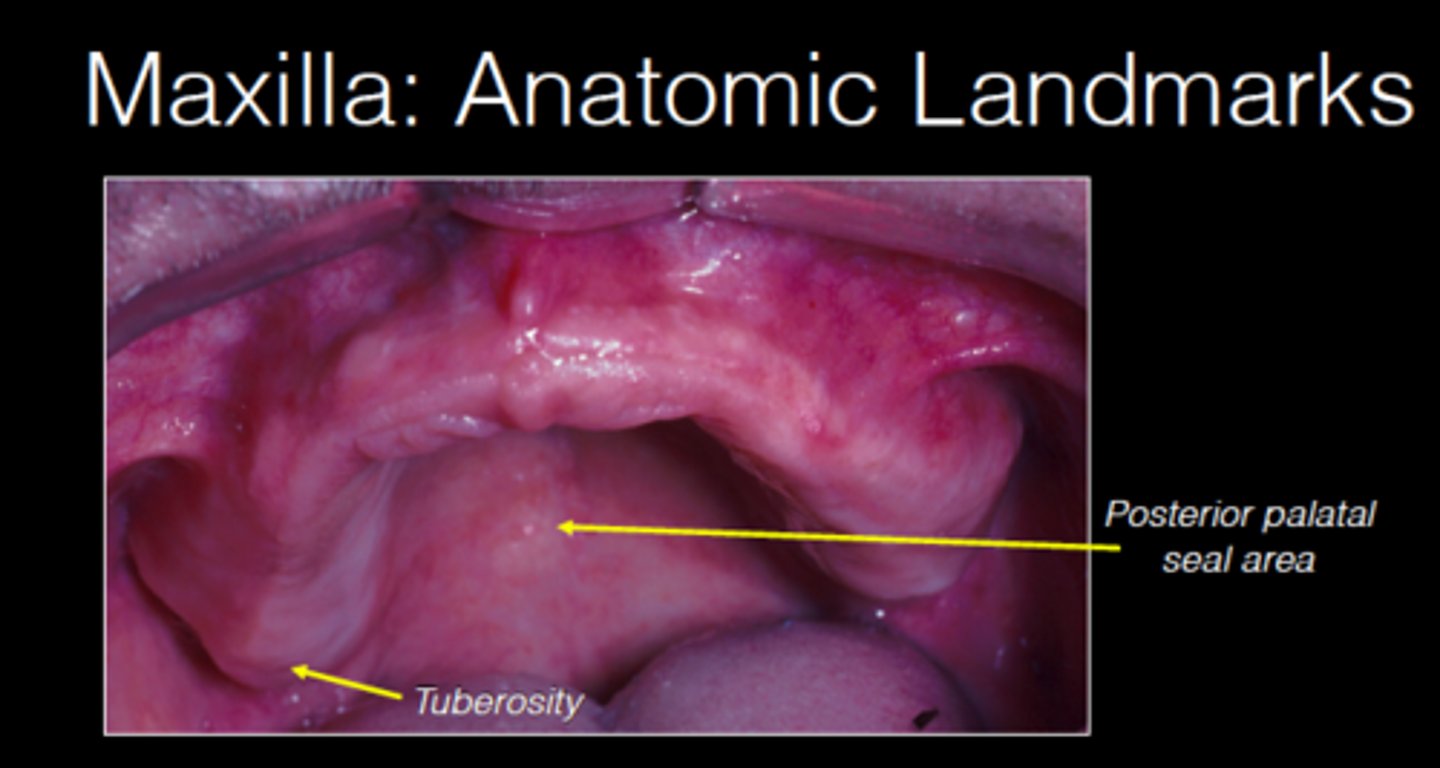
Maxillary and Mandibular Tuberosity
important denture support area.
Provides resistance to horizontal movements of the denture
tuberosity
Posterior Palatal Seal Area
distal to the junction of the hard and soft palate at the vibrating line
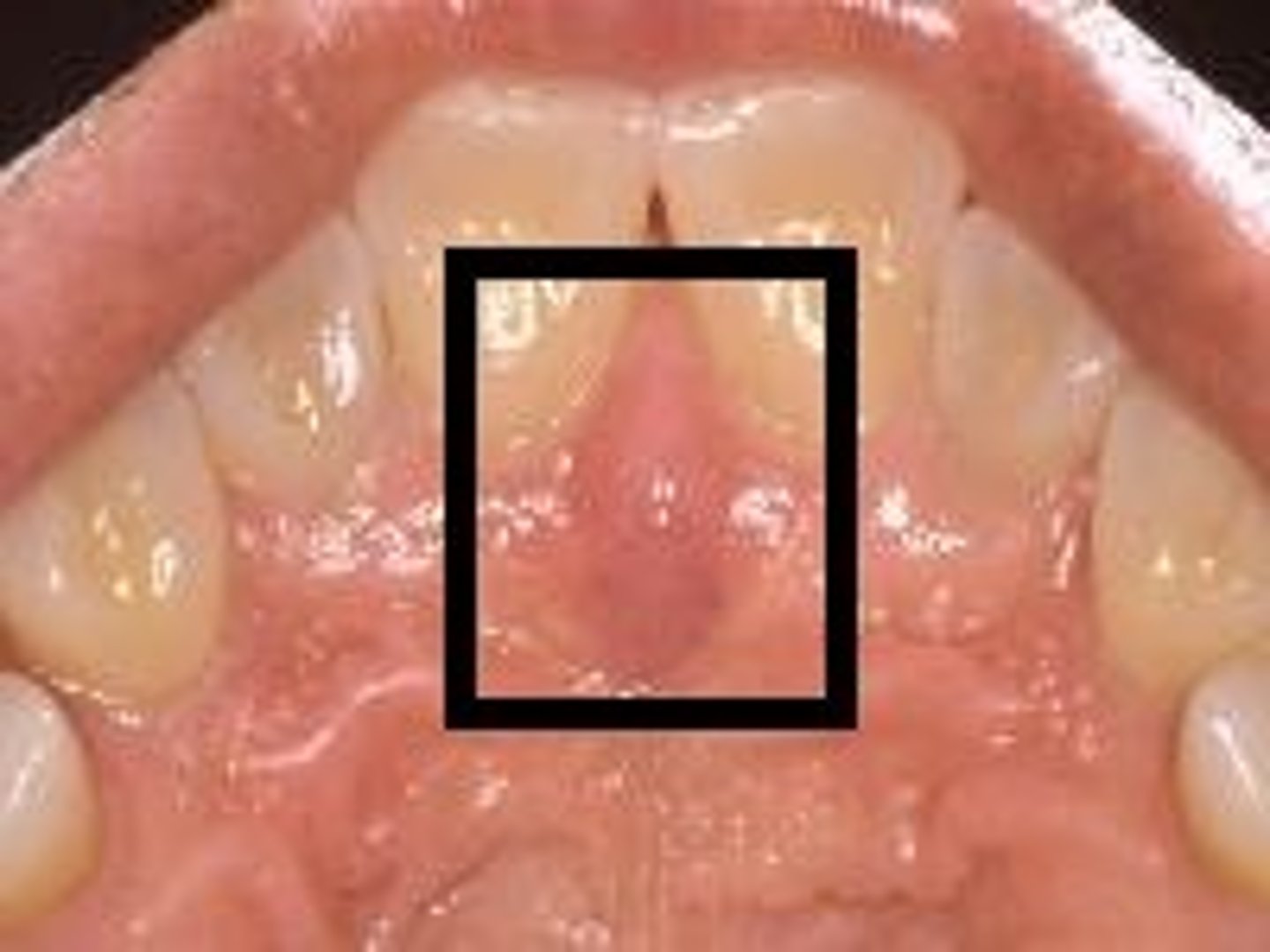
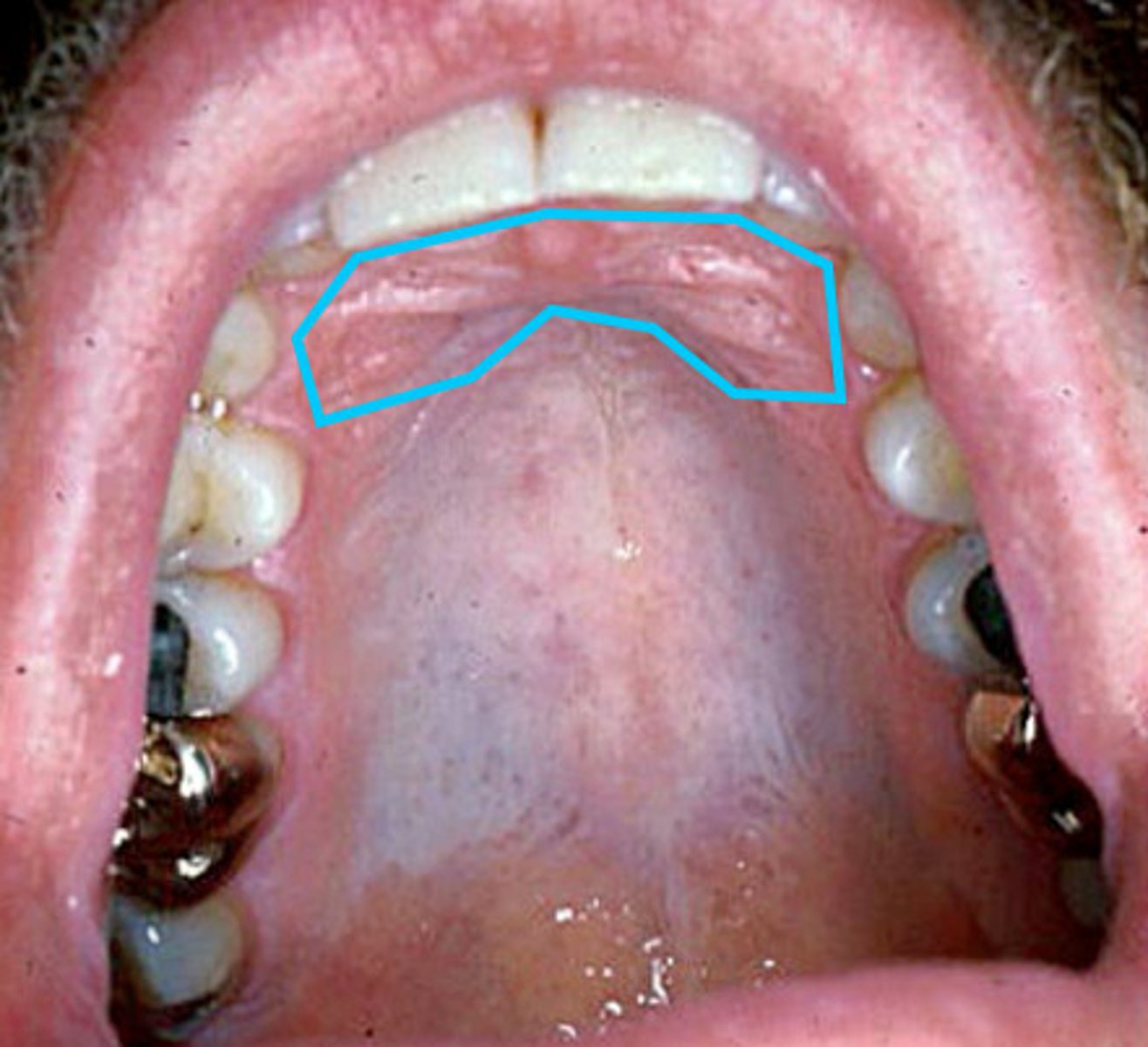
Rugae
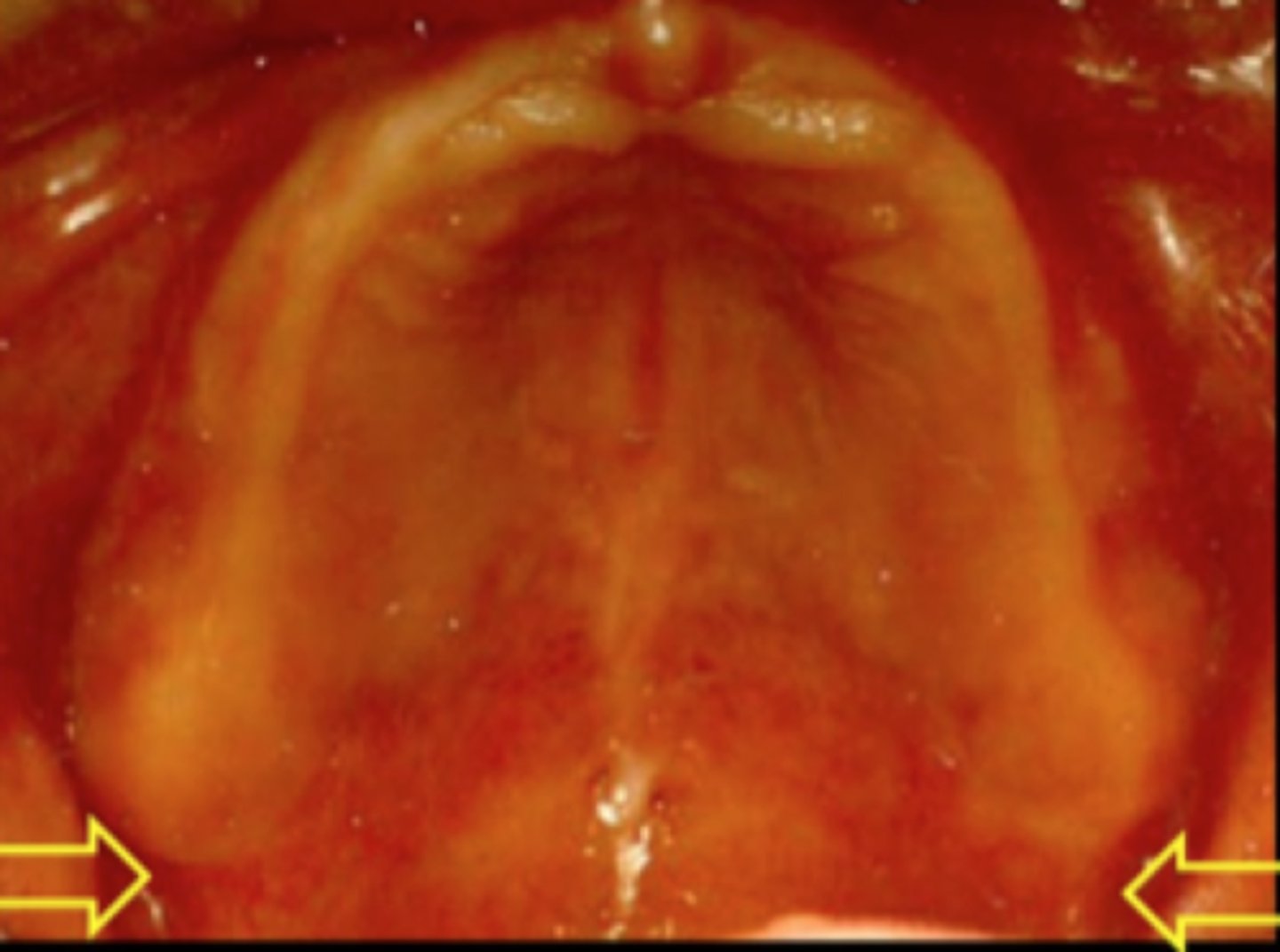
raised area of dense connective tissue in the anterior 1/3 of the palate.
This area resistance anterior displacement of the denture and is a secondary support area for maxillary
Rugae
Hamular Notch
narrow cleft that extends from the tuberosity to the pterygoid hamulus muscles. The pterygomandibular ligament attaches to the pterygoid hamulus which is a thin curved process at the terminal end of the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Capturing ___in an impression is critical to the retention of the maxillary denture.
hamular notch
Coronoid Process
the patient is instructed to open wide, protrude and go into lateral movements.
The width of the distobuccal flange will then be contoured by the anterior border of the coronoid process.
Fovea Palatina
two small pits or depressions in the posterior aspect of the palate, one on each side of the midline, at or near the attachment of the soft palate to the hard palate and slightly anterior to the termination of the denture.
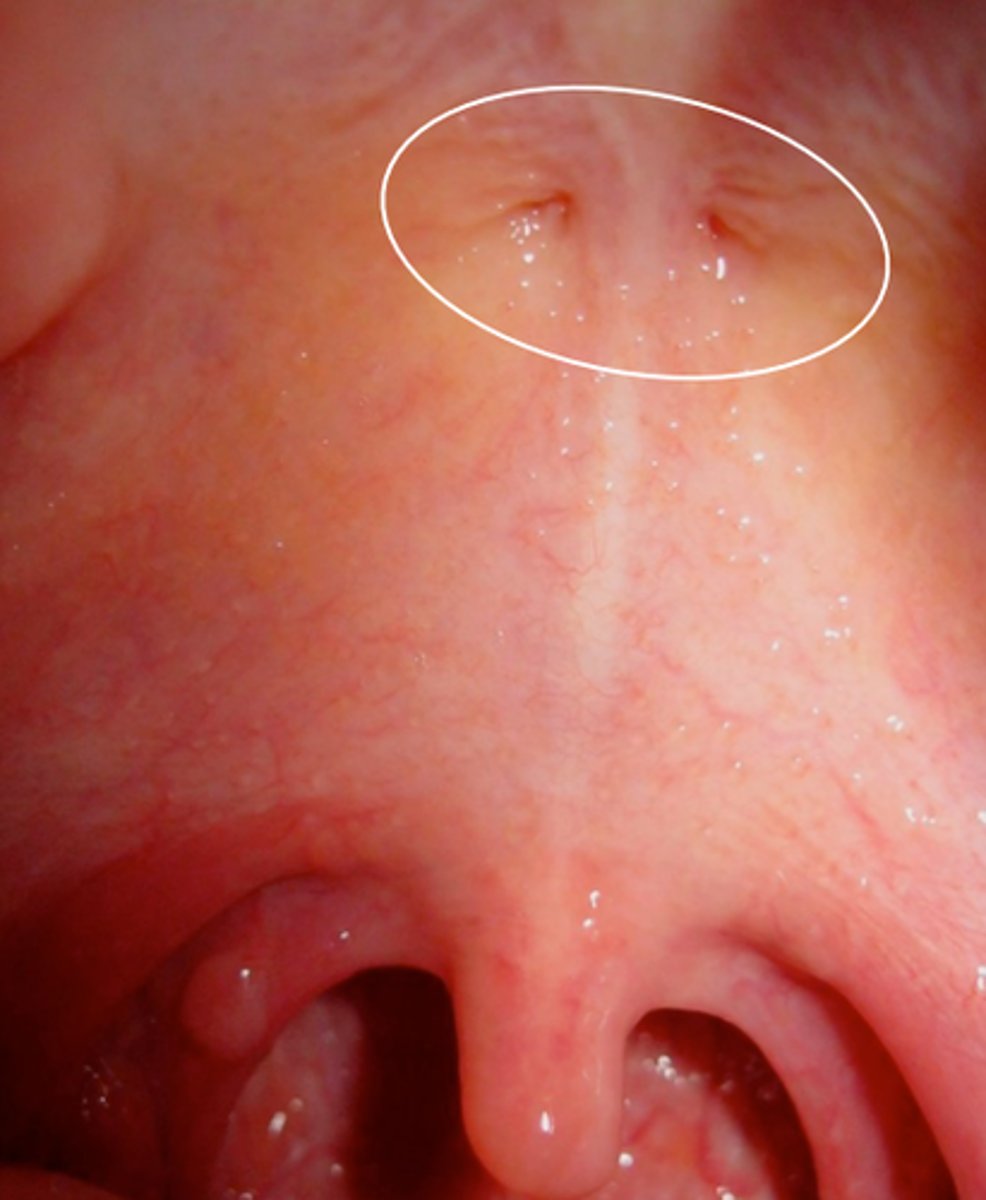
Minor Salivary Glands
located at the posterior 1/3 of the hard palate the tissue is very glandular and displaceable.
Zygomatico-Alveolar Crest
the crest has been likened to the buccal shelf in the mandible as a stress bearing area.
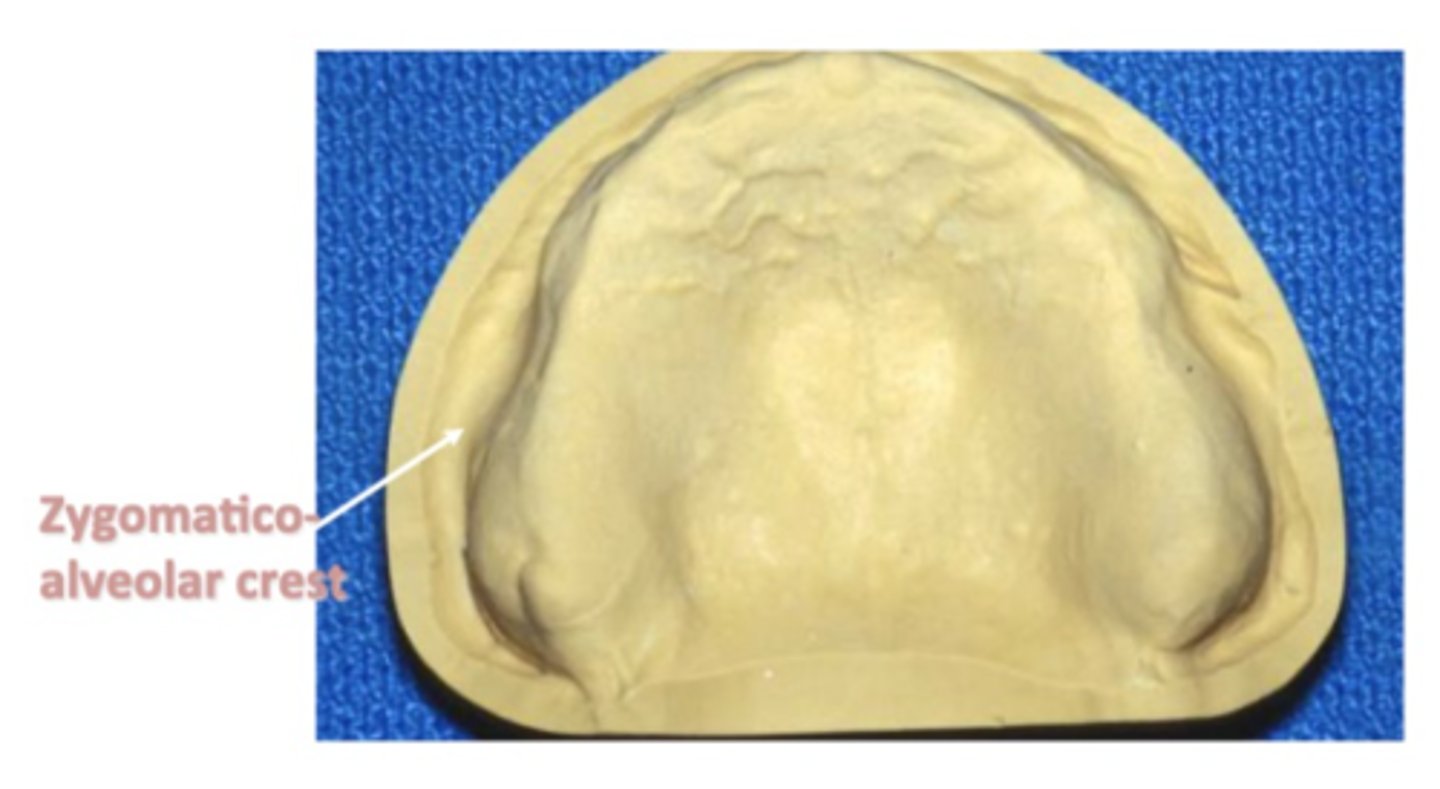
What is very thin and not good for stress bearing (poorly keratinized mucosa)
Zygomatico-alveolar crest
Hard Palate
consists of the two horizontal palatine processes and appears to resist resorption.
What is the primary support area for the maxillary denture?
Hard Palate
Midline Palatal Suture
extends from the incisive papilla to the distal end of the hard palate.
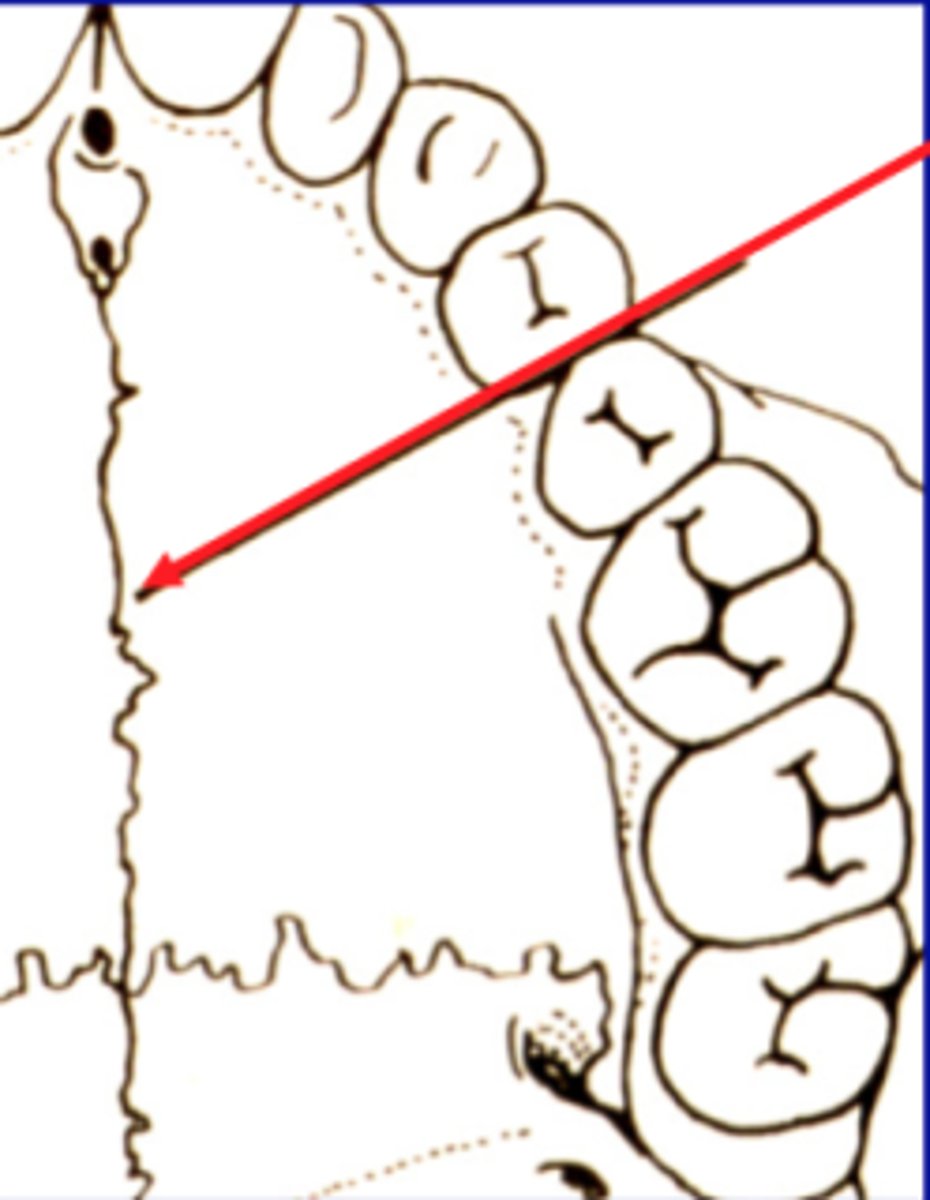
Major Palatine Foramen
the orifice of the anterior palatine nerve and blood vessels
Ideal maxillary Ridge
abundant keratinized attached tissue
square arch
palate U-shape in cross-section
moderate palatal vault
absence of undercuts
frenum attachments not approximating the crest of the ridge
well-defined hamular notches
Mentalis
elevates the skin of the chin and turns the lower lip outward.
What dictates the length and thickness of the labial flange extension of the lower denture?
mylohyoid m
Buccal Sheft
bordered externally by the external oblique line and internally by the slope of the residual ridge
What is the primary stress bearing area in the mandibular arch?
Buccal Shelf
Why is the buccal shelf is a primary stress bearing area?
parallel to the occlusal plane and the bone is very dense
Mental Foramen
the anterior exit of the mandibular canal and the inferior alveolar nerve.
Retromolar Pad
glandular tissue, loose areolar connective tissue, the lower margin of the pterygomandibular raphe, fiber of the buccinator and superior constrictor and fibers of the temporal tendon.
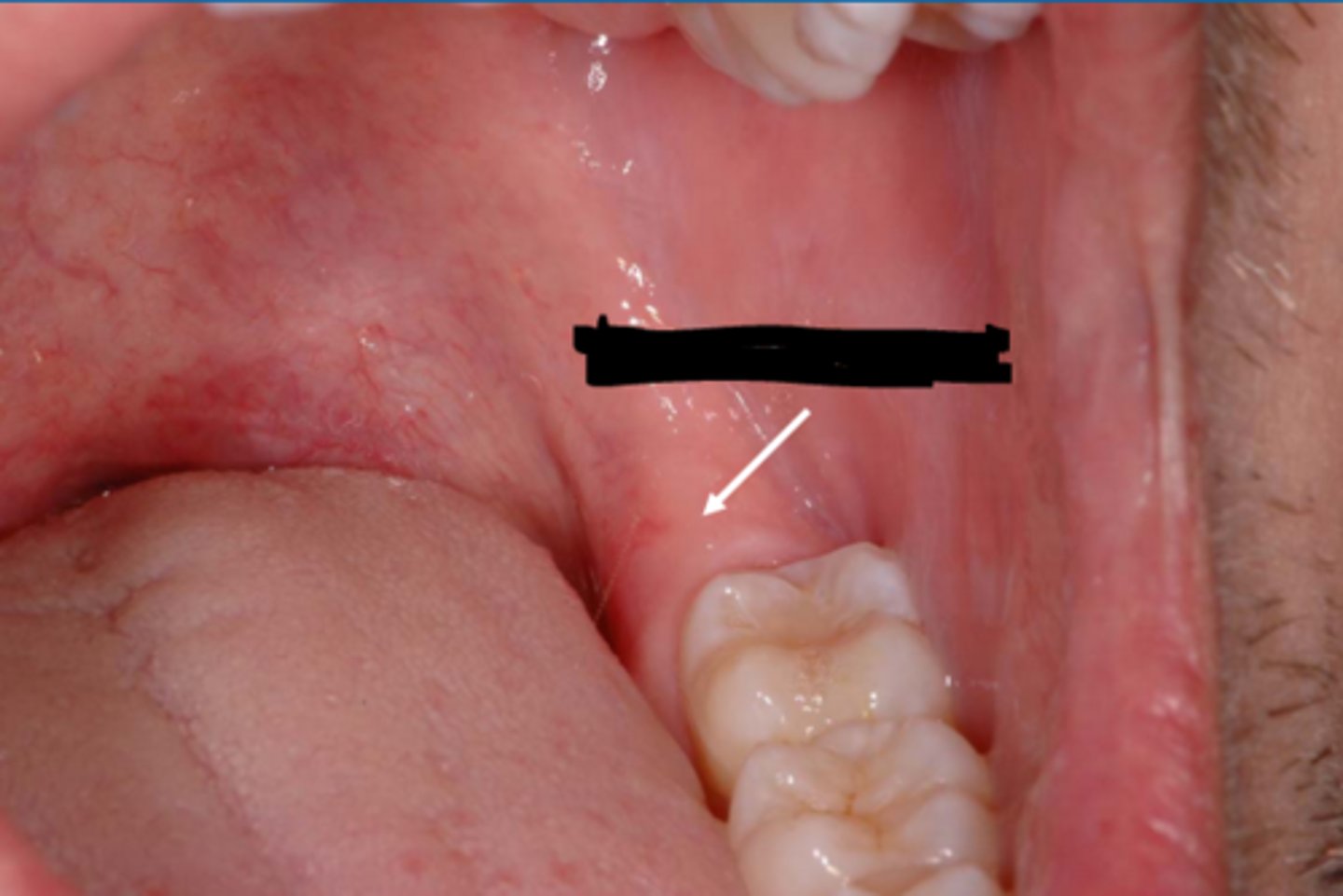
What is another primary support of the mandibular denture?
retromolar pad
External Oblique Line
ridge of dense bone from the mental foramen coursing superiorly and distally to become continuous with the anterior region of the ramus.
The External Oblique Line is an anatomic guide for the ___ termination of the buccal flange of the mandibular denture
lateral
Masseter Groove
where distobuccal flange of t3he denture should be contoured to allow freedom for the superior and medial buccinator movements.
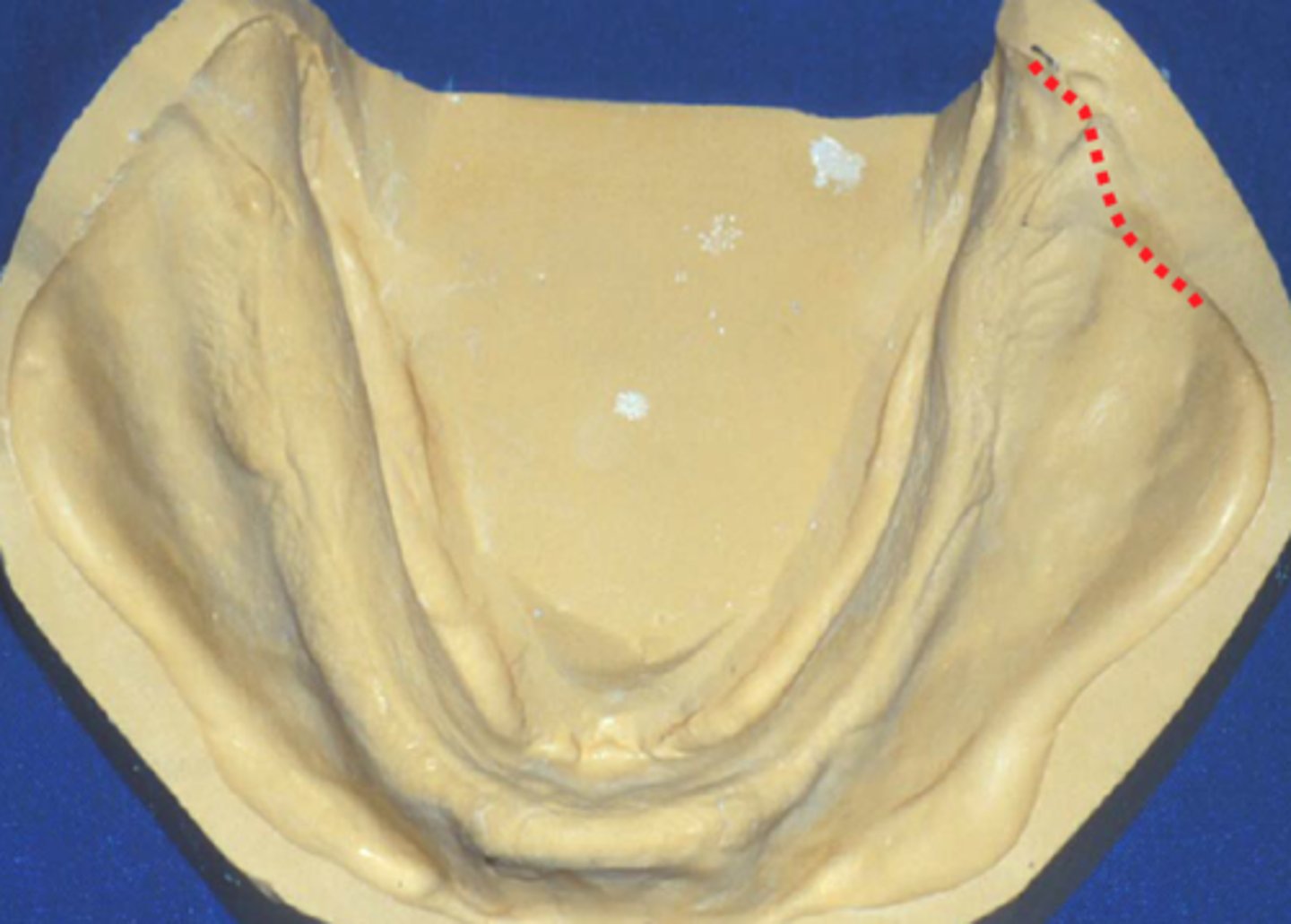
Function in the elevation of the hyoid bone and depression of the mandible
Suprahyoid Muscles
Suprahyoid Muscles
digasatric
stylohyoid
mylohyoid
geniohyoid
What forms the muscular floor of the mouth?
mylohyoid muscle
What determines the lingual flange extension of a denture?
mylohyoid muscle
Geniotubercle (Mental Spines)
attachment sites of the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles
Lingual frenum
overlies the genioglossus muscle, which makes origin from the superior genial spine
Sublingual Folds
formed by the superior surface of the sublingual glands and the ducts of the submandibular glands
What is important for the denture stability and retention?
Retromylohyoid Space
Ideal Mandibular Ridge
well defined retromolar pad
blunt mylohyoid ridge
deep retromylohyoid space
low frenum attachments
absence of undercuts
abundant keratinized mucosa
adequate alveolar height
Intrinsic Muscles
originate and inset within the tongue and produce changes in the shape of the tongue
What type of muscles originate and inset within the tongue?
Intrinsic muscles
What type of muscles originate outside of the tongue ?
Extrinsic muscles
Extrinsic Muscles
originate in structures outside the tongue and move the tongue and alter its shape
What are the Extrinsic Muscles ?
Genioglossus
Styloglossus
Hyoglossus
Palatoglossus
Facial Muscles for Expression
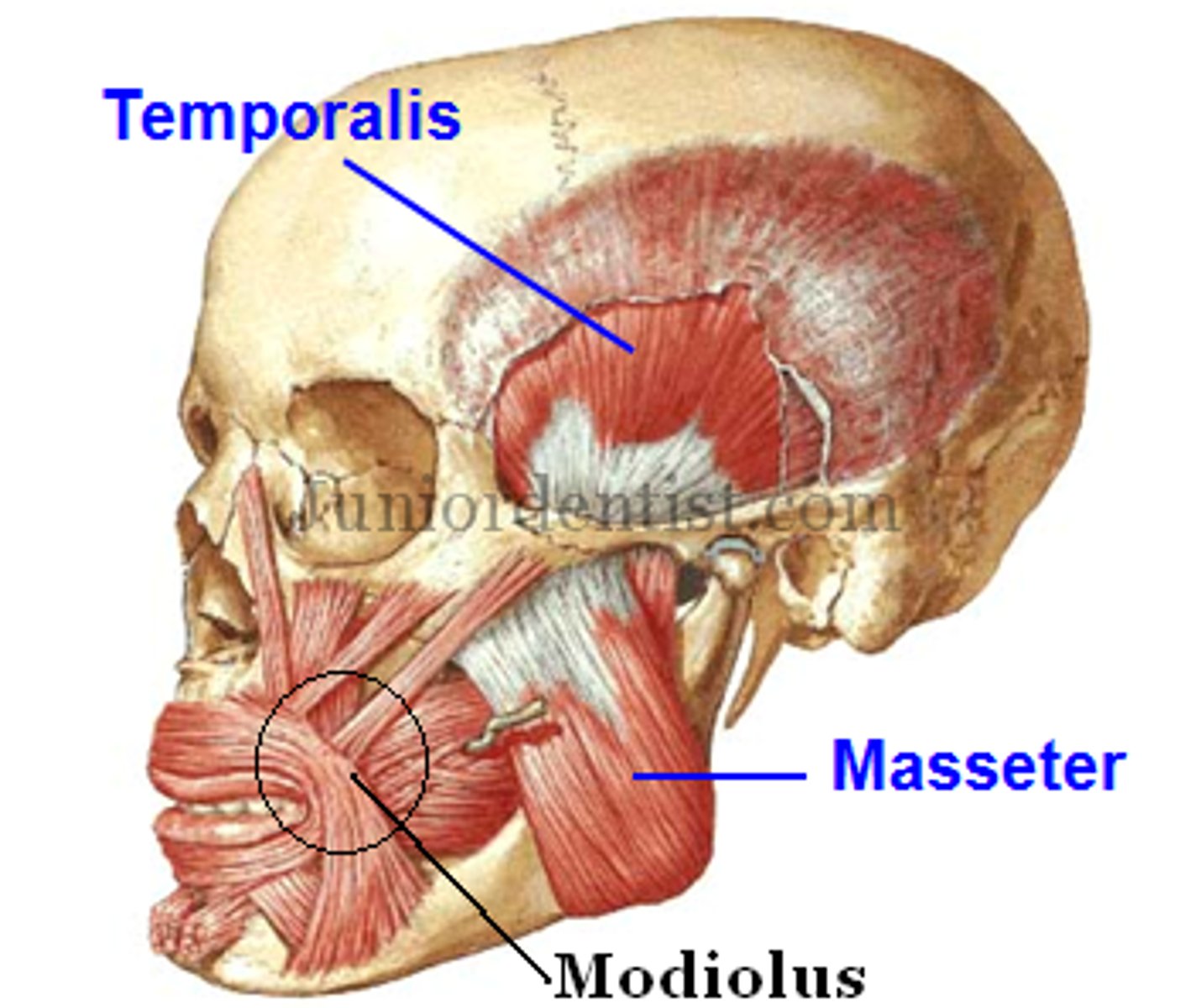
modiolus
mentalis
buccinator
orbicularis oris
incisivus labii superiorus & inferiorus
Modiolus
forceful area that influences the labial flange thickness of the maxillary denture
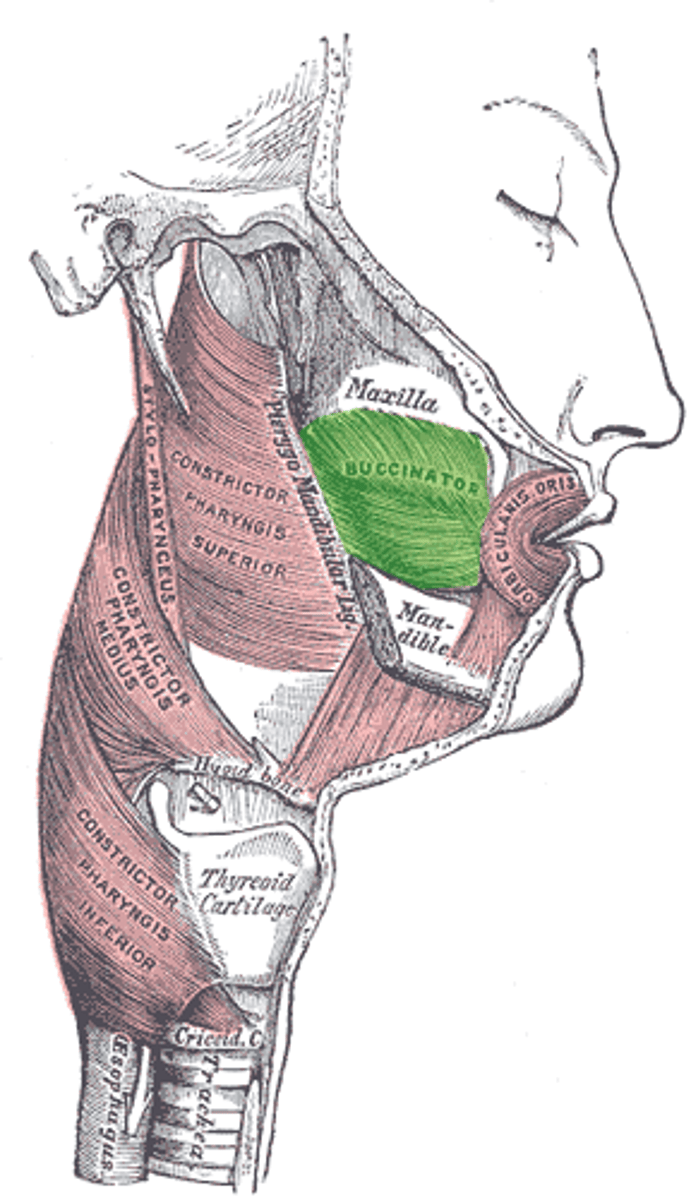
Buccinator
support and mobility of soft tissues of the cheek
As a person ages, this area tension is lost which predisposes to cheek biting
Buccinator
Mentalis
elevates the skin of the chin and turns the lower lip outward
Dictates the length and thickness of the labial flange in mandibular
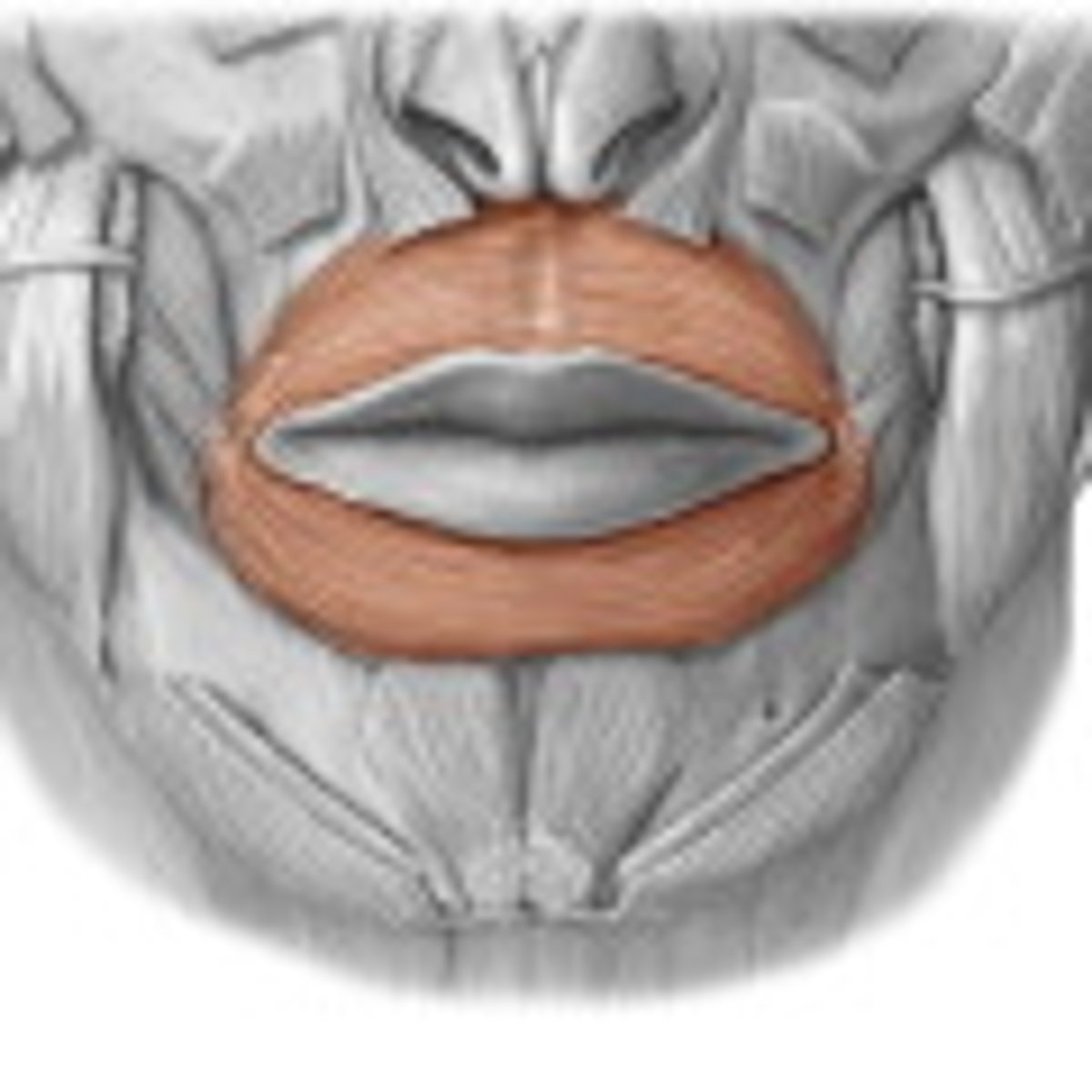
Orbicularis Oris
sphincter muscle
T/F: Muscles of Facial Expression insert in bone and do not need support from the teeth and denture flanges
FALSE
Ridge Form is in how many classes?
7
Class I
dentate
Class II
immediate post extraction
Class III
well rounded ridge form, adequate in height and width
Class IV
knife edge, adequate height with INadequate width
Class V
flat ridge, inadequate in height and width
Class VI
depressed ridge form with basalar bone loss
Anatomy and the Ridge form have a ___ influence on patient satisfaction
positive
There are __ classes for muscles of mastication and expression
3
Class I Muscles
tissues are normal in tone and function
Class II Muscles
tissues are slightly impaired in tone, and approximately normal in function
Class III Muscles
Tissues are greatly impaired in tone and function
___ is critical for retention of and comfort in wearing removable prosthesis
Saliva
Adhesion
bond between the oral mucosa and the denture base
Cohesion
the bonding between salivary components that lead to greater retention of the prosthesis
Surface Tension
saliva allows for the formation of a vacuum pressure on seating of the denture
__gland is a very important gland
palatal
___ salivary flow is correlated with ___ patient satisfaction
decreased
decreased
___ muscle tone is correlated with ___ maxillary denture retention
decreased
decreased
Parameters we can change for denture satisfaction
quality of denture
JRR
Occlusion
Clinical techniques/lab techniques
JRR
jaw relationship records
Correct assessment of ___ and ___ is positively correlated to patient satisfaction
VDO
Occlusion