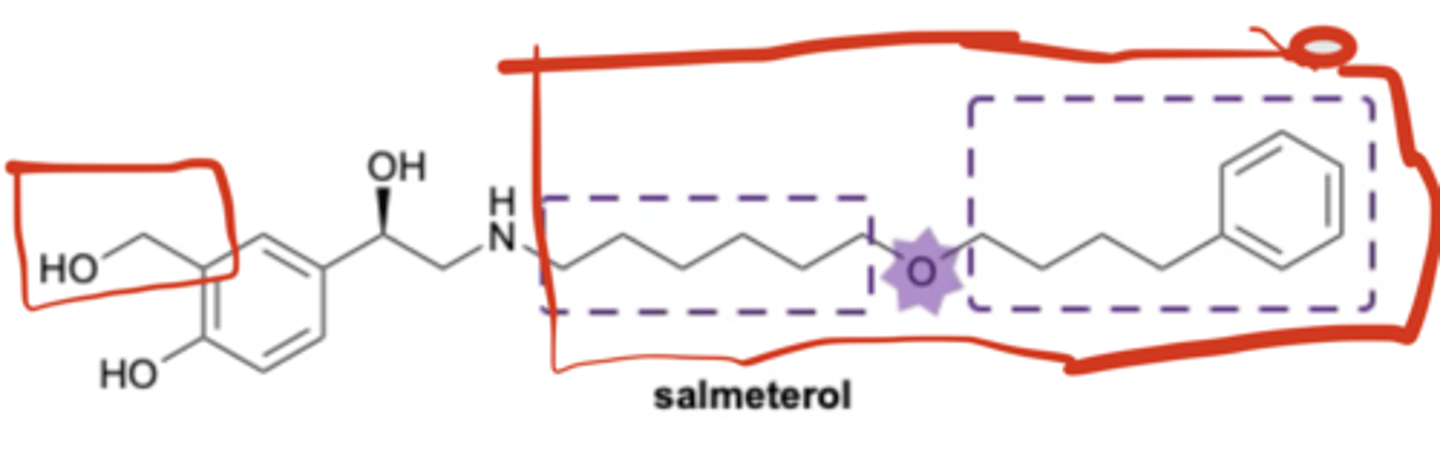
Adreno receptors
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the steps of noreadrenaline regulation?
1. Synthesis
2. Storage
3. Release
4. Uptake
5. Metabolism
What are adreno receptors?
GPCR's which bind to noreadrenaline.
What are GPCRs?
Cell surface membranes that work with G-proteins to activate cellular processes.
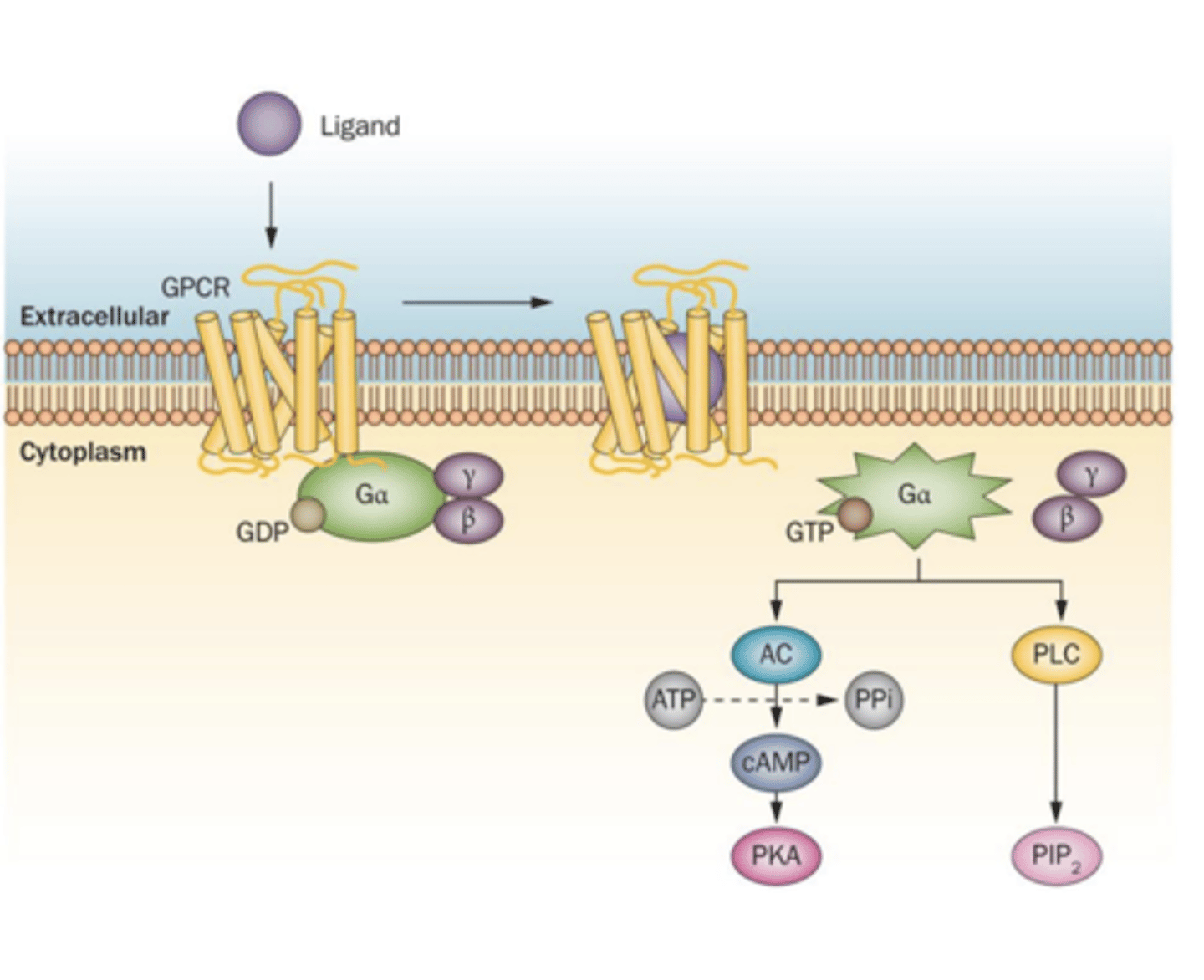
How do GPCRs activate second messengers?
When ligands attaches to the GPCR, this causes GEFs to replace the GDP, attached to the G-protein, with GTP.
This activates the G-protein causing it to disassociate and move to second messengers and activate them.
What are the types of adreno receptors?
Alpha (α) and Beta (β)
What are the types of β receptors?
- β1
- β2
- β3
What are the types of α receptors?
- α1
- α2
How do adreno receptors differ from each other?
- Located in different areas.
- Use different G proteins.
- Activate different second messengers.
What G-protein do α1 receptors use?
Gq
What G-protein do α2 receptors use?
Gi
What G-protein do β1, β2 and β3 receptors use?
Gs
Which adreno receptors work on blood vessels?
α1, α2 and β2
Which adreno receptors work in the heart?
α1 and β1
Which adreno receptors work in the bronchi?
β2
Which adreno receptors work in the adipose tissue?
β3
Describe what happens when noreadrenaline binds to α1 receptors.
- Upon binding, the Gq protein is activated which then activates phospholipase C.
- Phospholipase C catalyses the breakdown of PIP2 to IP3 and DAG.
- IP3 causes the opening of calcium channels on the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- This causes smooth muscle in the heart and blood vessels to contract increasing blood pressure.
Describe what happens when noreadrenaline binds to α2 receptors.
- Upon binding, the Gi protein is activated which has an inhibitory effect on adenylate cyclase causing it to inactivate.
- This decreases cAMP concentration maintaining the inactive protein kinase A.
- This causes calcium channels to remain closed preventing vesicles containing noreadrenaline to be released reducing blood pressure.
Describe the negative feedback α2 receptor.
α2 receptors are present on the presynaptic neurone and noreadrenaline, once released, can bind to α2 receptors which then inhibit the release of noreadrenaline causing a decrease in concentration of noreadrenaline in the synapse.
Describe what happens when noreadrenaline binds to β1 receptors.
- Upon binding, the Gs protein is activated which causes adenylate cyclase to activate.
- This increases cAMP levels causing protein kinase A to activate.
- Protein kinase A then phosphorylates calcium channels, in the heart, opening them.
- This induces contraction of the heart which increases blood pressure.
What affects does the activation of β1 receptors have on the heart?
- Increased force of contraction.
- Increased rate of contraction.
- In severe cases, can cause arrhythmias.
Describe what happens when noreadrenaline binds to β2 receptors.
Noreadrenaline binds to Beta-2 receptors which cause the Gs subunit to activate. This can then activate Adenlyl cyclase which cause an increase in cAMP production. Increase in cAMP production can then activate/bind protein kinase A which phosphorylates calcium ion channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This prevents calcium ions being released and binding to calmodulin and therefore preventing MLCK activation, which inhibits myosin activity. This prevents contraction of smooth muscle causing bronchodilation to take place allowing a greater diameter of airways for air to pass through.
Describe what happens when noreadrenaline binds to β3 receptors.
- Upon binding, the Gs protein is activated which causes adenylate cyclase to activate.
- This increases cAMP levels causing protein kinase A to activate.
- Protein kinase A then stimulates the breakdown lipids in adipose tissue.
What do β3 receptors regulate?
Lipolysis
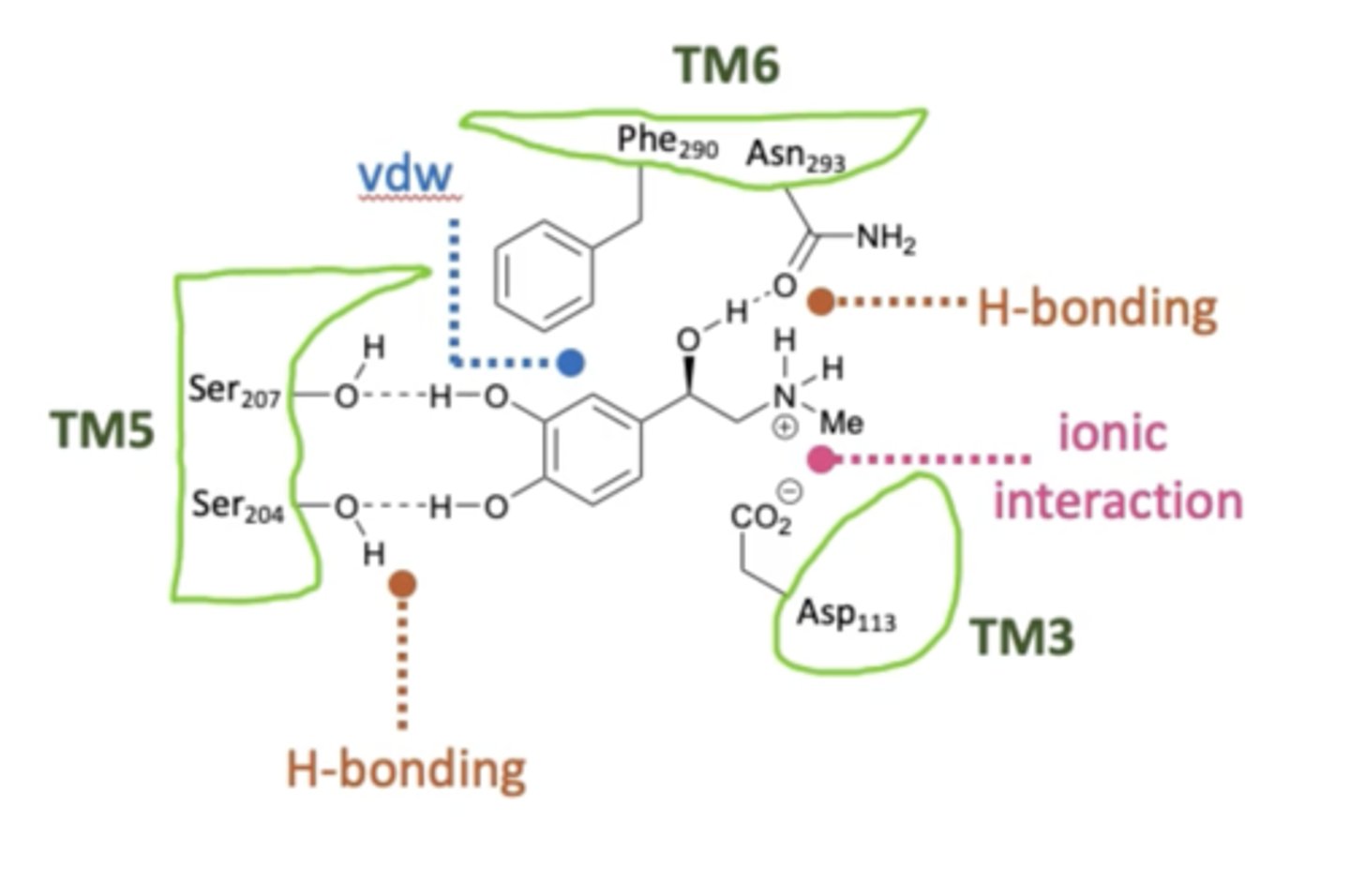
What are the general interactions that must be present for noreadrenaline to bind to alpha and beta receptors?
- Two hydrogen bonds with donors on the catechol group.
- Hydrogen bond with hydroxyl donor group on the chain.
- Ionic bond with amine group at physiological pH.
- Pi-Pi stacking with aromatic ring.
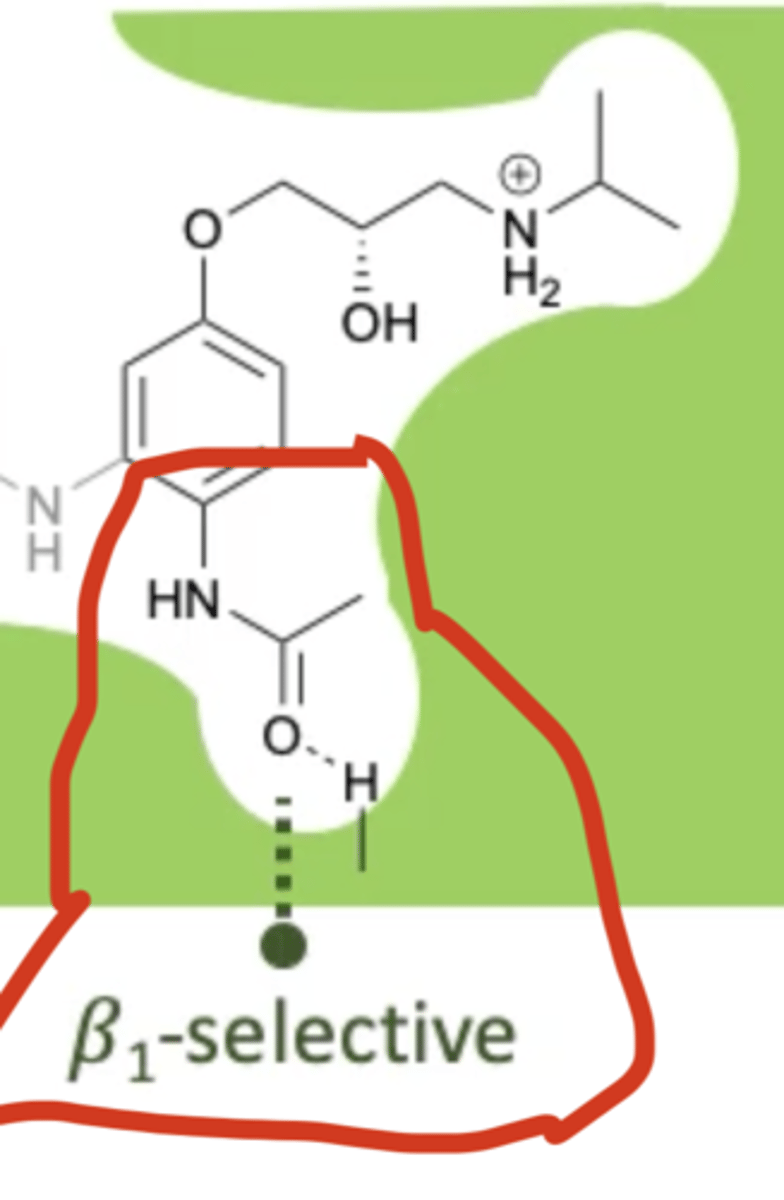
What groups can increase selectivity of β1 receptors?
A substituent at the para position of the aromatic ring that can form a hydrogen bond.
What groups can increase the selectivity of β2 receptors?
- A substituent on the meta position of the aromatic ring that can form a hydrogen bond.
- A longer alkyl chain after the amine group.
These increase selectivity to the β2 receptor.