ZOOL 2013 Exam 1
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
anatomy
describes the structures of the body
Divisons of anatomy
macro/micro anatomy
macro anatomy
BIG structures that can be seen without a microscope
mircoanatomy
structures that need a microscope in order to be seen
cytology
cells
histology
tissue
physiology
study of how structures work together
Study of function
"form follows ___________"
function
levels of structural organization of the human body
atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organ, organ systems, organism
11 organ systems of the body
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive
metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions in the body ( anabolism + catabolism)
anabolism
small molecules combined to make large structures, uses energy
catabolism
breaks materials down, releases energy
requirements for life
-oxygen
-nutrients
-narrow range of temperature,
-narrow range of atmospheric pressure
homeostasis
all body systems working together to maintain a stable internal environment
failure to be in a homeostatic range causes what?
diseases
intrinsic regulation
internal response of cells, tissue, organs
extrinsic regulation
organ or system is controlled by an outside force like nervous system or endocrine
negative feedback loop
the body counteracts a change to restore homeostasis (balance)
four parts of a negative feedback loop
stimulus, sensor, control, effector
what's regulated by negative feedback loop?
body temperature
positive feedback loop
results in a change in the body's, rather than a return to homeostasis
what's an example of positive feedback loop?
child birth
anatomical postion
standing upright, facing forward, arms at side, palms facing forward
anterior view
front of the body
posterior view
back of body
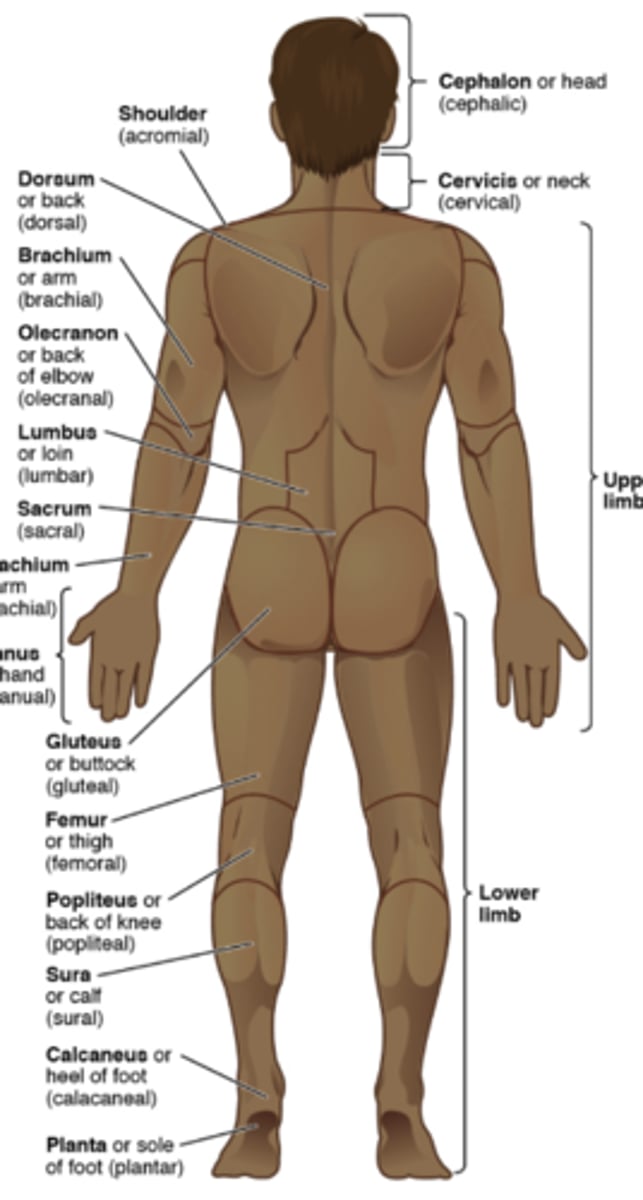
directional terms to the human body
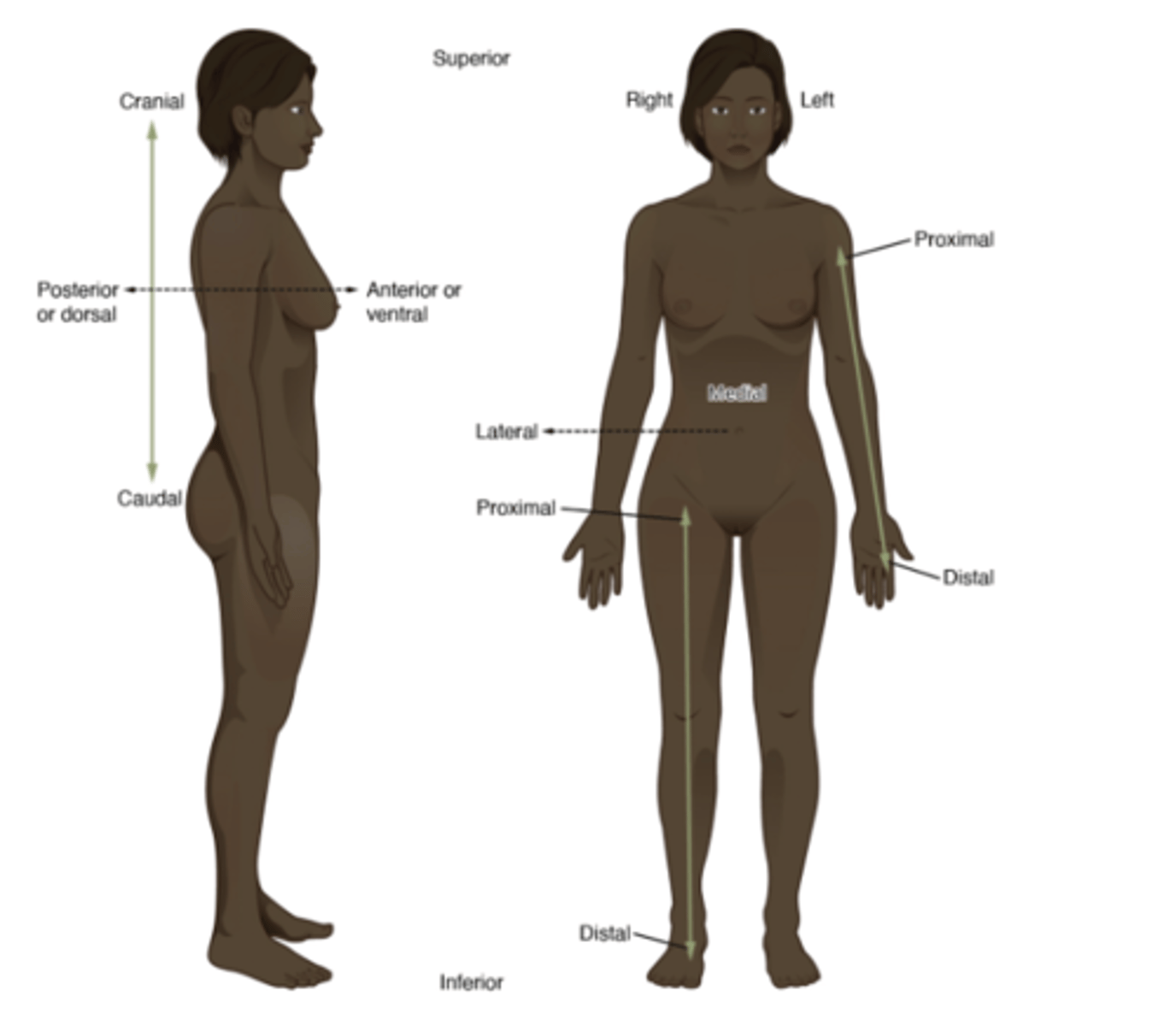
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
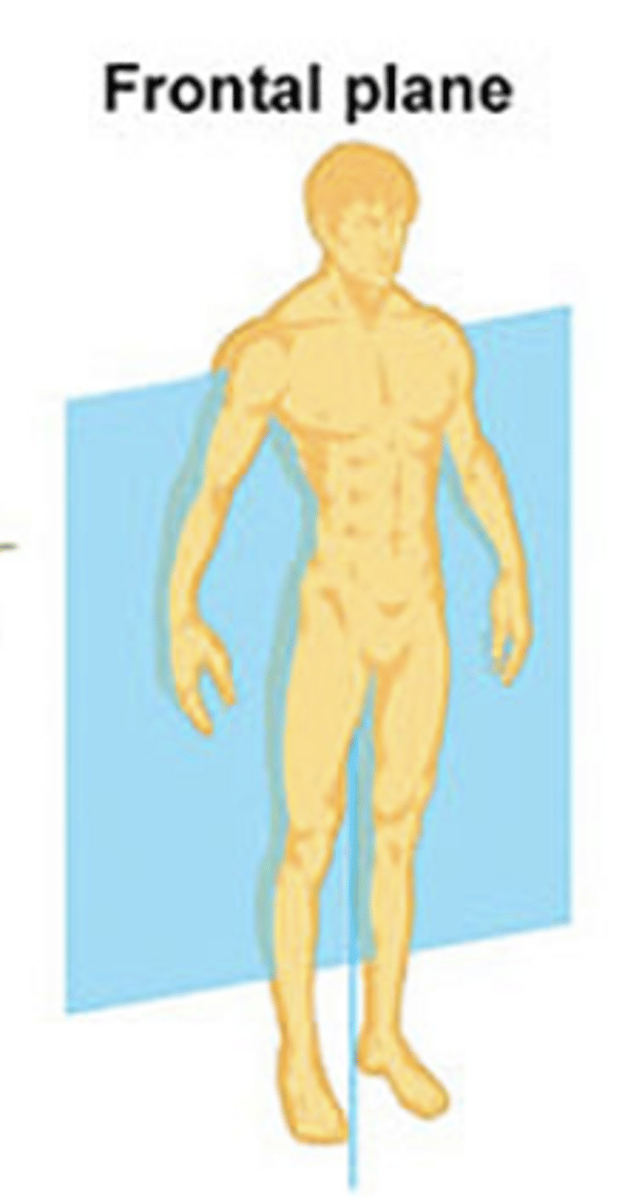
frontal plane (coronal)
divides body into front and back
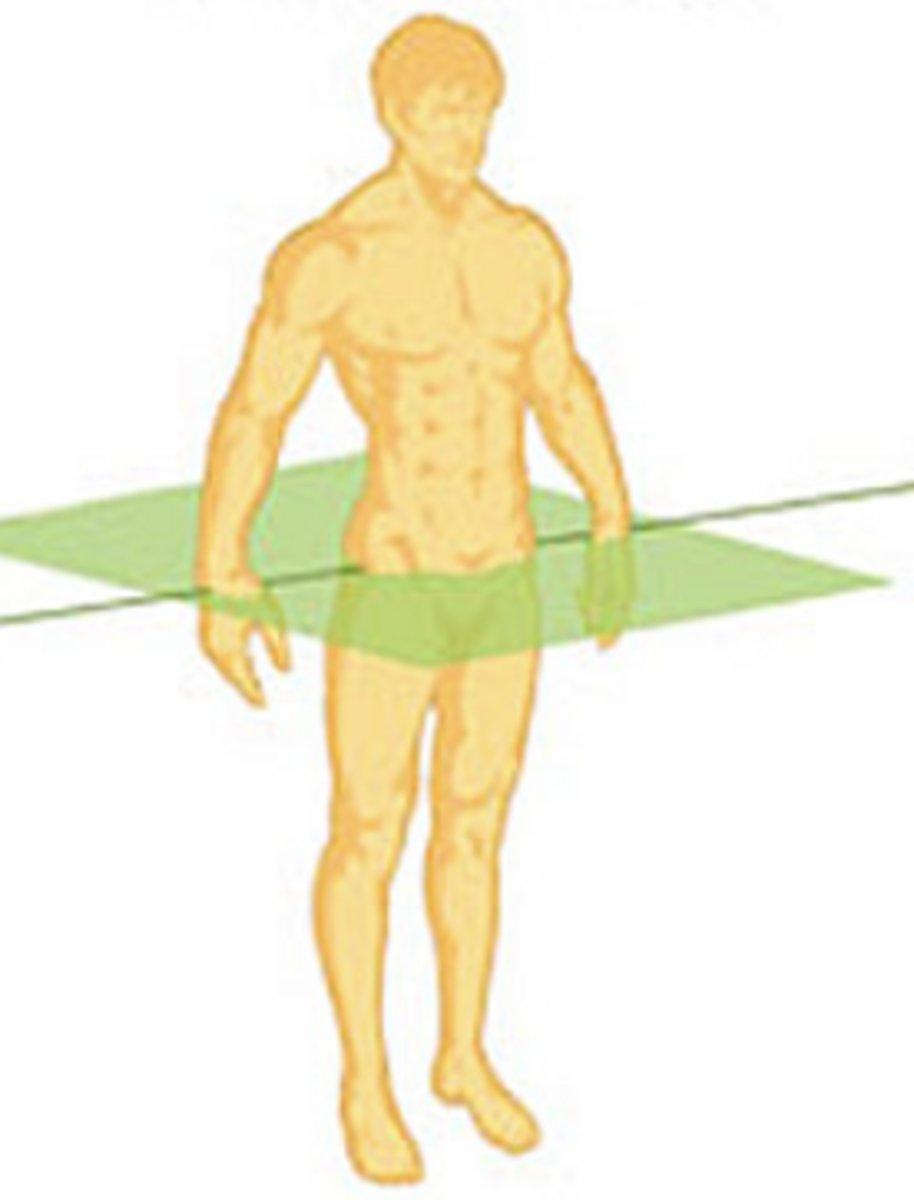
transverse plane
divides the body into upper and lower sections
ventral cavity includes?
thoracic and abdominopelvic
dorsal cavity includes ?
cranial and spinal cavities
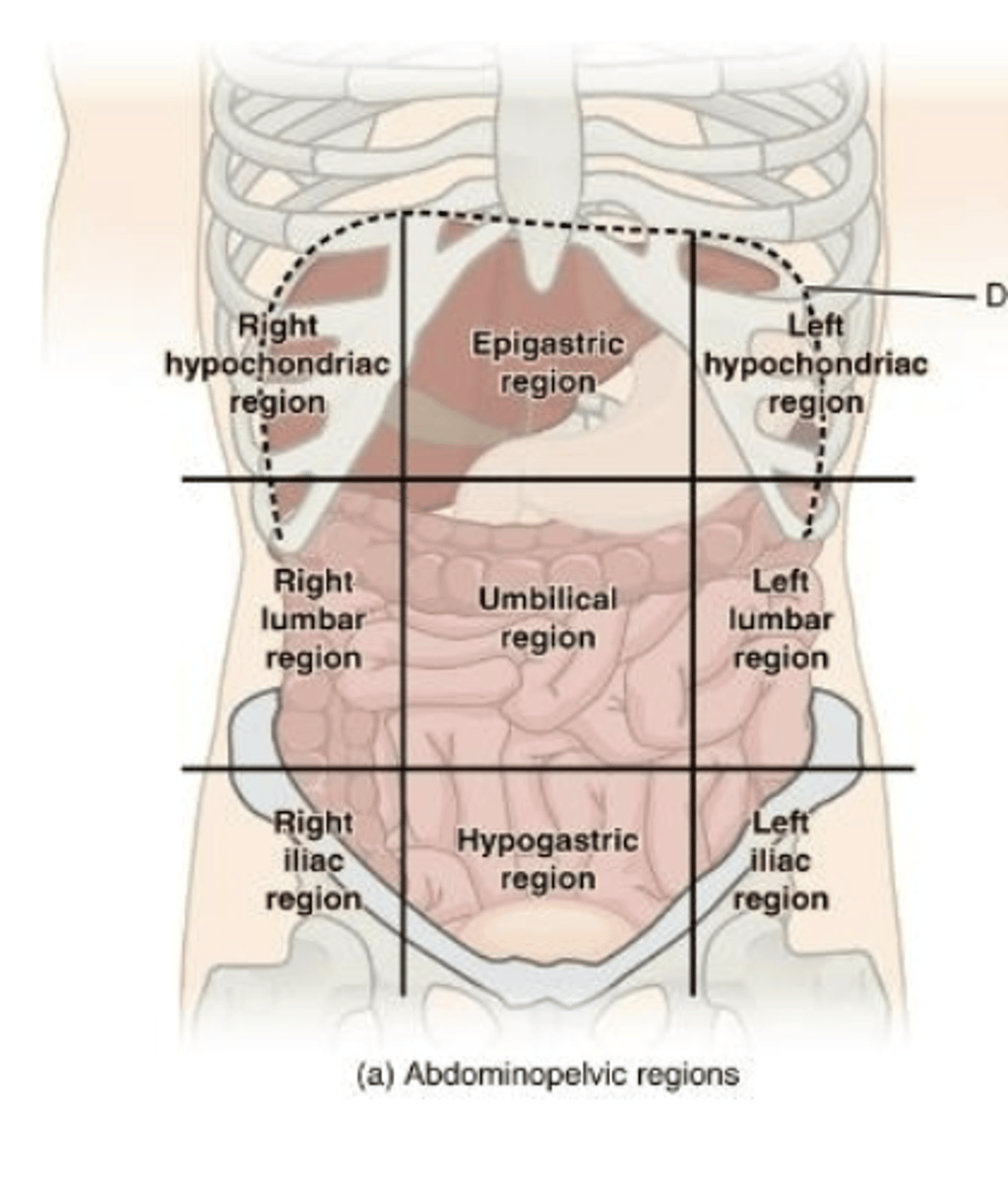
abdominal regions
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac
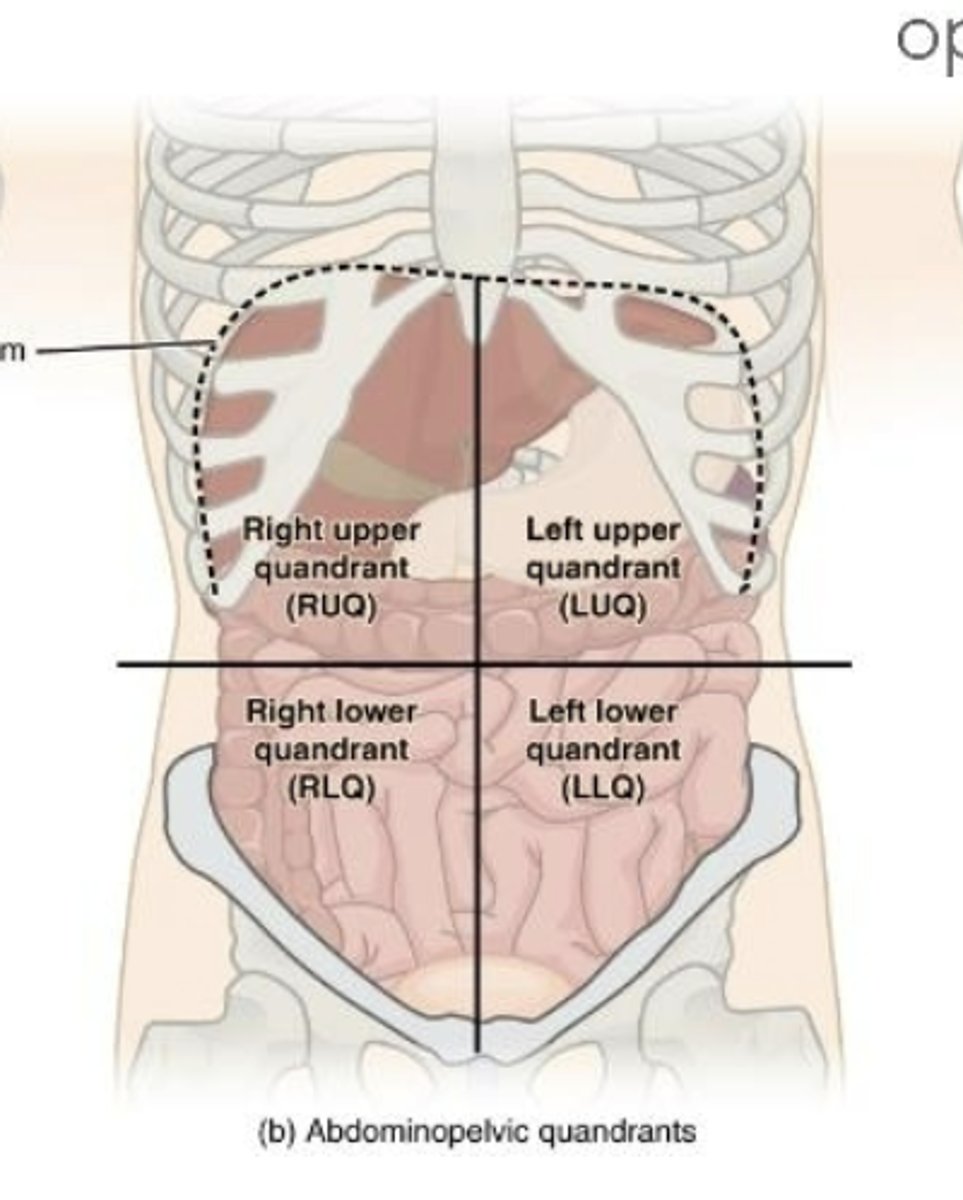
Abdominalpelvic quadrants
right upper, left upper, right lower, left lower
serous membrane
lines the pericardial cavity and covers the heart.
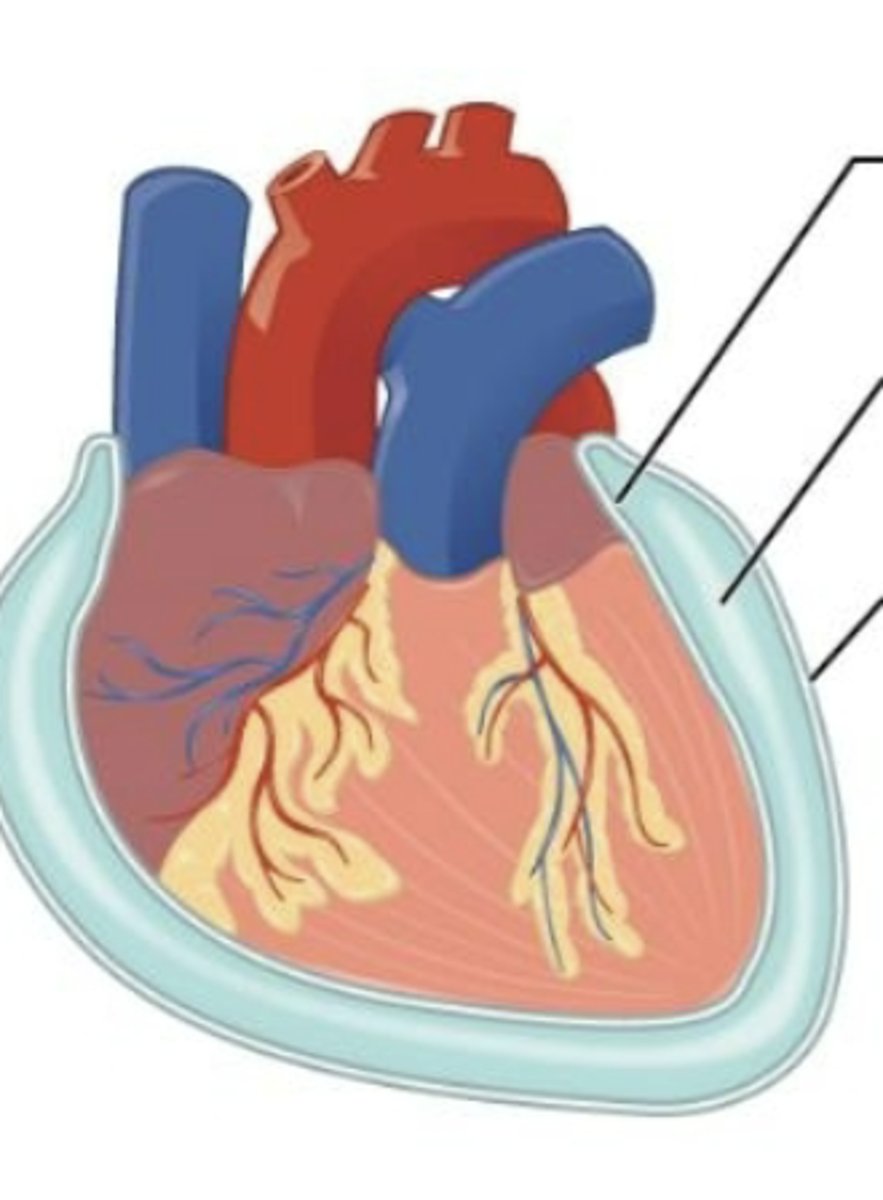
medical imaging
x ray, CT, MRI, PET, ultrasound
element
pure substance that cannot be broken down or created
compound
two or more elements join to make a new substance
atom
Smallest particle of an element
charges of atoms
protons (+)
Neutrons (no charge)
Electron (-)
which elements make of up 95% of the body
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen
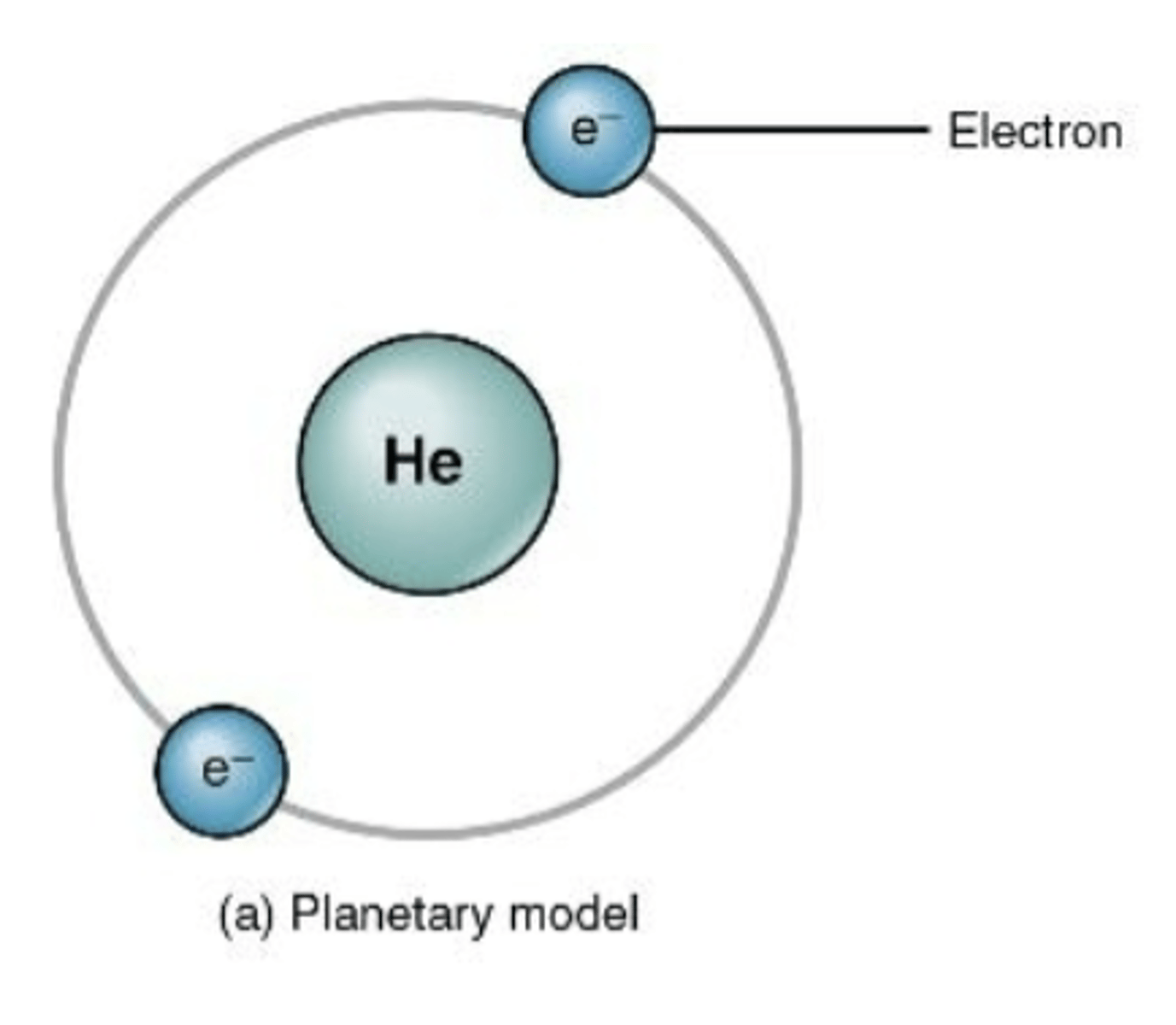
planetary model
electrons move around the nucleus in fixed, circular orbits
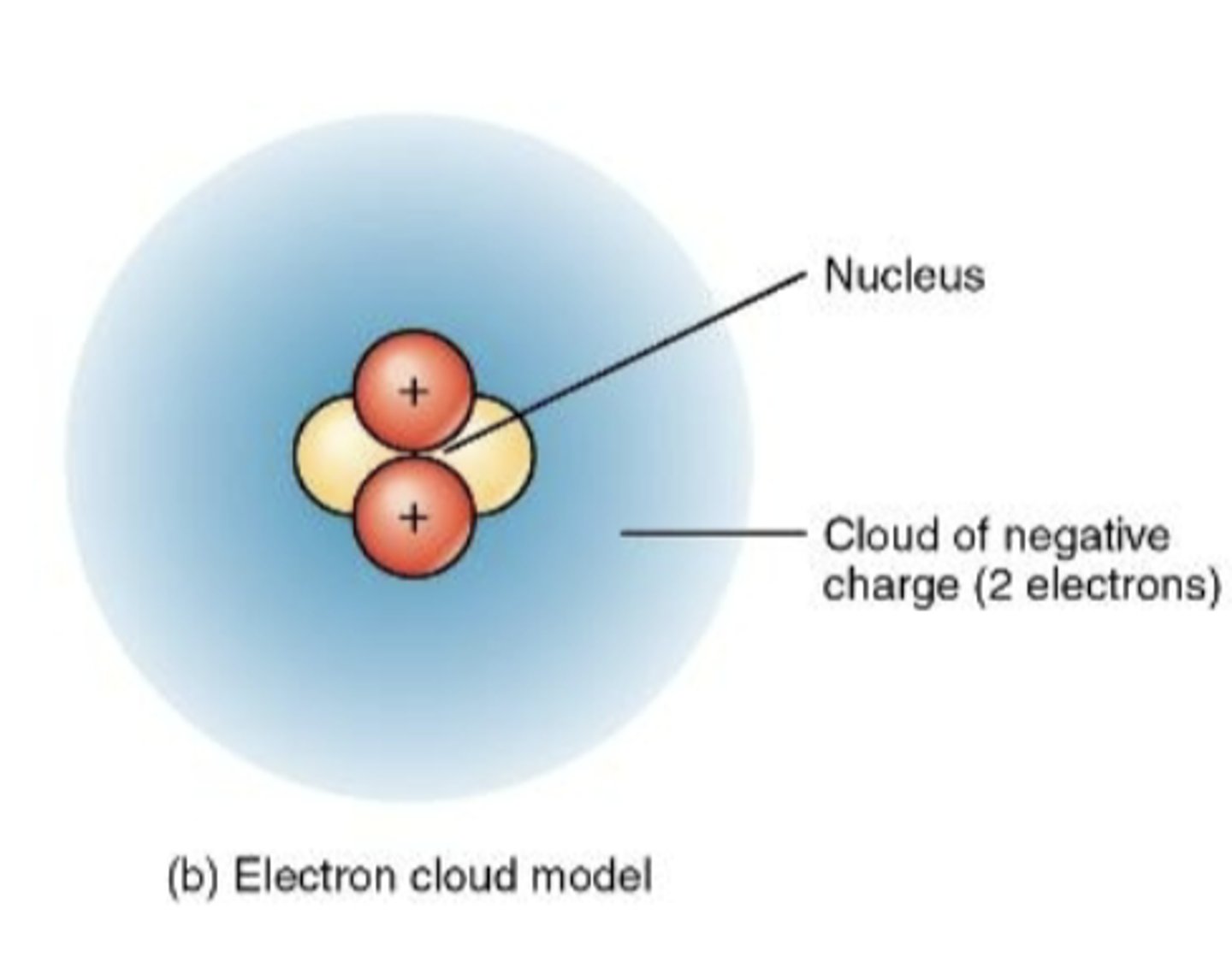
Electron Cloud Model
model of atom in which the electrons seem to form a cloud as they move around the nucleus
atomic number
number of protons in the nucleus
atomic mass
counts both protons and neutrons (1:1 ratio)
isotopes
the same element with different numbers of neutrons but the same number of protons.
what happens to unusual isotopes?
since they are unstable and radioactive, they release extra neutrons as they decay
radioactive isotopes are used in what field?
medical
Atoms with equal number of protons and electrons are?
chemically neutral
ions
number of protons and electrons are different
cations
has more protons then electrons and are (+) charged
anions
has fewer protons than electrons and are (-) charged
oxidation
the loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
molecule
two or more atoms held together by a chemical bond
compound bond
molecule with two or more different types of atoms
ionic bond
close association between ions of opposite charge
covalent bonds
two atoms share electrons to fill their valence shell
hydrogen bonds
postive hydrogen is attracted to a negative molecule
chemical reaction
reaction occurs during the formation or breaking of chemical bonds
chemical reactions can be influenced by
temperature, molecule size, concentration of reactants and products, catalysts
decomposition reaction (catabolism)
breaks chemical bonds AB-->A+B
Synthesis Reaction (Anabolism)
forms chemical bonds; A + B ---> AB
exchange reaction (reversible)
reactants are rearranged AB --> A + B
activation energy
gets a reaction started
exergonic reactions
produces more energy than used
endergonic reactions
consumes more energy than produced
reactants
materials going into a reaction
products
materials coming out of a reaction
enzymes
proteins that lower the amount of activation energy required.
organic molecules and compounds are based on?
carbon and hydrogen
inorganic substances
water
salts
acid/bases
water
-makes up 70% if the human body
- universal solvent
- necessary for chemical reactions
- transfers heat around the body
salts
-dissolves in water into cations and anions
- electrolytes
-ions form ionic bonds
acids
dissolves to release a hydrogen ion (H+)(proton)
strong acid
releases all hydrogen into solution
weak acid
does not ionize completely
bases
dissolves to release a hydroxide ion (OH-)
strong base
releases all OH- into solution
weak base
does not ionize complete or can also use small amounts of H+ to create water
buffer
solution that consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base
acidosis
pH below 7.35
alkalosis
pH above 7.45
chemically neutral pH
7
pH scale
lower the pH, the greater aciditiy
the higher pH, the greater alkalinity(nuetral)
functional group
group of atoms bonded together to act as a single unit
carbohydrates are categorized by the number of?
monomers
monosaccharides
simple sugars / 1 carbon base (ex: glucose, fructose)
disaccharides
2 simple sugars (ex: sucrose and lactose)
polysaccharides
chains of simple sugars ( glycogen and starches)
Lipids are hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
fatty acids
chains of carbon and hydrogen that end in a carboxyl group
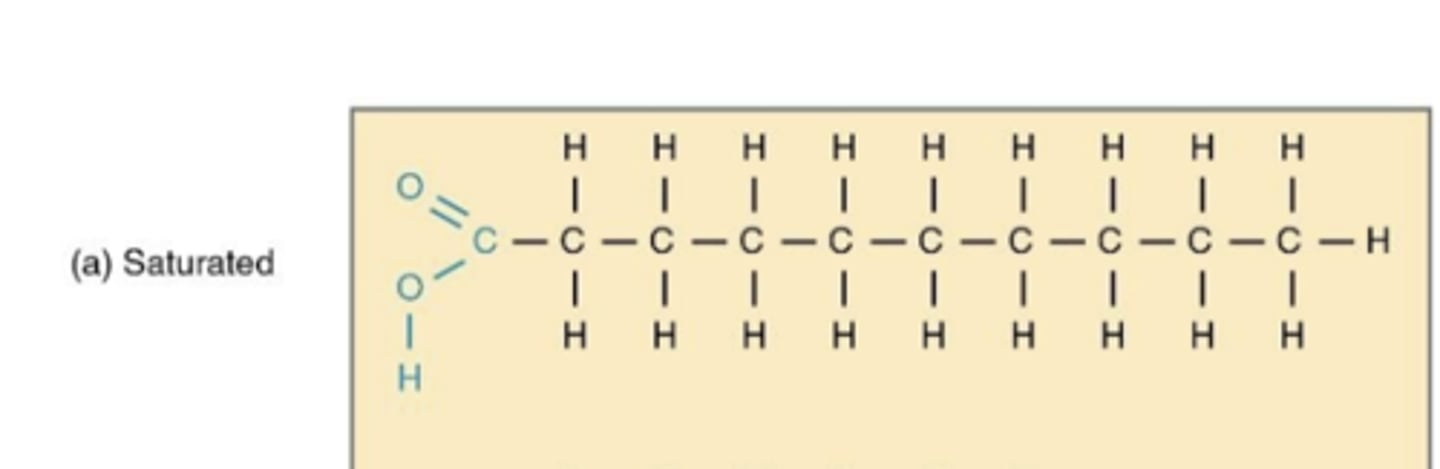
saturated acids
no double bonds
packed tightly together
max # of hydrogens
solid at room temp
a straight chain
unsaturated acids
has double bonds
causes structure to kink (bend or curve)
liquid at room temperature
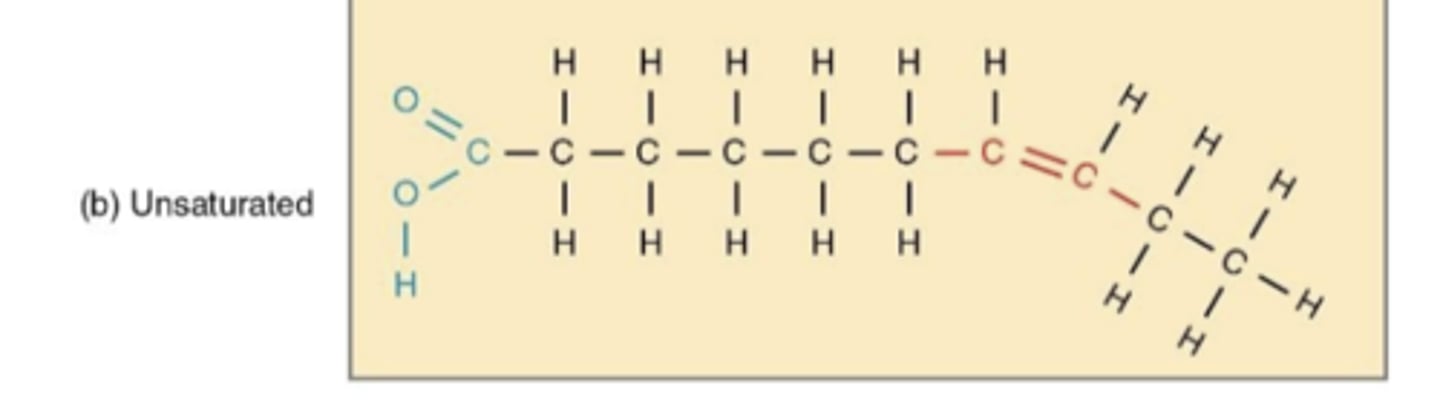
triglycerides
most abundant lipids in your body and the richest source of energy
phospholipids
has hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
two fatty acids, glycerol, and phosphate group
sterols/steroids
basis for cholesterols and hormones
ringed shaped
prostaglandin
includes leukotrienes
meditates blood pressure and inflammation
derived from unsaturated fatty acids
what is the most abundant organic molecule in the body that contains nitrogen?
proteins
what is the building blocks of proteins?
amino acids (20 different types)