UCI Bio 93- Midterm 1
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
atoms
smallest unit of chemical elements
molecules
two or more atoms combined
compound
two or more elements combined in a fixed ration
C, O, H, N
... are 4 elements that make up 96% of all living matter
covalent bond
what is the strongest bond?
covalent
sharing of electrons by two atoms
ionic
transfer of electrons between two atoms
hydrogen bond
what is a weak bond?
hydrogen bond
the H atom forms one covalent bond and a second weaker bond with an atom in another molecules
nonpolar
equal sharing of electrons
(two of the same element)
polar
unequal sharing of electrons
has a charge
(water)
negative
what is the charge of O in water?
positive
what is the charge of H in water?
cohesion
interactions between water molecules
(H2O with H2O)
solvent
interactions between water and other molecules
4 bonds
what is the maximum amount of bonds that hydrogen can form?
15%
in room temperature of water what % is the maximum amount of bonds going to be made?
more acidic
when H+ concentration increases...
more basic
what H- concentration decreases...
hydrophilic
affinity for water
(polar and ionic bonds)
hydrophobic
repel water
(nonpolar covalent bonds)
buffers
chemical processes are sensitive to pH changes and resist change in the pH solution
7.4
the pH of human blood is...
carbonic acid and bicarbonate
what are the main buffers in blood?
right
response to a rise in pH in blood (becomes more basic)
left
response to a drop in pH in blood (becomes more acidic)
carbon atoms
building blocks for biological molecules
4 VE
how many VE does carbon have?
covalent bonds
how do functional groups join to the carbon skeleton?
hydroxyl
-alcohols
-polar
-dissolves organic compounds (like sugars)
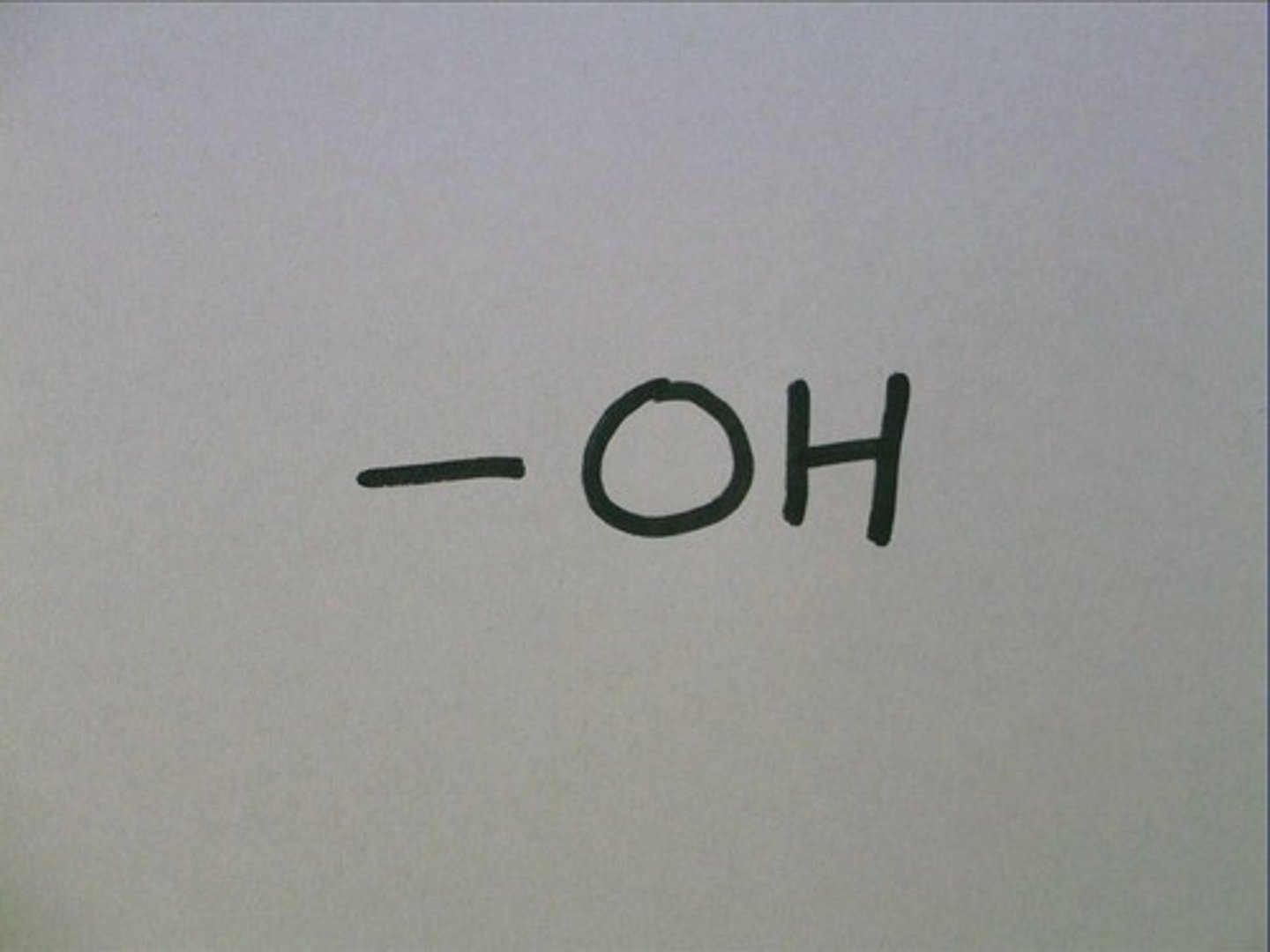
carbonyl
-ketones (within skeleton)
-aldehydes (at the end of skeleton)
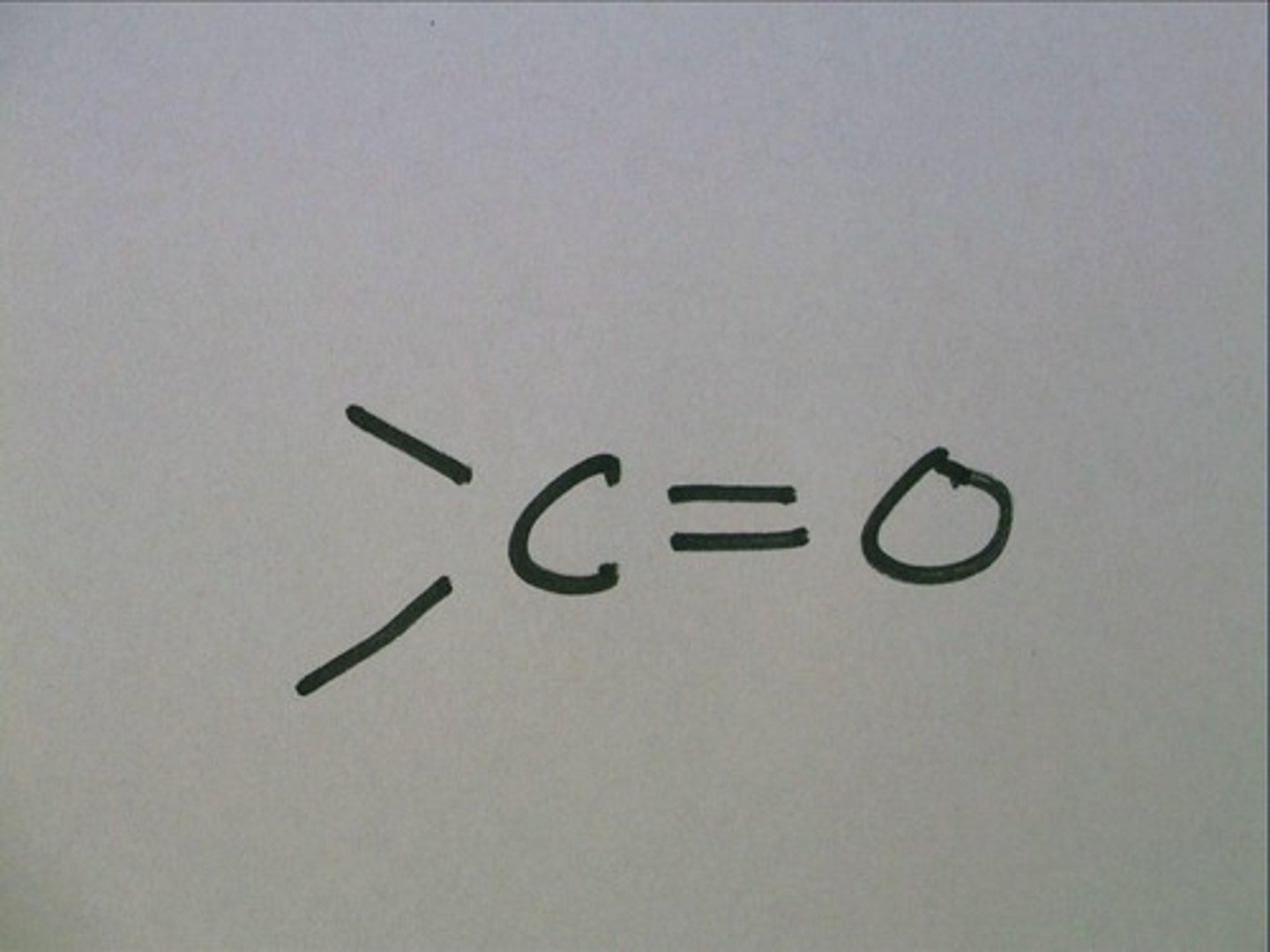
carboxyl
-is acidic
-weak acid
-hydroxyl+carbonyl
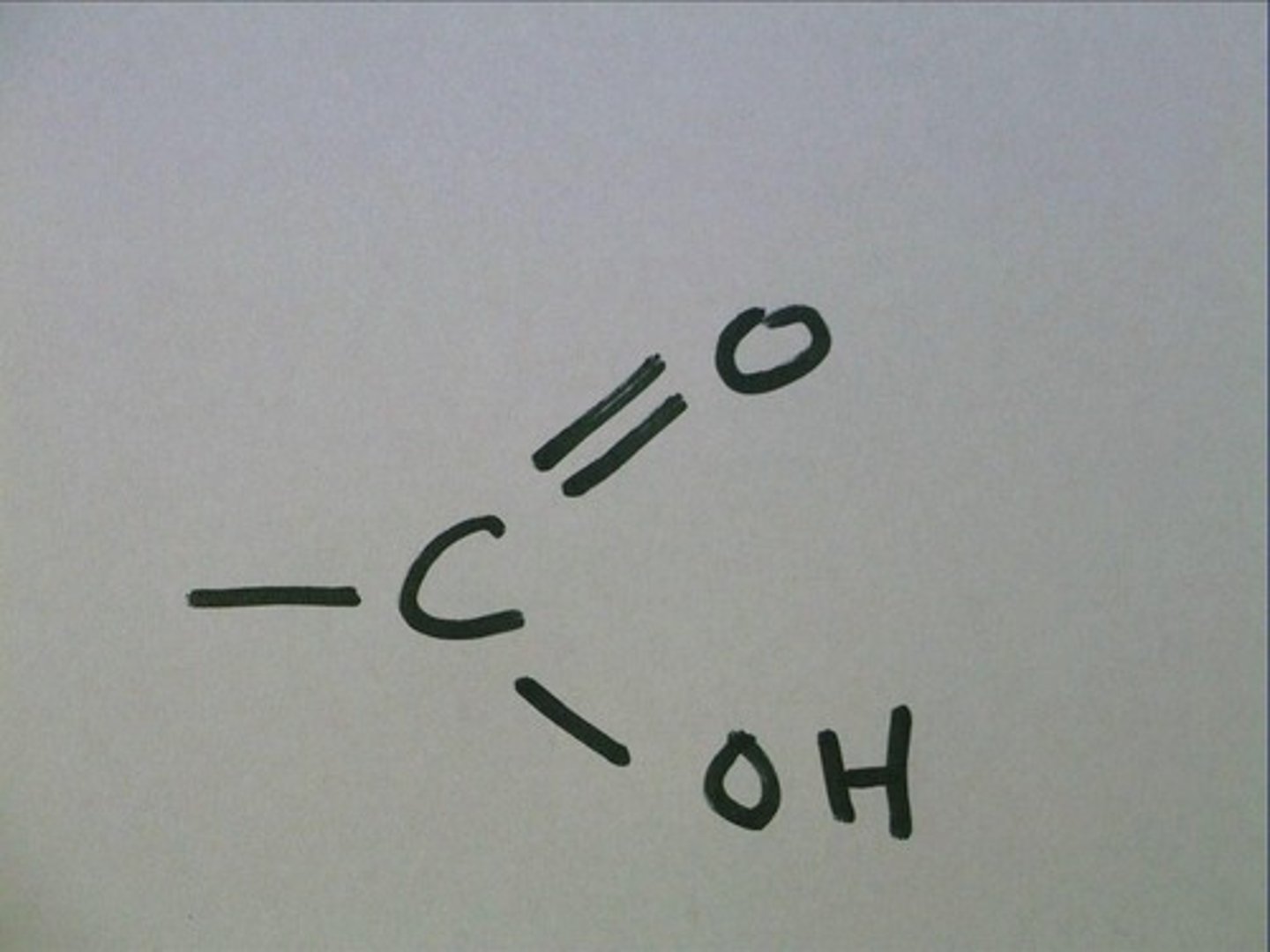
amino
-base
-animes
-can pick up H from surrounding solutions
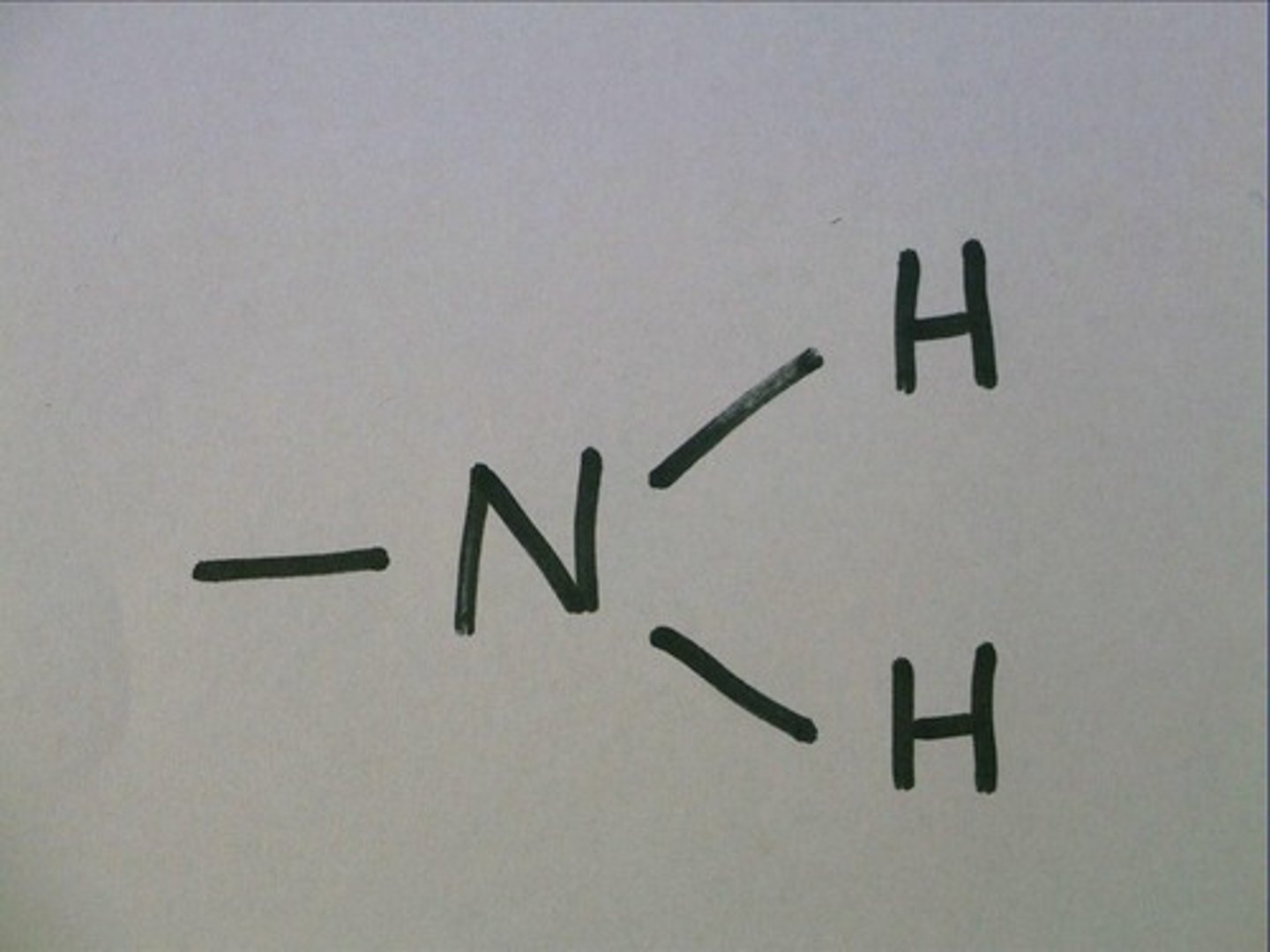
amino and carboxyl
what functional groups make up an amino acid?
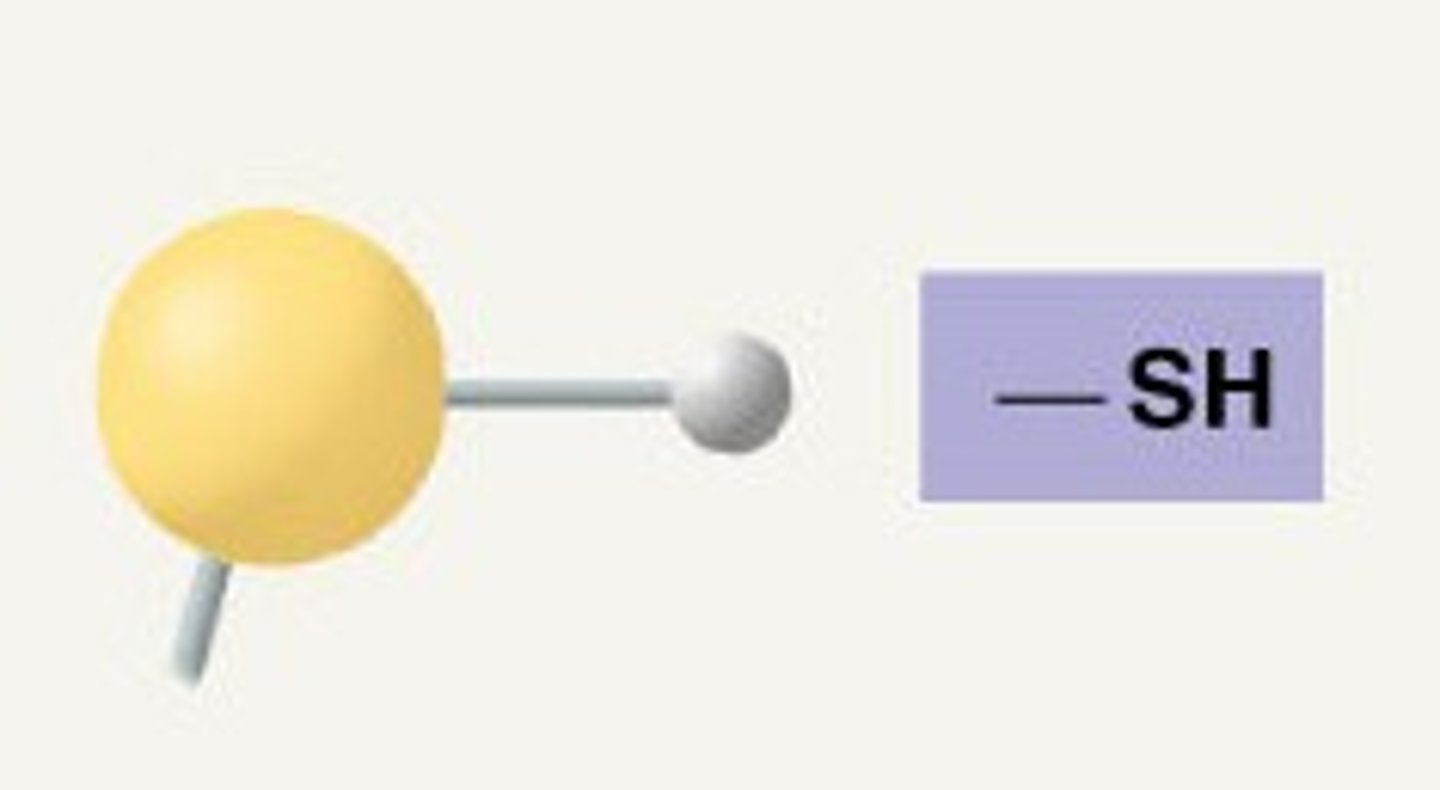
sulfhydryl
-thiols
-cross-linking of cysteines
-stabilizes protein structure
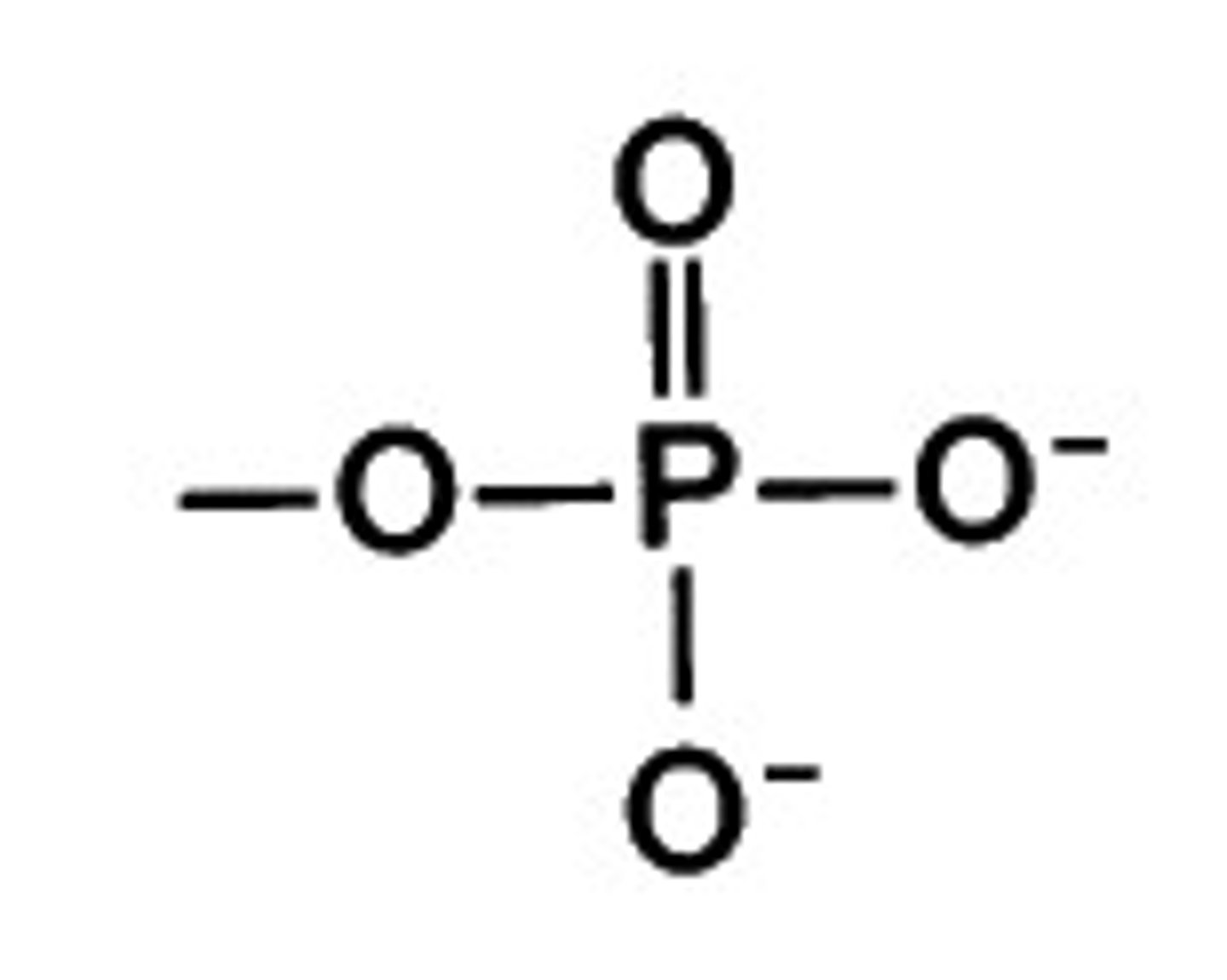
phosphate
-backbone for phospholipids
-negative charge
-hydrophilic
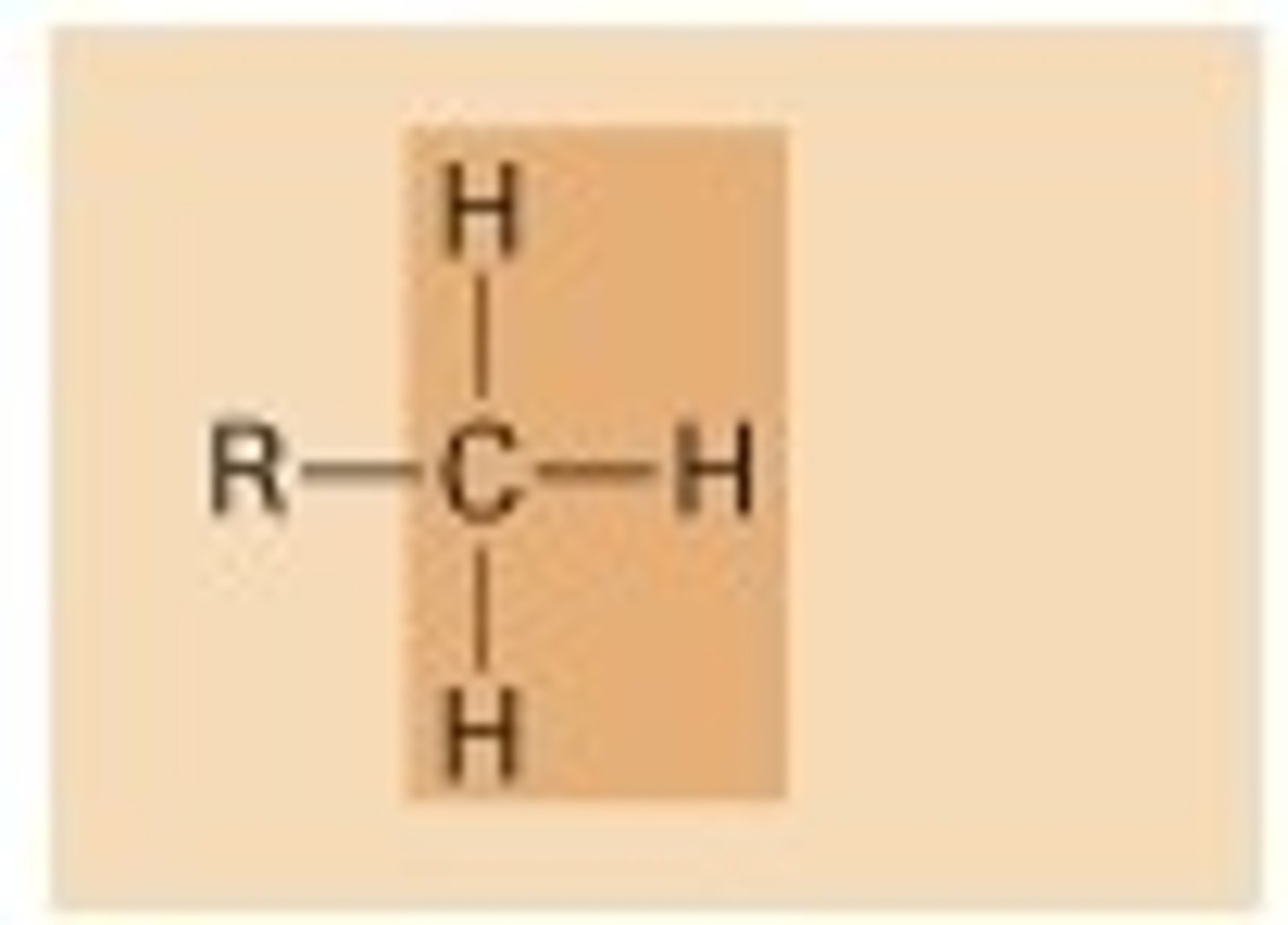
methyl
-expression of genes
-sex hormones (shape and function)
carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins
what are the 4 types of macromolecules?
carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids
which macromolecules are made of polymers?
lipids
-diverse group of hydrophobic macromolecules
-built from two or more DIFFERENT small subunits
dehydration reaction
removal of water molecules to form a polymer (makes a bond)
hydrolysis
addition of water to polymers to break bonds
carbohydrates
sugars and their polymers
monosaccharide
single monomer, form rings in aqueous solutions
disaccharide
2 monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkage
(covalent bond)
polysaccharides
polymers of 100s and 1000s of monosaccharides
(connected by glycosidic linkage)
starch and glycogen
what forms of energy storage are in plants and animals?
fats, phospholipids, and steroids
what are the 3 types of lipids?
ester linkages
what types of bonds are in fats and phospholipids?
saturated and unsaturated
what forms do fats come in?
saturated fats
-No C=C double bonds
-more dense
unsaturated fats
-C=C double bonds
carbohydrates
fuels cellular respiration
polyunsaturated fat
more than one unsaturated carbon bond
polyunsaturated fat
fat that reduces cholesterol in blood and lower the risk of heart problems
9
how many calories is in 1 gram of fat? (all fats)
phospholipids
glycerol+ two fatty acids+ phosphate group+ choline
-hydrophilic head
-hydrophobic tail
steroids
carbon skeleton with 4 rings and varying functional groups
cholesterol
molecules that stabilize membrane fluidity
proteins
-one or more polypeptide with specific 3D conformation
-support, storage, transport, signaling, receptors, movement, catalysis, defense
polymer of amino acids to polypeptide
what is the structure of proteins?
amino group, hydrogen and carboxyl
what are composed in the structure of amino acids?
r-group
variable side chain
covalent bond
what type of chemical bond joins a functional group to the carbon skeleton of a large molecule?
they release a water molecule
what happens when 2 monosaccharides join to make a disaccharide?
serine, threonine and tyrosine
what can be replaced by a phosphate group?
no
is a fatty acid a monomer?
peptide bond
bond that connects carboxyl and amino group to make amino acid
N terminus
what is the amino end of a polypeptide?
C terminus
what is the carboxyl end of a polypeptide?
primary structure
the amino acid sequence and its shape
secondary structure
hydrogen bonding in the backbone, makes fold and coils (alpha helix-coils) (beta pleated sheets-folds)
tertiary structure
dependent on 1st and 2nd, R group interactions
-disulfide bridges (strong)
-H bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic, & van der waals interactions (weak)
quaternary structure
-two or more polypeptides
-stabilized by interactions between the R groups
single base change in DNA and RNA and amino acid change in protein
sickle cell anemia is caused by
changes in shape of cell does not allow H to travel easily
what happens what there is a sickle cell anemia mutation?
pH, high salt concentration, and temperature
denaturalization
chaperone proteins
-promote proper folding and refolding by providing cell with proper environment
-found throughout the cell
ubiquitin
damaged proteins are tagged with this to be recycles
proteasome
where ubiquitin leads tagged proteins and gets chopped into proteins
DNA and RNA
what are the two types of nucleic acids
store and transmit hereditary information
what functions do nucleic acids perform?
pentose sugar, nitrogen base, and phosphate group
what make up a nucleotide monomer?
sugars, DNA has thymine, and RNA has uracil
what is the structural different between DNA and RNA?
purines
guanine and adenine are...
2
how many rings do purines have?
pyrimidines
cytosine, thymine, and uracil are...
1
how many rings do pyrimidines have?
phosphodiester linkage
for nucleotides
A-T because it has 3 hydrogen bonds
what DNA bond is stronger and why? (A-T or C-G)
DNA (nucleotides) to transcription to mRNA (nucleotides) to translation to protein (amino acids)
Information flow in cells
hydrogen bonds
the strands and bases of DNA are held by
lipids, proteins and carbohydrates (all MACROmolecules except for nucleic acids)
what is the plasma membrane composed of?
amphipathic
molecule has two domains (one hydrophobic/hydrophilic side)
forms the bilayer
what do lipids do in P.M.?
regulates traffic
what do proteins do in P.M.?
cell to cell recognition, glycoproteins and glycolipids
what do carbohydrates of in P.M.?
heads up, tails down
what is the direction of the phospholipids?
weak hydrophobic interactions?
what is the plasma membrane held together by?
cholesterol
stabilizes the membrane fluidity