04.1B BIO Homeostasis & Feedback Loops (PART B)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions
Variable
Any factor in the body that can change (temperature, concentrations of chemicals, etc.)
Set point
The normal range of a variable
Stimulus
Any change to a set point that is maintained in the body
Receptor
Detects changes in temperature, chemicals, water, touch, pressure, pain, etc.
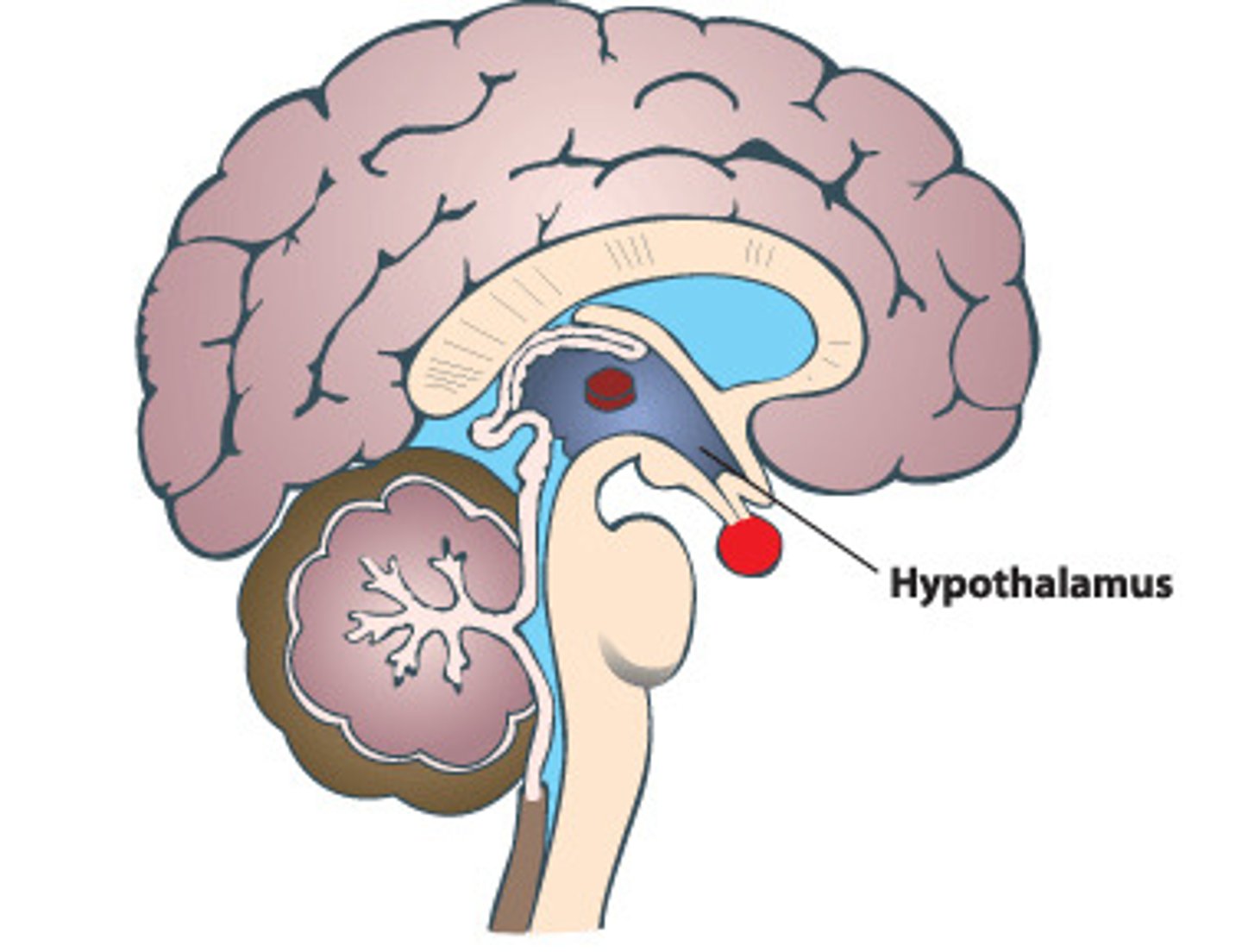
Control Center
A region in the brain called the hypothalamus analyzes the information recieved from receptors and then determines the appropriate response or course of action
Effector
Organs, glands, tissues or cells that maintain the body's homeostatic set points
Response
The action taken by an effector to bring about homeostatic balance
Feedback
Always the opposite of the stimulus; receptors receive feedback when they sense desired changes have been made
Negative Feedback Loop (Description)
Produces a response that opposes the original stimulus and once the desired state is reached the feedback loop shuts off
Negative Feedback Loop (Examples)
Examples include maintaining body temperature and blood sugar levels
Positive Feedback Loop (Description)
Increases the initial stimulus during childbirth, lactation, blood clotting to amplify the response
Positive Feedback Loop (Examples)
Examples include labor contractions (birth), production of milk when nursing a baby, and blood clotting
Homeostatic Imbalance results in
Disease, illness and possibly death
Afferent pathway
The nerve pathway sending an electrochemical message from the receptors to the control center (hypothalamus of brain).
Efferent pathway
The nerve pathway sending an electrochemical message from the control center (hypothalamus of brain) to the effectors (muscles and glands).