Atmospheric system
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what are the 4 layers of the atmosphere?
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere
properties of the troposphere
extends 8-10km above poles and 15-17 above equator
temps decrease from 25° at ground level to -40 to 80 towards the top
most weather processes occur here
properities of the stratosphere
10-50km above surface
lower temps constant then increase with altitude
due to solar radiation at the top
features ozone layer which filters out harmful UV radiation
very little water vapour, dust, and clouds
properities of the mesosphsere
extends between 50-80km above surface
temps fall rapidly (low as -90C) with elevation because there is no water vapour, cloud, or dust to absorb incoming radiation
wind velocities reach up to 3000km/hr
properties of thermosphere
atmosphere becomes thinner with elevation
temps rise rapidly (high as 1500C) due to more oxygen in the air, which absorbs incoming radiation
what are the boundaries between each layer called
tropopause, stratopause, mesopause,
what is insolation
amount of short wavelength solar radiation received from the sun
what is albedo
the percentage ratio between incoming radiation and the amount reflected back into space
what is terrestrial radiation
cool, long wavelengths of energy emitted by Earth
what is the natural greenhouse effect
a natural process that warms Earth’s surface as water vapour and CO2 absorb terrestrial radiation
what is diffuse radiation
the scattering of solar energy when it hits a molecule of gas which still reaches the Earth’s surface
what are jet streams
extremely fast moving air, reaching up to 230km/hr
located in the troposphere
helps rapidly transfer heat energy
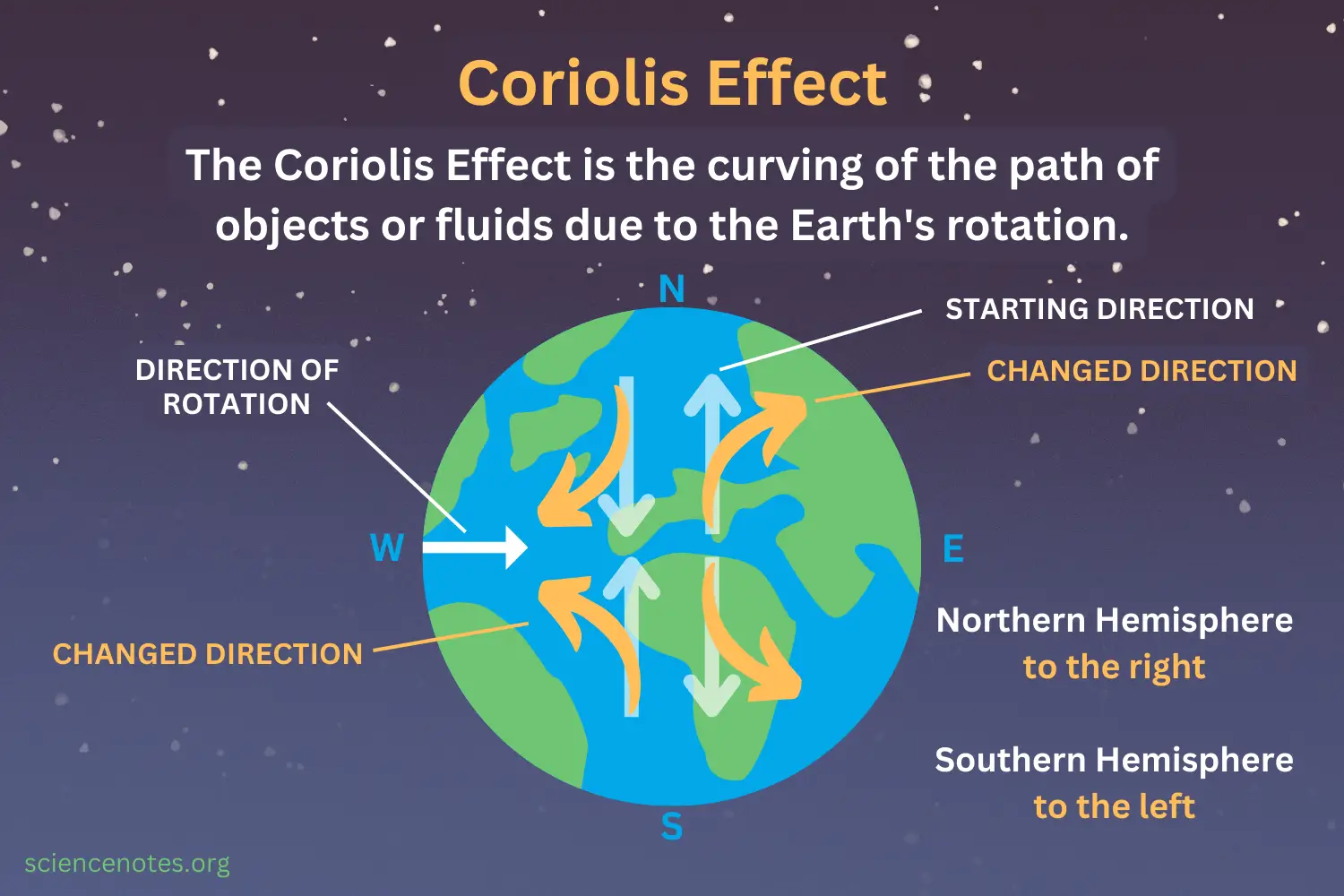
what is the Coriolis effect?
the curving of an objects or fluids path due to the Earth’s rotation
Features of the hadley cell
occurs at 30° north and south
descending air at equator causes high pressure system
clear skies and dry, stable conditions
Trade winds move air back towards equator to replace rising air
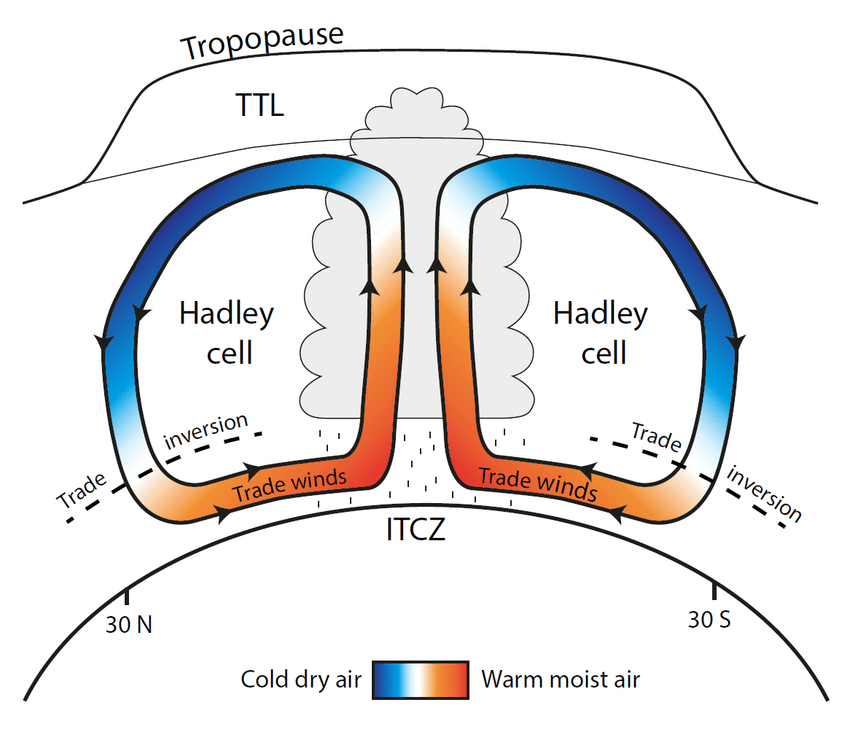
features of the ferrel cell
some of the warm, dry air from Hadley cell continues towards the poles, picking up moisture from the ocean
meets cold air from the poles at 60° north and south
this caused the warm, moist air to rise, creating a low pressure system and thus unstable weather
features of the polar cell
at the poles, air is cooled and sinks, forming a high pressure system called the Polar Highs
cold air moves away from the poles until it meets the warm air of the Ferrel cell
which way do high and low pressure systems spin in the southern hemisphere
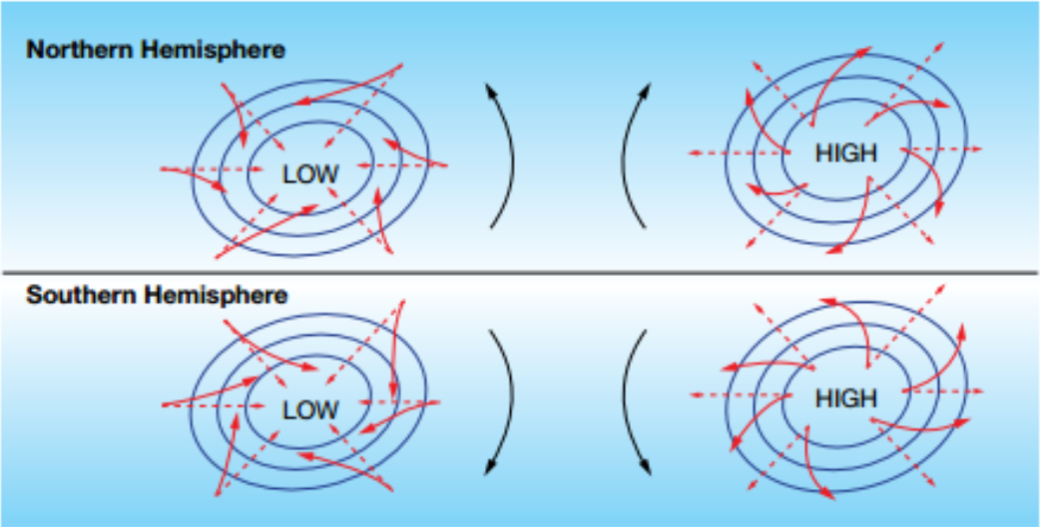
features of low pressure systems
called cyclones, and it has;
formed over warm topical water
water ocean → evaporation → clouds → low air pressure pulls clouds in and they begin to rotate
the ‘eye’ is the center and is calm due to cool sinking and is generally 40km but ranges from 10-100km
light wind and clear skies
cyclone gets weaker and fades out over land because it doesn’t have warm water to evaporate
isobars are spaced closely together
consists of warm, rising air
produces windy, rainy, and unstable weather
features of high pressure system
called highs or anticyclones
isobars are spaced widely apart
consists of cold, descending air
produces stable and dry weather
insolation variations
latitude
earth’s revolution and rotation
length of day and night
atmosphere components
distribution of continents and oceans
topography
what does a synoptic chart/weather map do
records atmospheric conditions in a particular place at a particular point in time
provides air pressure, location of air masses, extent of cloud cover, wind speed and direction, and rainfall
the lines on synoptic charts are called isobars, which are lines of equal amount of barometric pressure
signs of a low pressure system on synoptic chart
isobars close together
hPa less than 1013
literally says LOW
signs of high pressure system in synoptic charts
isobars far apart
hPa higher than 1013
literally says HIGH