G6 - The Living World
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Ecosystem
The living organisms in a particular area, together with the non-living components of the environment.
What are examples of living components in an ecosystem?
Flora
Fauna
Bacteria
What are examples of non-living components in an ecosystem?
Climate
Soil
Water
Climate - affecting ecosystem
The temperature and amount of rainfall are very important in determining which species can survive in an ecosystem.
Soil - affecting ecosystems
The soil type is important as this provides nutrients that will support different plants.
Water - affecting ecosystems
The amount of water available in an ecosystem will determine what plants and animals can be supported.
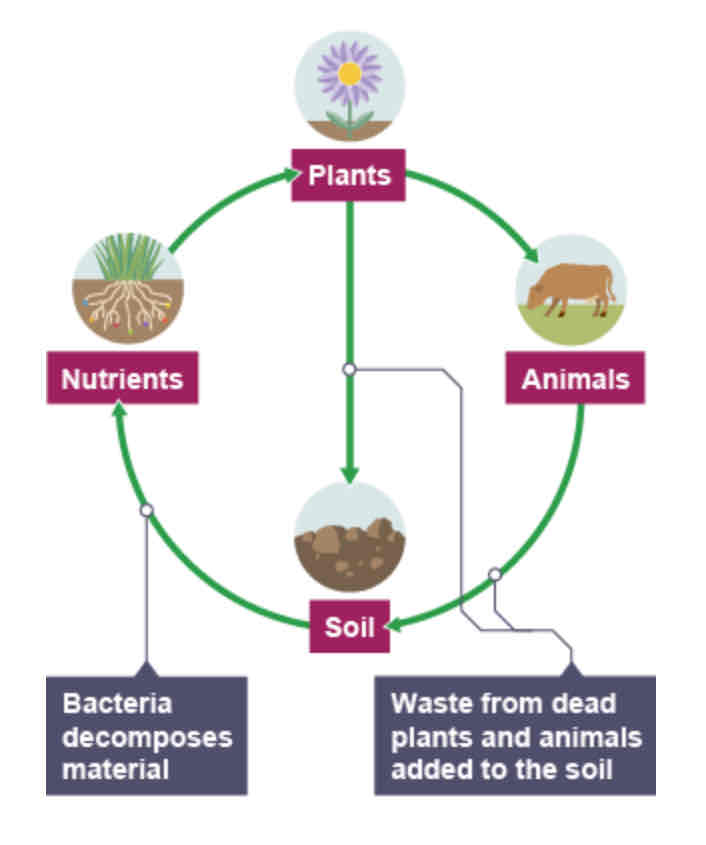
The biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem have a ______ relationship.
complex
Simple ecosystem diagram
What is a common ecosystem in the UK?
The freshwater pond ecosystem
What does the freshwater pond ecosystem consist of?
Pond Bottom - very little oxygen/light, so decomposers and scavengers live here
Mid water - fish are main predators here, food is found on the pond bottom/surface. Animals breathe through their skin/gills
Pond surface - animals here breathe through their gills, skin or lungs. Animals include: ducks, tadpoles.
Pond margin - plants provide a sheltered habitat for insects and small animals, eg. Frogs, lots of light and O2.
Above the pond surface - birds eg. Kingfishers and insects eg. Dragonflies are common here.
The freshwater pond ecosystem is finely _______.
This is because…
Balanced
Because of the food chain and food web.
Food chain
A sequence if feeding relationships between organisms, showing the transfers of energy through trophic levels.
Food web
A network of food chains, showing how they all link together.
What is passed on in a food chain?
Energy and nutrients, from one organism to the next.
Producer
Plants that begin food chains by making energy from carbon dioxide and water.
Ecosystems are/are not sensitive to change.
Are
What natural factors may cause changes to ecosystems?
Drought
Flood
Fire
Disease
What human management may cause changes to ecosystems?
Fish stocking (introducing more fish)
Altering drainage of land (influences amount of water)
Changing pH of water
Altering nutrient levels of water if fertilisers are leached into water → results in eutrophication
Eutrophication
‘Hyper-nutrition' resulting from fertiliser pollution of aquatic ecosystems.
Leached
When nutrients are washed out of the soil by heavy rainfall.
What can changes to the ecosystem lead to?
A negative impact, and possibly a collapse of a food chain.
Biomes
A large-scale ecosystem.
What is the distribution of biomes determined by?
Climate
What factors determine the climate of a place?
Latitude
Air pressure
Winds
In lower latitudes, temperatures are ____.
high
eg. around the equator, latitude is 0*.
In it her latitudes, temperatures are ____.
Low
Eg. polar regions
Why do temperatures drop the further an area is from the equator?
Due to the curvature of the Earth.
Why are temperatures higher near the equator?
Sunlight has a smaller area of he atmosphere to pass through (due to the curvature), and so the sun’s rays are concentrated in a smaller area.
Why are temperatures lower near the poles?
Sunlight has a larger atmosphere to pass through and the sun is at a lower angle in the sky. This means more energy is lost, ans the temperatures are cooler.
Low-pressure areas are created when the air ____.
rises
At what height is low and high pressure? Why?
Air near the ground is at high pressure because it is experiencing the force of the column of air above it. The air high up in the sky has much less air pressure.
Low pressure areas are associated with…
Clouds
Precipitation
Why are low pressure areas associated with precipitation?
As air rises it cools, condenses and forms clouds
Water droplets in clouds increase in size
Eventually they become too heavy o be held, and fall as precipitation
Does the equator experience rainfall? Why/why not?
Yes - very high amounts.
The air there is hot and so it rises, creating an area of low pressure. This means it experiences high amounts of rainfall, resulting in a warm and wet (humid) climate, and tropical rainforests.
What weather conditions are associated with high pressure?
Dry
Warm
Why do high-pressure areas result in dry weather conditions?
The pressure is high and the air sinks, so it does not result in precipitation.
Where does air sink after rising from the equator?
30° North and 30° South of the equator. This creates areas of high pressure in these zones.
What biomes occur at 30° north and 30° south of the equator?
Hot desert climates, eg. Sahara and Kalahari deserts.
What biomes occur at the equator?
Tropical rainforests
Winds blow from areas of high → low pressure.
True or false?
True
They blow from areas of high → low pressure.
How are different global climatic zones created?
As the winds are transferred from high → low pressure, they are transferred from where they are sinking → where they are rising. This continual transfer of winds maintains the pressure belts of high and low pressure, creating different global climatic zones.
Pressure belt
A band of high or low pressure found approximately 30° north and 30° south of the Equator.
Map of global distribution of ecosystems
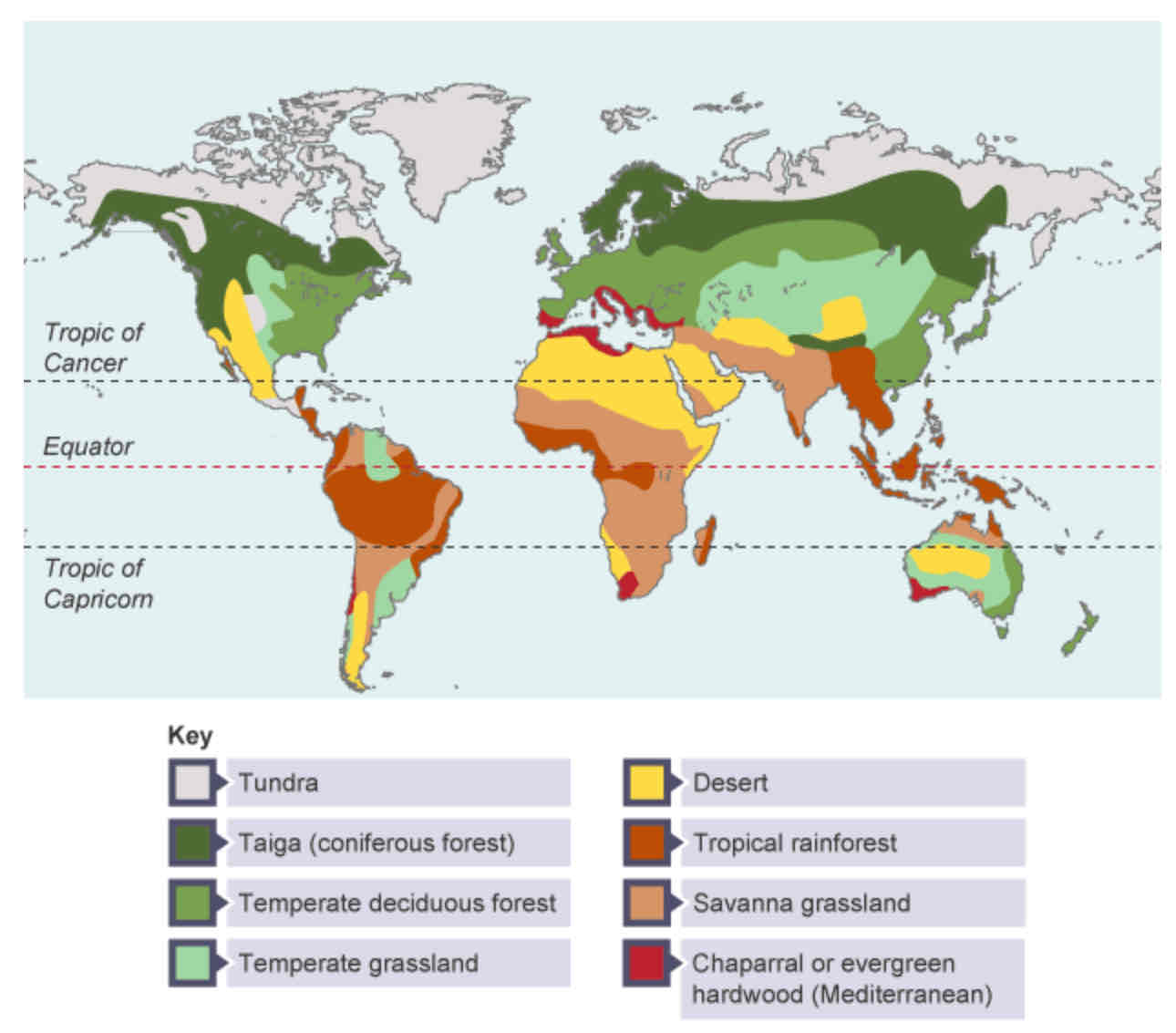
Tundra - characteristics
Near North and South poles
Very few plants and animals can survive here
Taiga is also known as…
…coniferous forest.
Taiga - characteristics
Evergreen trees thrive in this cool temperature climate
Found in Scandinavia, Russia and Canada.
Temperate deciduous forest - characteristics
Trees lose their leaves every year and thrive in mild and wet conditions known as temperate maritime climate.
Found across Europe and in the USA.
Temperate grasslands - characteristics
Consists of grass and trees that thrice in a temperate continental climate or moderate rainfall and mild conditions.
Found in Hungary, South Africa, Argentina and the USA.
Chaparral is also known as…
…evergreen hardwood or the Mediterranean.
Evergreen hardwood - characteristics
Found around the Mediterranean Sea, around Perth and Melbourne in Australia and California in the USA.
Desert - characteristics
Conditions are hot and dry.
Plants and animals specially adapted to survive in the harsh conditions.
Found near the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
Tropical rainforest - characteristics
Climate is hot and humid.
Many different species can be found here.
Found near the equator.
Savanna grassland - characteristics
Hot and dry conditions.
Long grasses and a few scattered trees are found here.
Found mainly in central Africa, southern India, northern Australia and central South America.
Distribution of ecosystems between the equator and the poles - diagram
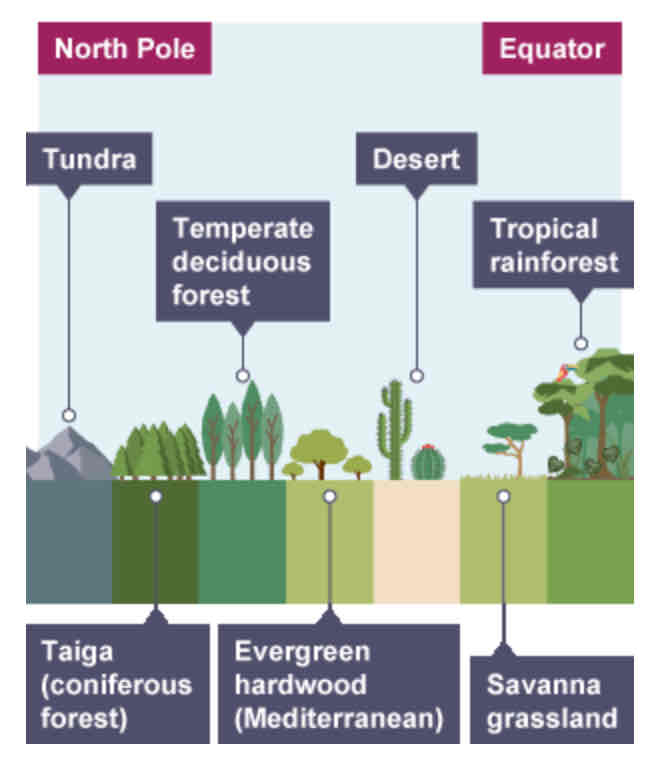
Tropical rainforests have distinct characteristics that support a wide/small variety of species.
This means…
Wide
This means they have a high biodiversity.
Do the biotic and abiotic components in the tropical rainforest depend on one another?
Yes - a change in one leads to a change in the other.
Tropical rainforest - climate (5)
Very wet - over 2000mm rainfall/year
Very warm with average daily temperature of 28°C.
Temperature never falls out of the range of 20-35°C.
Atmosphere is hot and humid.
The climate is consistent all year round - no seasons.
Tropical rainforest - soil (4)
Most soil is not very fertile.
A thin layer of fertile soul is found at surface, where dead leaves decompose.
Red in colour as it is rich in iron.
Nutrients are washed out of soil due to heavy rainfall.
Tropical rainforest - Plants and animals (3)
Warm and wet conditions are perfect for plant growth.
Wide range of species supports many different animals, birds and insects.
Species have adapted to rainforest conditions, eg. trees and plants have shallow-reaching roots to absorb nutrients from the thin layer of fertile soil.
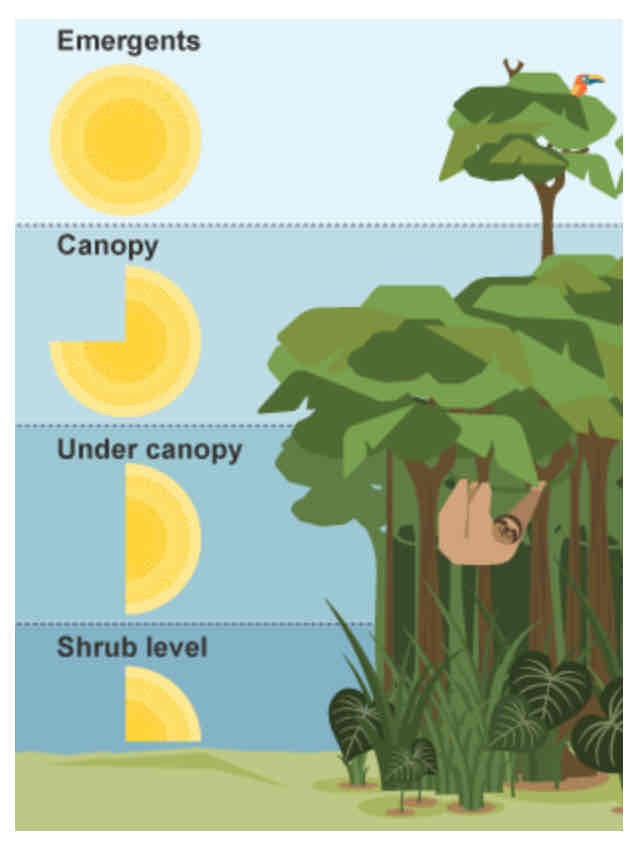
Structure of a tropical rainforest
Ground level
Shrub layer
Under canopy
(Main) canopy
Emergents
Plant adaptations in tropical rainforests
Lianas
Tree trunks
Drip tips
Buttress roots
Epiphytes
How are lianas an adaptation for the tropical rainforest?
These are woody vines that have roots in the ground but climb up the trees to reach sunlight. Their leaves and flowers grow in the canopy.
How are tree trunks an adaptation for the tropical rainforest?
Tall and thin, to allow trees to reach sunlight. The bark on these is smooth to allow water to flow down to the roots easily.
How are drip tips an adaptation for the tropical rainforest?
The leaves have pointy tips, allowing water to run off the leaves quickly without damaging/breaking them.
How are buttress roots an adaptation for the tropical rainforest?
Large roots growing above the forest floor to absorb nutrients on the ground’s surface.
Have ridges, creating a large SA to support larger trees.
How are epiphytes an adaptation for the tropical rainforest?
These are plants living on branches of trees in canopy. They get nutrients from air and water, not soil.
Animals adapted in tropical rainforests
Sloth
Spider monkey
Flying frog
Toucan
How are sloths adapted to the tropical rainforest?
Use camouflage and move slowly, making themselves difficult for predators to spot.
How are spider monkeys adapted to the tropical rainforest?
Long, strong limbs to help climb through rainforest trees.
How are flying frogs adapted to the tropical rainforest?
Fully webbed hands and feet and a flab of loose skin between its limbs. This allows it to glide from plant to plant.
How are toucans adapted to the tropical rainforest?
Have a long, large bill so it can reach and cut fruit from branches too weak to support its weight.
Example of tropical rainforest experiencing a threat…
Amazon Basin, experiencing threat of deforestation.
Deforestation - causes on Amazon Basin rainforest
Farming
Logging
Mining
Roads
Population
Deforestation - how is it caused by farming?
Large areas are caused for pastoral farming. Cattle farms are opening in Amazon Basin for beef farming. Arable farming is responsible for loss of tropical rainforests as many farmers clear land to grow cash crops.
Pastoral farming
When animals are reared, eg. cows for their meat.
Arable farming
When crops are grown.
Cash crops
Crops which are sold for profit.
Deforestation - how is it caused by logging?
Valuable trees like mahogany can be accessed/sold for timber, to make furniture.
Deforestation - how is it caused by mining?
Amazon Basin is rich in natural resources such as iron ore, copper, tin, aluminum, magnanese and gold, so mines have been developed.
Deforestation - how is it caused by roads?
Access of roads for farmers/loggers/miners results in large parts of tropical rainforest being destroyed.
Deforestation - how is it caused by HEP stations?
Creation of HEP stations in the Amazon Basin has resulted in large areas of forest being flooded to create reservoirs and dams, flooding miles of tropical rainforest.
Flooding of Balbina dam in Brazil resulted in the loss of 920 square miles of tropical rainforest.
Deforestation - how is it caused by population?
Population growth → land cleared to build houses and infrastructure → loss of tropical rainforests
Impacts of tropical rainforest loss…
Soil erosion
Loss of biodiversity
Climate change
Economic development
How does deforestation = soil erosion?
Soil is left bare after deforestation, and when it rains, nutrients in soil are washed away, and nutrient cycle stops as there are no plants or trees shedding leaves to replace nutrients in the soil.
Soil becomes infertile.
How does deforestation = loss of biodiversity?
Many species die as their habitats are destroyed, and as animals are closely connected through the food web, other species will also die. This leads to lack of biodiversity.
How does deforestation = climate change?
Trees/plants absorb CO2 through photosynthesis, so less plants means less CO2 removed from the atmosphere, leading to heightened global warming.
How does deforestation = economic development?
Creation of mines, farms and roads leads to economic growth as they create profit and allow a country to generate foreign income, which can be used to pay off debts or be invested in development of country.
Tropical rainforests - ways to control deforestation
Selective logging only mature trees, then replanting. Means younger trees have more space/sunlight to grow
Educating people on benefits of biodiversity
Ecotourism, encouraging sustainability, while generating money (to be used on improving environment) and jobs
International agreements to protect tropical rainforests made through debt-for-nature swaps
Debt-for-nature swaps
Part (or all) of debt is cancelled by one country if the debtor country agrees to ensure the conservation of its tropical rainforests.
What is an example of a case study for sustainable management?
Malaysia
What have the Malaysian government done to conserve tropical rainforests? (7)
Implemented the following policies:
Public awareness of value of tropical rainforests
Local communities involved in forest conservation projects
Alternative timber sources eg. Rubber trees
Selective Management System
Ecotourism promoted in tropical areas
Permanent forest estates created, where no change of land use is allowed
National parks created to protect biodiversity.
Selective Management System
The selective logging of mature trees over a 40-year cycle to ensure that trees have time to re-establish themselves.
Where are hot desserts found?
Near the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn
Which is the largest hot desert?
Where is it located?
Sahara
in Africa
Where does the Sahara cover Africa?
Spans the whole width of the continent
Hot deserts have an _________ climate and a __________ environment.
extreme
challenging
Is there a lot of biodiversity in hot deserts?
Why?
No, because of the harsh climate.
Few species are specialised enough to survive there.
What has happened to the plants and animals which live in the hot deserts?
They have adapted to the difficult conditions.
What is the relationship between biotic and abiotic factors?
They rely on each other - a change in one causes a change in the other.
Hot deserts - Climate
Hot days - summer temps can be 40°C+
Cold nights - can be less than 0°C
Dry - less than 250mm rainfall annually
2 distinct seasons - summer and winter.