Development 3: Social Development
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are the three primary reasons attachment forms?
1. To meet basic survival needs (food, safety) → who are the people who will provide me with basic survival needs?
2. To learn from others → who do I learn information such as social norms from?
3. To receive emotional comfort → who will reliably provide me with emotional comfort?
What is attachment?
Emotional and social bond that forms between individuals; in infants, typically measured between child and caregivers, while in adults measured between individual and partners and friends.
What did the Wire Mother Experiment demonstrate about attachment?
Baby monkeys preferred the cloth mother (comfort) over the wire mother (food), showing emotional security is more important than physical sustenance alone.
Wire mother monkeys showed atypical and problematic social behaviors later in life. (Though monkeys raised by cloth mother still have social development issues but to less of an extent)
What did research on Romanian orphanages show about attachment?
Children who received only physical care but not emotional support developed significant social and emotional difficulties.
Upon their eventual adoption and release from the orphanage, many children showed significantly dysfunctional behaviour during social situations.
These effects were minimized if children were taken out of the orphanage early enough.
What is the Strange Situation task?
A behavioral test that examines children's attachment style by observing reactions to caregiver departures and returns.
The child spends some time playing with an experimenter with the caregiver present.
2. The caregiver then leaves the room for a few minutes, and the child’s reaction is observed.
The caregiver then returns and the child’s reaction is again examined.
Reactions at phase 2 and 3 are used to determine attachment “style”.
Describe the characteristics of secure attachment.
Some distress when the caregiver leaves
Calms down when the caregiver returns
Found in 60-70% of children
Describe the characteristics of avoidant attachment.
- No visible reaction when the caregiver leaves or returns
Describe the characteristics of anxious (ambivalent) attachment.
- Extreme distress when the caregiver leaves
Continued distress when the caregiver returns
Describe the characteristics of disorganized attachment.
- Inconsistent or contradictory behavior that does not fit into the other categories
Found in <5% of children
How do parenting styles influence attachment?
Secure attachment: Consistent, empathetic parenting
Insecure attachment: Parental conflict, inconsistent responses, and non-empathetic reactions (E.g., unpredictable routines, rewards and punishments for same behaviour)
How does temperament influence attachment?
Children with high emotional reactivity (temperament) can influence parental responsiveness, creating a feedback loop in attachment development.
What is the socialization-selection effect in adult attachment?
- Early attachment is influenced by socialization (parenting and environment).
Adult attachment is more influenced by personal experiences and selected environments.
What is the False Belief (Sally-Anne) Task?
A test measuring whether children understand that others can hold beliefs different from reality.
children are told a story about Sally who hides a toy in a basket and leaves the room; Anne comes in and moves the toy from the basket to a box. When Sally returns, where will she look for the toy?
Children typically pass the task at 4.5-5 years old
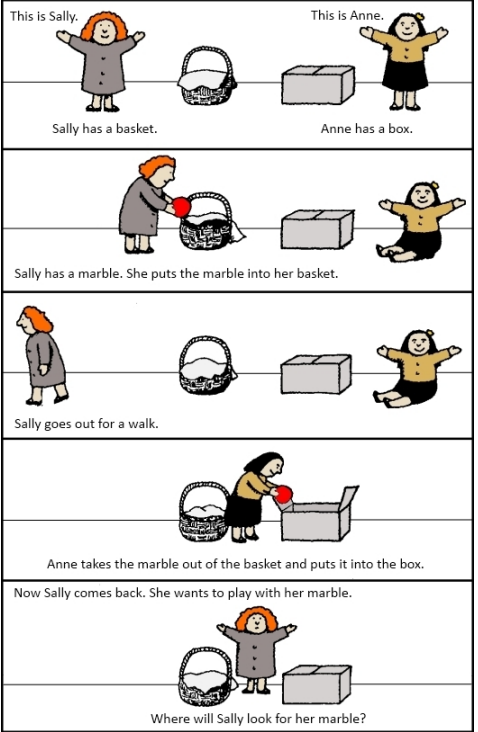
What is a major criticism of the False Belief Task?
It may be too complex; younger children may understand false beliefs but struggle to express it.
What evidence suggests theory of mind may develop earlier than 4.5 years?
Studies using looking-preference tasks show 2-year-olds anticipate the correct answer even if they verbally fail the task.
What is the Helper/Hinderer Infant Experiment?
Infants watch a helpful character and a hindering character, then choose which one they prefer.
What do results of the Helper/Hinderer Infant Experiment show?
By 6 months, infants prefer the helper, suggesting early prosocial tendencies.
What does the Transgressions Task reveal about children's lying behavior?
Transgressions task: children are given an opportunity to secretly cheat to win a prize (most children do), and we then ask if they cheated or not.
- At age 2, ~30% of children lie about cheating.
By age 3-4, ~80% of children lie when their desires conflict with social norms.
What is the current consensus on morality in children?
Children have innate prosocial tendencies (helping, empathy).
They are highly influenced by social norms and rewards.
In-group biases and cultural influences shape their moral development.
children become increasingly aware of their own desires and willing to sacrifice prosocial norms to reach these desires
The transgressions task is a(n):
a) Experiment
b) Instrument
c) Longitudinal study
d) Cross-sectional study
b) is correct → situation where we have something that we’re measuring; not an experiment with independent variables
Task itself is an instrument on how we collect this data