Blood Bank Final Exam
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
What are the three ways you can do a crossmatch?
- Instant spin
- AHG
- Electronic
What is the weak D phenotype?
a quantitative reduction in the amount of D antigen on a RBC
---- no antibody made/normal D epitope -----
What is the partial D phenotype?
a qualitative change in the expression of the D epitope or missing parts of the D epitope
What happens in the "regulator pathway" that forms a Rh Null phenotype?
There is a mutation in the RHAG gene and/or RhAG protein, so even though the RHD and RHCE genes are normal their proteins do no get expressed
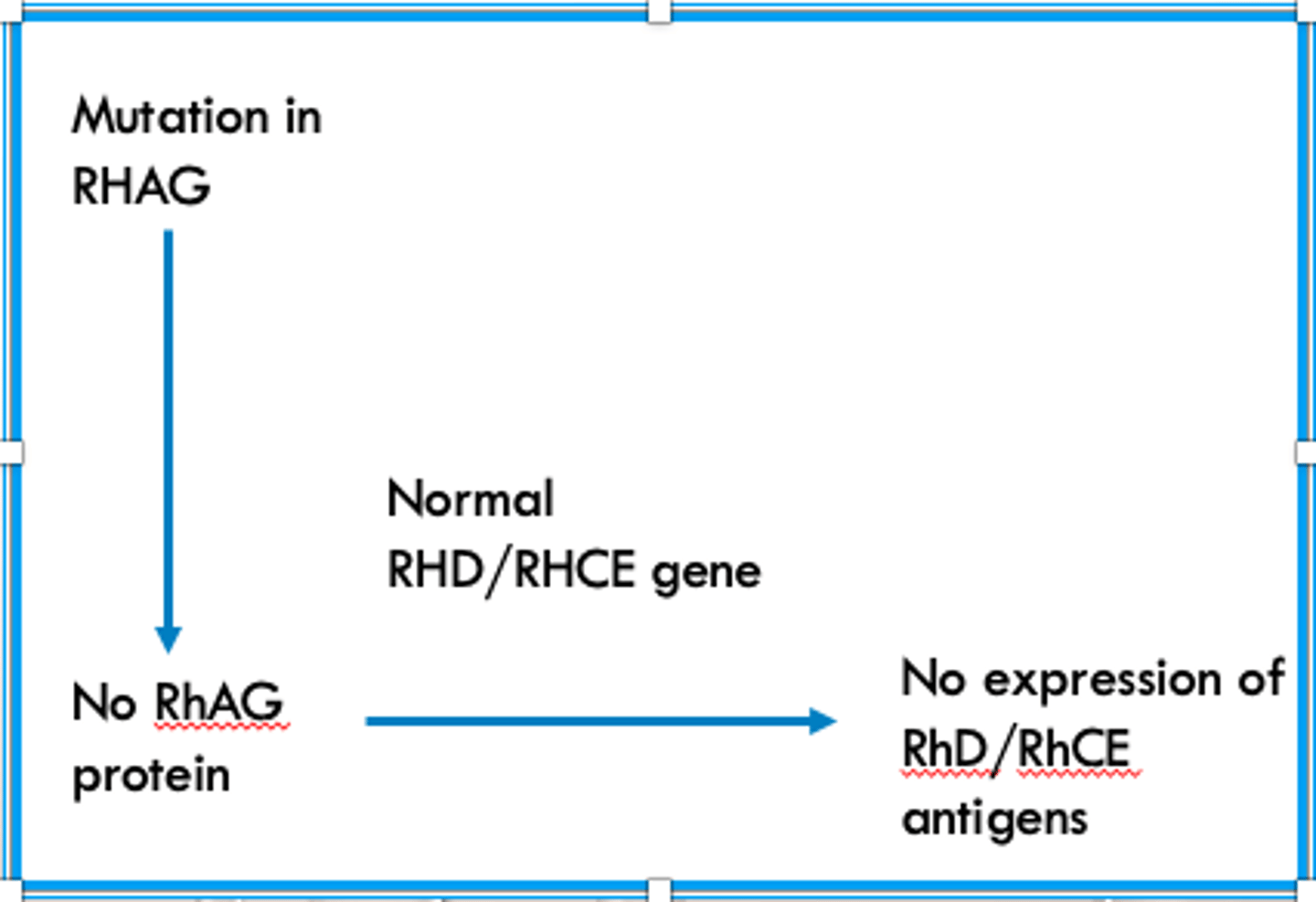
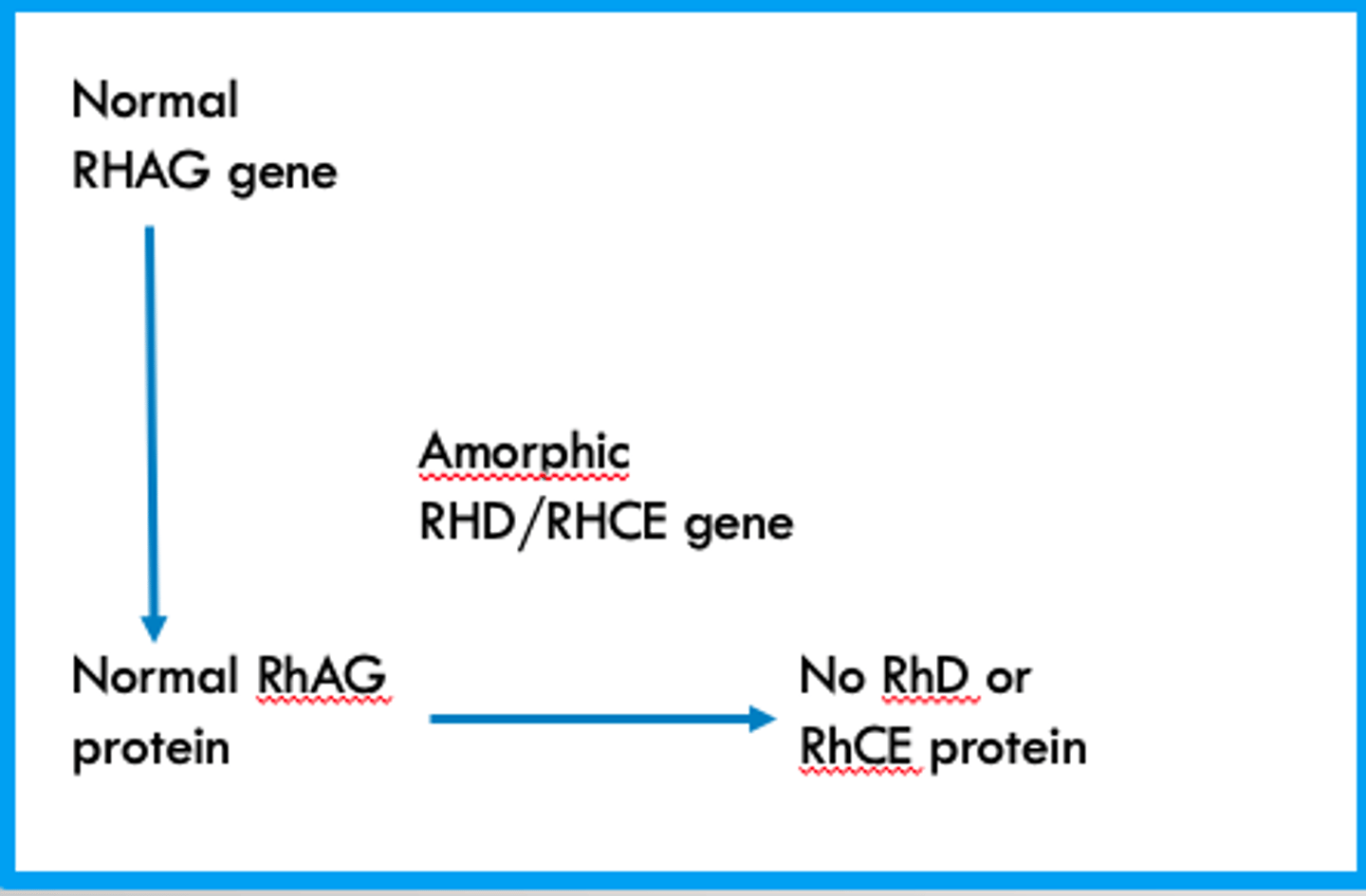
What happens in the "amorph pathway" that forms a Rh Null phenotype?
The RHAG gene and Protein are normal and functioning correctly but a mutation in the RHD/RHCE genes results in their proteins not being expressed
weak expression of Kell BGS antigens due to point mutations in the KEL gene
Kmod
weak expression of Kell BGS dues to the lack of XK protein
McLeod phenotype
What null phenotype can be found in Polynesians and Pacific Islanders?
JK (a-b-)
What null phenotype is found in the African American population? What evolutionary advantage comes with it?
Fy (a-b-)
Resistant to Plasmodium vivax
What is the F antigen?
- present when c and e antigen are present (r and R0)
- anti-f is often seen with anti-e and anti-c
What is the G antigen?
Present when either D or C are present
What is the clinical significance of G antibodies?
•Patients with anti-G should receive units negative for D and C antigens
•Pregnant women with anti-D and -C should be investigated for anti-G. If it is only anti-G, they are still candidates for RhIg.
What pre-analytical factors are required for pre-transfusion testing?
- Full name, MRN, and DOB should be on tube and easy to read
- Must be able to obtain the time of draw, date of draw, and the initials of the person who drew it
- SAMPLE MUST BE LABELED BEDSIDE
What does AHG bind?
The Fc portion of IgG
List characteristic components of a DAT
- In-vivo
- Testing patient RBC's
- No enhancement used
- AHG
- Validate negative results with check cells
List characteristic components of a IAT
- In-vitro
- Testing patient plasma/serum
- Liss commonly used for enhancement
- IS → 37 → AHG
- Validate negative results with check cells
What is used to neutralized α-ABO ?
Saliva
What is used to neutralize α-Le ?
Saliva
What is used to neutralize α-P ?
Pigeon Egg Whites
What is used to neutralize α-Sda ?
Urine (Tamm-Horsfall)
What is used to neutralize α-Ch/Rg ?
Fresh Plasma
What transferase does the AA/AO gene code for? What is the sugar?
N-Acetylgalactosaminyl transferase
N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine
What transferase does the BB/BO gene code for? What is the sugar?
Galactosyl transferase
D-Galactose
What transferase does the AB gene code for? What is the sugar?
Both N-Acetylgalactosaminyl transferase and Galactosyl transferase
N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine and D-Galactose
Which antigens have IgM antibodies?
ABO, H, Lewis, Lu
Which antigens have IgG antibodies?
Fy, Kell, Kidd, MN, Rh
Which antigens are carbohydrates?
H, I/i, Lewis
Which antigens are proteins?
ABO, Fy, Kell, Kidd, Lu, Rh
Which Duffy is most common in white people?
Fy (a+b+)
Lack of H or h + lack of Se =
Bombay
Lack of H or h + functional Se =
Para-Bombay
What does the H gene code for? What is it's function?
L-fucosyltransferase which transfers L-fucose on the terminal end of PS2
In regards to the I/i antigens, virtually all adults are ____ and babies are ___
Adults = I
Babies = i
What are the most common haplotypes of the Kell BGS?
k, Kpb, Jsb
These antigens are rich in disulfide bonds
Kell antigens
What are the three antigens of the Kidd BGS?
Jka, Jkb, JK3
If a person is JK null, they can form _________ which will react with any cell that possesses a JK antigen
α-JK3
How can you differentiate JK null RBC's from normal RBC's?
By using 2M Urea, JK null RBC's will not lyse like normal RBC's
Why do "Kidd's Kill"?
The α-JK3 are known for falling below detectable level and then responding with a very strong anmnestic response
What does the Lewis gene code for?
L-fucosyltransferase that adds a fucose on PS1
Nonsecretor (se) + functional Lewis =
Le(a+b-) in secretions
Secretor (Se) + functional Lewis =
Le(a-b+) in secretions
Pregnant women can transiently type as
Le(a-b-)
What is the most common Lewis antigen formed?
Le(a-b+)
Which Lutheran antigen is high frequency?
Lu(a-b+)
Which antigens can absorb reversibly onto RBC's?
Lewis
Where are M and N located?
Glycophorin A
_______ haplotype is 2x as likely as the ________ haplotype
MS / NS
Where are Ss antigens located?
Glycophorin B
______ will be present if Glycophorin B is, _____ will be present depending on what is inherited
U / S or s
If an individual lacks U, that individual would also lack .....
S and s
U-S-s-
R1 =
DCe
R2 =
DcE
R0 =
Dce
Rz =
DCE
r =
dce
r' =
dCe
r" =
dcE
ry =
dCE
_____________ is essential for RhD and RhCE expression
RhAG protein
_____ is the receptor of the Human Parvovirus B19
P
Early abortions are associated with _____ or _____
α-PP1PK or α-P
Which antibodies are clinically significant?
ABO, Rh, Kell, Duffy, Kidd, SsU, Lu, H
- Thermal range >30C
- Titer >1000
- Reactivity strongly enhanced with albumin
- Anti-I
- Capable of binding complement
- Clinically significant
- Associated with disease
Pathological Autoantibodies
- Mild to life threatening intravascular hemolysis
- Broad thermal range (confirm identity w/ thermal amplitude test)
- Occurs in the elderly
Cold Hemagglutinin Disease (CHD)
- Biphasic
- Intravascular hemolysis
- IgG w/ P antigen specificity
- Most common in children
- Confirm w/ Donath-Landsteiner test
Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria (PCH)
- Penicillin
+ DAT IgG
Drug binds RBC membrane → Induces Ab formation → Abs bind drug on RBC membrane → Extravascular hemolysis
Drug adsorption
- IgG
- Reacts best at AHG
- May activate complement
- React w/ high incidence antigens → mimics Rh allo-antibodies (like α-e)
Warm Autoantibody
- Quinidine and Phenacetin
+ DAT C3
Drug-Immune complex forms → Binds nonspecifically to RBC and activates complement → Intra/Extravascular hemolysis
Immune complex
- Cephalosporin
- Non-immunogenic
+ DAT IgG and C3
Modifies RBC membrane → other proteins adsorb to the cell
Protein adsorption
- Methyldopa
- Neoantigen
- Down regulates normal immune system
+ DAT IgG and C3
Induction of Autoimmunity
Associated w/ ABO incompatible blood
- Febrile
- Abdominal, flank, or back pain
- Pain at transfusion site
- Feeling of impending doom
- Hemoglobinemia, hemoglobinuria
- Hypotension
- Renal failure
- Shock
- DIC
- Positive DAT
Acute Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction (AHTR)
An acute non-immune transfusion reaction caused by transfusion of bacteria-contaminated blood component (mostly platelets)
- temperature spike of ≥2C
- rigors
- hypotension
Transfusion associated sepsis (TAS)
- at least 1C spike in temperature
- Chills, nausea or vomiting
- Tachycardia
- Increase in BP
- Tachypnea
Febrile Non-Hemolytic Transfusion Reaction (FNHTR)
- IgE
- Urticaria
Acute Allergic Reaction
Usually seen in IgA deficient individuals
- Bronchoconstriction (wheezing)
- Angioedema (tongue swelling)
- Diarrhea
- Hypotension, cardiac arrythmia, loss of consciousness, shock, cardiac arrest
Severe Allergic Reacion
Acute non-immune complication due to too much input and not enough output
- Respiratory distress
- Chest tightness
- Hypertension
- Jugular vein distension
- Elevated central venous pressure
- Pulmonary edema, cardiomegaly, distended pulmonary artery
- BNP
Transfusion associated Circulatory Overload (TACO)
Leading cause of transfusion associated fatalities. Caused by α-HLA/HNA (1 hit) or neutrophils damaging pulmonary endothelium in capillaries (2-hit)
- Respiratory distress
- Severe hypoxemia
- Fever
- Hypotension
Transfusion Associated Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)
Replacement of one total blood volume in 24 hours or replacement of 50% of total blood volume in 3 hours
- May see metabolic and coagulation abnormalities
- Hypothermia
- Chelating affects→ tingling, shivering, light headedness, tetany, hyperventilation
- Hyperkalemia
Massive Transfusion (MT)
Due to:
- Newly formed antibody due to exposure
- Anamnestic response
- Positive DAT
Delayed Serologic/Hemolytic Transfusion reaction (DHTR)
A delayed immune response due to an attack by viable donor lymphocytes
- Maculopapular rash
- Fever
- Watery diarrhea, bloody stools, abdominal pain
- Elevated liver function
- Pancytopenia 3-30 days post transfusion
Transfusion Associated Graft vs Host Disease (TA-GVHD)
A delayed immune complication resulting in thrombocytopenia
- Mostly seen in females of child bearing age
- 1-24 days post transfusion
- Sometimes febrile reactions
- Patient must be previously sensitized to human platelet antigens
Post Transfusion Purpure (PTP)
Non-immune complication of transfusion dependency/chronic transfusion
Iron Overload
What is the deferral period for ASA/ASA-drugs/Feldene (aspirin)?
2 full days (>48 hours)
What is the deferral period for Plavix or Ticlid?
14 days
What is the deferral period for Finasteride or Isotretinoin?
1 month
What is the deferral period for Avodart?
6 months
What is the deferral period for Soriatane?
3 years
What is the deferral period for Tegison?
Permanent
What is the deferral period for Human GH or bovine insulin?
indefinite
What is the deferral period for measles, mumps, typhoid, and yellow fever vaccines?
2 weeks
What is the deferral period for German measles (rubella) and chicken pox (varicella zoster)?
4 weeks
What is the deferral period for HBIG and unlicensed vaccines?
12 months
What is the deferral period for Hep B and Flu vaccines?
no deferral
What is the deferral period for someone who had lived in a malaria-endemic area?
3 years
What is the deferral period for someone who has traveled to a malaria-endemic area?
1 year
What is the deferral period for someone who had lived > 3 months in the Uk or who was associated with a military base in certain European countries between 1980 and 1996?
Indefinite
What are the physical requirements to donate blood products?
- Age >16yo
- Not intoxicated or ill
- No rash or evidence of drug use
- >110 lbs
- <99.5 F (37.5C)
- Women: 12.5 Hgb/ >38% Hct
- Men: 13.0 Hgb/ > 39% Hct
Which diseases are screened with questions only?
Malaria, Prions, CJD/vCJD
Which diseases require a look back?
- HBsAg
- HBV DNA NAT
- total anti-HBc