Calcium and Phosphate
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Function Ca2+, Mg2+ PO2- in ECF, Know physiologocal and pathological states for mineral regulation, PTH, calcitriol,calcitonin reg of Ca2+ and PO42-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Calcium summary
Hypocalaemia
Hypocalaemia
PTH secreted
Bone → increased resorption
(both calcium and phosphate released into blood)
Kidney → increase reabsorption PCT
less phosphate reabsorption → increased secretion
Kidney increases 1,25 D3 → increased gut absorption
both reabsorped from gut but phosphate excreted
1,25 D3 → acts on bone (synergistic with PTH)
higher plasma calcium → negative feedback
Parathyroid gland → inhibits PTH secretion
1, 25 D3 → inhibiting PTH secretion
Calcium summary
Hypercalaemia
Hypercalaemia
Calcitonin released (parafollicular C cells)
acts on bone → reduce resorption → less Ca2+ & phosphate released to blod
→ low PTH secretion due to low calcium
hence low phosphate → FGF-23 made
means inactive 24,25DHCC (D3) produced
stimulates PTH inhibition (via phosphate and FGF-23)
bone inhibition
decreases gut absorption → lost to faeces
DCT reabsorption inhibition → decreased transport protein expression
decreased activity of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger basolaterally
PCT influenced by PTH in terms of phosphate but DCT for more calcium reabsorption
Decreased plasma Ca2+ levels
when phosphate higher due to no PTH → FGF-23 broken down
Calcium role
Stabilises excitable cell membranes
Ca²⁺ binds to negative charges CSM → neutralises CSM → less likely small depolarisations reach the threshold potential
Second messenger via ER release
Clotting cascade → CF activation
3 forms
albumin bound
alkaline → Ca2+ bind to albumin (less ionised (H+) molecules in plasma)
acidic → H+ and ions bound to albumin
competition btw anions and cations
complexed → plasma phosphate (least → 10%)
ionised (majority)→ free form → closely regulated (hormones)
Mineral homeostasis
intake = requirement + excretion
high requirements: growth, lactation, pregnancy
more difficult for Ca2+ and PO42- absorbed from GI (Na+ easier)
compartment distribution → deficit uses bone storage → redistribution
mostly kidney excretion
Dietary calcium
upper small intestine absorption (caltriol upregulates absorption)
Calcitriol → expression of Ca2+ binding protein in intestinal cells
inefficient → 80% lost in faeces
lactation → stimulates increased uptake
‘steaming up’ TOO EARLY in dairy cows (leading up to peak lactation)
milk fever = hypocalcaemia
reduced Ca2+ if stimulation too early
diet provides high Ca2+ → PTH and calcitriol never stimulated
Release of Ca2+ from bone
Osteoclasts
release Ca2+ and PO42-
osteoblasts → osteoid → mineralisation
bone turnover = balance
Ca2+ and Kidney
free and COMPLEXED filtered
70% passive cotransport in PCT
high blood pressure → higher GFR → increased Ca2+ excretion
active reabsorption via PTH in DCT
No tubular sectetion
Stones = calcium oxalate or sulfate
free Ca2+ solubility aided by presence of anions (competing for albumin)
Phosphate 1&2
Role → organic molecules → phosphorylation → ATP energy store
urinary buffer
plasma conc not as tightly controlled as Ca2+
high phosphate → less Ca2+ dissolved → form complexes
more solid Ca2+ → mineralisation
Phosphate and Ca2 daily turnover → lost in faeces, urine, milk
or stored in bone
Ca2+ and phosphate close to limit (being complexed) in ECF
soft tissue calcification/precipitation
Protection → calciprotein particle evolution
CPPs trap the minerals in a safe, soluble form → phagocytosis (macrophages + liver) → before deposited in tissue
Kidney failure
more phosphate + fewer factors for suspension → precipitation
vascular calcification → hard to control phosphate
what kills dialysis patients
absorbed → active vit D from diet
bound to proteins (organic phosphate)→ digested before phosphates release → no rise on phosphate after meal
UNBOUND → passive diffusion → rise following meal
Multivalent cation (aluminium) → complexes to phosphate → inhibits phosphate absorption from the gut
After feeding → insulin → glucose phosphorylation
PTH release Ca2+ and phosphate from bone
Renal handling of phosphate & Phosphate excretion rate factors
urine: H+ + monohydrogen phosphate → dihydrogen phosphate → increases pH
Na2HPO4 + H+ → NaH2PO4 + Na
60% phosphate in diet → absorbed active transport → PCT cotransport with Na
Na/K (baslolateral) - maintains electrochemical gradient
normallt in urine
PTH → reduces phosphate transport → more excreted in urine → lowers phosphate plasma levels
load of ions → PTH decreases NUMBER of phosphate transporters in PCT
excess phosphate in filtrate excreted → transporters saturated
high GFR → more excretion
high plasma phosphate → more excreted
but conserves Ca2+ in DCT → promotes reabsorption
Parathyroid tumour → more PO42- excreted
FGF-23 - may become diagnostic marker in mineralised bone disorder with kidney disease
Magnesium 1&2
Major intracellular cation
60% → bone
40% in plasma
protein bound
complexed to small cations (least)
64% free → hydrated cations
Balance not well understood
small intestinal absorption → normally passive
active in ruminants → grass staggers if deficient
Renal
only 20-30% filtered load absorbed in PCT
thick ascending loop → major site of absorption → PTH reg perhaps?
Aldosterone increases Mg excretion
Hypomagnesemia associated with hypocalaemia and high Na+ in blood → digoxin poisoning
Hormone summary
regulates plasma conc → Ca2+ important (narrow range)
gut absorption, distribution, excretion
PTH
increases Ca2+ reabsorption
decreases PO42- absorption (reducing cotransporter numbers)
Active D3 → gut absorption
expression of Ca2+ binding protein in intestinal cells
multivalent cation → inhibits phosphate absorption
protein bound not absorbed
unbound is passive diffusion
Calcitonin
protects against hypercalaemia
active in young animals and salmon (potent calcitonin salt water → fresh water)
FGF-23
mechanism for sensing specific phosphate levels unknown
needed for negative feedback to reduce or increase → not clear
PTH
84 amino acids
chief cells of parathyroid gland
2 internal, 2 external (bilateral)
externals on cranial thryoid
high risk hypocalaemia when removal of thyroids → removes internals + BLOOD SUPPLY to externals
Effects
secretion regulated by Ca2+ conc
Calcitriol and FGF-23 inhibit PTH via -ve feedback
severe hypomagnesemia → may inhibit PTH secretion → hypocalcaemia in ruminants
promotes high Ca2+ reabsorption, PO42- excretion
bone resorption
stimulates SYNTHESIS of calcitriol → gut absorption
promotes Mg absorption from loop of Henle
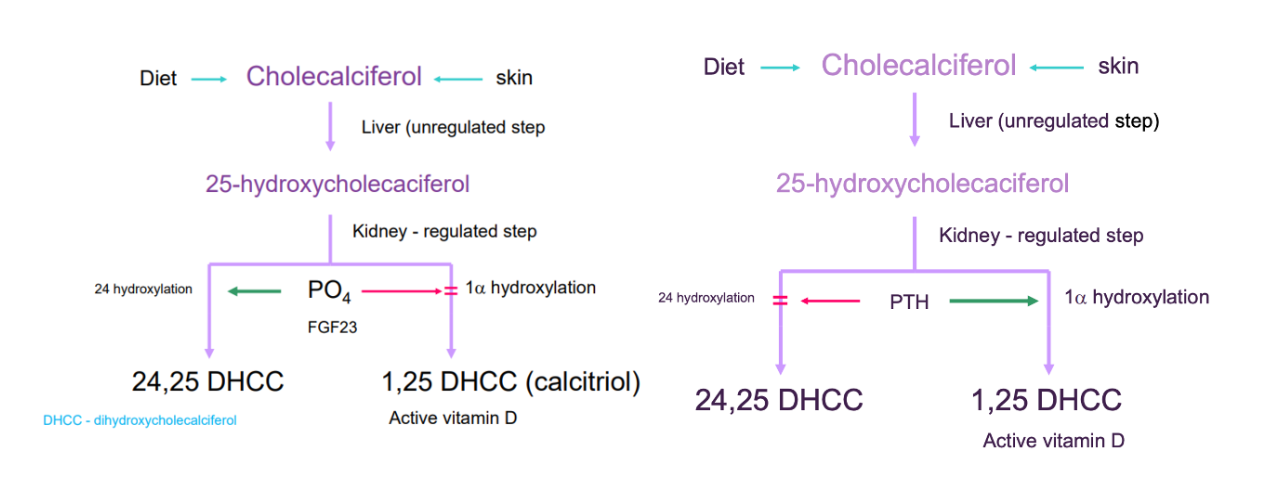
Vit D} cholecalciferol → calcediol (liver)→ calcetriol (kidney)
cats cannot synthesis from skin → diet only
D2 → calciferol → irradiation of ergo-sterol (plant form)
D3 → cholecalciferol → irradiation (sunlight) of 7-dehydrocholesterol [provitD]
Main role → calcium and phosphate intestinal absorption
Diet/skin → cholecalciferol
→ calcidiol (liver - unregulated)
25-hydroxycholecaciferol
→ calcitriol (kidney - regulated)
active calcitriol = 1 alpha hydroxylation process
1,25 de-hydroxy-cholecalciferol
phosphate or FGF-23 may inhibits 1 alpha hydroxylation enzyme
PTH enhances reaction
inactive = 24 hydroxylation process
24,25 de-hydroxy-cholecalciferol
phosphate or FGF-23 stimulation
PTH inhibition
Stimulates synthesis of osteocalcin → major Ca2+ binding protein
Negative feedback - inhibts PTH
But synergistic with PTH in bone and kidney
Calcitonin
C cells of thyroid or ultimobranchial bodies
reduces blood Ca2+ → decreases osteolysis and increases osteogenesis
important in growing mammals
not as important in adults
FGF-23
produced by osteoblasts and osteocytes in response in order to increase ECF phosphate (and calcium)
not immediate increase in response to high ECF
not stored only processed
stimulated by low phosphate
negative feedback → high phosphate → FGF-23 broken down
Inhibits phosphate entry
from gut → inhibiting calcitriol (1,25 + formation of 24,25)
bone → PTH inhibition (prevents resorption)
inhibits proximal tubular reabsorption (PTH inhibited)
Needs cofactor klotho to work
calcification + early death due to excess PO4
Klotho antiaging
regulation knowledge incomplete
Kidney pathology → disease
Cat endstage kidney disease → emasciated
white chalky deposits →nephrocalcinosis
unable to control phosphate while GFR falls → build up of phosphate in plasma
reduces Ca2+ → complexes form
stimulates PTH production
bone resorption releases Ca2+ and more phosphate (repeats)
kideys progresses to end stage