unit 3.2-3.3 - K-selected & r-selected species & survivorship curves
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
reproductive strategies/patterns
species have different reproductive strategies that increase chances of survial
K-selected
r-selected
K-selected species
species with LOW intrinsic growth rate, causes pop. to increase slowly until it reaches CARRYING capacity
population is largely determined by carrying capacity, pop fluctuations are small
large mammals, birds of prey, long-lived plants like oaks
carrying capacity
(K) maximum number of individuals that can exist in poplation in given environment
K-selected species
large organisms, reach maturity late
few offspring / reproduction event
substantial parent care
K-selected species
mature after many years of parent care
long life span and life expectancy
reproduce few times in lifetime
K-selected species
live in stable, predictive environments
competition for resources in K-selected habitats is usually high
more likely to be affected by invasive species (r-selected)
r-selected species
species with high intrinsic growth rate, leads to population overshoots and die-offs
algae, bacteria, rodents, frogs, annual plants, most insects
intrinsic growth rate- r
maximum potential for growth of population under ideal conditions with unlimited resources
overshoot
population becomes larger than environments carrying capacity
die-off
rapid decline in population due to death
r-selected species
tend to be small
have many off-spring
invest minimal energy for each offspring
r-selected species
mature quickly
have short life span
may reproduce many times in lifetime
r-selected species
competition in r-selected species habitat is low
minimally affected by invasive species
r-selected species are opportunist
opportunist
reproduce rapidly when conditions are favorable
biotic potential
maximum reproductive rate of population in ideal conditions
large individuals = low biotic potential
small individuals = high biotic potential
intrinsic rate of increase - r
rate at which a population would grow if it had unlimited resources
individuals with high intrinsic rate:
reproduce early
short generation times
reproduce many times
many offspring in each generation
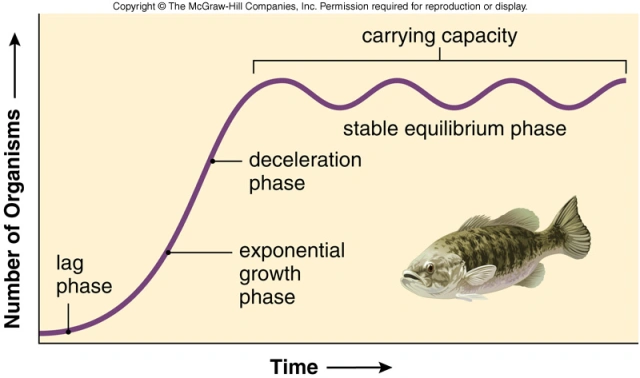
environmental resistance
environmental factors (limited resources/competition) restrict the biotic potential of an organism & impose limit on # of individuals in population
carrying capacity is reached
sea turtle
although large with long life-spans, they produce many, un-nutured offspring
reproductive strategies that are neither r-selected or K-selected
wind pollinated trees
long life spans & highly competitive
produce thousands of widely dispersed offspring
survivorship curves
graph that represents distinct pattern of species survival as function of age
type I
type II
type III
most populations are mix of 3 types
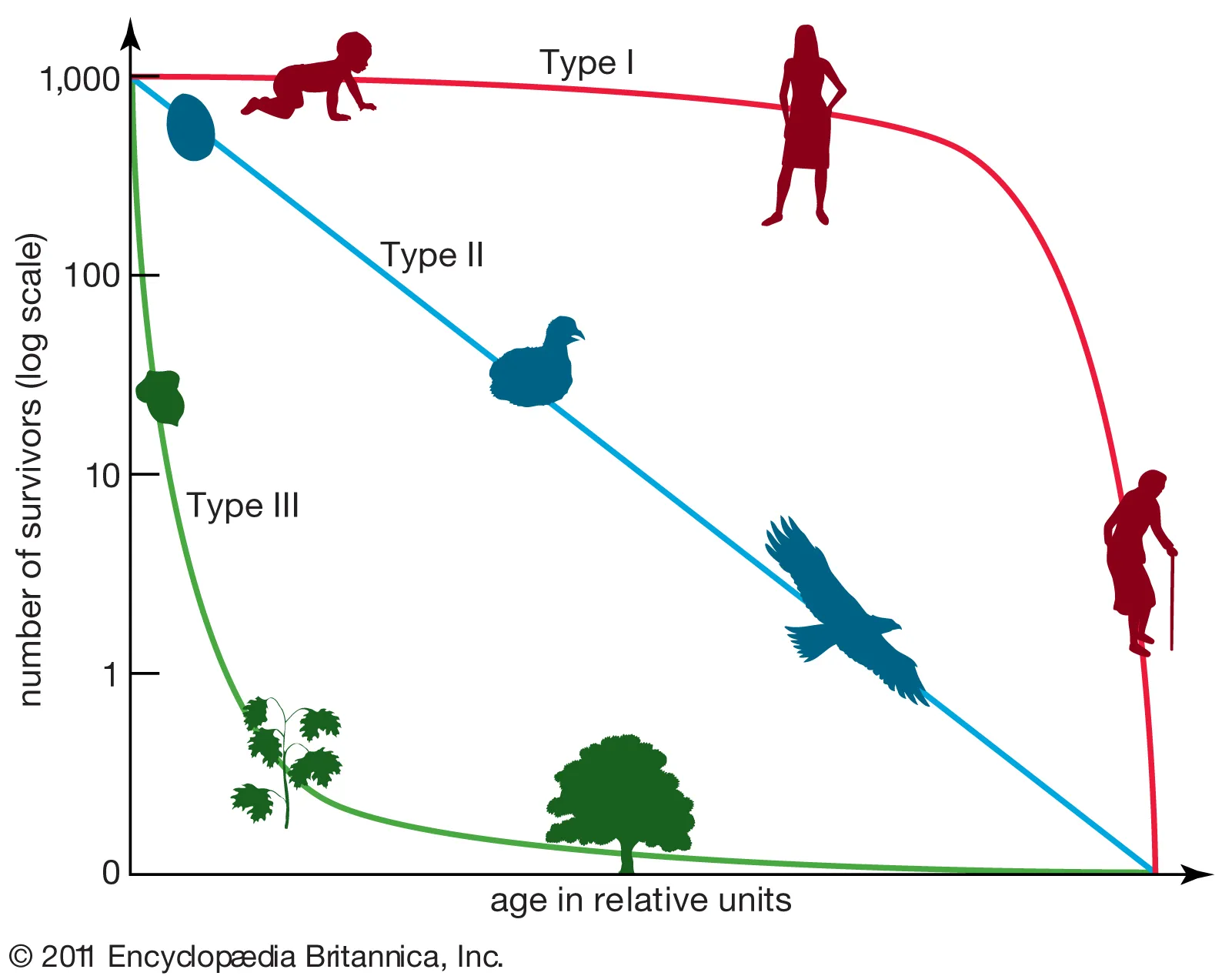
type I survivorship curve
high survival throughout most of life span
individuals begin to die in large numbers as they approach old age- late loss pop m
lot of energy/parental care invested in individuals, result in high survivorship throughout life cycle
K-selected - humans, elephants
late loss population
high mortality at old age
type II survivorship curve
relatively constant decline in survivorship throughout most of life span
constant loss pop - mortality of individual does not depend on age
some rodents, some birds
constant loss population
individuals die at all ages
type III survivorship curve
low survivorship early in life with few individuals reaching adulthood
early loss pop - produce many thousands of individuals, most die after birth, few individuals survive to maturity
r-selected
ex. oysters, redwood trees, some fishes, marine larvae