4 Genetic Disorders
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
define genetic disorder.
a health condition caused by abnormalities in the genome
what causes these abnormalities?
a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality.
How can these mutations occur?
spontaneously before embryonic development (de novo).
autosomal recessive inheritance - inherited from 2 parents who are carries of a faulty gene.
autosomal dominant inheritance - inherited from a parent with the disorder.
is Huntingdon’s disease an autosomal dominant or recessive disorder?
autosomal dominant
mutated allele 1 parent is sufficient for child to be affected.
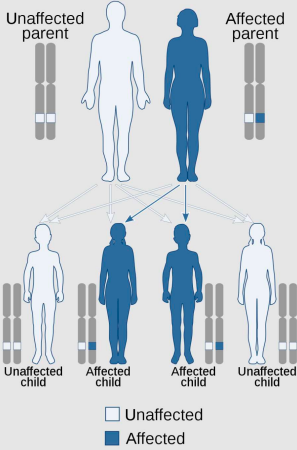
is Cystic fibrosis an autosomal dominant or recessive disorder?
autosomal recessive
mutated alleles have to be inherited from b oth parents for child to be affected.
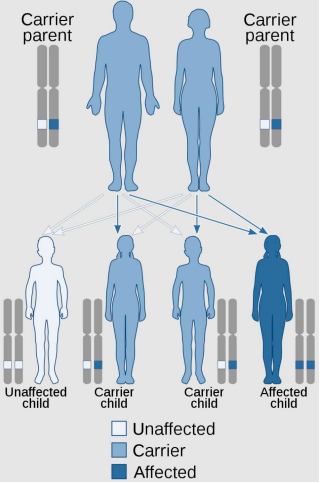
what is X-linked recessive inheritance?
when a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes disease in:
males who are hemizygous for the mutation (XY - they have only 1 X chromosome)
females who are homozygous for the mutation (XX - they carry mutation on both X chromosomes)
define hemizygous
a person with one copy of a gene rather than 2, e.g. males have 1 X & Y chromosome, so they’re hemizygous for genes on the X chromosome.
why are males more likely to display phenotypes for genes that are sex-linked?
males have only 1 X chromosome
cos they have 1 copy, they express the characteristic of this allele even if its recesive.