HB Evolution & Population Genetics: Key Terms & Definitions
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
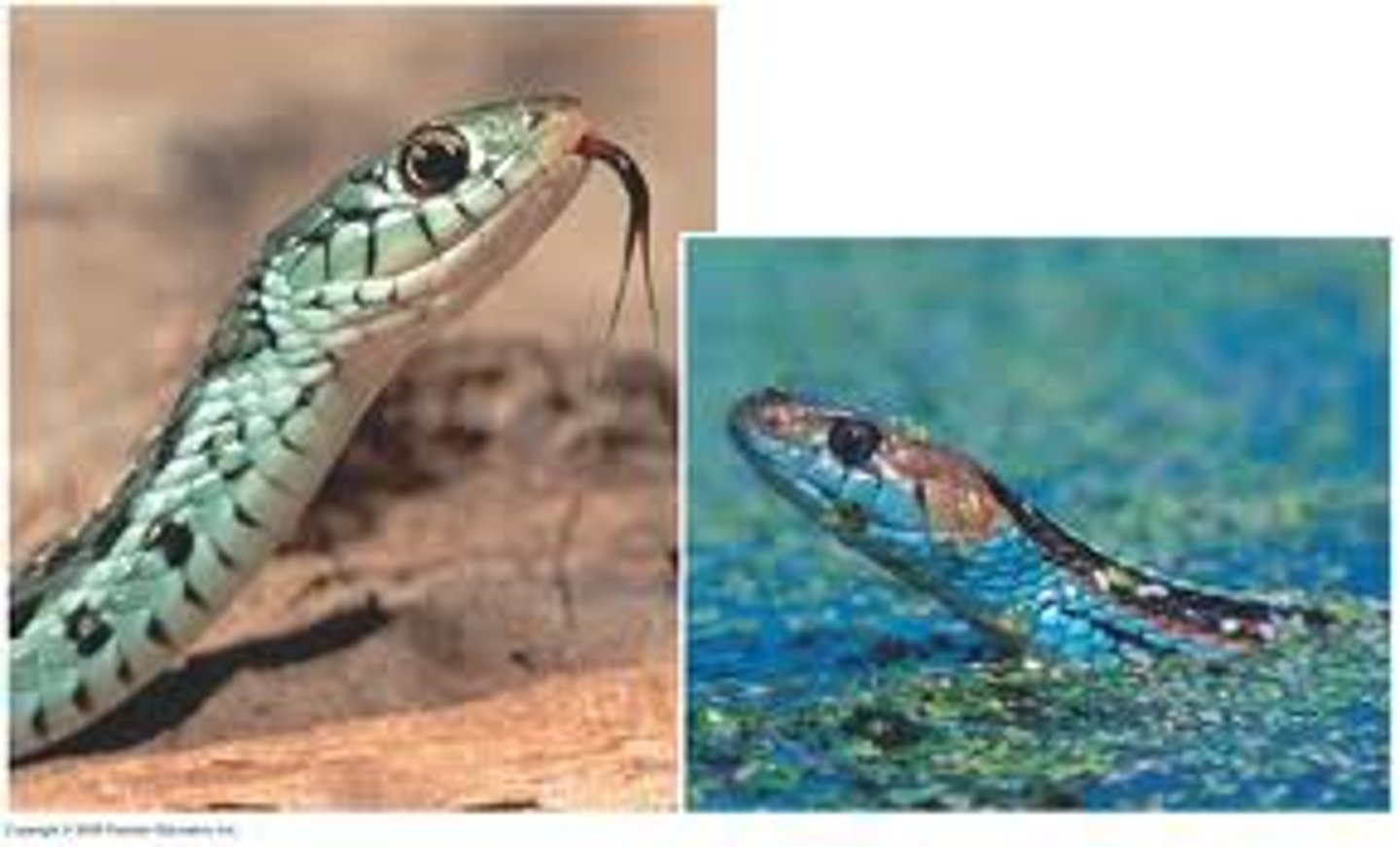
Analogous structures (convergent evolution)
When very different animals look similar but are distant; insects have wings, bats have wings
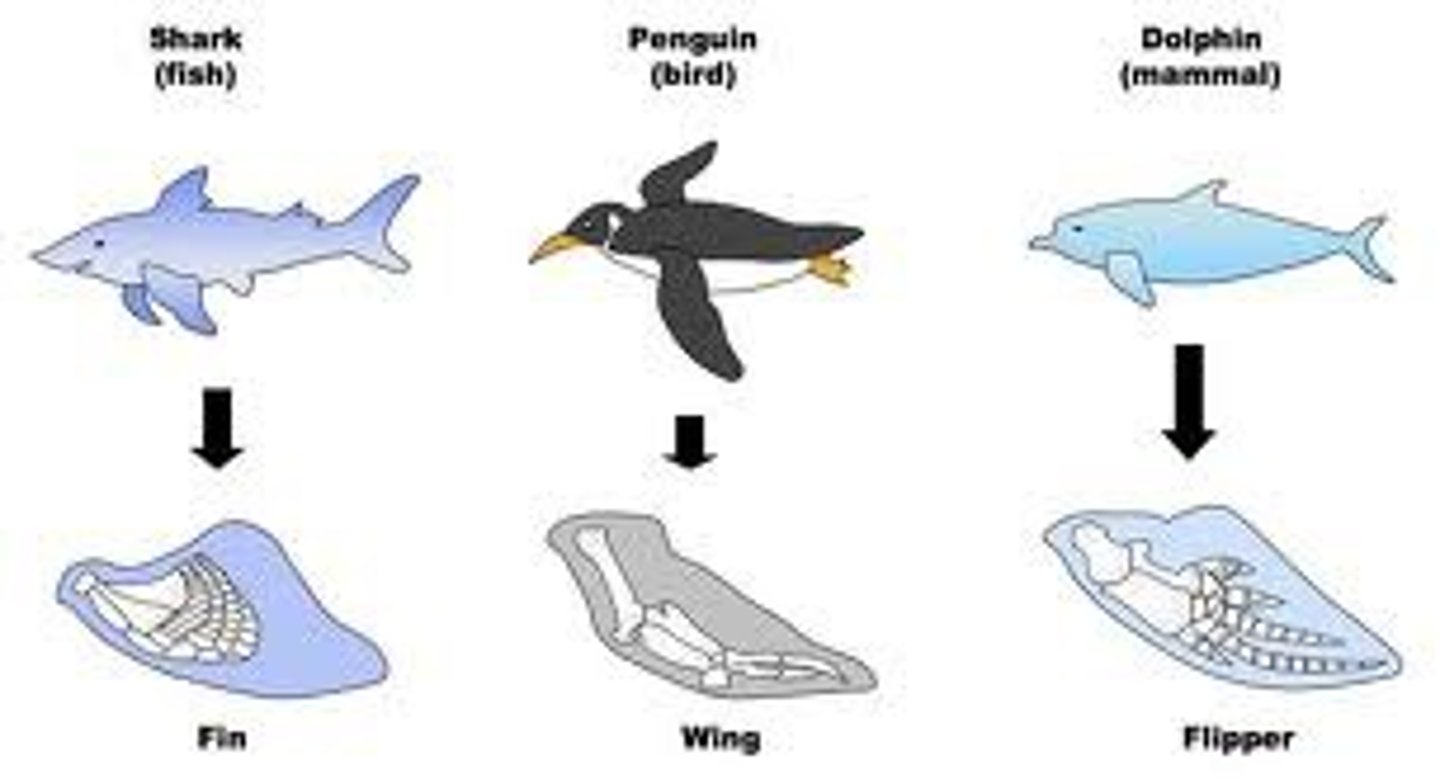
homologous structures
similar structures that related species have inherited from a common ancestor
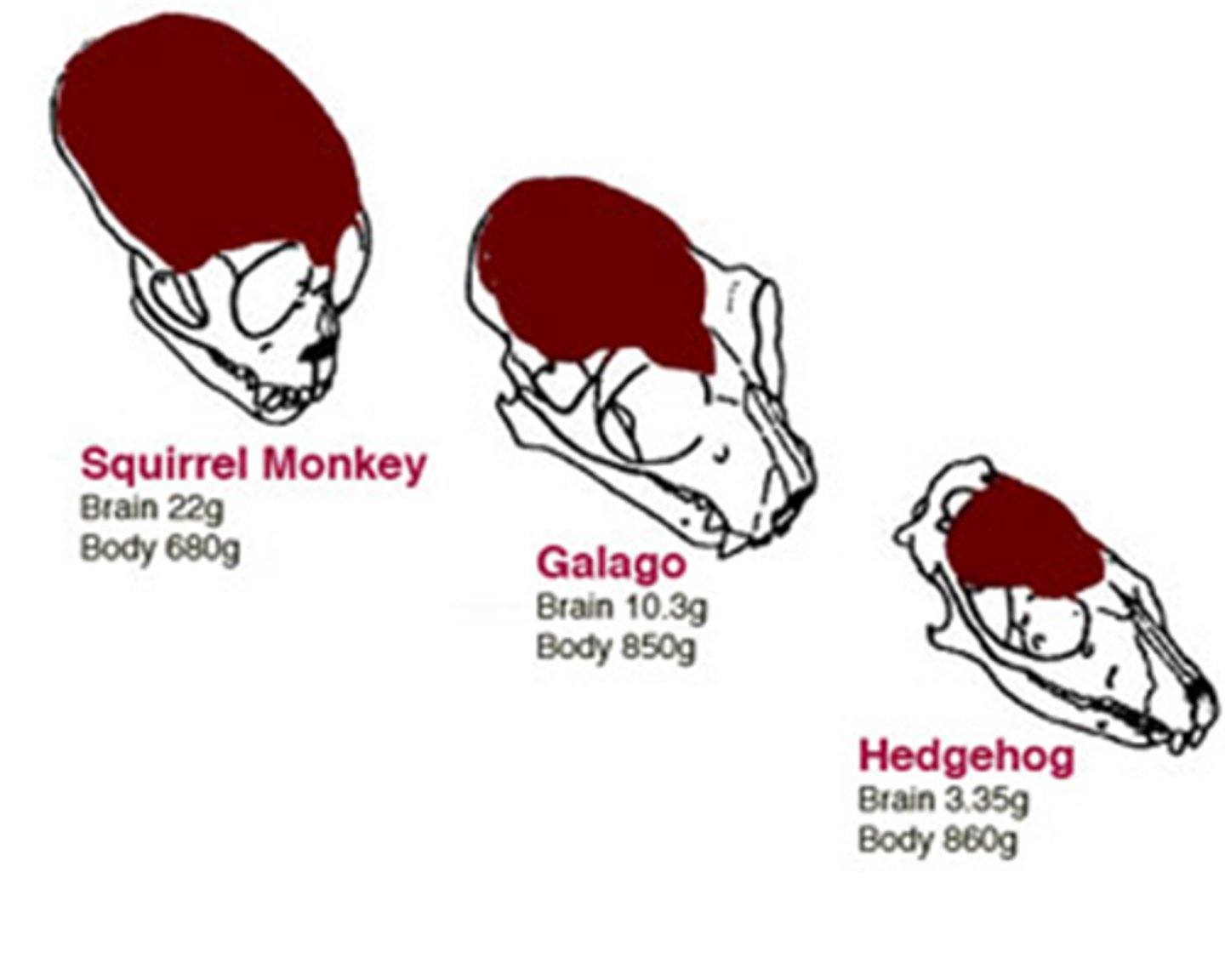
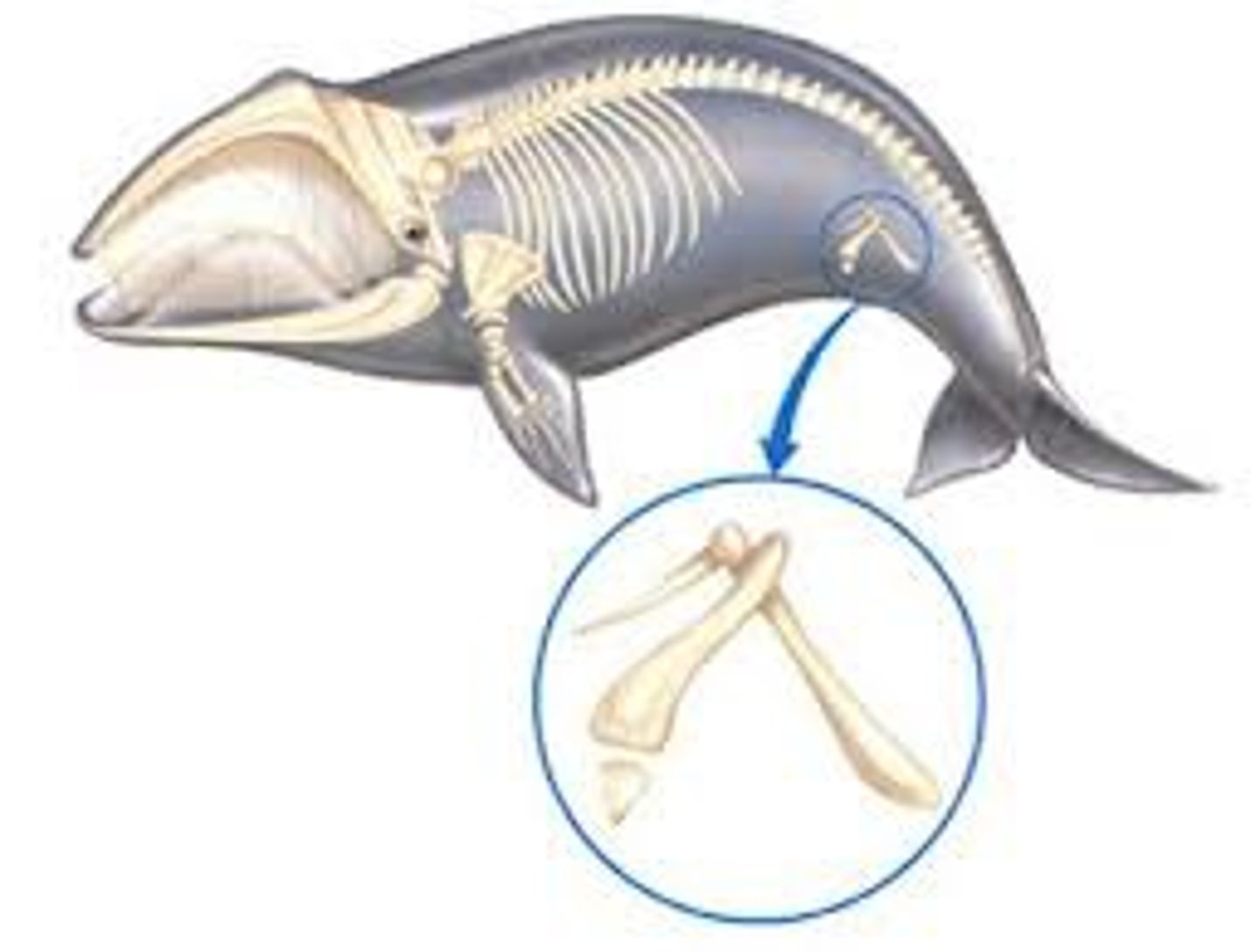
vestigial structures
Are little or no importance to organism, but remain from an ancestor.
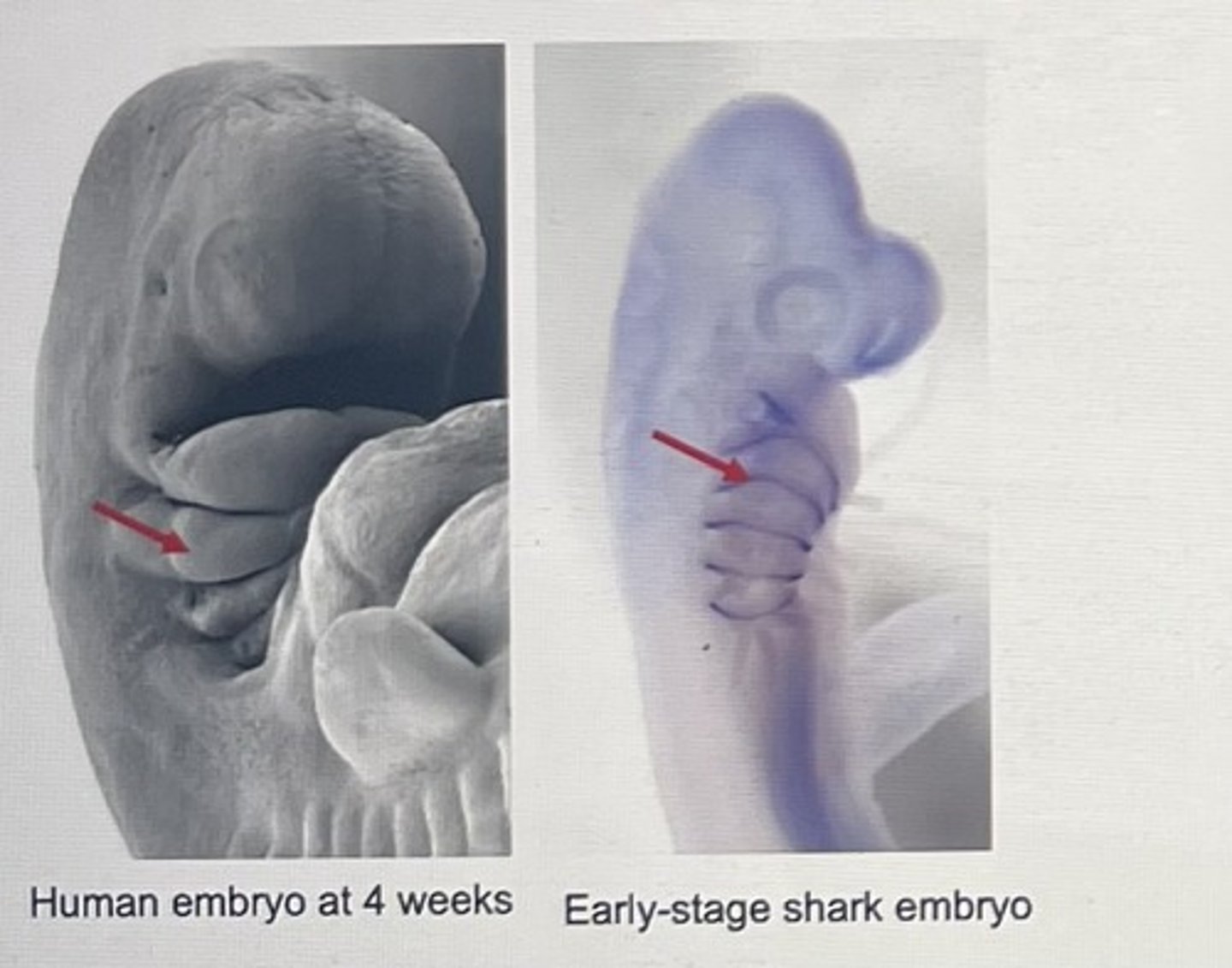
embryological evidence for evolution
The embryos of vertebrates have similar stages of development and have similar structures during these stages.
Biochemical Evidence for Evolution
Sequence of amino acids, similar proteins, similar DNA in various forms of life demonstrates relationships. The closer a group of animals or plants are, the more amino acids, proteins, DNA they have in common.
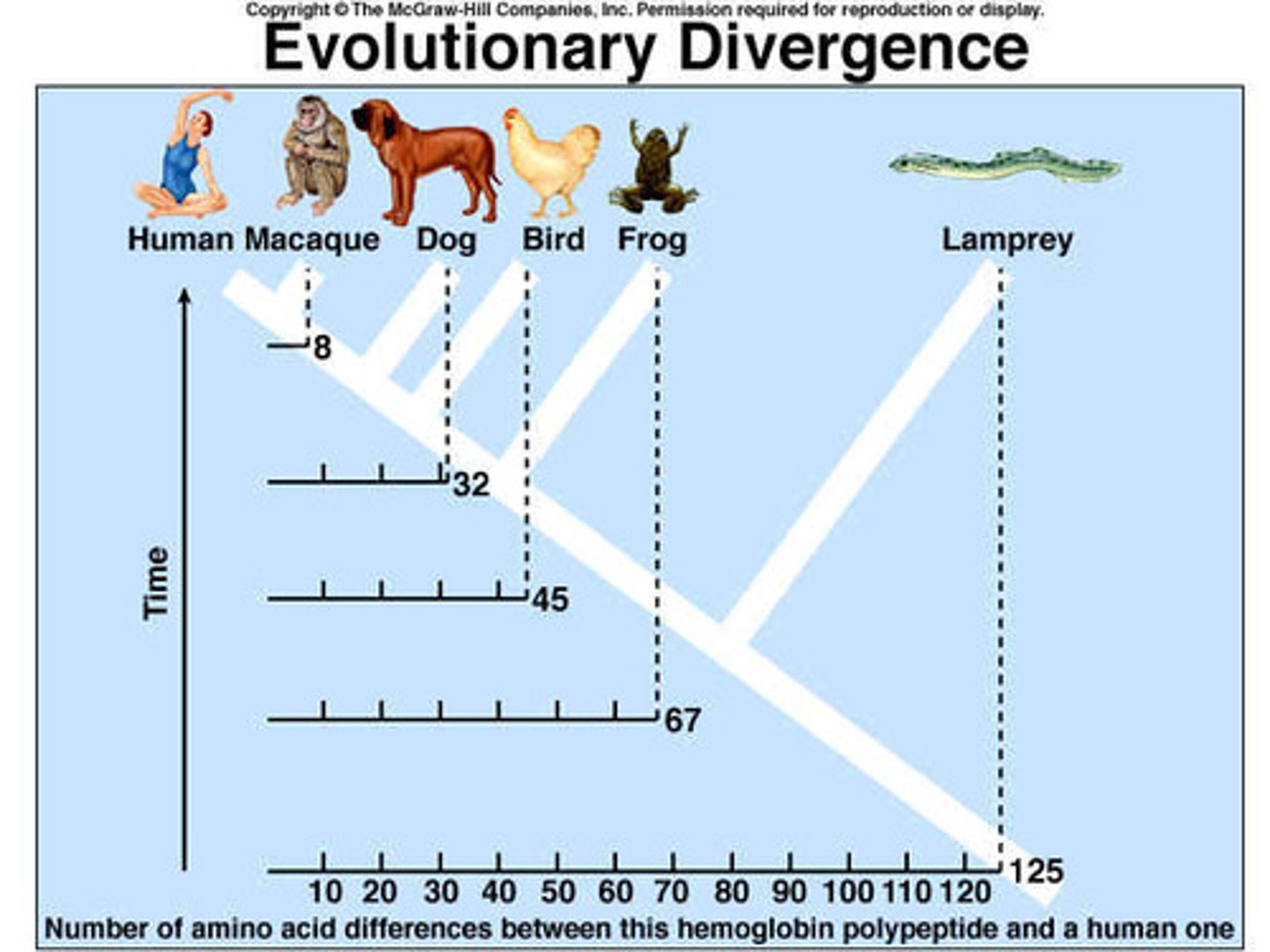
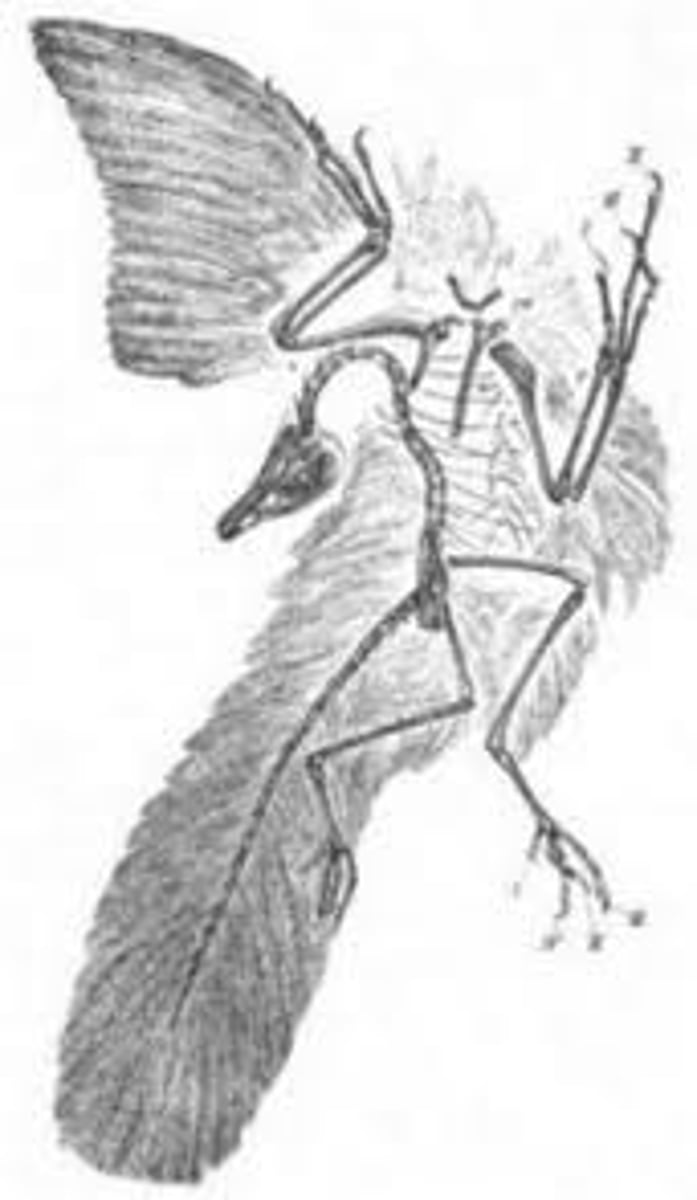
Fossil Evidence for Evolution
looking at historical organisms for change and similarities to present day organisms

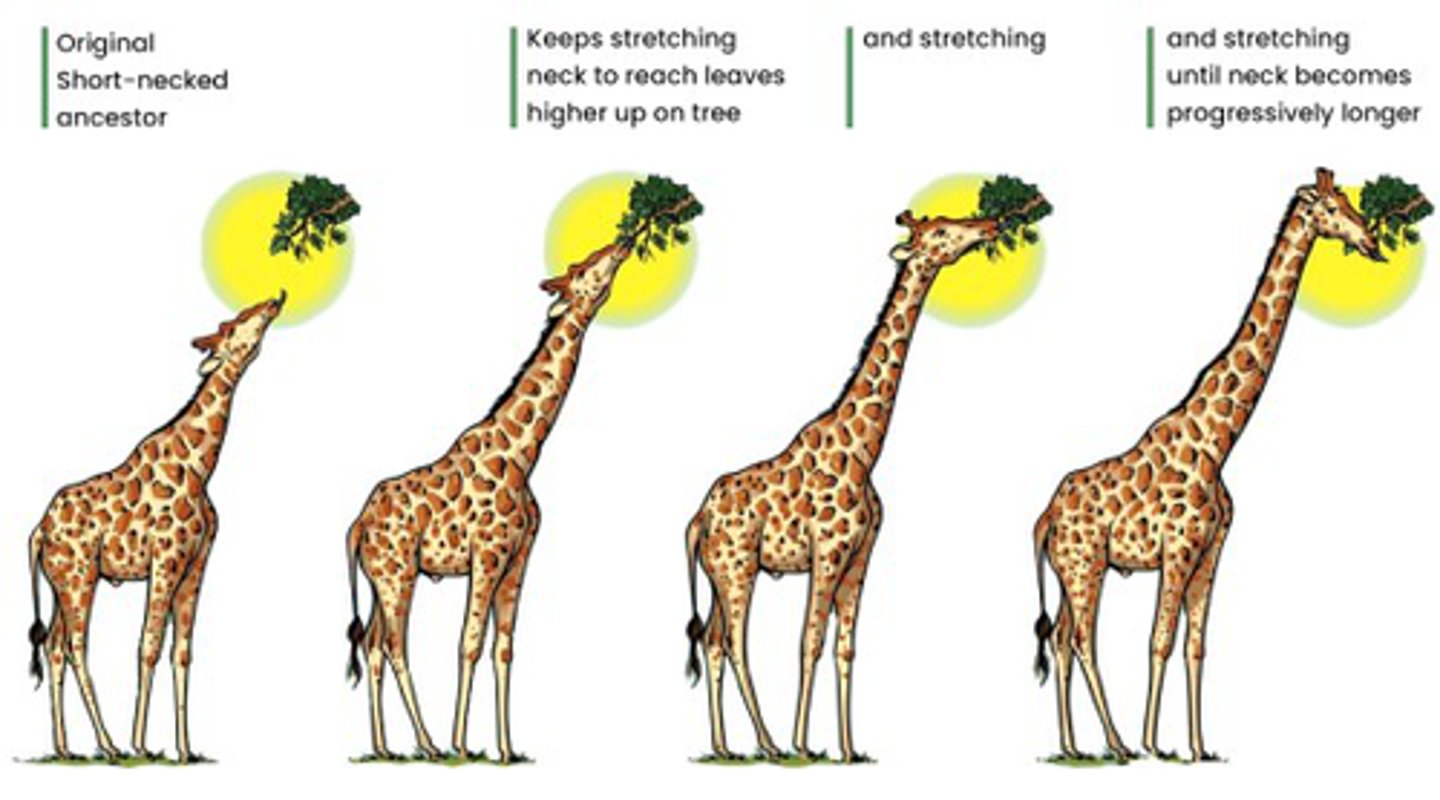
Larmarck's Theory of Evolution
Animals develop structures and organs they need to adapt to the environment
These structures and organs are passed on to its offspring
Use IT or Lose IT
Darwin's Theory of Evolution
all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that increase the individual's ability to compete, survive, and reproduce.
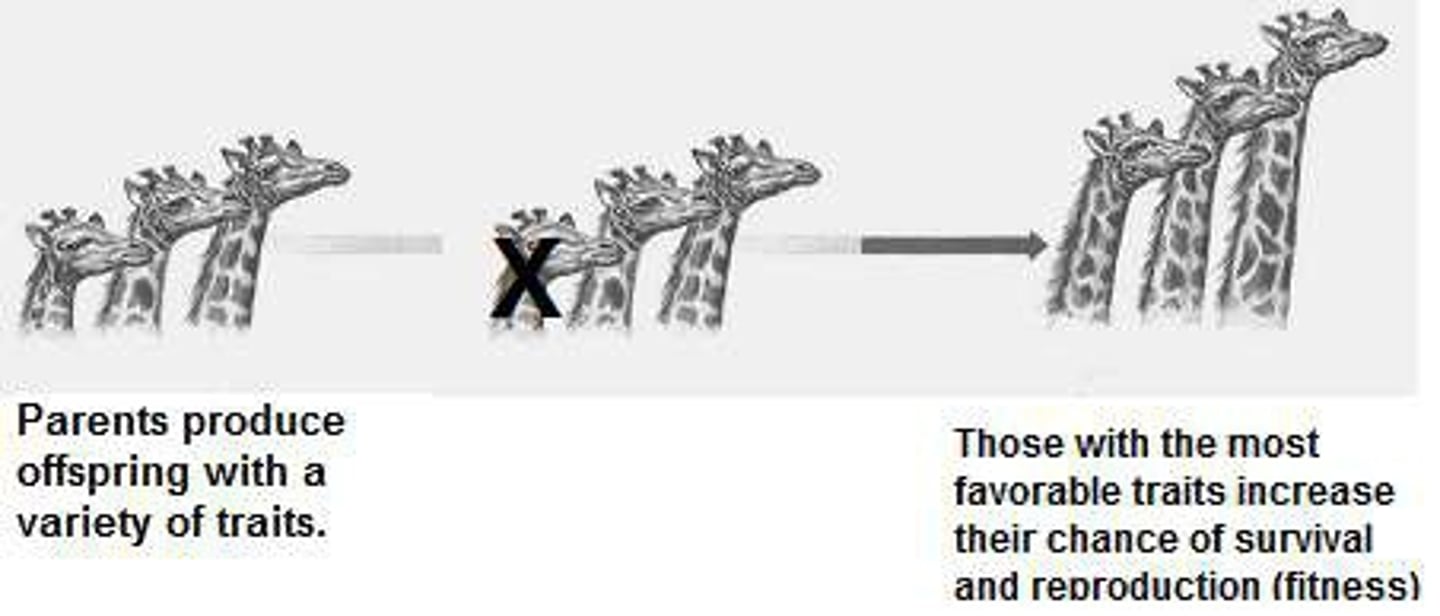
Variations in population
Arise by chance but the ones with better adaptations have better survival and their genes are carried on

Overproduction of offspring
produce more offspring that can survive

competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources

Adaptation
inherited characteristic that increases an organism's chance of survival
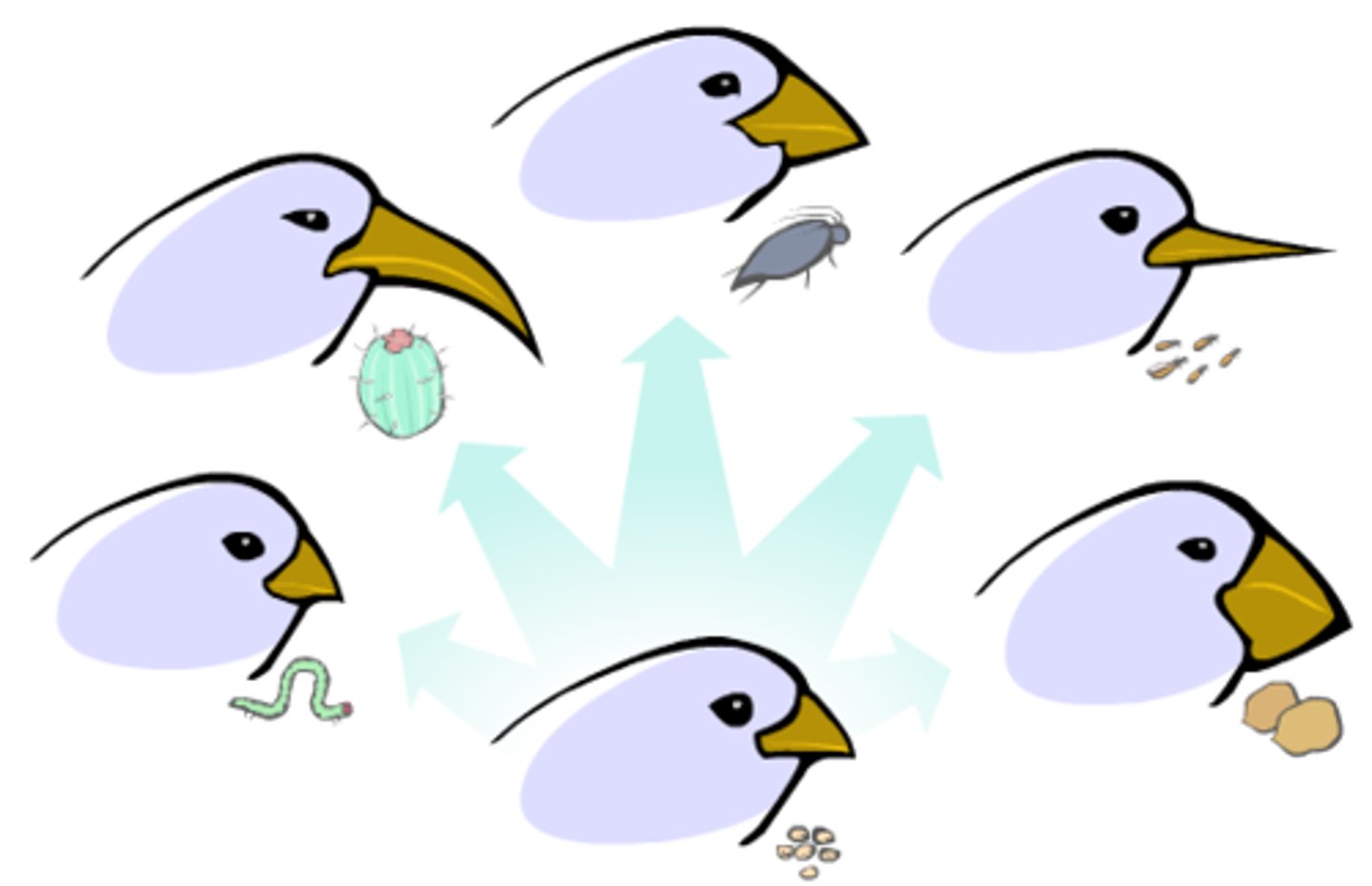
Speciation
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
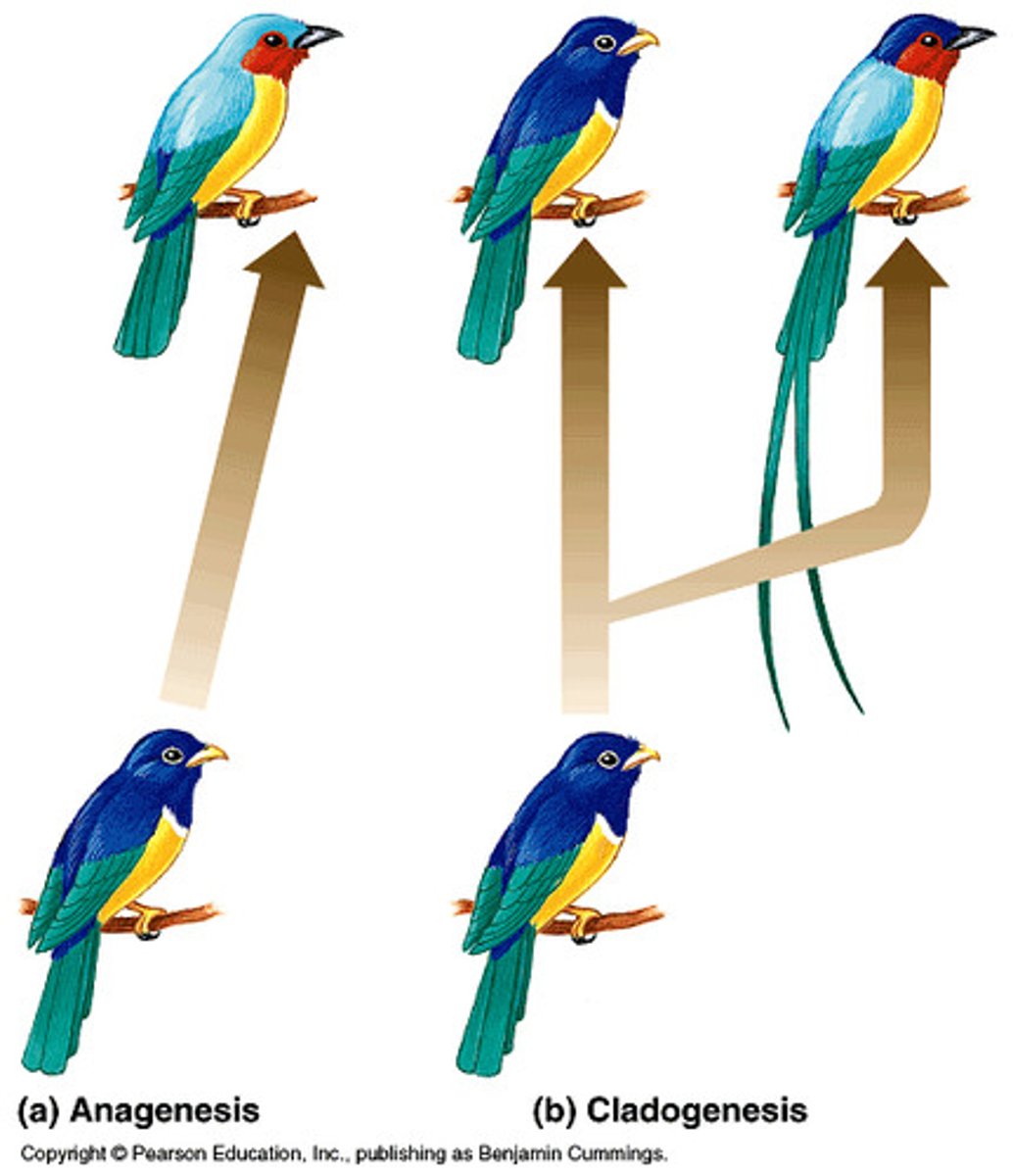
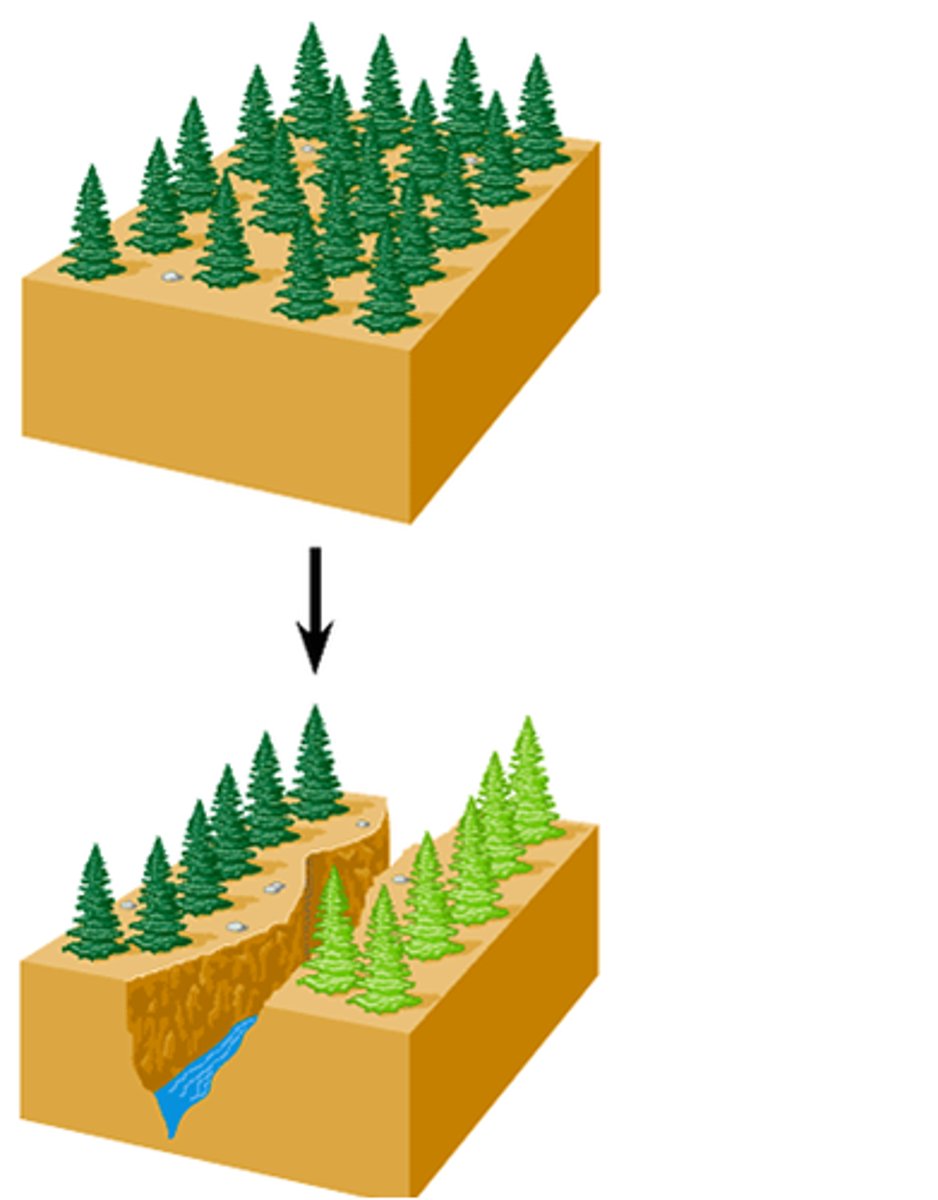
allopatric speciation
the process of speciation that occurs with geographic isolation
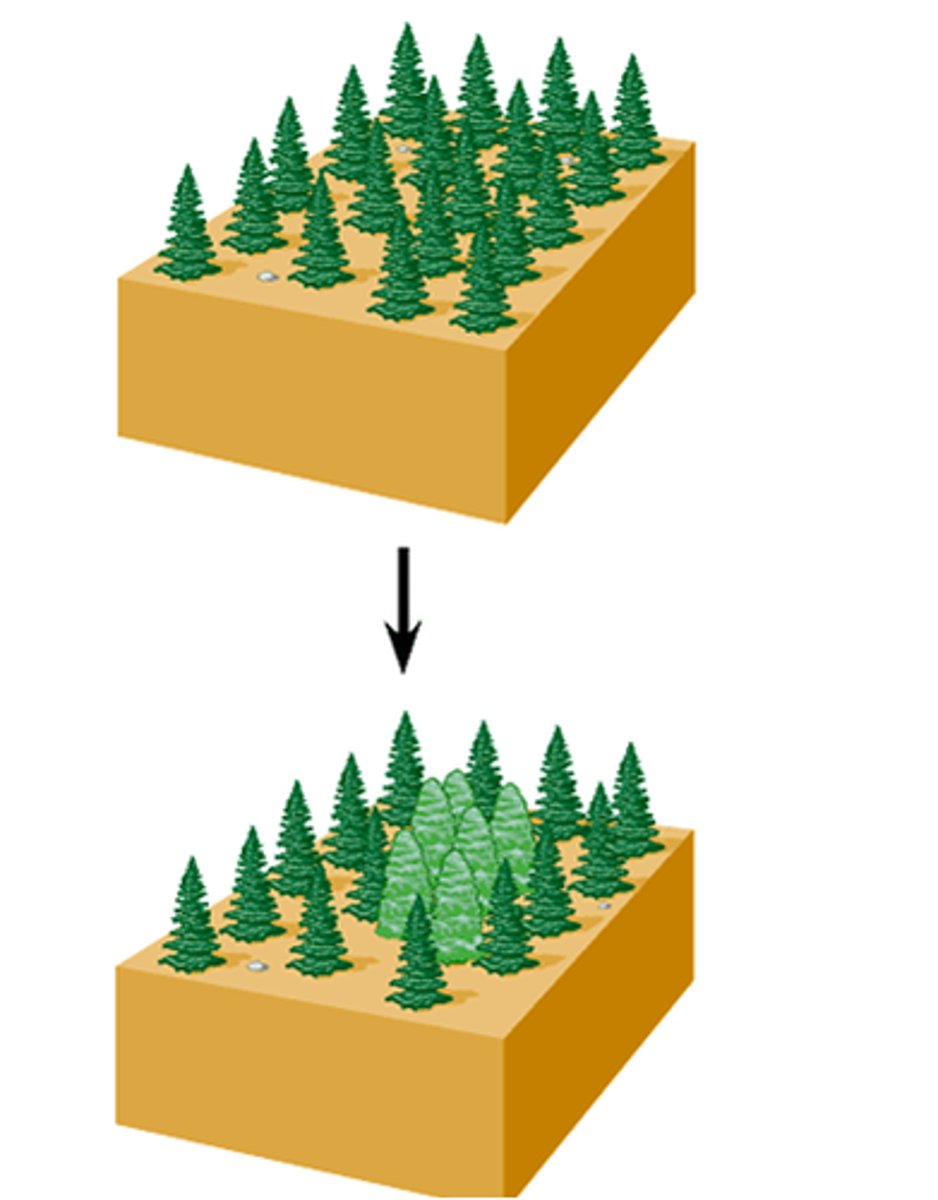
sympatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area
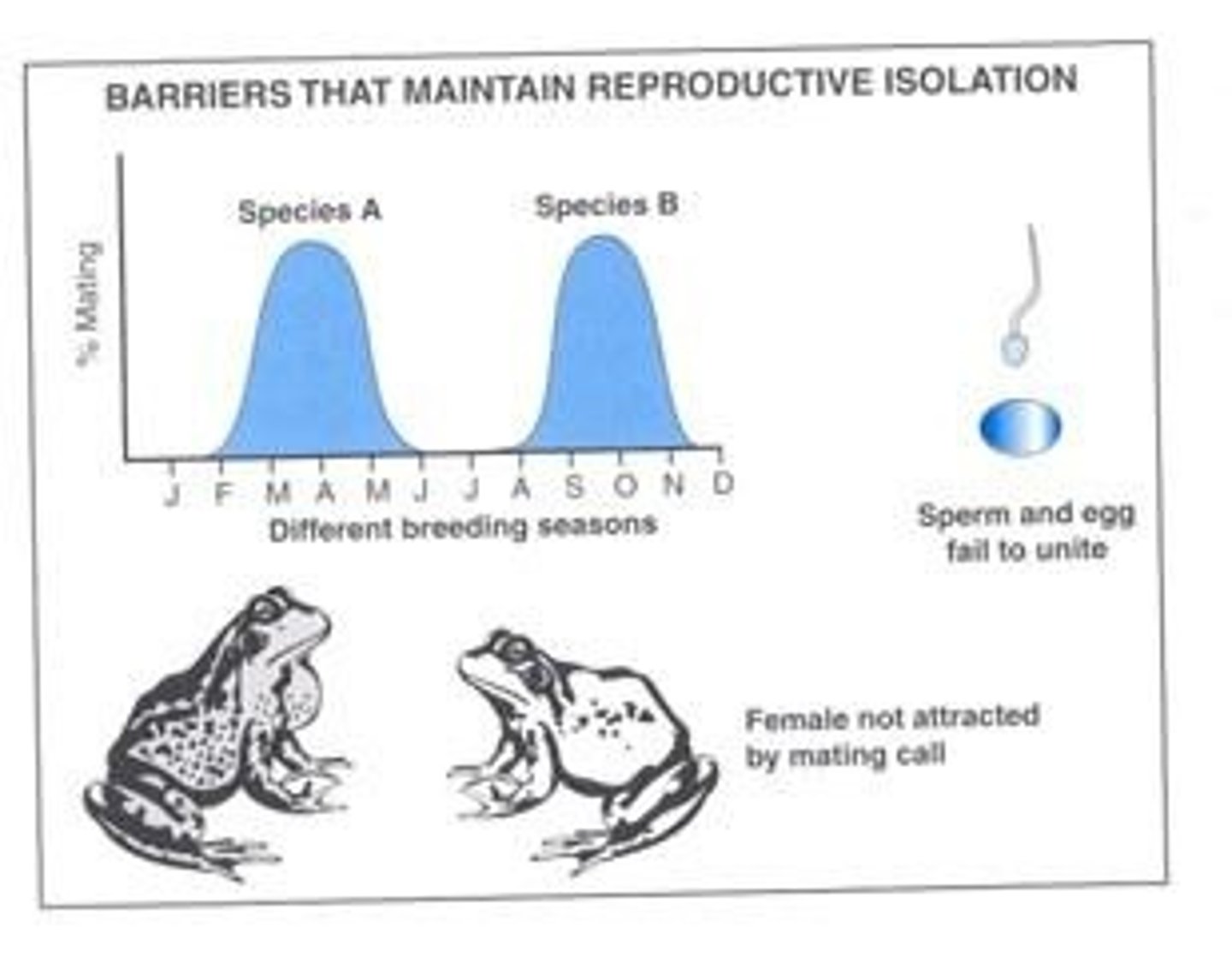
temporal speciation
reproducing at different times; pollinating on different days
mechanical isolation
mating is attempted, but morphological differences prevent its successful completion

gametic isolation
Sperm of one species may not be able to fertilize eggs of another species

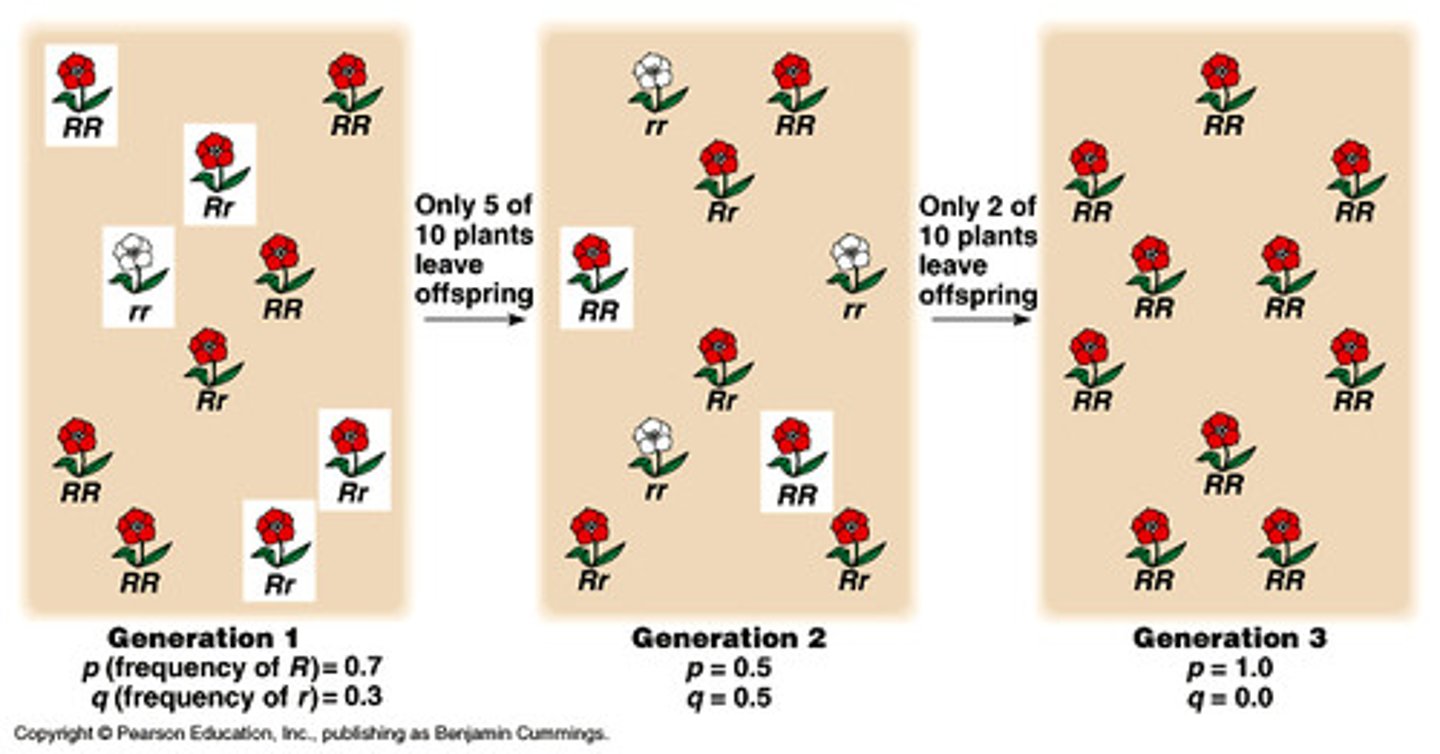
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
condition that occurs when the frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time
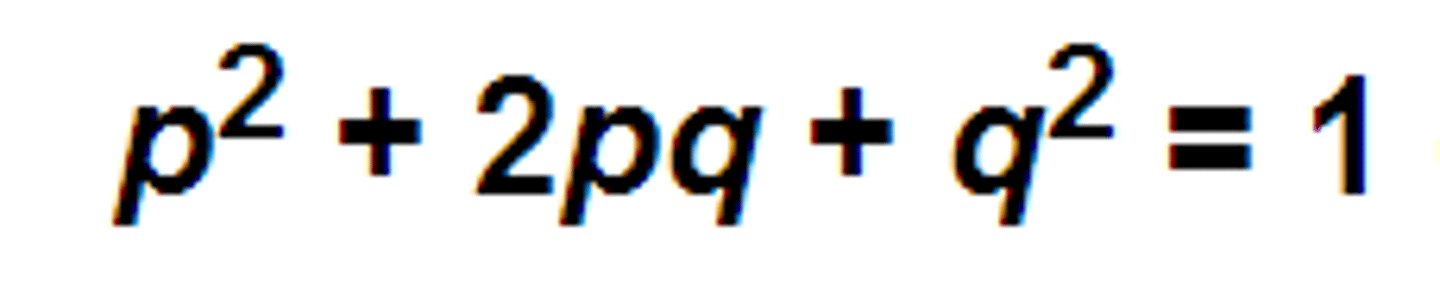
p (in hardy-weinberg)
frequency of dominant allele
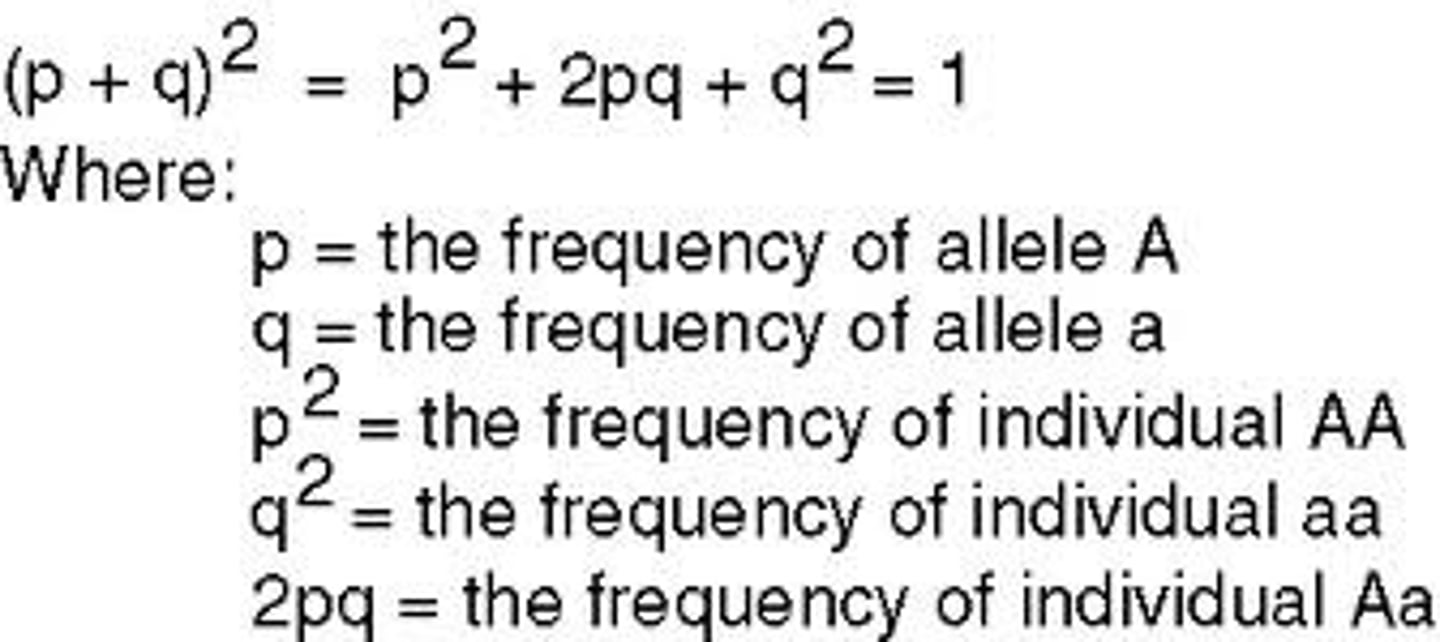
p2 (Hardy Weinberg)
frequency of homozygous dominant
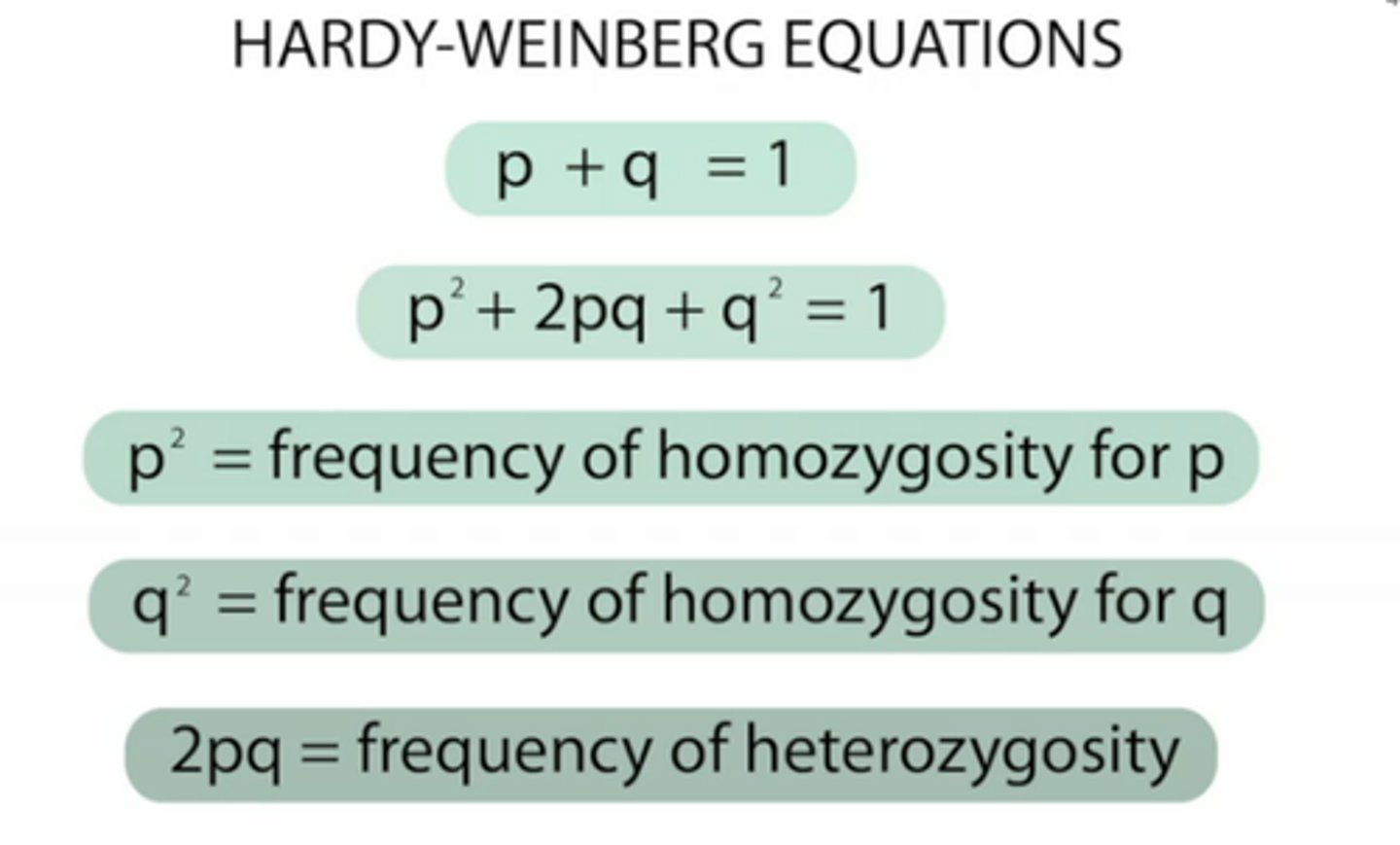
2pq
frequency of heterozygous genotype
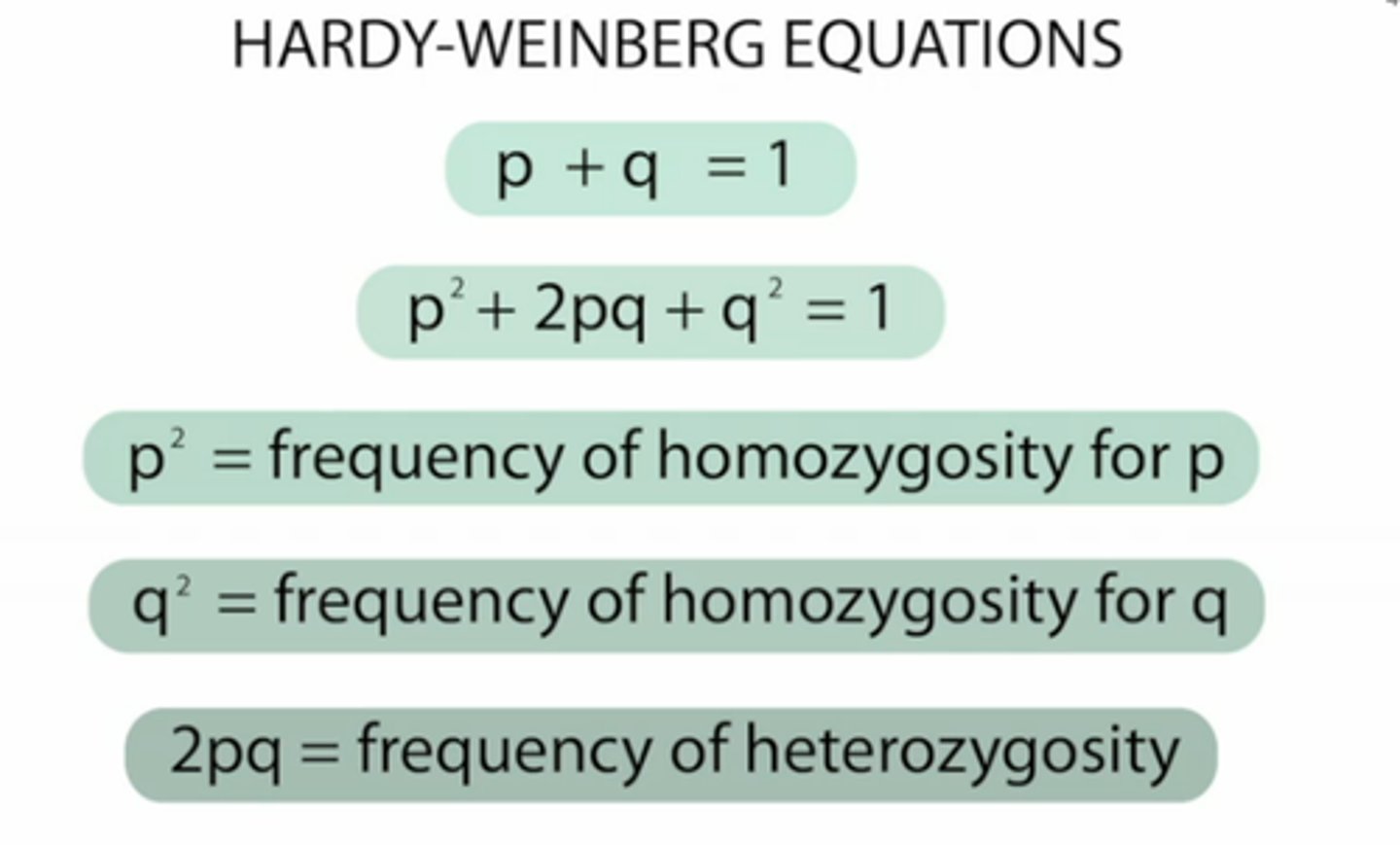
q (in hardy-weinberg)
frequency of recessive allele
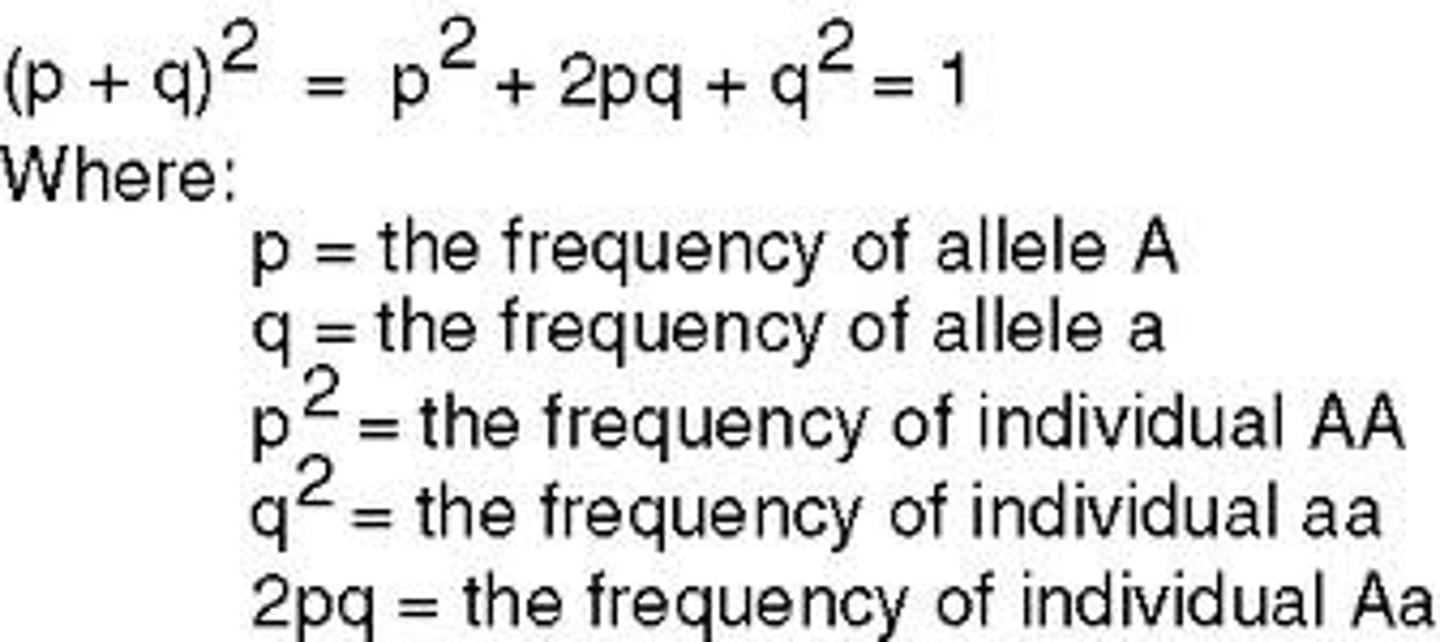
q2 in Hardy-Weinberg
frequency of homozygous recessive genotype
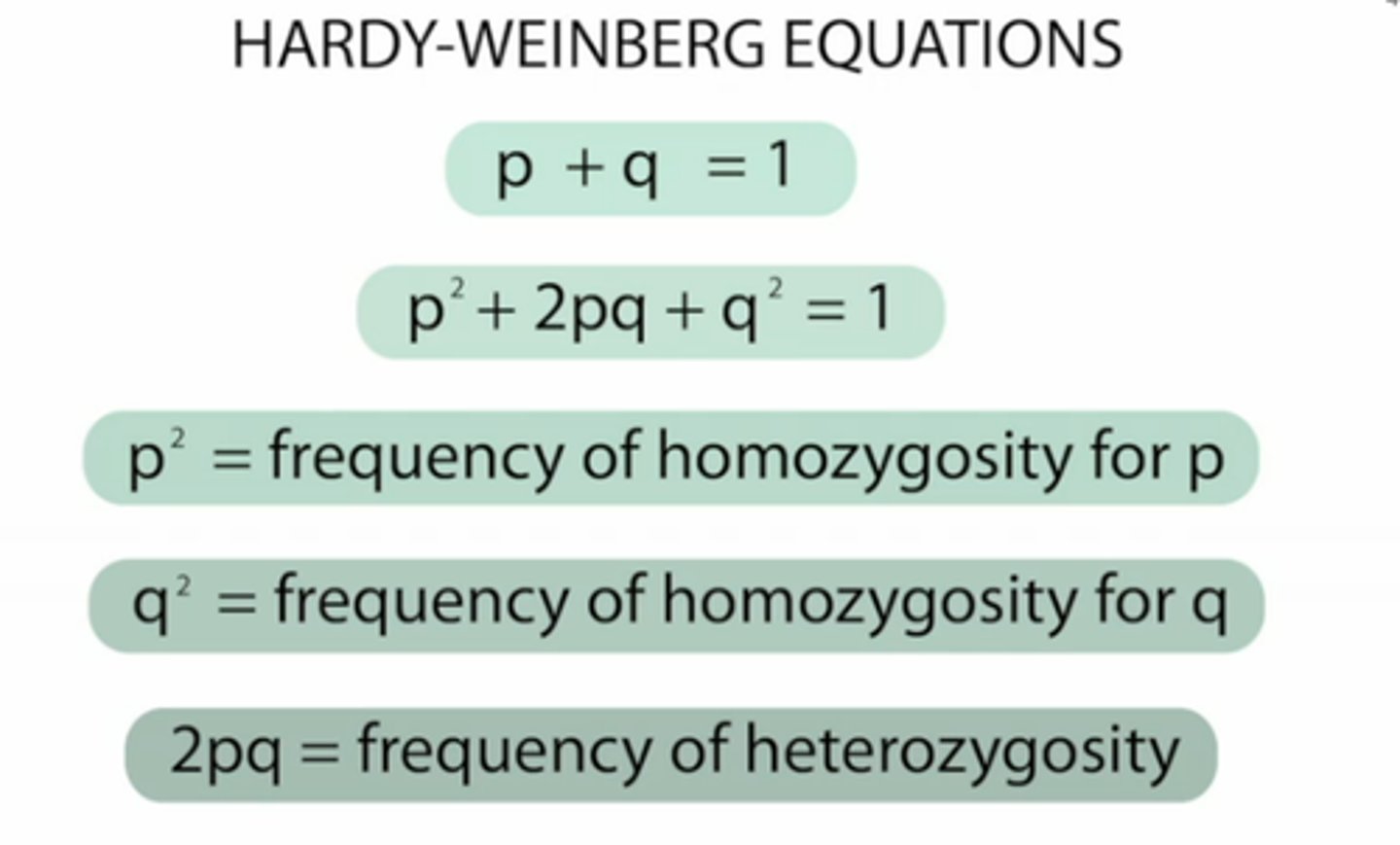
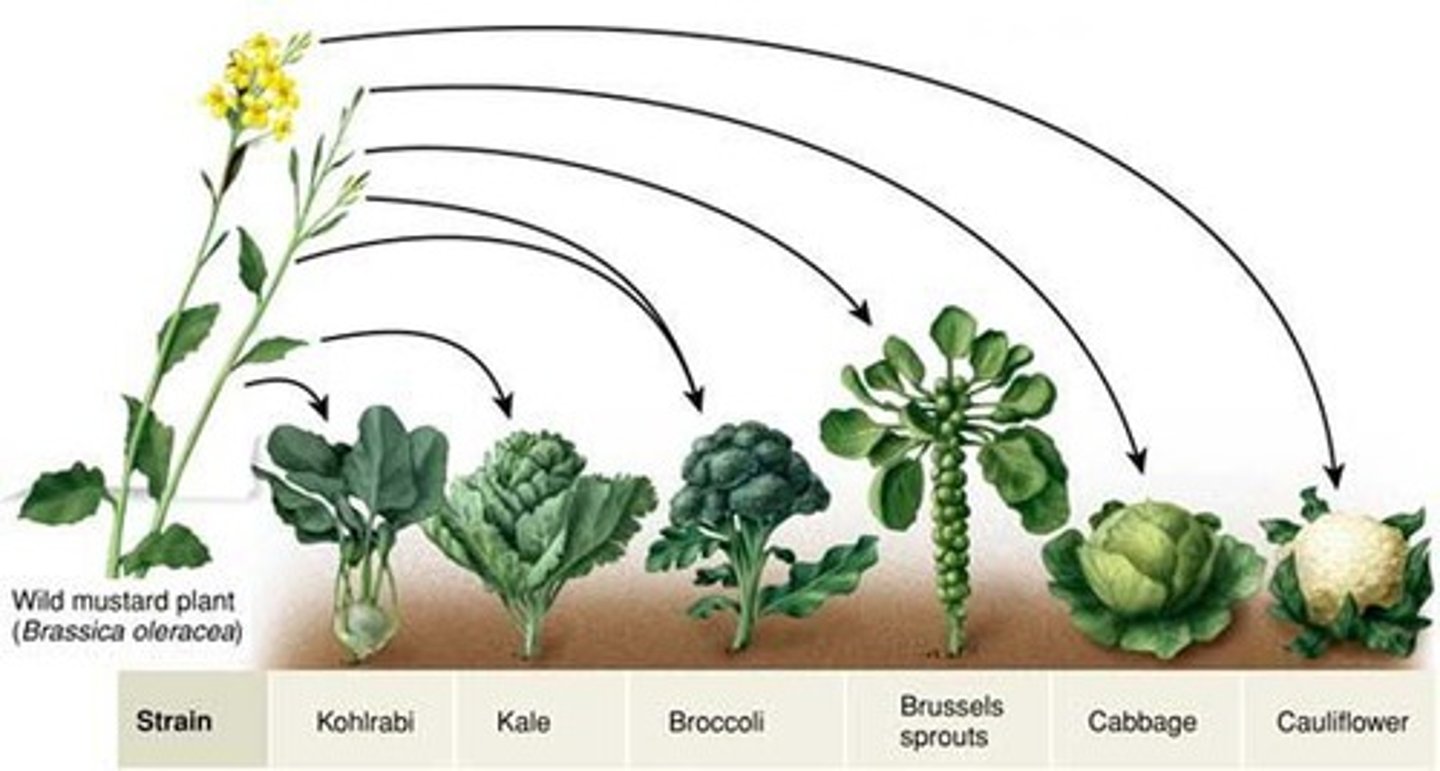
artificial selection
Breeding organisms with specific traits in order to produce offspring with identical traits.
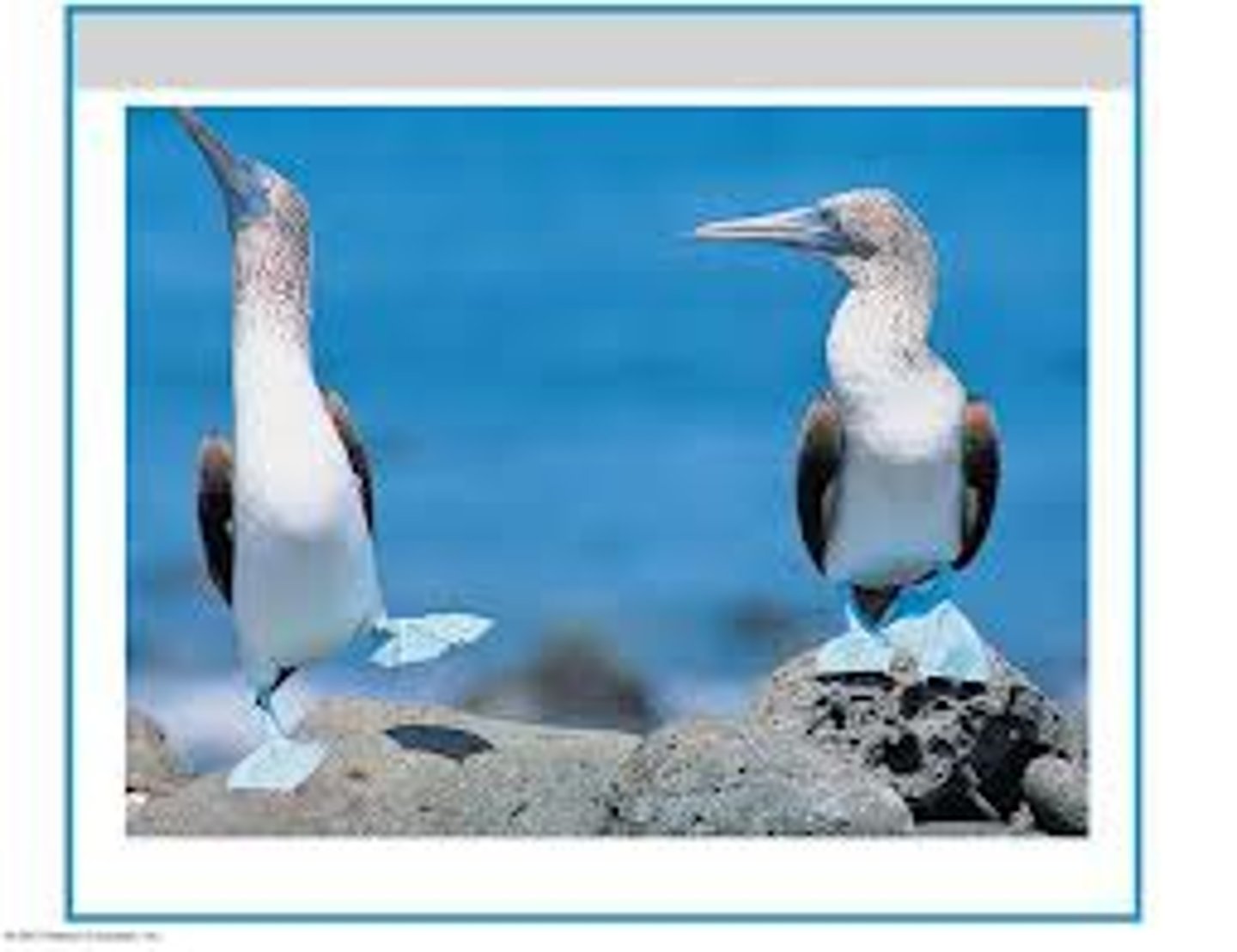
sexual selection
when individuals select mates based on heritable traits
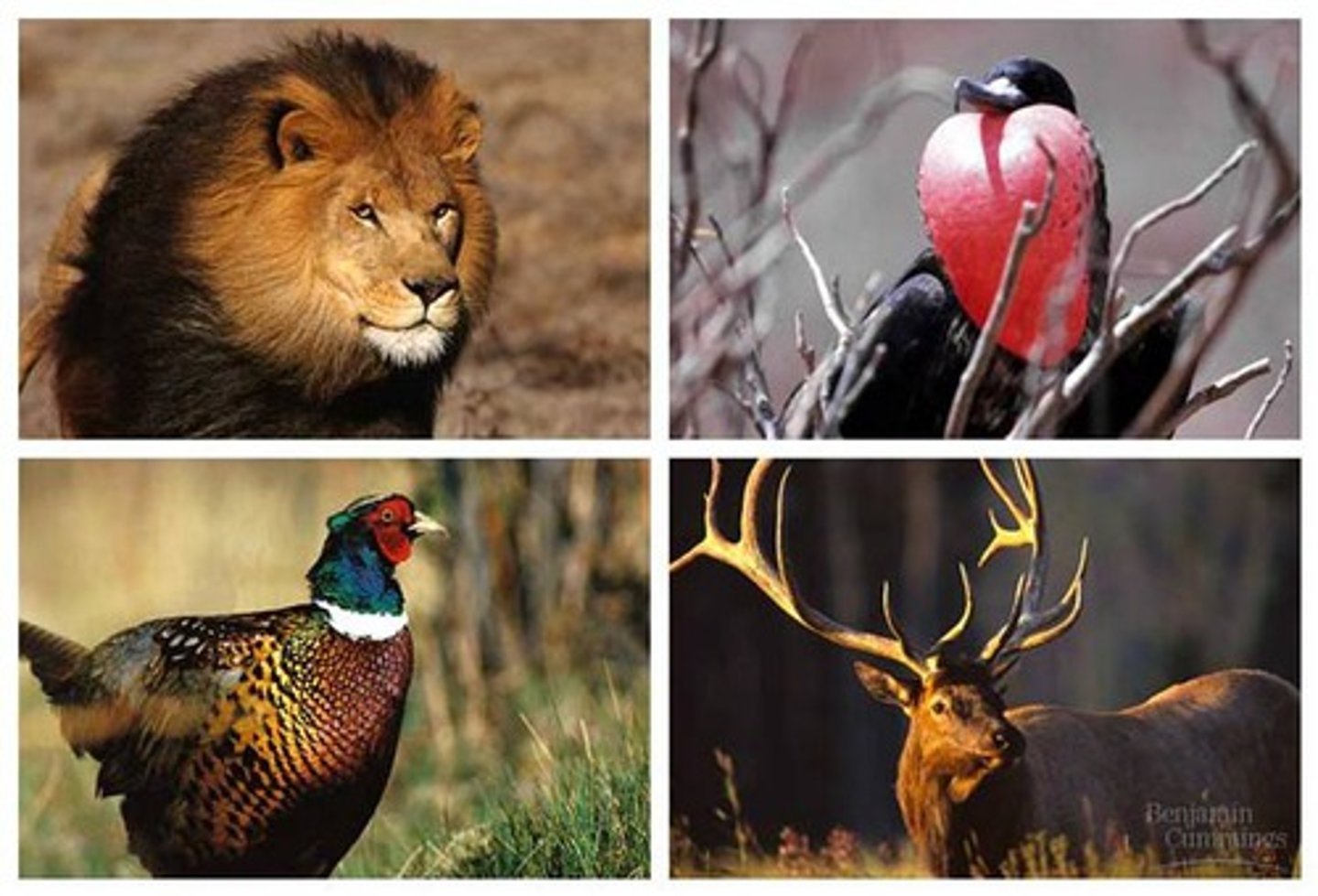

behavioral isolation
isolation between populations due to differences in courtship or mating behavior

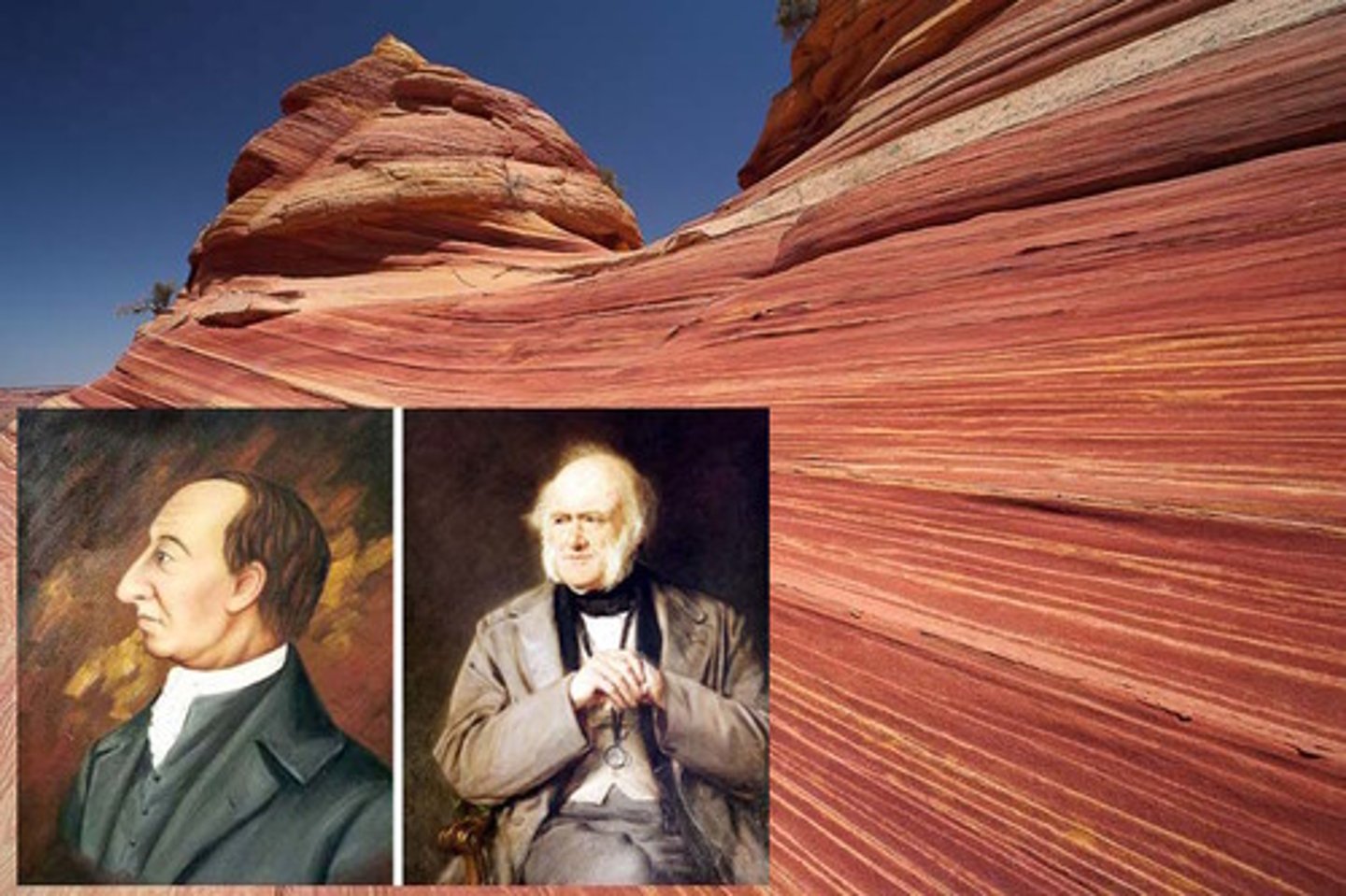
Lyell and Hutton
Geologists who said the world was old and slowly, but constantly changing

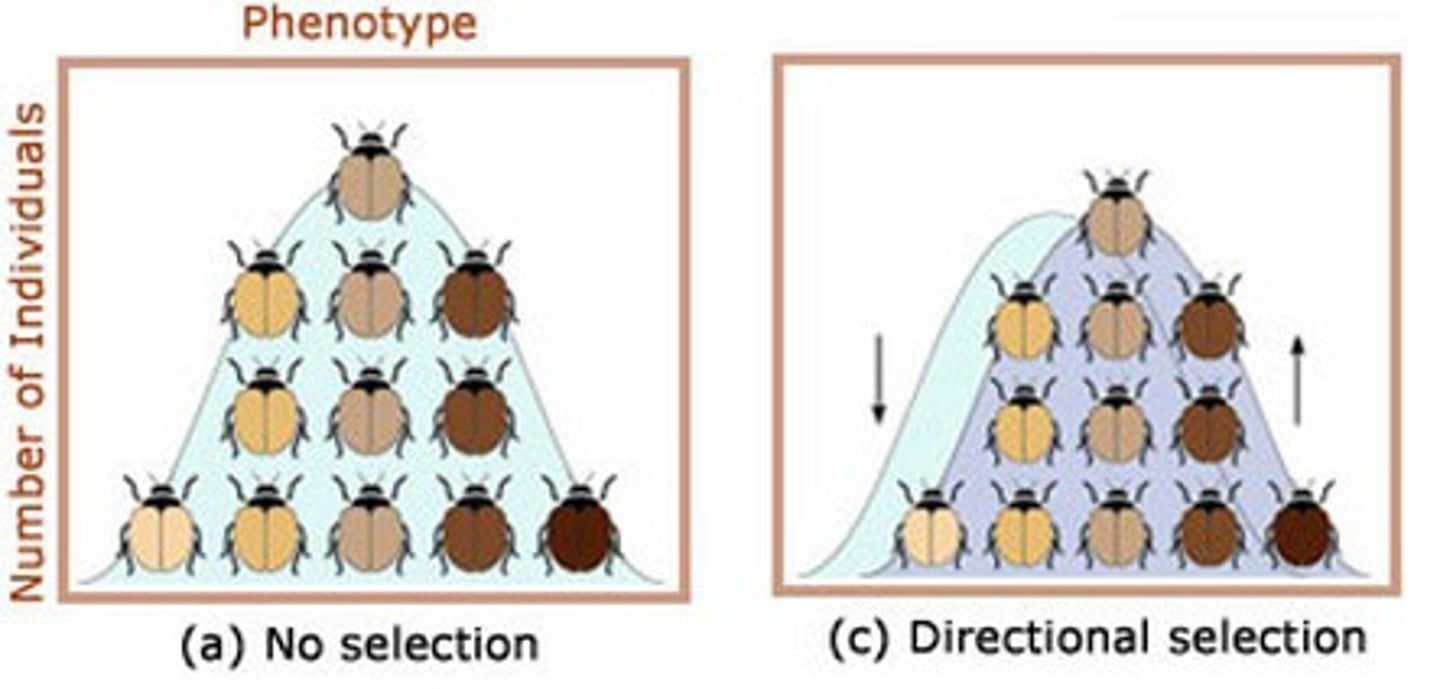
directional selection
occurs when natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of a trait
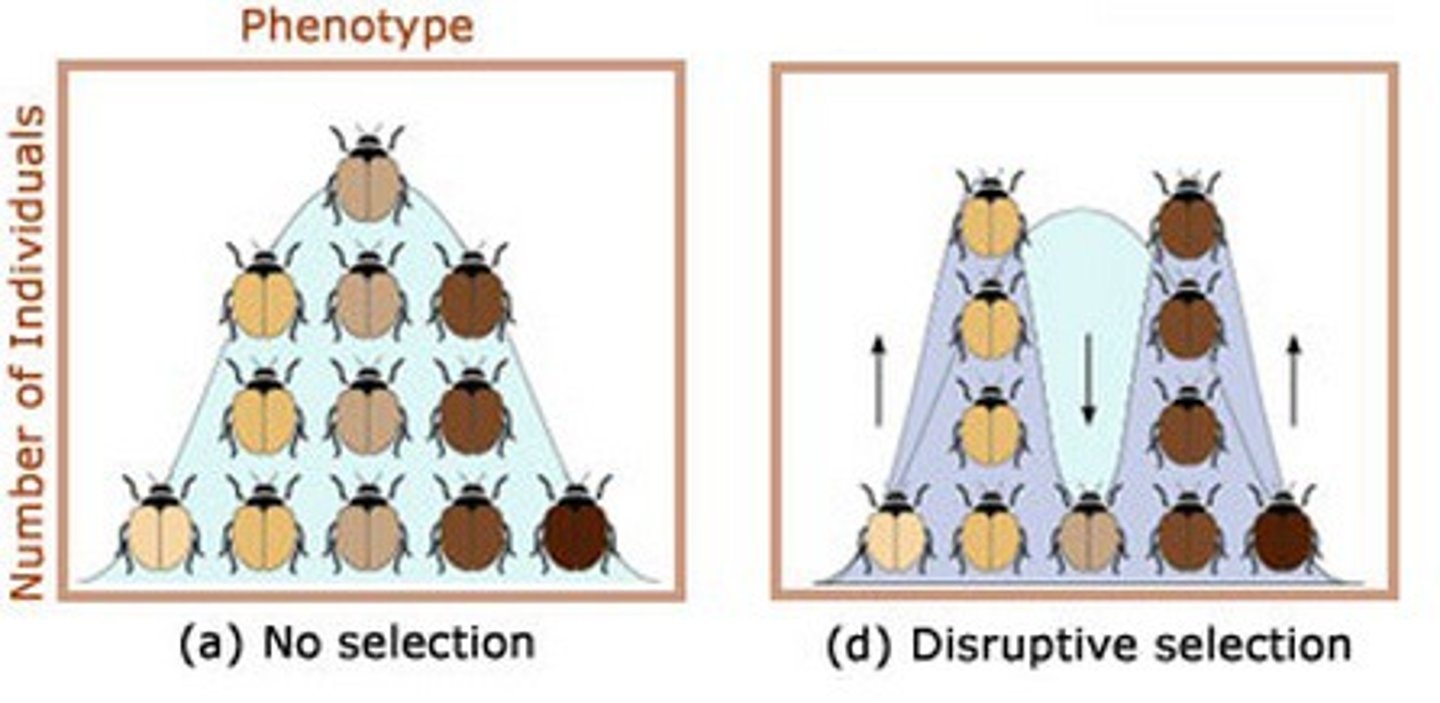
disruptive selection
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
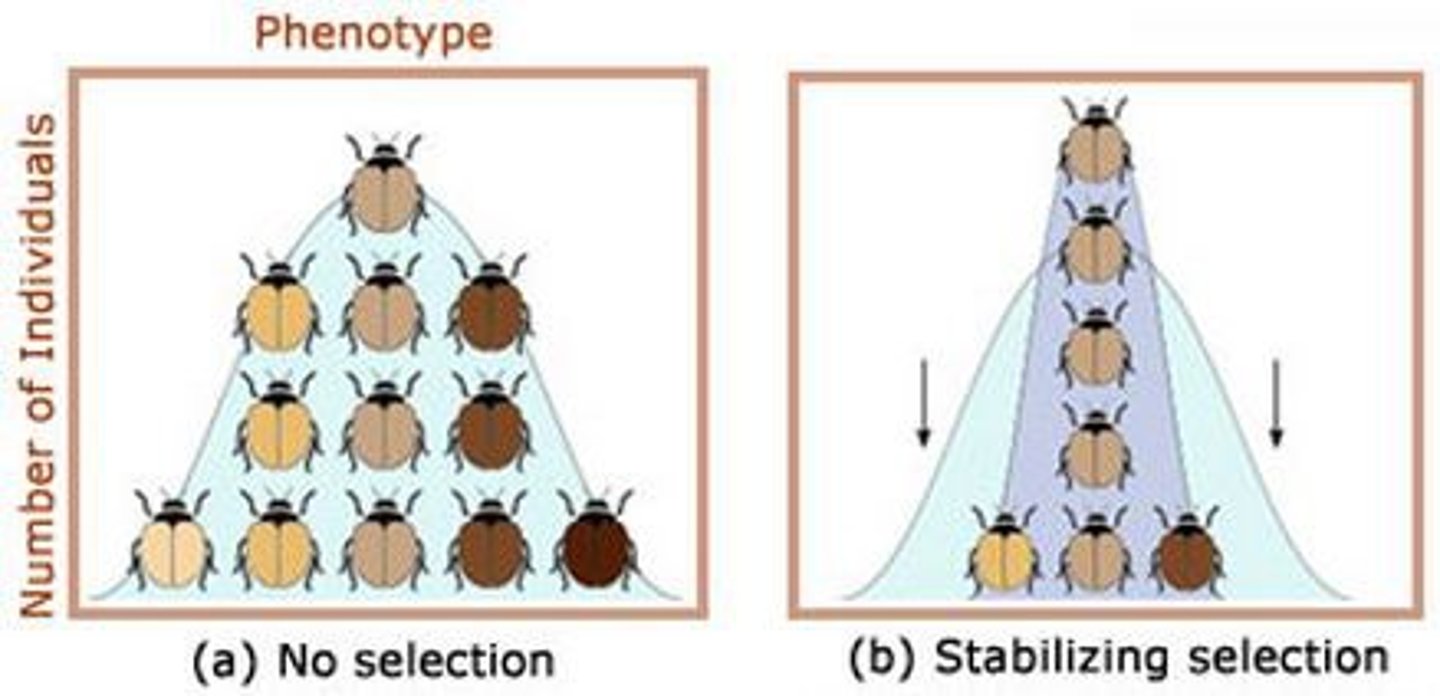
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
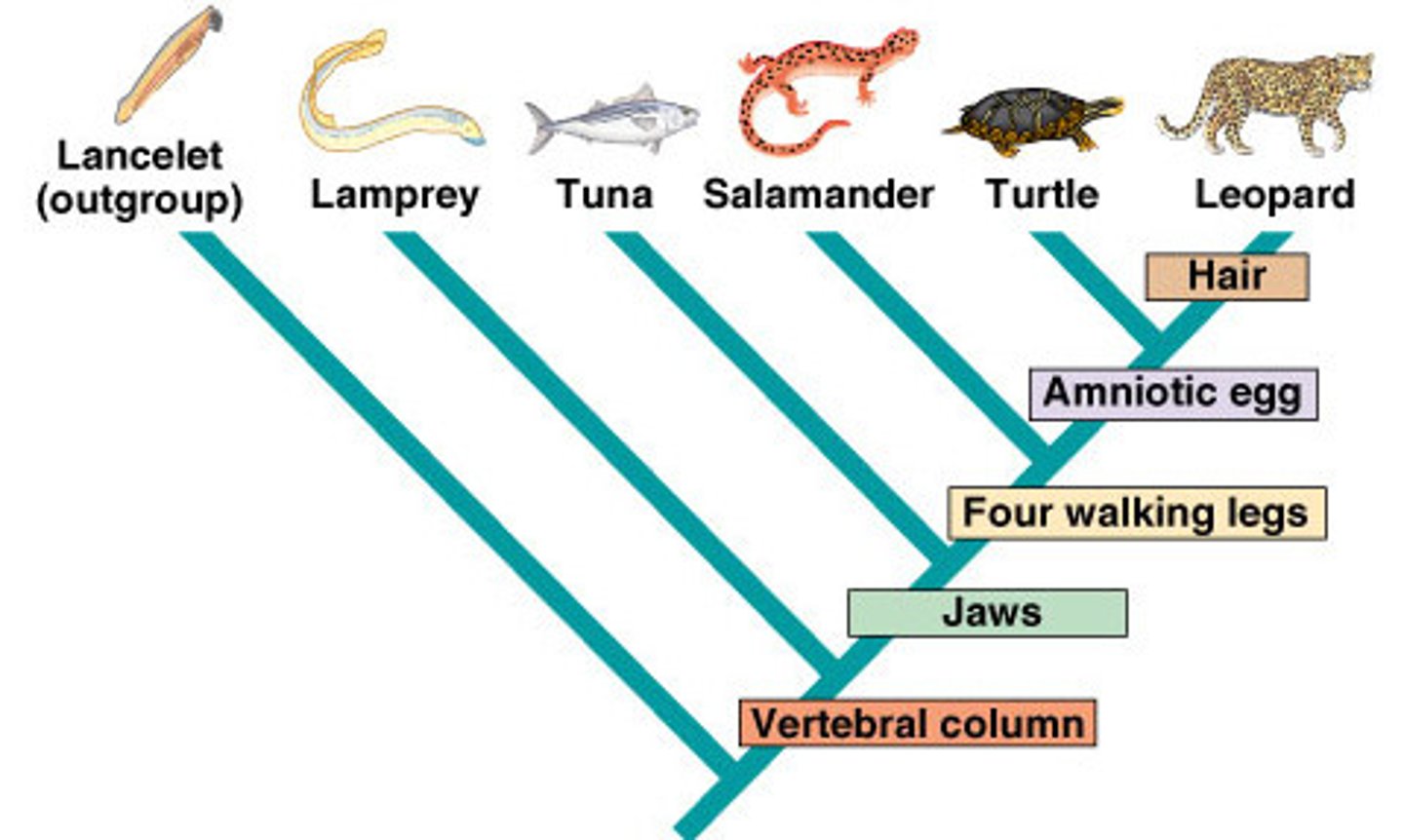
phylogenetic tree (cladogram)
a diagram that depicts the ancestral relationships between organisms
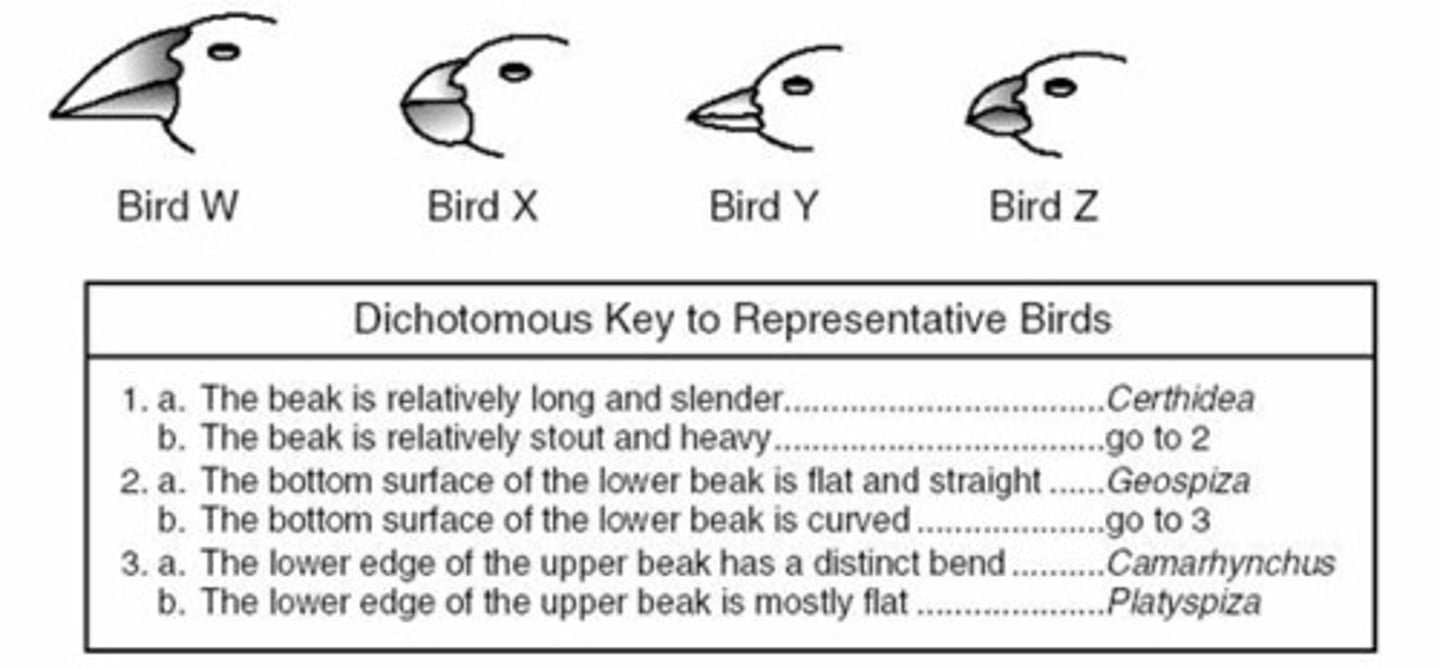
Dichotomous key (classification key)
Classification tool used in identifying organisms or materials
genetic drift
random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations
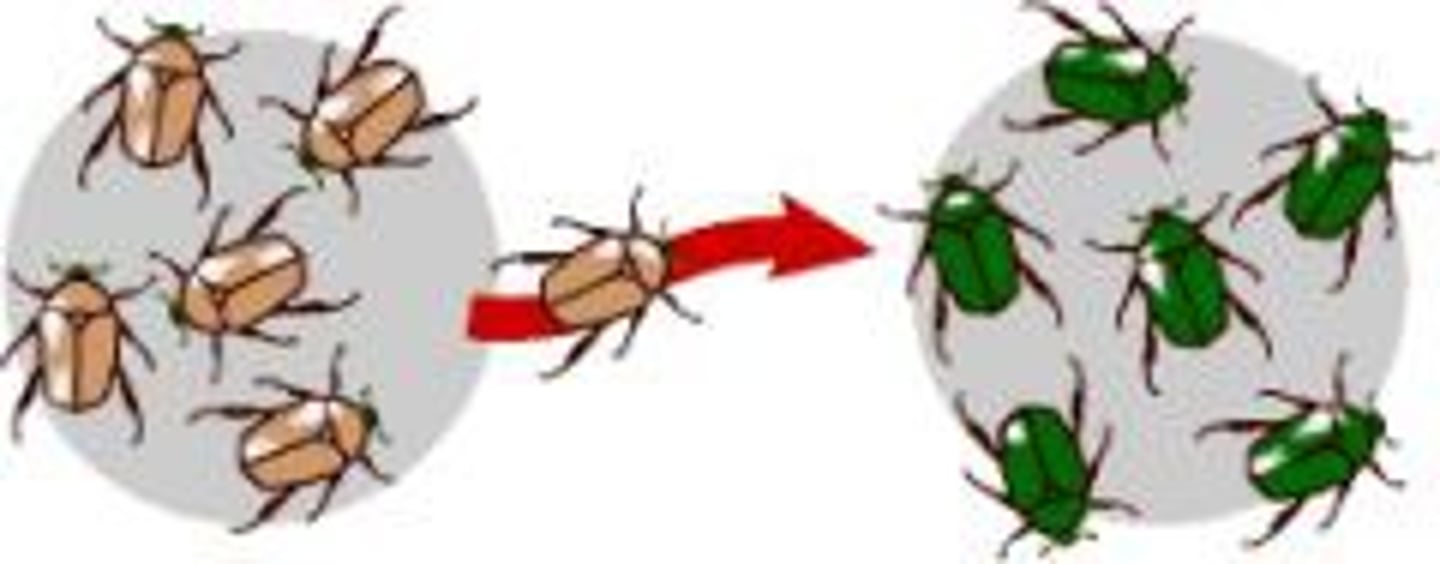
gene flow (migration)
movement of alleles from one population to another
Phylum
Group of closely related classes
Bacteria Domain Characteristics
Prokaryote and live in regular environments
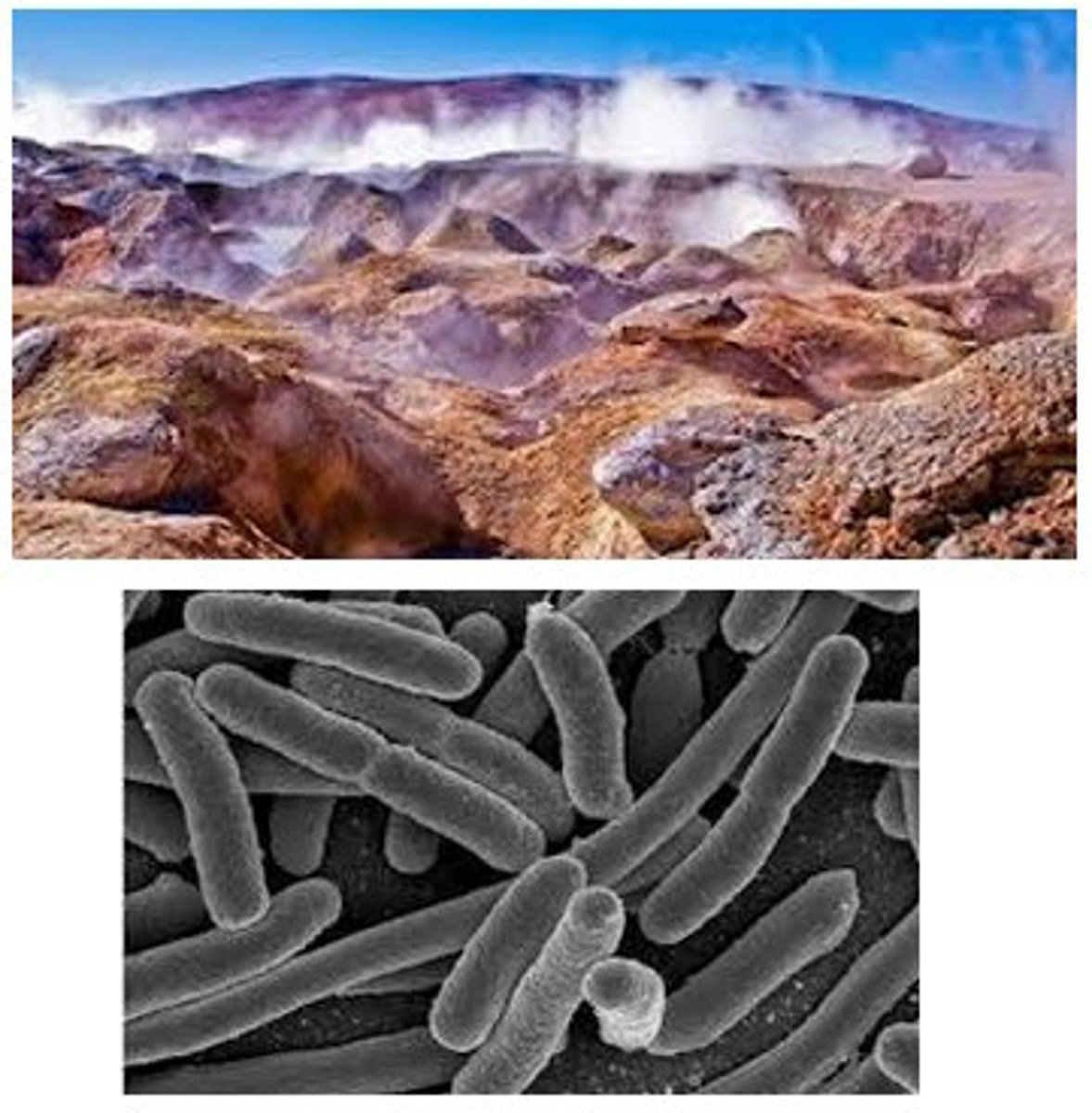
Archaebacteria Domain Characteristics
Prokaryote and live in EXTREME environments

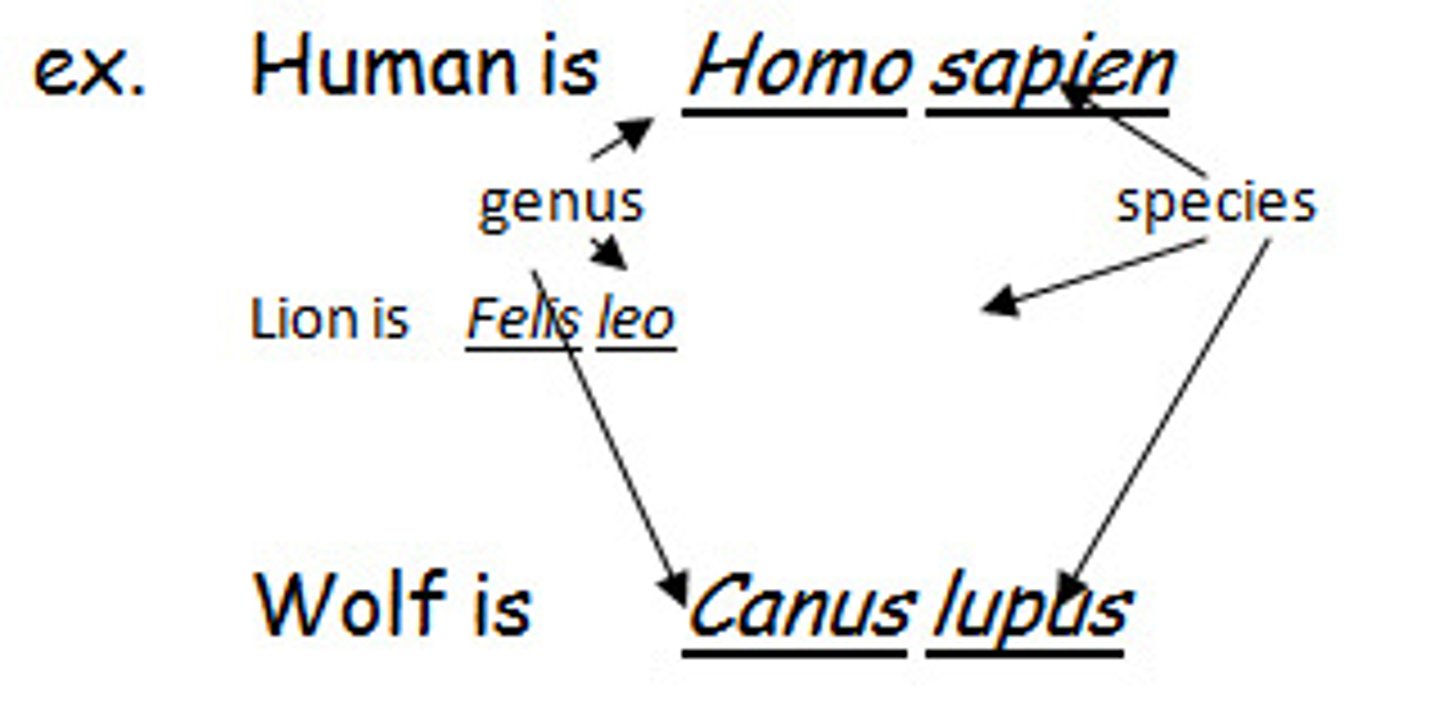
genus-species name
The unique two-word name of a particular organism.
Levels of classification (largest to smallest)
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
habitat isolation
Two species encounter each other rarely, or not at all, because they occupy different habitats, even though not isolated by physical barriers
