Managerial Exam 3
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Standards are also used in managerial ____ where they relate to the ____ and acquisition price of inputs used in manufacturing goods or providing services.
quantity , price
______ specify how much of an input should be used to make a product or provide a service.
Quantity Standards
_____ specify how much should be paid for each unit of the input.
Price Standards
If either the quantity or acquisition price of an input departs significantly from the standard, manager investigate ____
the discrepancy to find the cause of the problem and eliminate it.
Standard Quantity Per Unit
The amount of direct materials allowed for each unit of finished product, including an allowance for normal inefficiencies, such as scrap and spoilage.
Standard Price Per Unit
The price that should be paid for each unit of direct materials. It should reflect the final, delivered cost of those materials.
Standard Hours Per Unit
The amount of direct labor time allowed to complete a single unit of product, including allowances for breaks, machine downtime, cleanup, rejects, and other normal inefficiencies.
Standard Rate Per Hour
The labor rate allowed per hour of labor time, including employment taxes and fringe benefits.
Standard Cost Per Unit
The standard quantity allowed of an input per unit of a specific product, multiplied by the standard price of the input.
Material Price Variance
(Actual Price - Standard Price) x Actual Quantity
OR (AP - SP) x AQ
Materials Quantity Variance
(Actual Quantity Used - Standard Quantity Used) x Standard Price
OR (AQ used - SQ used) x SP
Labor Rate Variance
(Actual Rate - Standard Rate) x Actual Hours
OR (AR - SR) x AH
Labor Efficiency Variance
(Actual Hours - Standard Hours) x Standard Rate
OR (AH - SH) x SR
Standard Quantity Allowed
The amount of direct materials that should have been used to complete the period’s actual output.
(Actual #’s produced x Standard Quantity per unit)
Standard Hours Allowed
= Actual Output x Standard Hours per unit
How do you know when the variance is Favorable or Unfavorable?
Favorable = Actual < Standard
Unfavorable = Actual > Standard
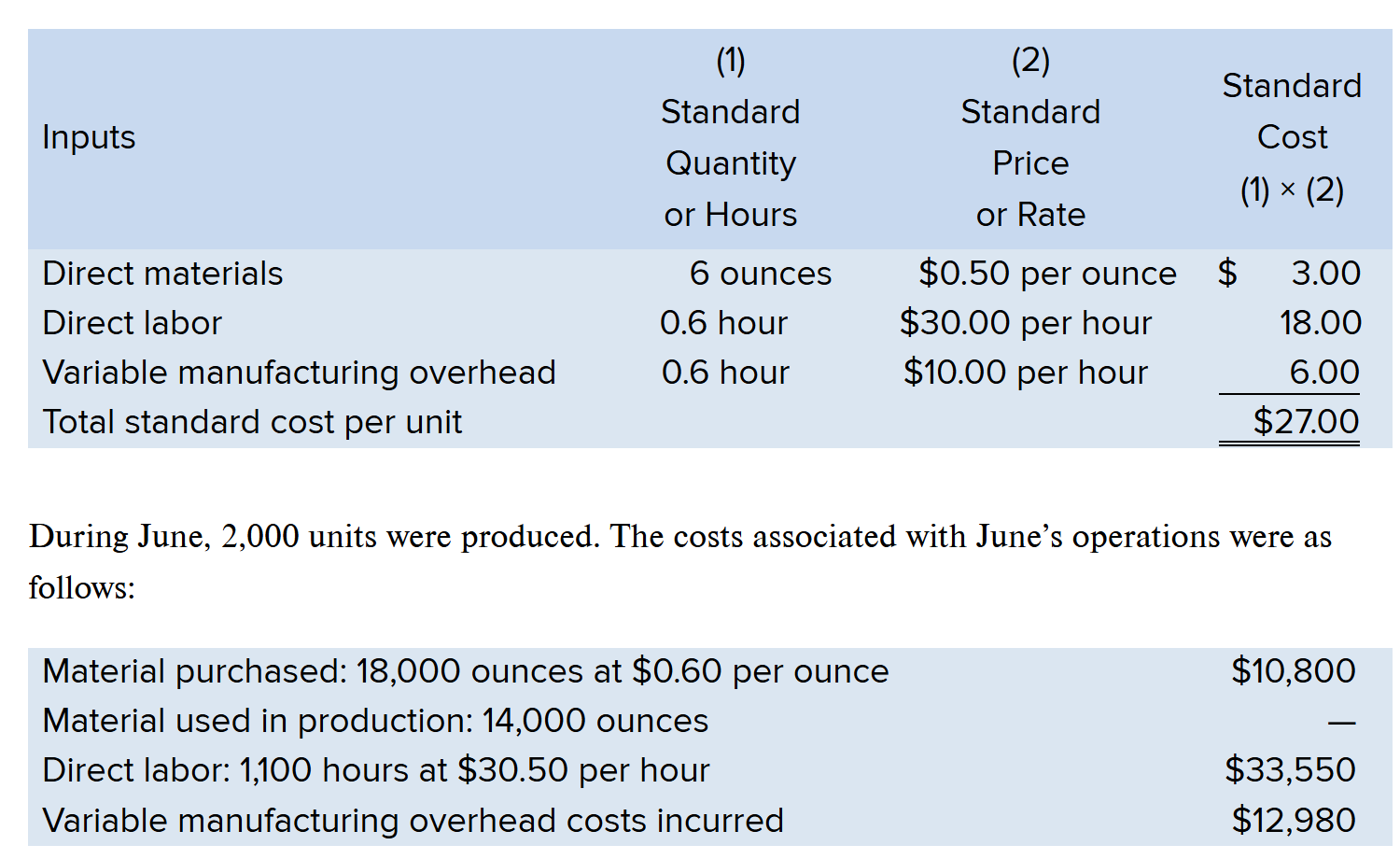
Compute the Materials Price Variance
(AP - SP) x AQ
(.60 - .50) x 18,000 = $1,800
Since .60 is HIGHER than .50, the variance is Unfavorable
Answer: $1,800 U
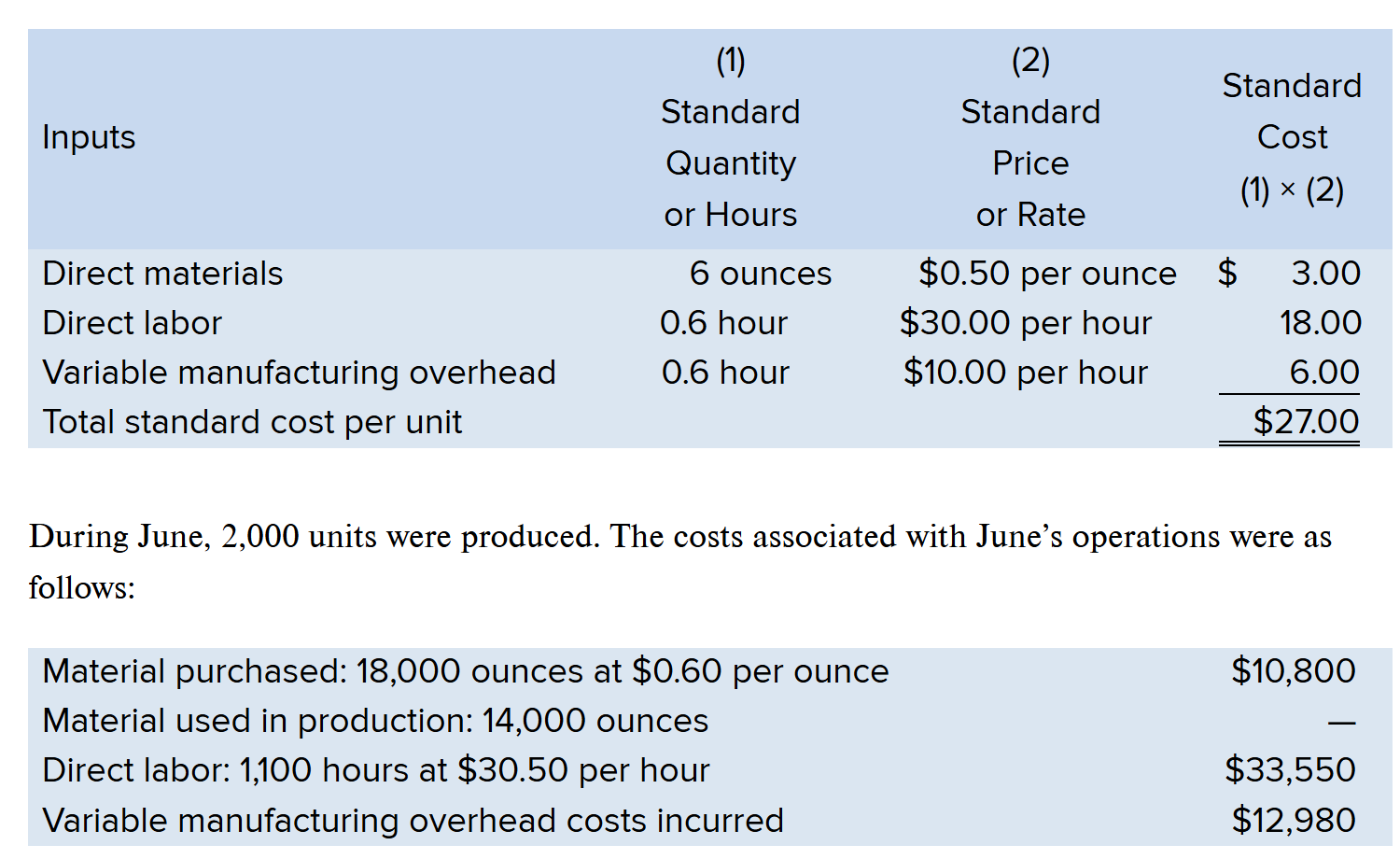
Compute the Materials Quantity Variance
(AQ - SQ) x SP
(14,000 - 12,000) x .50 = $1,000
Since 14,000 is HIGHER than 12,000, the variance is Unfavorable
Answer = $1,000 U
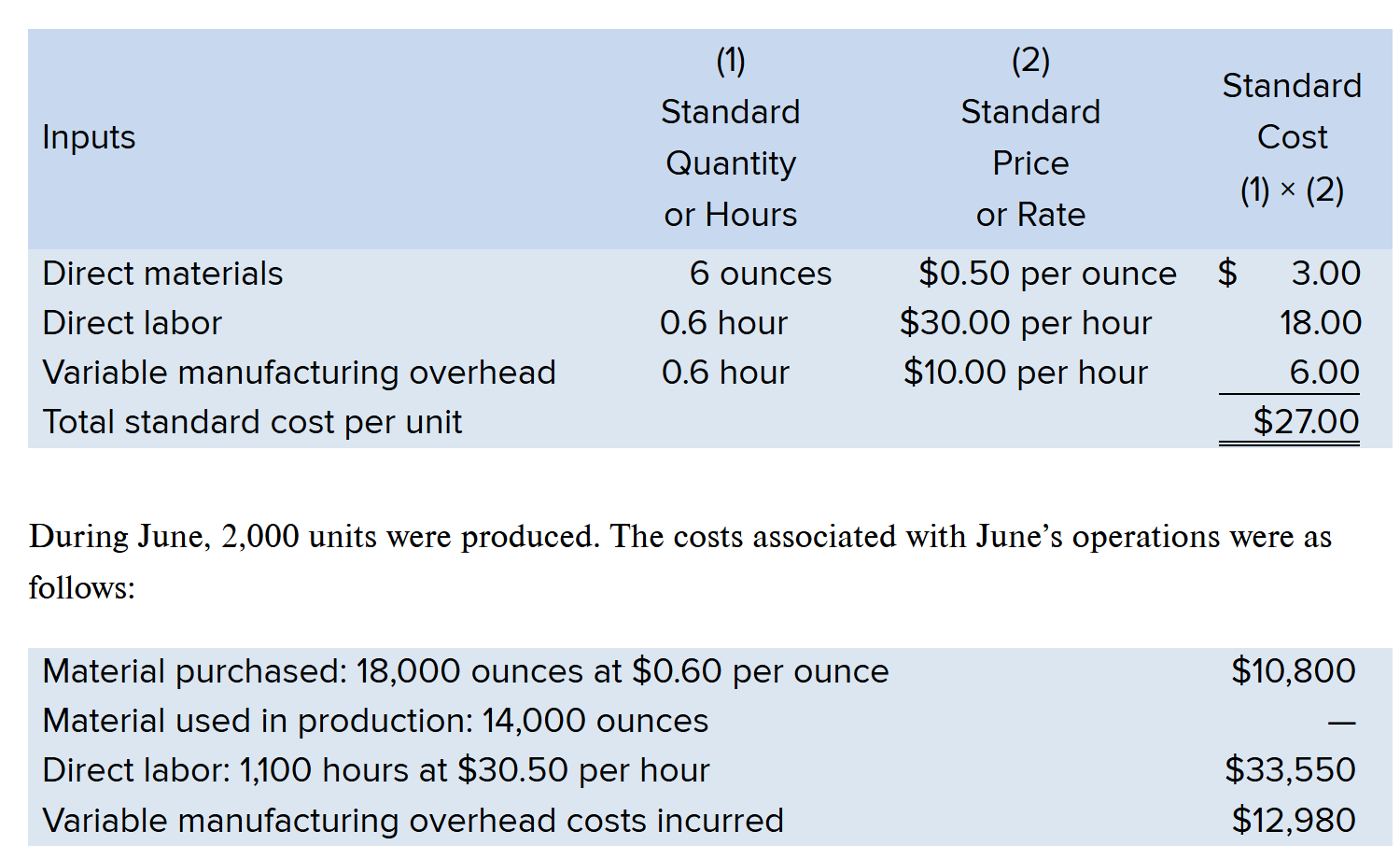
Compute the Labor Rate Variance
(AR - SR) x AH
(30.5 - 30) x 1,100 = $550
Since 30.5 is HIGHER than 30, the variance is Unfavorable
Answer = $550 U
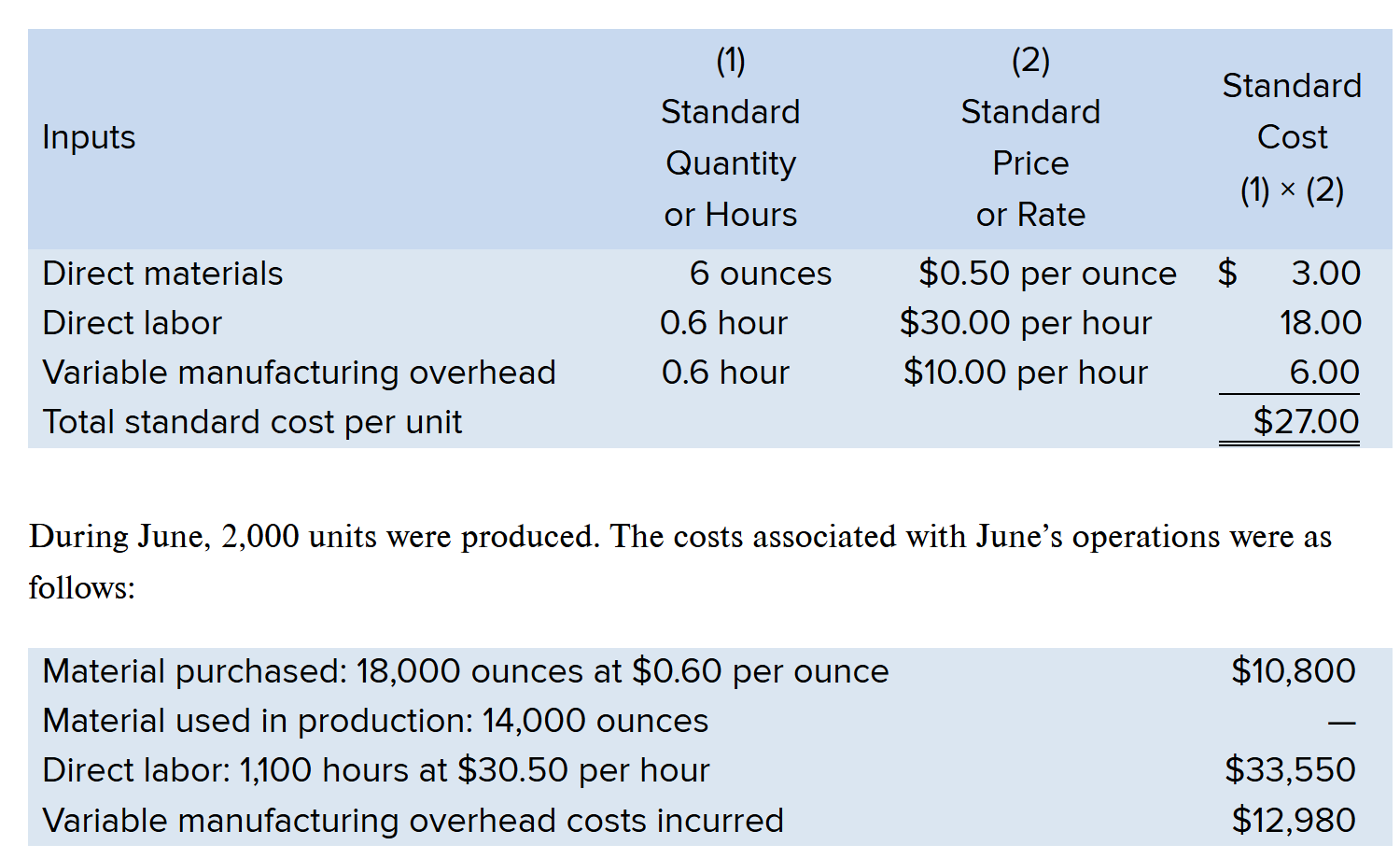
Compute the Labor Efficiency Variance
(AH - SH) x SR
(1,100 - 1,200) x 30 = $3,300
Since 1,100 is LESS than 1,200, variance is Favorable
Answer = $3,300 F
What are the 3 types of responsibility centers?
Cost
Profit
Investment
Cost Center
Cost ✅
Revenues ❌
Investment ❌
Profit Center
Cost ✅
Revenues ✅
Investment ❌
Investment Center
Cost ✅
Revenues ✅
Investment ✅
Return on Investment (ROI) Formula
Net Operating Income / Average Operating Assets
What is Net Operating Income
Income before interest and taxes and is sometimes referred to as EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes)
What is Average Operating Assets
Include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, plant and equipment, and all other assets held for operating purposes.
The equation for ROI can also be expressed in terms of ____ and ____
Margin ; Turnover
Margin =
Net Operating Income / Sales
Turnover =
Sales / Average Operating Assets

What is the expected Return on Investment?
NOI / AOS » $10,000 / $50,000 = .20 » 20%

pt. 2: now suppose the manager of the Montvale Burger Grill is considering investing $2,000 in a state-of-the-art soft-serve ice cream machine. This new machine would boost sales by $4,000 but would require additional operating expenses of $1,000. Thus, net operating income would increase by $3,000, to $13,000. What is the new ROI?
$13,000 / $52,000 = .25 » 25%
_____ is another approach to measuring an investment center’s performance. Always in $’s
Residual Income
Residual Income formula
= Net Operating Income - (Average Operating Assets x Min. Required Rate on Return)
Ways to improve ROI?
Increase Net Operating Income
Decrease Operating Assets
Decrease Expenses
Increase Sales
Ways to improve R.I.?
Decrease Rate of Return
What is The Balanced Scorecard (dashboard)
An integrated set of performance measures derived from the organization’s strategy.
Define Strategy
a ‘game plan’ that is difficult to replicate and differentiates a company from its competitors in ways that attract & retain customers.
What differentiates a company from others?
Customer values:
Customer intimacy
Operational Excellence
Product Leadership
What are the 4 Performance Measures?
Financial
Customer
Learning & Growth
International Business Processes
Throughput Time formula
= Process Time + Inspection Time + Move Time + Queue Time
Delivery Cycle Time formula
= Wait Time + Throughput Time
Manufacturing Cycle Efficiency formula
= Process Time / Throughput Time
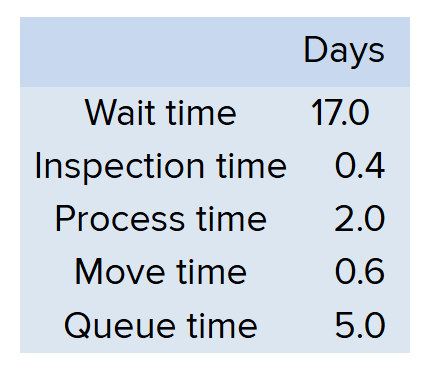
What is the Throughput time?
8 days
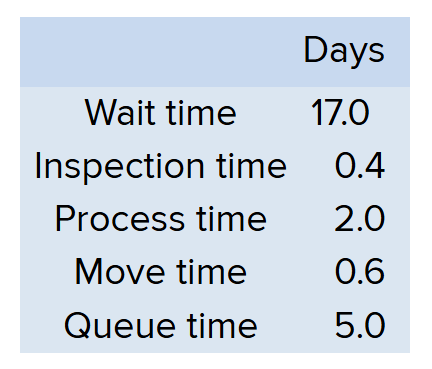
What is the Delivery Cycle?
25 days
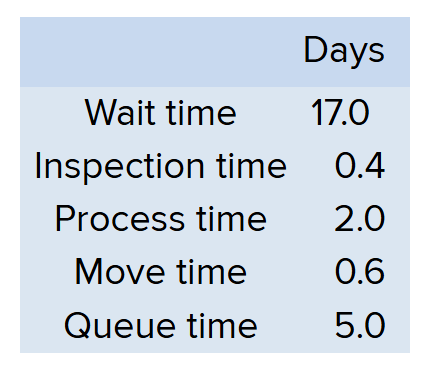
What is the MCE?
.25
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) formula
= Utilization x Efficiency x Quality
How to calculate the Utilization Rate?
= Actual Run Time / Machine Time Available
How to calculate the Efficiency Rate?
= Actual Run Rate / Ideal Run Rate
How to calculate the Quality Rate?
= Defect-free output / Total output

Calculate the Utilization Rate:
.70

Calculate the Efficiency Rate:
.95

Calculate the Quality Rate
.925

Calculate the Overall Equipment Effectiveness
.615