unit 2 flashcards: blood vessels
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this is only the beginning
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
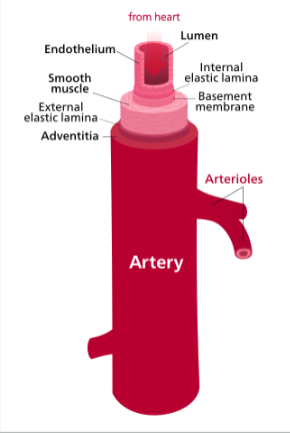
define arteries
carry blood AWAY from heart; elastic, muscular, arterioles; split repeatedly
thinner tunica externa than media, strong + thick tunica media, wavy tunica interna
oxygenated blood exceptions - pulmo trunk, artery, umbilical artery
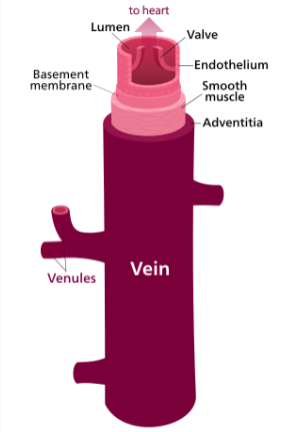
define veins
carry blood TOWARDS the hear; venules - smallest veins; converge
tunica externa thickest, thinner tunica media, smooth tunica interna (endothelium)
deoxy blood except - pulmo veins, umbilical vein
define capillaries
endothelium (single layer of cells); directly serve cellular metabolic demands of tissues and organs
exchange happens thru thin walls of caps; plasma + nutrients pass thru becoming the interstitial fluid that later returns thru lymphatic syst
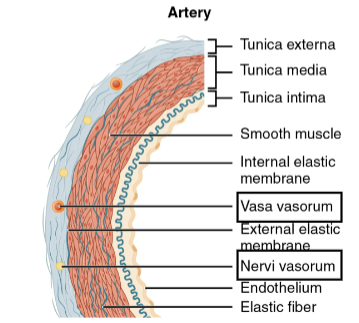
desc tunica externa
mostly made of CT w collagen + elastin; anchors it to surrounding structures, provides support, protects
contains numerous nerves + lymphatic vessels - vasa vasorum (bvs of bvs), nervi vasorum (nerves of bv)

desc tunica media
smooth musc + elastic fibers; mainly responsib for bp + maintain circulation
vasodilation vs vasoconstriction (vasometer nerve/symp NS): norepinephrine (NE) always released, maintaining arteries + arterioles partially contracted : more NE → more contraction
in brain + skel musc, ACh can be released and stim release of nitric oxide, which causes vasodilation
check chart in guided notes
desc tunica interna (intima)
endothelium, continuous w endocardium; reduces friction; wavy due to constriction of smooth musc
arteries - presence of internal elastic mm
which layer responsib for keeping bp
tunica media
name of neurotransmitter involved in keeping bp? explain connection between NT lvls and diameter of bv
norepinephrine: the more NE, the more contraction of bvs, and vice versa
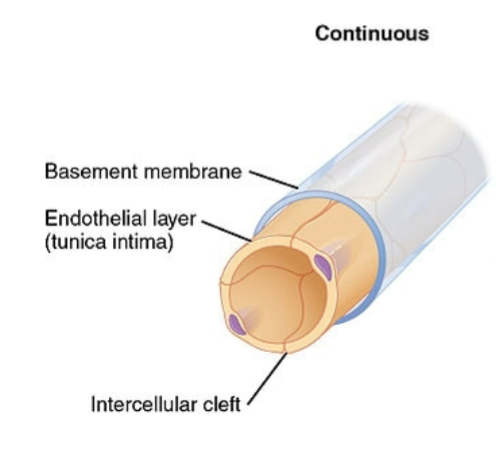
desc continuous capillaries (anatomical/physiological diffs)
most common, least permiable; plasma mm of endothelial cells form continuous tube w tight junctions interrupted by intercellular clefts (gaps between neighboring cells)
brain capillaries have tight junctions instead of intracellular clefts
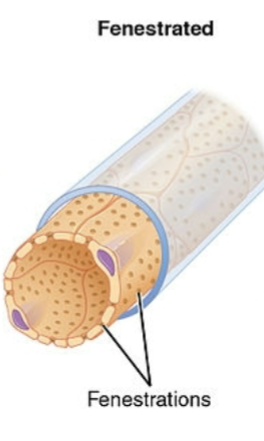
desc fenestrated caps (anatomical/physiological diffs)
fenestra = windows; small pores in plasma mm (more permiable)
allows for greater exchange of solutes; examples - kidneys (filtration), endocrine glands (hormones), villi of small intestine
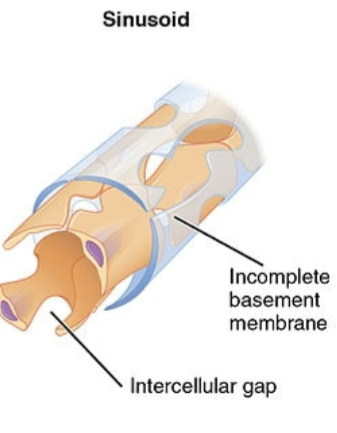
desc sinusoid caps (anatomical/physiological diffs)
most permiable, least abundant; v wide lumen w spaces between endothelial cells + lacking complete basement mm; large intercellular clefts + fenestrations; endothelium not continuous
blood flows v slowly thru these (for nutrient deposit/pick up)
kupffer cells: large macrophages form part of lining; remove + destroy contained bacteria; eg - liver, spleen, bone marrow (bc blood cells need to squeeze thru)
desc elastic arteries
largest in body: L common carotid, L subclavian, brachiocephalic, aorta, pulmo trunk
its tunica media dominated by elastic fibers; help propel blood even when ventricles are relaxed; accomm surge of blood + fxn as pressure resovoir; expands + contracts as heart pumps; elastic fibers recoil, pushing blood forward
desc musc arteries
throughout body, thickest tunica media, fewer elastic fibers; capable of greater vasoconst
dist blood in various parts of body (dist arteries); ex - brachial artery, femoral, external carotid, mesenteric
desc arterioles
literally means small arteries; all 3 layers, but externa + media shrink, interna stays same
smaller arterioles lead into capi bed; regulate blood flow to caps by arteriole diameter
terminal arterioles, metarteriole - ones before capi beds
what happens to elasticity in arteries during arteriosclerosis?
walls thicken and harden, elasticity decreases + bp inc
how is anat of capillaries + capillary beds well suited to their fxn?
thin, single walls so nutrients, hormones, gases, blood cells (prob other things) can pass thru walls and get into bloodstream to be distrib around body
which bv permits exchange of nutrients + gases between blood and tissue cells? why?
capillaries bc thin walls
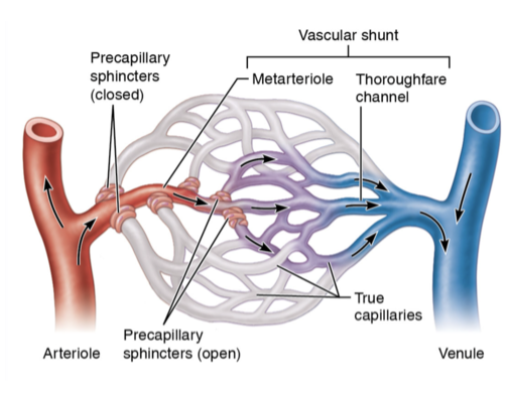
differ between metarteriole, true capillaries, and thoroughfare channel
metarteriole - act as bridge between arterioles and caps; w precap sphincter; ctrls blood flow into cap bed; chems released by endothelial cells such as nitric oxide causes vasodilation
true caps - (10 -100 caps) where actual exchange happens
thoroughfare channel - intermediate between cap and venule; provides direct route from arteriole to venule; if precap sphincter closed, blood flows from metarteriole to thoroughfare channel
what are veins and venules?
venules are smallest veins
venule’s smaller than veins, come after capillaries and lead to veins
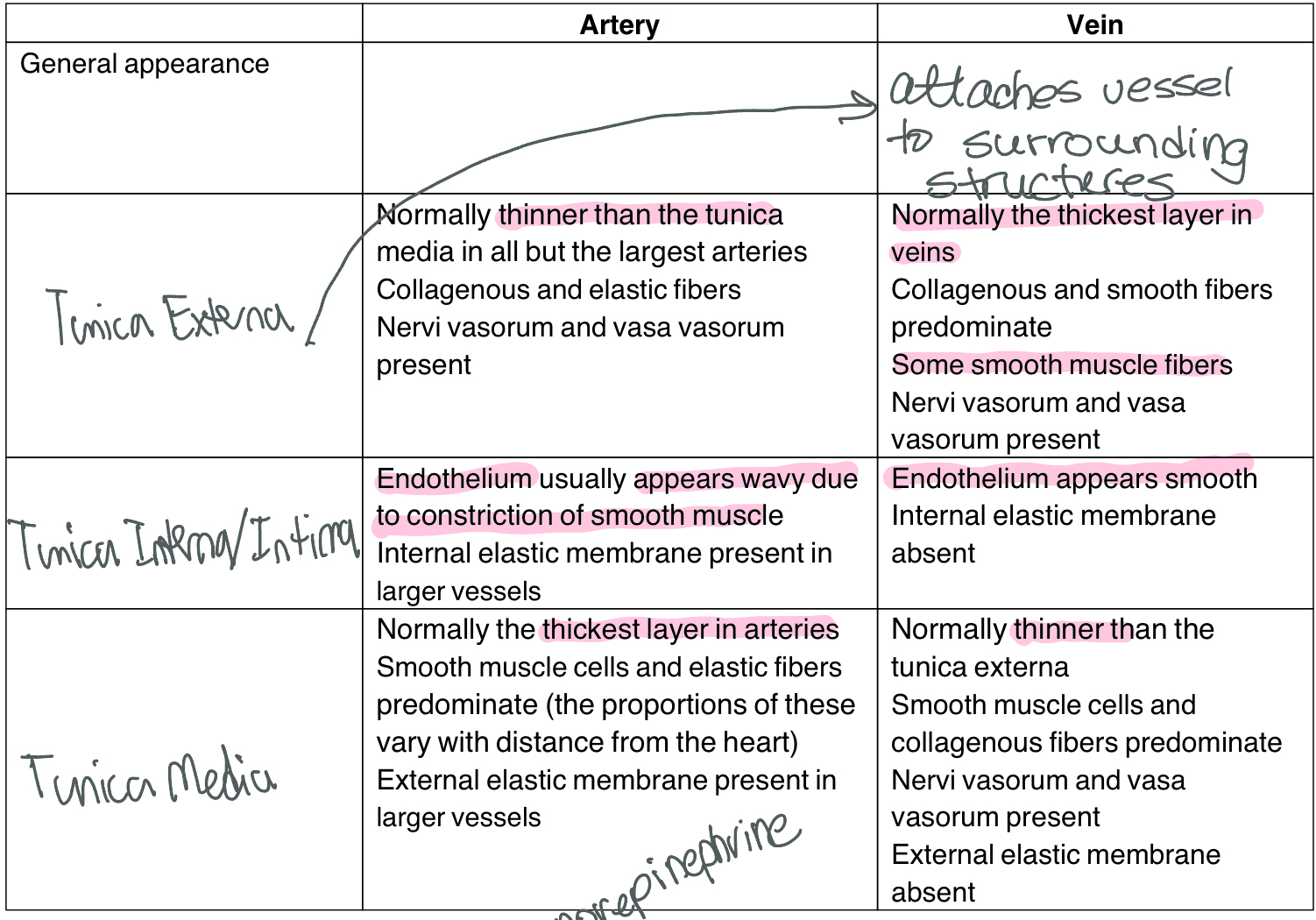
compared to arteries, veins have ______
thinner tunica media, thicker tunica externa, smoother endothelium (tunica intima), larger lumen, contain valves, ability to fold or grow to hold more blood, deoxy blood usually
desc pressures in diff bvs
veins contain lowest bp
arteries have highest bp, esp around heart; maintain bp thru thick walls + elasticity
cap bp lower than arteries in order to allow for efficient exchange of substances
is vasoconstriction the same in arteries and veins? explain
in arteries, vasconst capabilities greater bc thick tunica media,
in veins, thinner tunica media means less muscular strength and structure to be able to constrict
what is the fxn of valves in the veins?
prevent backflow of blood thru veins
how is the venous blood returned to the heart?
venous return - occurs due to pressure generated by contractions of heart’s left ventricle
at rest, which vessel(s) act as blood resovoirs
veins bc large lumen
define anastomosis
in vasc syst creates backup pathway for blood flow if a bv becomes blocked
know info abt blood flow covered in lecture
as in the order of blood flow thru bvs?
define bp and what are norm vals?
force exerted by blood against bv wall (mmHg); determined by various factors - cardiac output, compliance, blood vol, blood viscosity, bv length + diameter
systolic/diastolic pressure - varies w elasticity of arteries close to heart and vol of blood
normal vals at rest: syst (highest pressure attained, heart contraction) 120mmHg; diast (lowest pressure attained, heart relax) 60-80 mmHg
how is bp determined?
i think vasoconstriction and dilation of bvs?
what are the effects of vasodilation and vasoconstriction on bp?
vasodilation decreases bp, vasoconstriction inc bp
what does systolic and diastolic pressure mean?
systolic: first number - force of blood flow when blood pumped out of heart, less than 120 mmHg; highest pressure in aorta
diastolic: second num - measured between beats when your heart is filling w blood, 60-80 mmHg; lowest pressure S + i vena cavae
what is mean arterial pressure? why is it important?
ave pressure in aorta thruout cardi cyc; pressure propelling blood into tissues
MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3 (systolic BP - diastolic BP)
important bc determines how well blood flow is and if tissues are getting enough blood: 70 - 150 mmHg
MAP < 60 cause fainting, above 160 cause cerebral edema (build up fluid)
define pulse and give norm vals. define tachy and bradycardia
pressure wave felt by alternating expansion and recoil of arteries during cardi cyc; measure of hr (bpm); norm = 60-100bpm
tachycardia - rapid resting rate over 100 bpm
bradycardia - slow resting rate under 60 bpm
how does body regulate bp (neutral and hormonal ctrls)? (chart is best way to study this part)
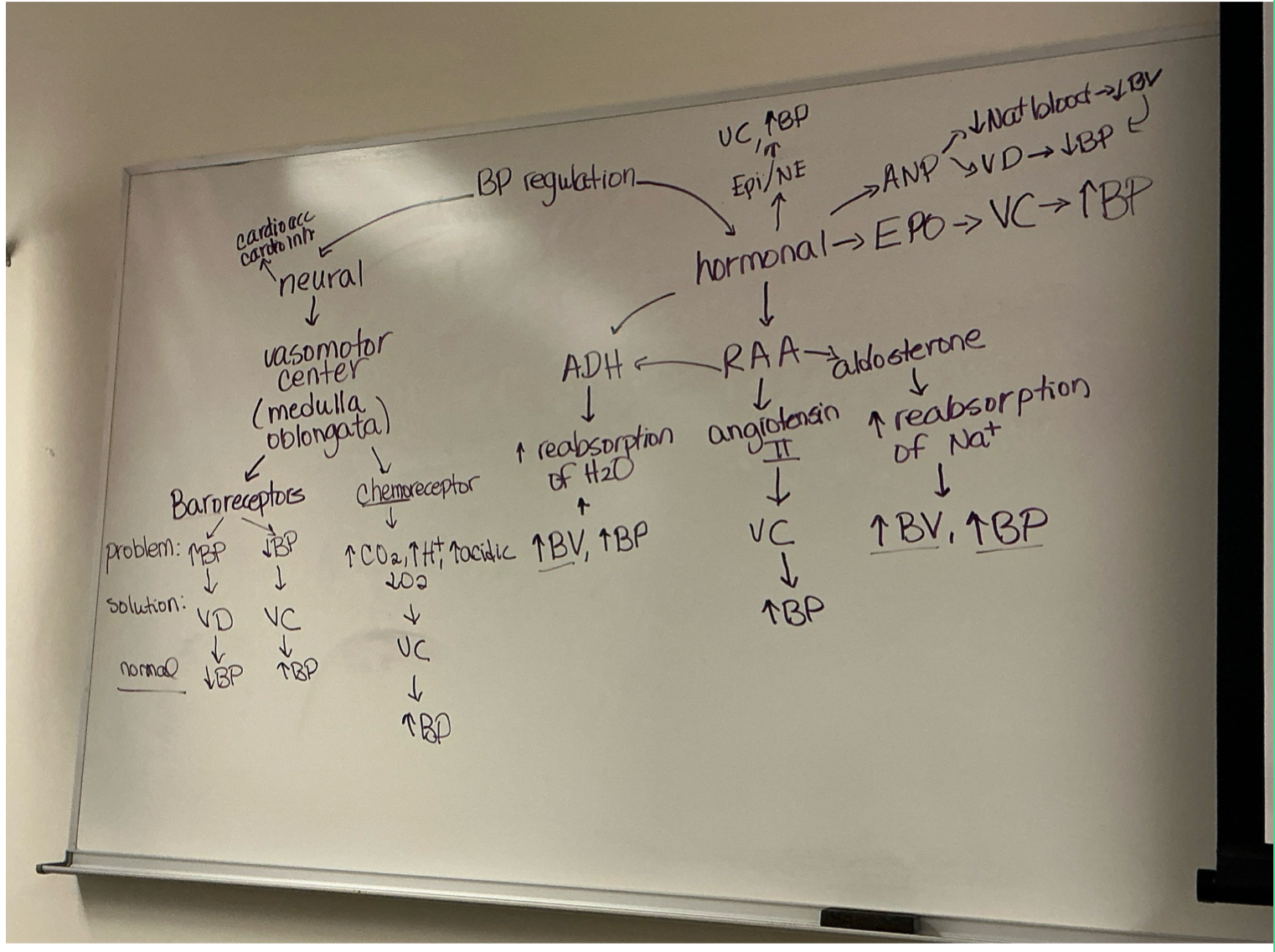
what is autoregulation?
ability of tissue to auto adjust own blood flow to match metabolic demand for delivery of oxy + nutrients + removal of wastes
phys + chem stim can lead to autoreg, like stretch, nitric oxide, inc lvl CO2
define bulk flow
passive process in which large num of ions, molecules, or particles in fluid move together in one direction down a pressure gradient; occurs from area of high pressure to low pressure, and continues if pressure diff exists
define hydrostatic + osmotic pressure. what are their norm vals in capillary and interstitial fluid at beginning (arterial end) and end of capillary (venous end)?
hydrostatic: force exerted by fluid pushing against wall; arterial end: 35mmHg, venous: 18mmHg
osmotic: equal thruout caps, created by presence in fluid of large nondifusible molecules; arterial and venous: 20mmHg
define hydrostatic pressure and ID its norm vals in capillary and interstitial fluid at beginning (arterial end) and end of capillary (venous end)
force exerted by a fluid pressing against a wall
arterial end: 35mmHg; venous end: 18mmHg
define osmotic pressure and ID its norm vals in capillary and interstitial fluid at beginning (arterial end) and end of capillary (venous end)
equal throughout caps; created by presence in a fluid of large nondiffusible molecules (plasma proteins)
arterial + venous end: 25mmHg
what is filtration and reabsorption? where in the capillary do they happen? where is fluid moving towards in each one?
filtration - fluid pushed out of cap; moving from bloodstream to tissues, high pressure in cap to low pressure externally
reabsorption - fluid pushed into cap; moving from interstitial fluid back into caps, high pressure externally to lower pressure in venous cap end
happens at arterial and venous ends of caps
what is the norm NFP (net filtration pressure) at the beginning of capillary and end?
beginning of cap: 10mmHg
end: -7mmHg
what happens to extra fluid left in interstitial fluid after capillary exchange
goes back thru lymph syst