BIOLOGICAL COMPOUNDS
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Name 4 important inorganic ions for life
Magnesium, Mg2+
Calcium, Ca2+
Phosphate, PO43-
Iron, Fe2+
Which inorganic ion is an important part of chlorophyll
Magnesium Mg2+
Which organic ion is constituent of haemoglobin
Iron Fe2+
2 functions of phosphate ions
To produce nucleotides (DNA, ATP, ) Phospholipids ---- Cell Membranes
Which inorganic ion is an important component of bones
Calcium Ca2+
What condition do plants suffer from, if they do not get enough of the magnesium ion?
Chlorosis - lack of chlorophyll leading to the color of the leaves turning yellow.
Water is a dipole molecule. What does this mean?
It has a positively charged end (hydrogen) and a negatively charged end (oxygen)
What forms between adjacent water molecules.
Hydrogen bonds form between oppositely charged dipoles on adjacent water molecules
What can dissolve in water?
Ions and polar molecules as they can interact with water dipoles
What cannot dissolve in water?
Non polar molecules such as lipids do not dissolve
Why is water important as a solvent
Acts as a medium for chemical reactions and as a medium to transport molecules
Give 2 ways water can be used as a metabolite.
As a reactant e.g water used in photosynthesis and in hydrolysis
Water has a specific high heat capacity. What does this mean
A large amount of heat is needed to raise it's temperature
Why is a high specific heat capacity important for life on earth?
Prevents large fluctuations in water temp keeping aquatic habitats stable for enzyme actions.
Water has a high latent heat of vaporisation. What does this mean?
A lot of heat energy is needed to change it from a liquid to a vapour
Why is high latent heat of vaporisation important for life on Earth?
Important in temperature control e.g. sweat cools skin as it vaporises
Why are water molecules cohesive
Water molecules attract each other forming hydrogen bonds between oppositely charged dipoles
Why is cohesion of water molecules important for life?
Water molecules stick together as a column in xylem allowing transpiration. Also creates high surface tension (pond skater)
What can be said about the density of ice?
The solid form (ice) is less dense than the liquid form as H bonding spaces molecules out into an open lattice structure
Why is the density of water important for life on Earth?
Ice floats on liquid water insulating water beneath keeping it a liquid for aquatic life
Water is transparent. Why is this important for life?
Allows light to pass through it - allows aquatic plants to photosynthesise
What is the general formula of a monosaccharide?
(CH₂O)n
How many carbon atoms are in a:
triose
pentose
hexose
3
5
6
What are the two isomers of the hexose sugar glucose?
Alpha and beta glucose
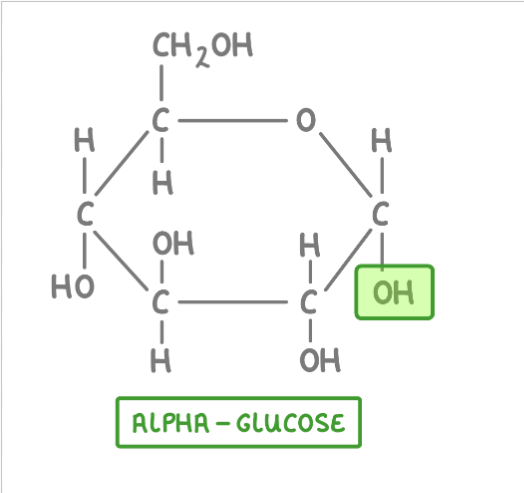
A molecule of alpha glucose?
A molecule of beta glucose
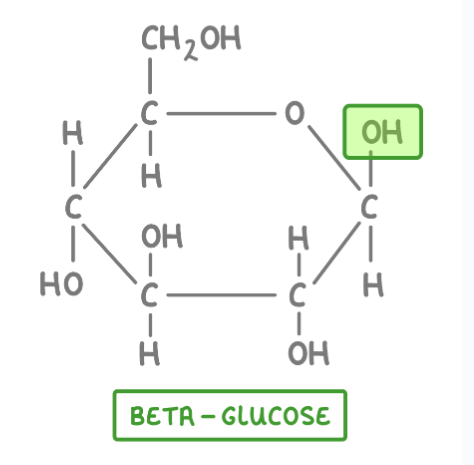
How is beta glucose different to alpha glucose?
In alpha glucose the OH group on carbon 1 points downwards, on beta glucose it points upwards.
What type of reaction joins 2 monomers together? What is made? Name the bond formed?
Condensation Reaction
Glycosidic Bond
Molecule of water is released
4 function of monosaccharides
Source of energy for respiration
Building blocks for larger molecules
Intermediates in reactions
Constituents of nucleotides
Name the component monosaccharide for the disaccharide maltose and state where it is found
Maltose is made up of 2 alpha glucose molecules
Found in germinating seeds
Name the component monosaccharide for the disaccharide sucrose and state where it is found
sucrose is made up of a glucose and a fructose
it is the transport sugar inside the phloem of flowering plants
Name the component monosaccharide for the disaccharide Lactose and state where it is found.
lactose is made up of a glucose and a galactose
it is found in mammalian milk
What is the biochemical test for like a reducing sugar like glucose and maltose?
Strongly (80⁰C-5min) heat equal volumes of test solution and Benedict's reagent.
Brick red precipitate
What is the biochemical test for a non reducing sugar like sucrose.
Fails Benedict's test.
Fresh sample boil with HCl then neutralise excess with NaHCO 3 .
Redo Benedict's test
Where is starch found? What are the two types of starch and how do they differ?
Starch grains are found in plants stored in chloroplasts, in seeds and in storage organs like potatoes
What is the biochemical test for starch?
Iodine solution reacts with starch to change from orange-brown to blue-black
What is glycogen found and how does its structure compare to starch?
Glycogen is stored in animals e.g. liver. It is more branched than starch, with far more 1,6 side chain branches than amylopectin
Where do we find cellulose molecules?
Cellulose is the structural polysaccharide found in plant cell walls
What monosaccharide is cellulose made up of?
Beta Glucose
How do the monosaccharides join together to form a cellulose molecule?
repeated condensation reactions occur where adjacent beta glucose molecules are rotated by 180 to form a glycosidic bond.
What is a cellulose microfibril and how does it form?
60-70 parallel cellulose molecules cross link by hydrogen bonds
What is a cellulose fibre?
The micro-fibrils are held bundles called a cellulose fibre
What is chitin and where is it found?
A structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of fungi and insects
What is the subunit of chitin called and what type of side chain is on this molecule?
Subunit called N-acetylglucosamine Side Chain - Acetylamine group
What elements are in lipids?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Lipids are non- polar, how does this affect their solubility?
They are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents like propanone
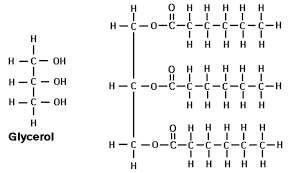
Give the structure of glycerol
What is a triglyceride composed of?
One glycerol bonded to three fatty acids molecules
What type of bond is made when triglycerides form?
Ester bonds form during condensation reactions.
What is a phospholipid molecule composed of?
One glycerol bonded to a phosphate group and two fatty acids
Which part of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic and what does this mean?
The hydrocarbon tails of the fatty acids are hydrophobic-cannot interact with water
Which part of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic and what does this mean?
The polar head (glycerol, phosphate and choline part) is hydrophilic - can interact with water
What are waxes and what are they used for by living organisms?
Lipids that melt above 45⁰C, have a waterproofing role in insect exoskeletons and leaf's cuticle
What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid?
Saturated fatty acids contain no double bonds in carbon chain (saturated with H) Unsaturated fatty acids contain at least 1 double bond in the carbon chain
Which type of fatty acid are usually found in animal lipids?
Saturated Fatty Acids
Which type of fatty acid are usually found in plant lipids?
Unsaturated or polyunsaturated
What are the roles of phospholipids in organisms?
Biological membranes (phospholipid bilayer )
What are the roles of triglycerides in organisms?
Energy reserves,
Thermal Insulation
Protection
Metabolic Water
Describe the test for fats and oils
Sample mixed with absolute ethanol (dissolves lipids) then shaken with equal volume of water - white emulsion formed
What causes LDL (low density lipoprotein) build up and why is it an issue?
Diet high in saturated fats, fatty deposits build up in cornonary arteries (atheroma) - cause angina and heart attacks
What causes HDL (high density lipoprotein) build up and why is this useful?
Diet high in unsaturated fats HDL carry fats to liver for disposal lowering risk of cardiovascular disease.
What is an atheroma?
Build up of fatty material on the endothelial lining of the artery.
Name the elements that are always in proteins and the elements that are in some proteins
C, H, O, N always present S and P sometimes present
Draw out a general formula for an amino acid
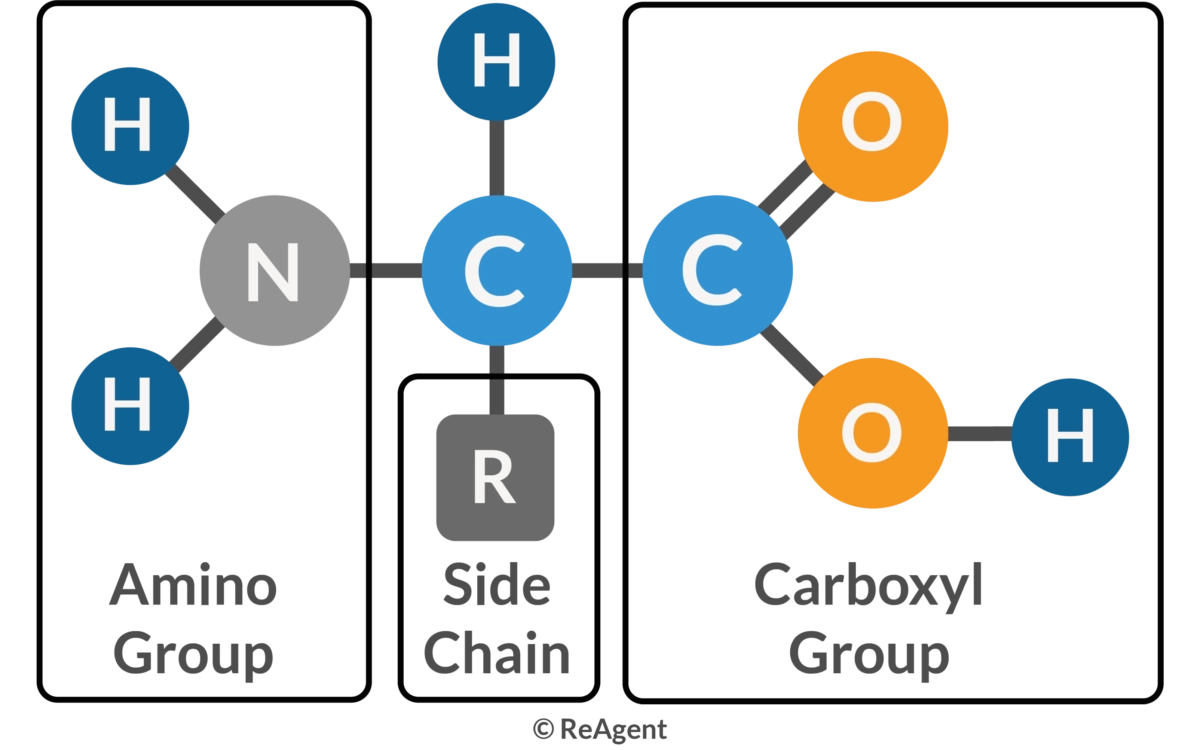
What is the bond called that forms between 2 amino acids to make a dipeptide?
Peptide Bond
Describe the biochemical test for a protein
Add a few drops of Biuret Solution (NaOH and CuSO4) are added to sample. Purple lilac colour indicates proteins
What is meant by the primary structure of a protein and what bonds hold it together?
Order of amino acids in peptide chain held by peptide bonds.
What is meant by the secondary structure of a protein and what bonds hold it together?
Primary Structure folds into a regular repeating pattern (alpha helix or beta pleated sheet) held by hydrogen bonds.
What is meant by the tertiary structure of a protein and what bonds hold it together?
The R group interacts to pull the secondary structure into a folded shape. Held together by H, ionic, disulphide bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
Describe the quaternary structure of a protein
Polypeptide chains associate with each other or with non protein (prosthetic) groups to make a large complex functioning complex.
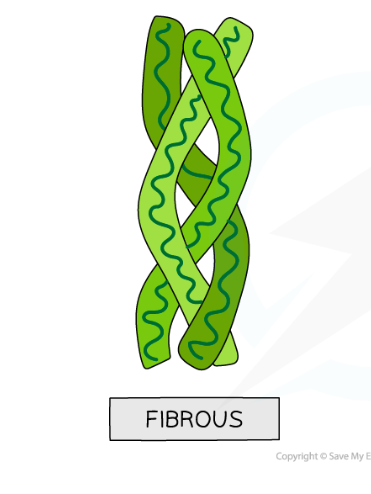
Describe fibrous proteins with examples
Long thin molecules are insoluble in wager and have a structural role. The polypeptides are in parallel chains sheets, with many cross links forming king fibres.
Describe globular proteins with examples
Compact and folded into a spherical molecules making the soluble in water.
Functions include enzymes, antibodies and hormones.