hydrophobic molecules
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
insoluble in water
fatrs, oils, steroids and some vitamins. high proportion of non polar c-h bonds cause it to be hydrophobic.
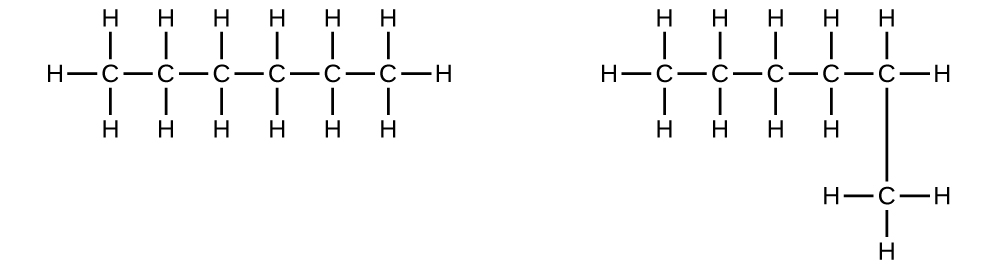
hydrocarbon chains
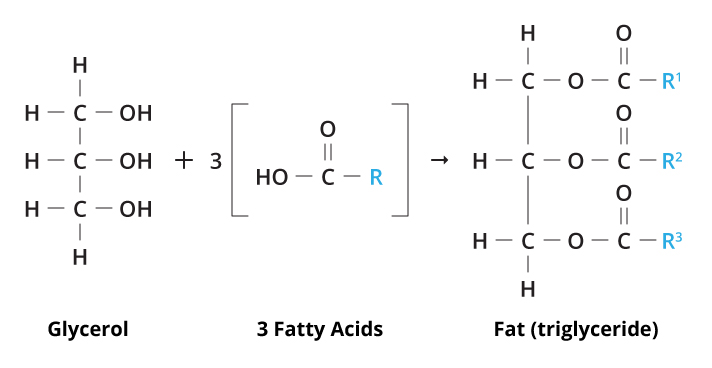
Fats
one glycerol and 3 fatty acids. 3 carbons with OH- dehydration reactiom with fatty acids
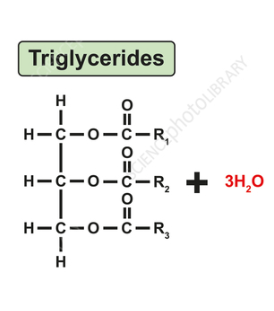
triglycerides
fatty acids don’t need to identical, chain lengths vary
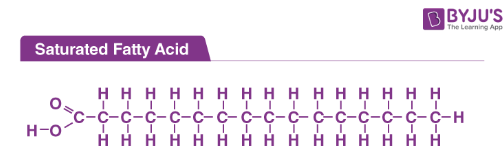
saturated chains
NO DOUBLE bonds between carbon atoms. FULL of hydrogen. solid at room temp-densley packed tg. higher melting point. ANIMAL ORIGIN.
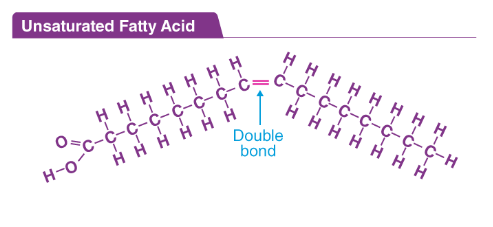
unsaturated fats
one or more DOUBLE BONDS. kinks form in the chain due to the presence of double bonds. liquid at room temp. cannot align. low meltng point. PLANT ORIGIN. trans fat-industrally.
fats: excellent energy storage molecules
c-c bonds in fatty acids have lots of energy.
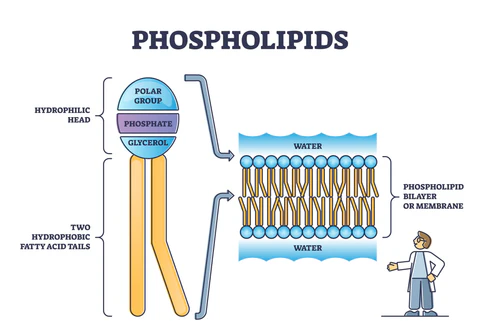
phospholipids
form membranes. glycerol 1 fatty acid-NONPOLAR “tails.” a phosphate group-POLAR “head”. form in all biological membranes. also for formations of lipid bilayer.
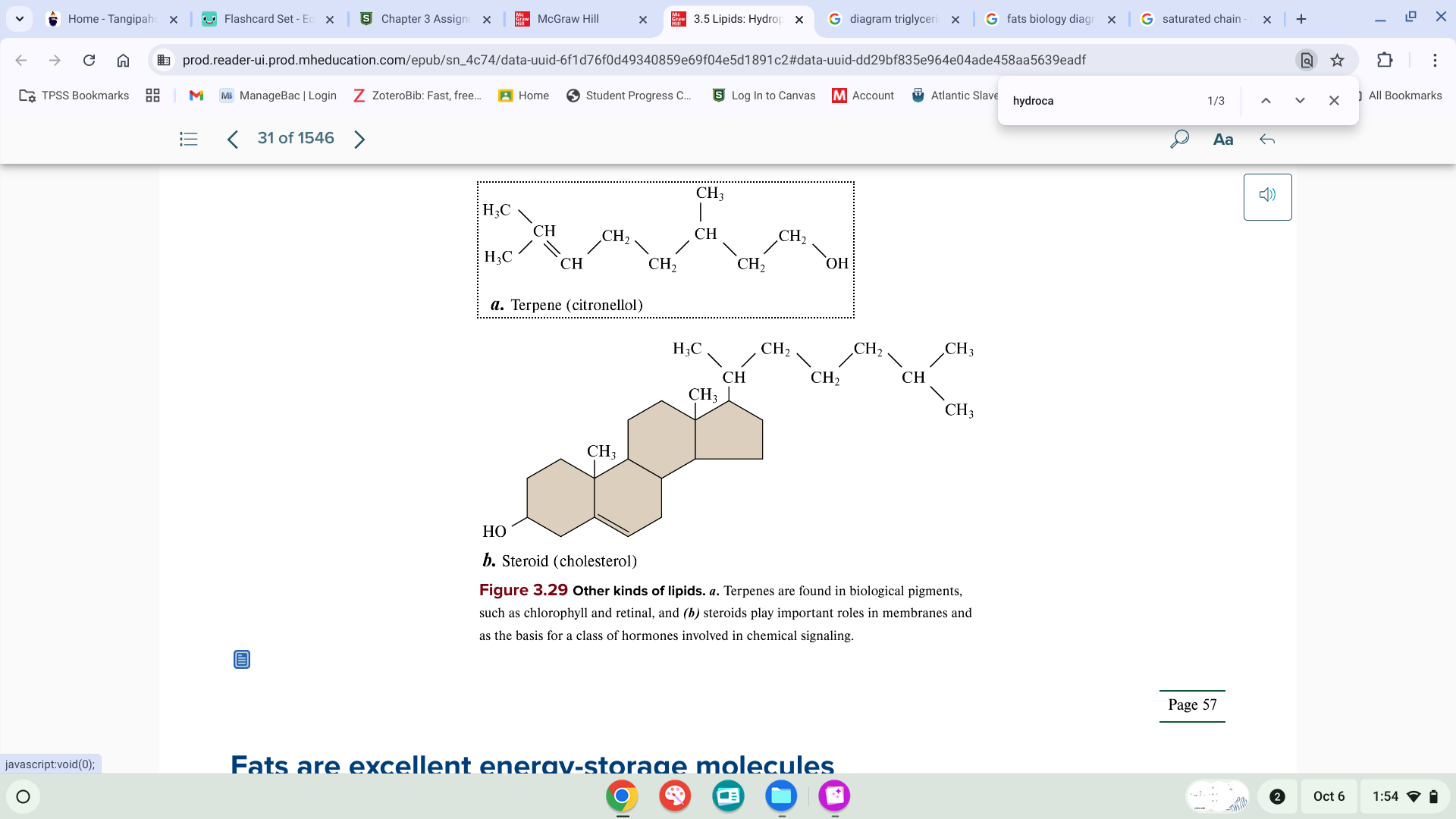
other kinds of lipids
waxes, vitamins, steroids(4 ring structure) hormones: testosterone and estrogen, cholesterol(found in cell membrane)
energy is stored in bonds
lipids have more bonds