chemistry a levels - foundations in chemistry
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
molar mass
(Mr) (g mol-1) this is the mass per mole of a substance
equation for moles
moles = mass/Mr
avogadros constant
number of particles in one mole of a substance 6.02 × 1023
mass defect
the small amount of mass that is lost
one atomic mass unit is
the standard mass which is 1/12th of C-12
relative atomic mass
the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th of the mass of carbon 12
relative isotopic mass
the mass of an atom of an isotope compared to 1/12of the mass of an atom of carbon 12
mass spectrometer
vaporisation
ionisation
acceleration
deflection
detection
calculating relative atomic mass using isotope abundance
mass number x percentage/100
electron relative mass is
1/1845
isotopes
atoms of an element with different number of neutrons and therfore different masses
physical properties of isotopes
higher mass means the isotope have a higher melting, boiling and density point
empirical formula
the simplest whole number ration of atoms of each element present in a compound
molecular formula
the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
empirical formula example
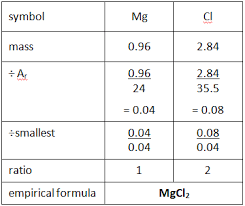
water crystallisation
colored crystals that are hydrated - water molecules are part of their crystalline structure.
example of water crystallisation
blue crystals of hydrated copper sulfate are heated, bonds holding the water within the crystals are broken and the water is driven off, leaving behind anhydrous copper sulfate
formula for water crystallisation
CuSO4 . 5H2O —> CuSO4 + 5H2O
a sample of hydrated calcium sulphate, CaSO4 . xH2O, has a relative formula mass of 172. what is the value of x
mr CuSO4 = 40.1 + 32.1 + 60 = 136.2
172 - 136.2 = 35.8
1H2O = 18
2H2O = 36 35.8 is nearest to 36 so x = 2
CaSO4 . 2H2O
11.25g of hydrated copper sulphate, CuSO4.xH2O, is heated until it loses all of its water. Its new mass is found to be 7.19g. What is the value of x?
mass of water = 11.25 - 7.19 = 4.06 g
CuSO4 H2O
mass 7.19 4.06
mr 159.6 18
moles 0.0451 0.225
/ smallest 0.0451 0.0451
= 1 4.99 = 5
CuSO4 . 5H2O
a sample of hydrated magnesium sulphate, MgSO4 . xH2O, is found 51.1% water. what is the value of x ?
MgSO4 xH2O
mass 48.9 51.1
mr 120.4 18
moles 0.406 2.838
/ smallest 0.406 0.406
= 1 6.99 = 7
MgSO4 . 7H2O