Session 3: Energy Production from Lipids (NEW)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Features of Lipids
- Hydrophobic
- Mostly contain C, H and some O
- More reduced than carbohydrates = release more energy when oxidised
The three classes of lipids
1) Fatty acid derivatives
- Fatty acids = fuel molecules
- Triacylglycerols from diet = fuel storage, insulation
- Phospholipids = membranes, lipoproteins
- Eicosanoids = Fatty acid metabolite, local mediator
2) Hydroxy-methyl-glutaric acid (HMG) derivatives
- Ketone bodies (alternative hydrophilic fuel molecule)
- Cholesterol = membrane and steroid hormone synthesis
- Cholesterol esters = cholesterol storage
- Bile acids and salts = lipid digestion
3) Vitamins
ADEK
Triacylglycerol function
Fuel storage and insulin
Phospholipid function
Component of membrane
Plasma lipoproteins
Eicosanoid function
Fatty acid metabolites
Local mediators
Triglyceride structure
Glycerol backbone + 3 fatty acid side-chains
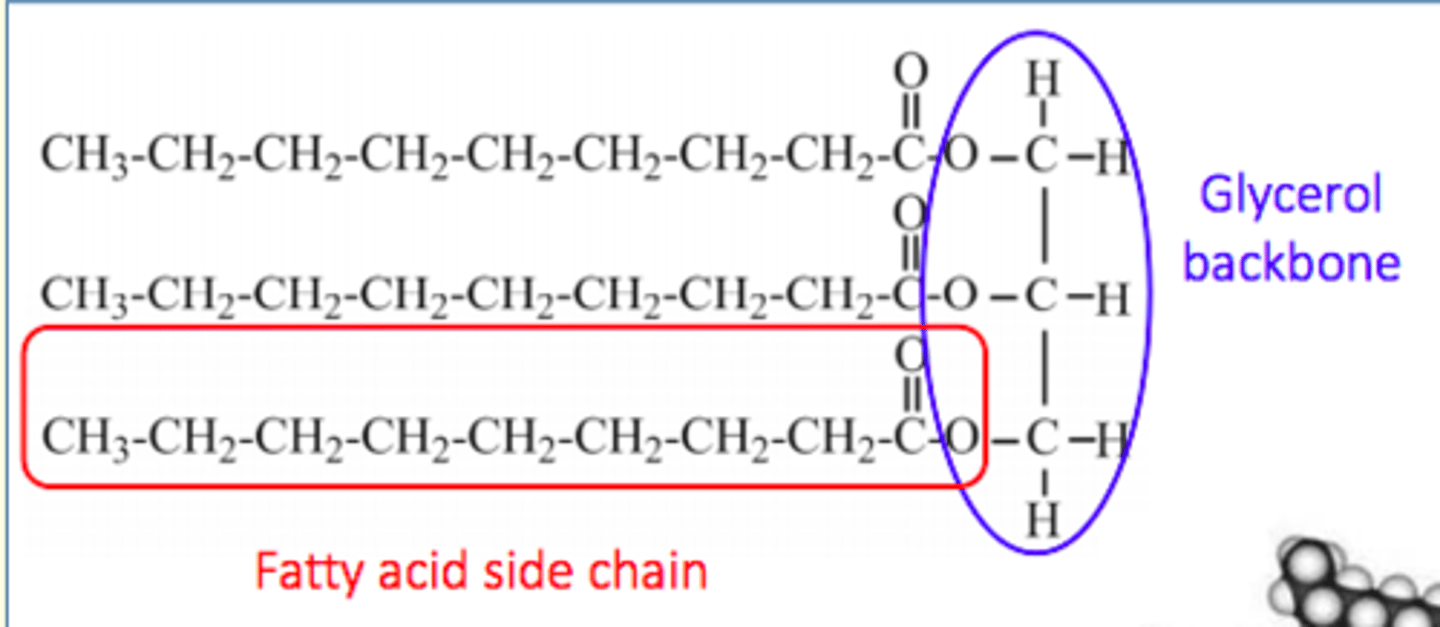
Triglycerides stored in an anhydrous form in ___ tissue
Adipose
Triglycerides are utilised during what specific situations?
- Prolonged exercise
- Starvation
- Pregnancy (increased metabolic load on woman)
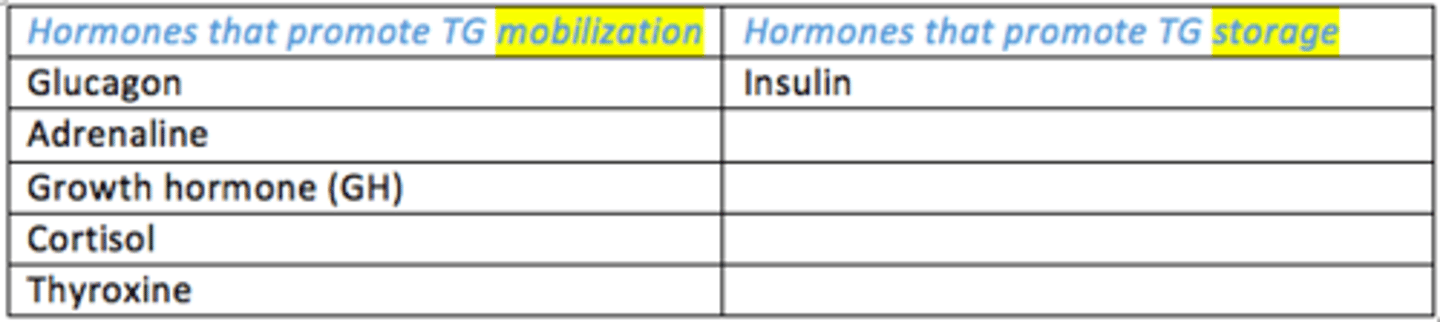
The metabolism of triglycerides is under hormonal control.
Which hormones promote TG mobilisation?
- Glucagon
- Adrenaline
- Growth hormone
- Cortisol
- Thyroxine
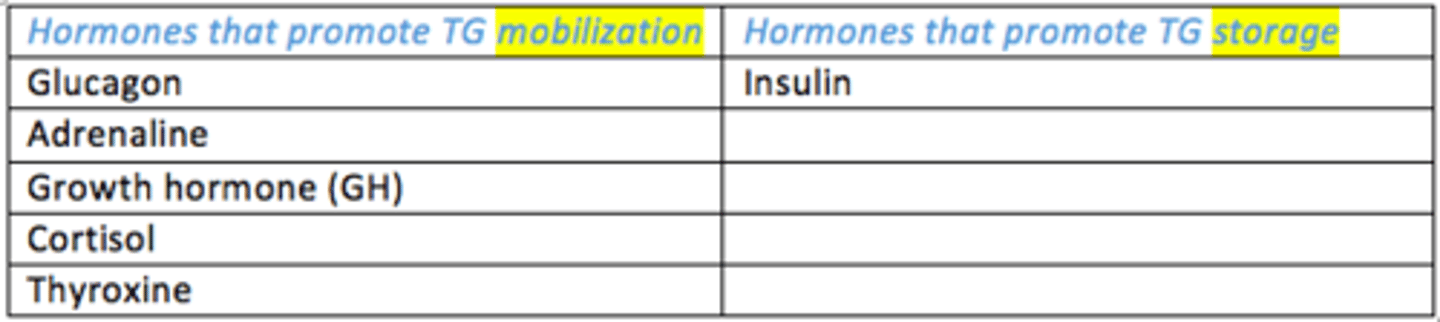
The metabolism of triglycerides is under hormonal control.
Which hormones promote TG storage?
- Insulin
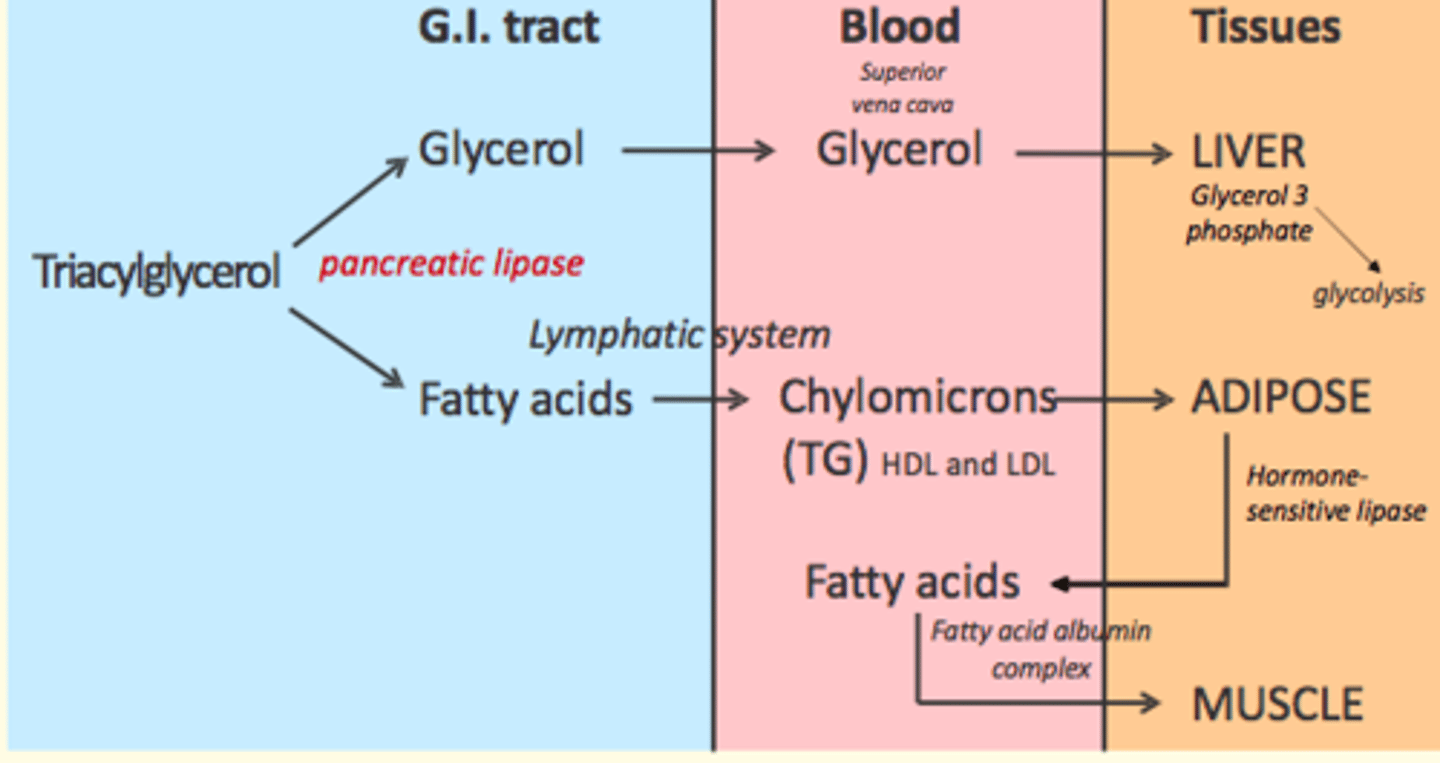
Stage 1 of triglyceride metabolism
Extracellular (GI tract)
- TGs digested into = fatty acids + glycerol
- Fatty acids + glycerol absorbed from GI into circulation
- No ATP produced
What enzyme catalyses the breakdown of triacylglycerols into glycerol and fatty acids in stage 1 of triglyceride metabolism in the GI tract?
Pancreatic lipase enzyme
Low extracellular [glucose] results in ___ ___ release as an alternative fuel
Fatty acid
Stage 2 of triacylglycerol catabolism focuses on the breakdown of fatty acid constituent
Where does this stage take place in the cell?
Intracellular (mitochondria)
- Fatty acids transported to tissues (especially adipose, liver, skeletal muscle) where they are oxidised
- This process requires H+ carriers which are reduced
- Reducing power released
Fatty acids contain hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups - they are ___
Amphipathic
Example of a saturated fatty acid
Palmitic fatty acid
Stearic acid
Example of mono-unsaturated fatty acid
Oleic acid
Example of poly-unsaturated fatty acid
Arachidonic acid
Give two examples of polyunsaturated fatty acids which are ESSENTIAL fatty acids?
- Alpha-linolenic acid (omega 3)
- Linoleic acid (omega 6)
Stages of fatty acid catabolism
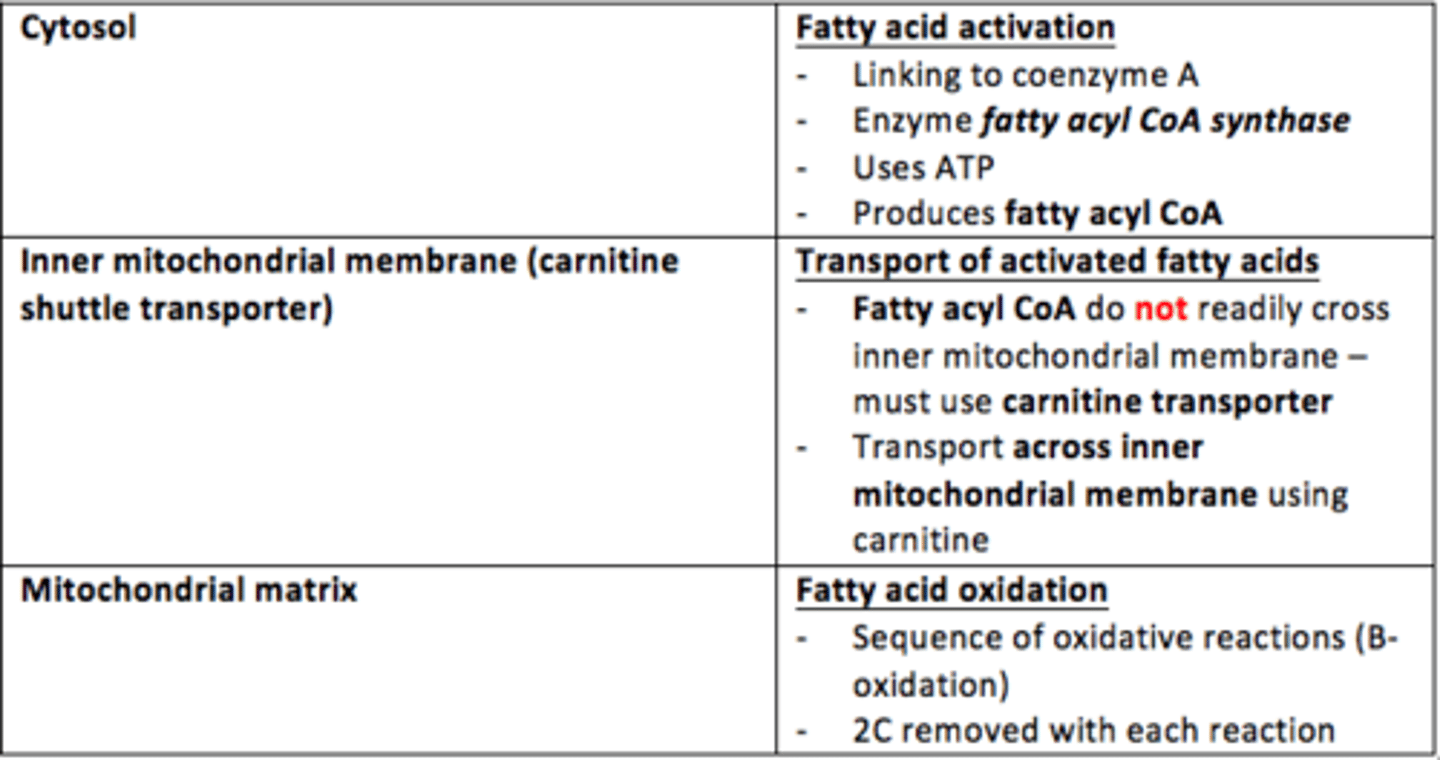
Enzyme which catalyses activation of fatty acids (linking of coenzyme A to fatty acid)?
Fatty acyl CoA synthase

Activated fatty acids (fatty acyl CoA) do not readily cross the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is used to help these fatty acyl CoA cross the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Carnitine shuttle transporter
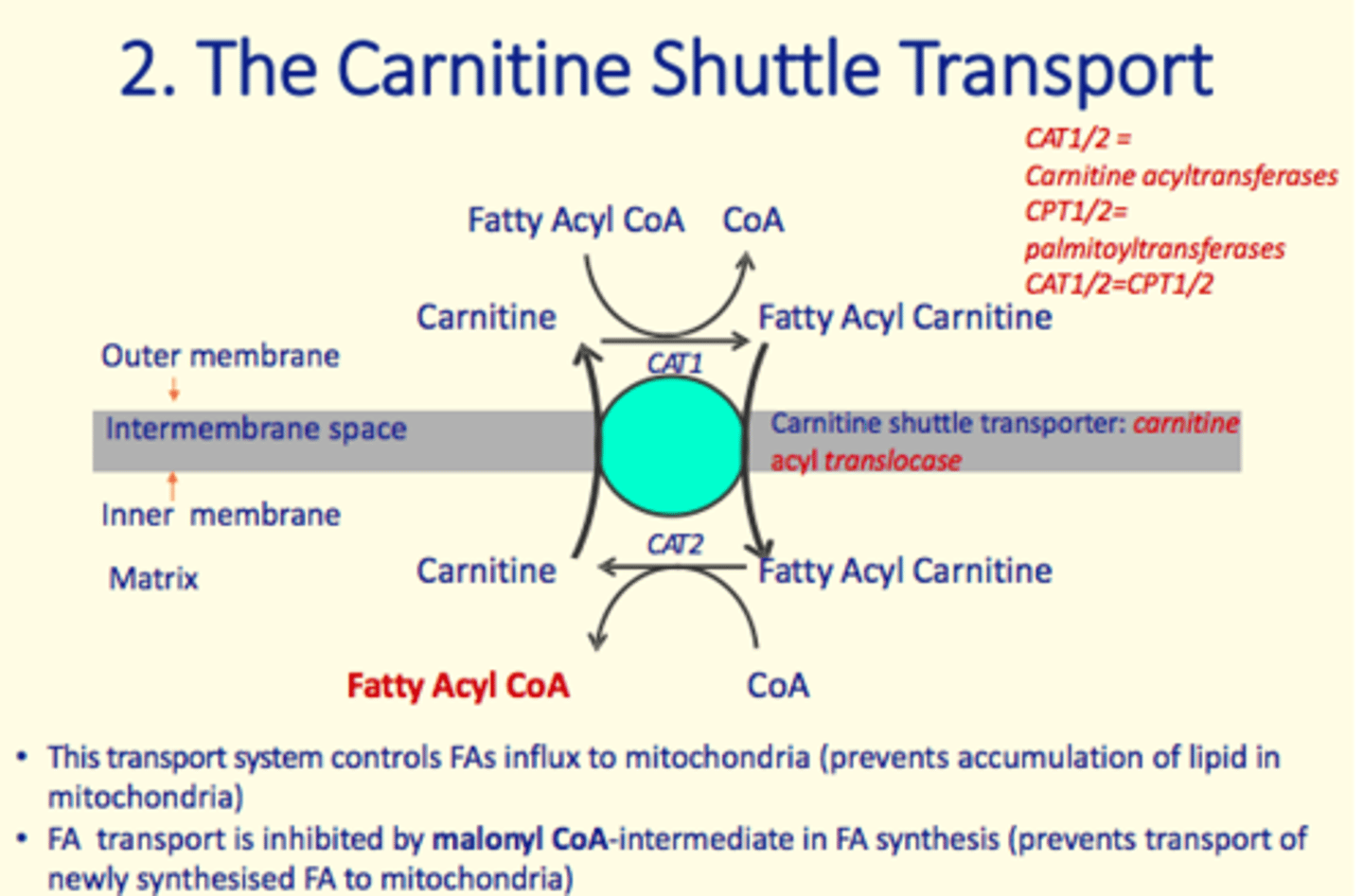
Molecule that inhibits fatty acid transport by carnitine shuttle transporter?
Malonyl CoA-intermediate in FA synthesis
Is fat a higher energy fuel than glucose?
Yes
C6 fatty acid = 41 ATP
C6 glucose = 32 ATP
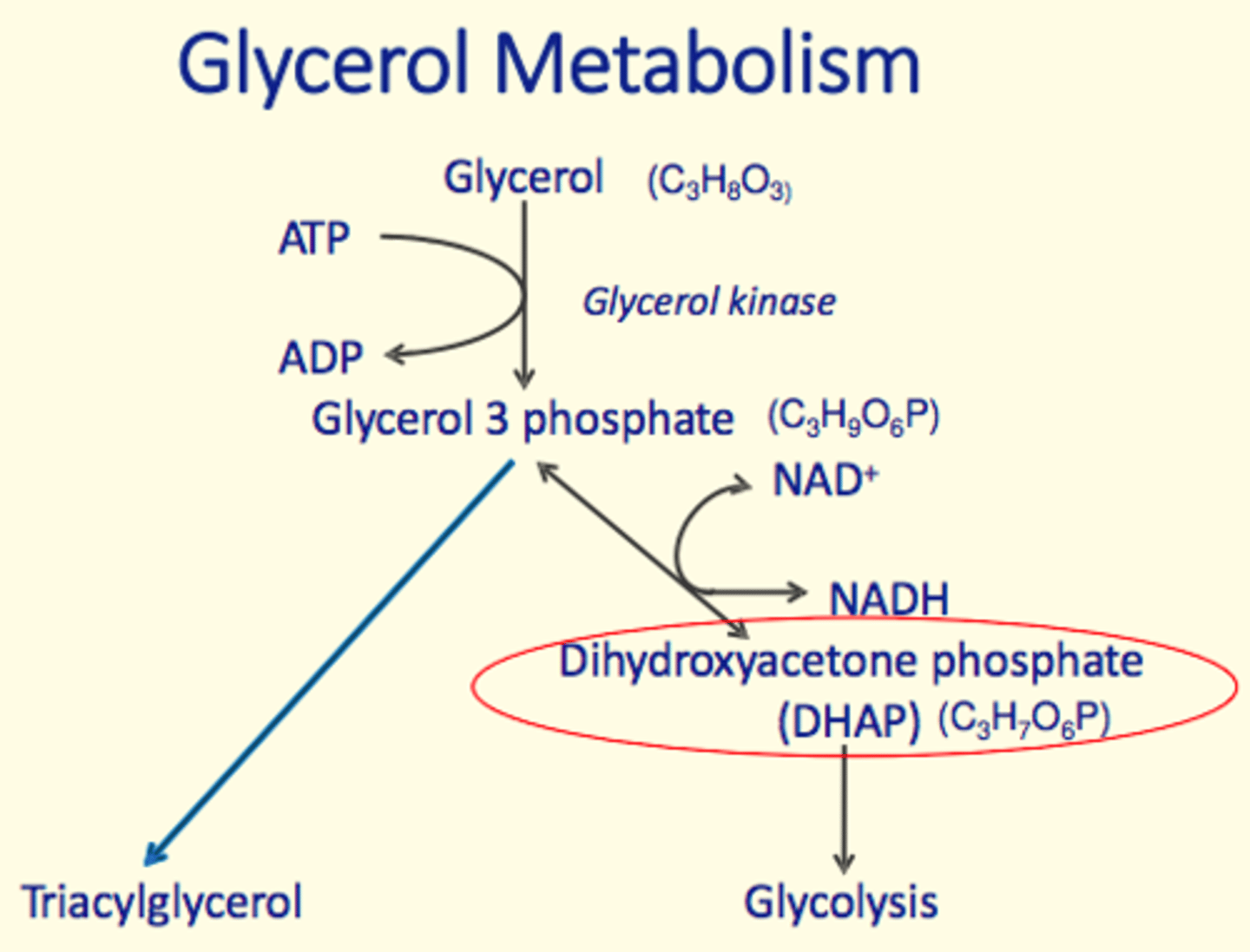
Glycerol metabolism occurs in the ___
Liver
- Intracellular (cytosol)
Glycerol metabolism process
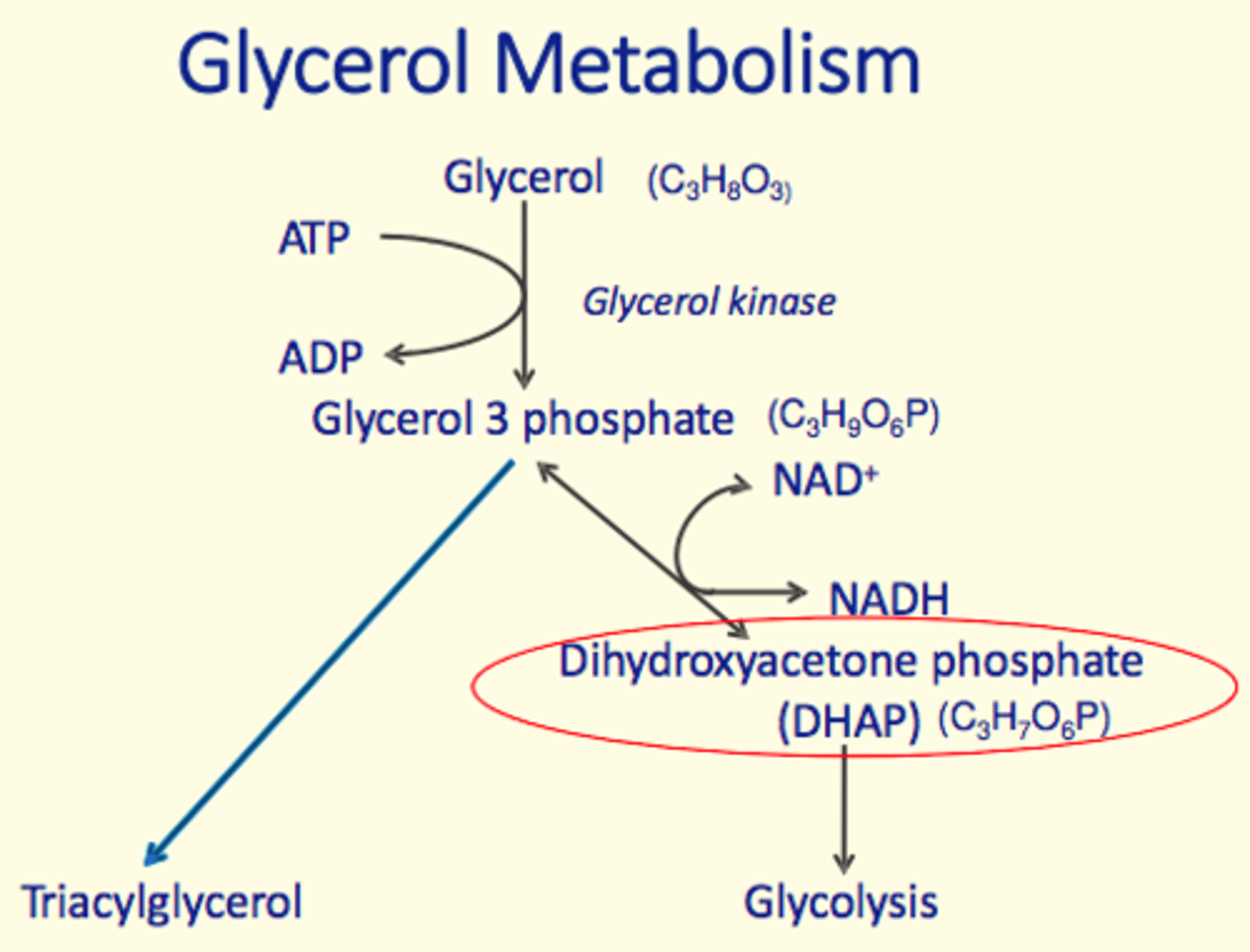
Enzyme which catalyses conversion of glycerol to glycerol-3-phosphate in glycerol metabolism
Glycerol kinase
Intermediate of glycerol metabolism which enters glycolysis?
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
CoA is derived from what vitamin?
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid)
Ketone bodies are an alternative ___ molecule
Fuel
Normal plasma ketone body concentration
< 1 mM
Ketone body concentration during physiological ketosis (starvation)
2-10 mM
Ketone body concentration during pathological ketosis (Type 1 Diabetes)
> 10 mM
Ketoacidosis
Excessive production of ketones, making the blood acidic
- Acetoacetate and Beta-hydroxybutyrate at high concentrations in the blood
Ketonuria
Ketones in the urine
- Occurs when the renal threshold of ketones is exceeded so ketone bodies excreted in the urine
Why may volatile acetone be excreted via the lungs of type 1 diabetics?
Acetoacetate spontaneously breaks down to acetone
- Characteristic smell of acetone can be smelt on the breath of T1D patients
When are ketone bodies synthesised by the liver mitochondria?
- When glycolysis is low e.g., prolonged exercise
- When glucose is low e.g., in starvation (physiological ketosis)
- In untreated type 1 diabetes (pathological ketosis)
What hormones influence ketone body synthesis (ketogenesis)?
Insulin/Glucagon ratio
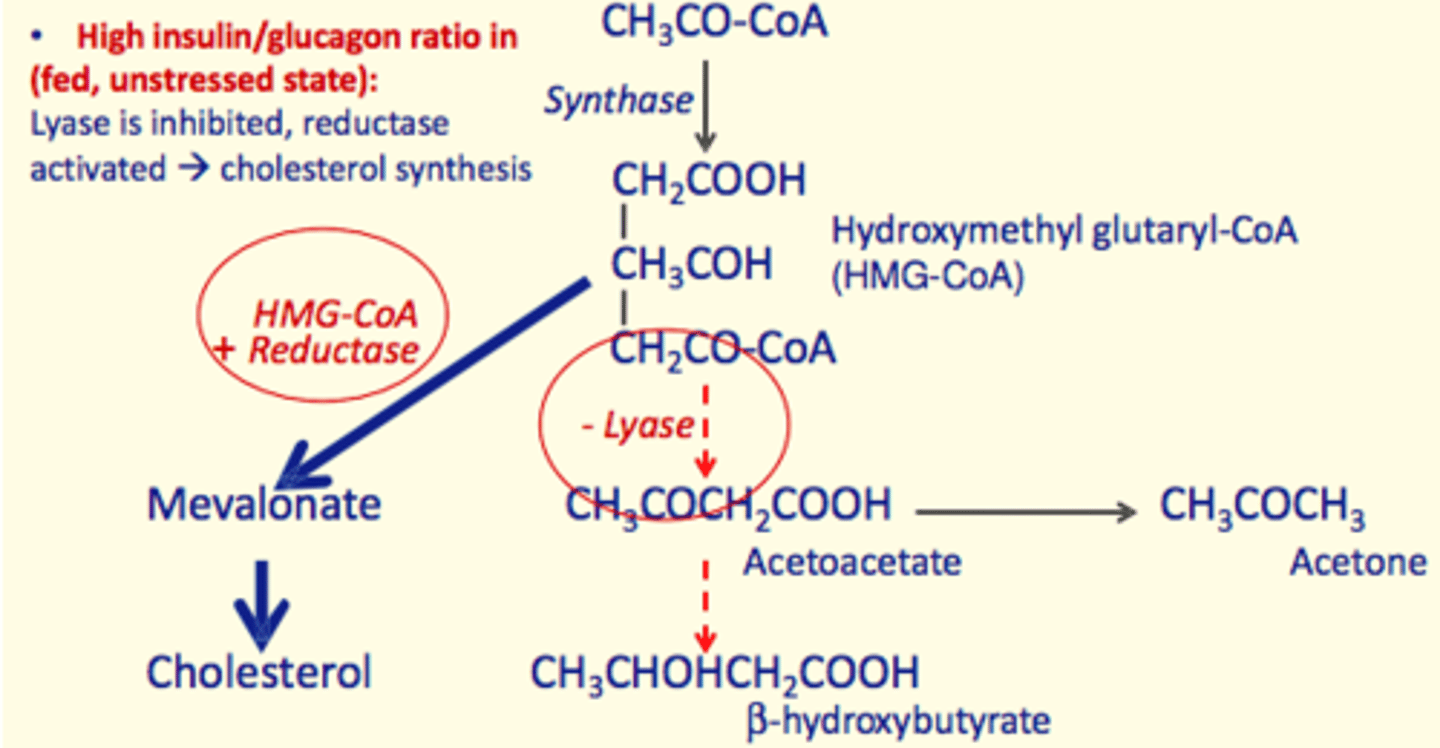
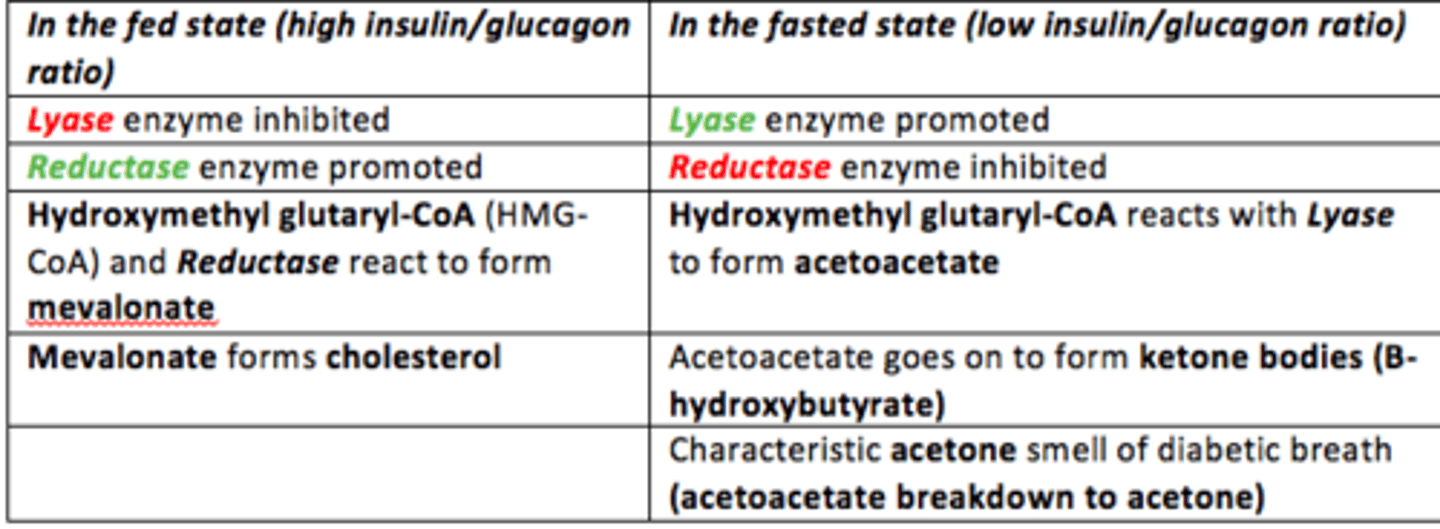
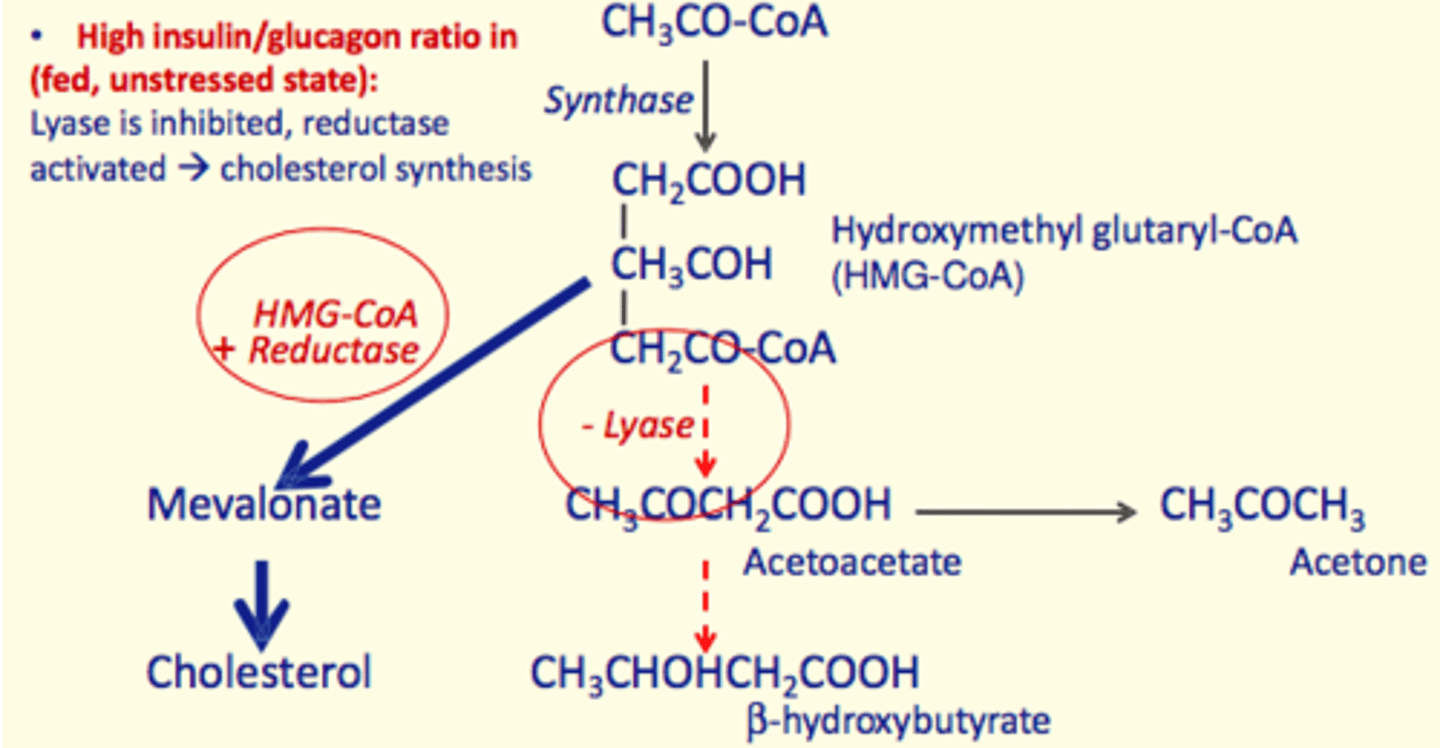
In the fed state - how is ketogenesis affected?
Fed State = High Insulin/Glucagon Ratio
- Lyase inhibited
- Reductase activated
- Hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) + Reductase react
- Production of Mevalonate which forms Cholesterol
- Cholesterol synthesis favoured in the fed state
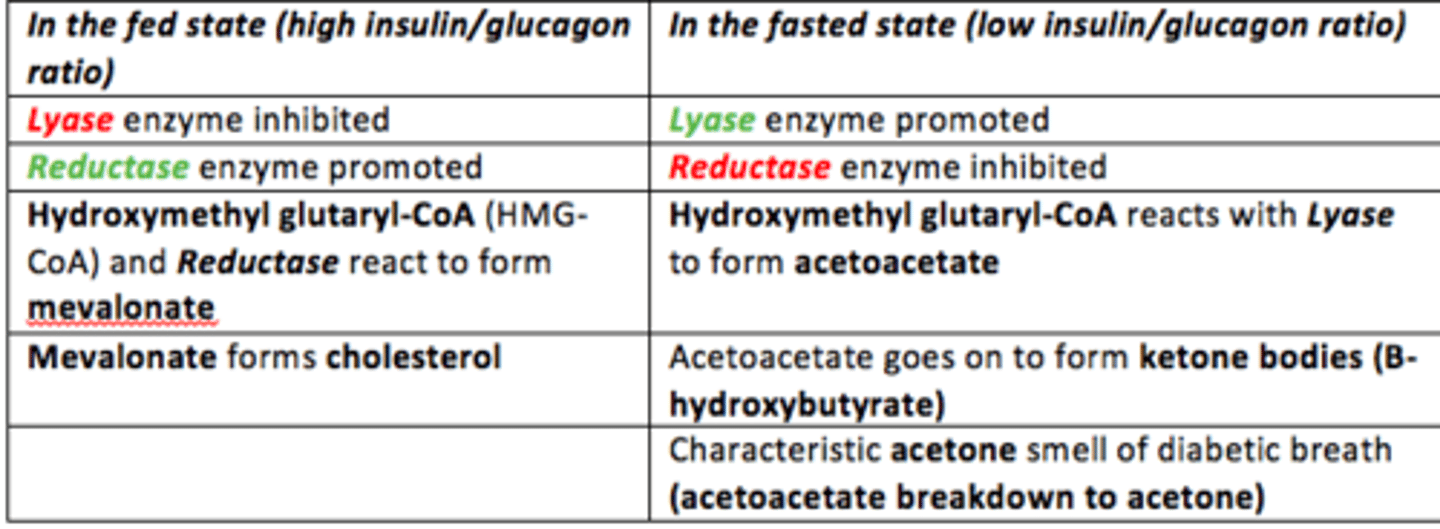
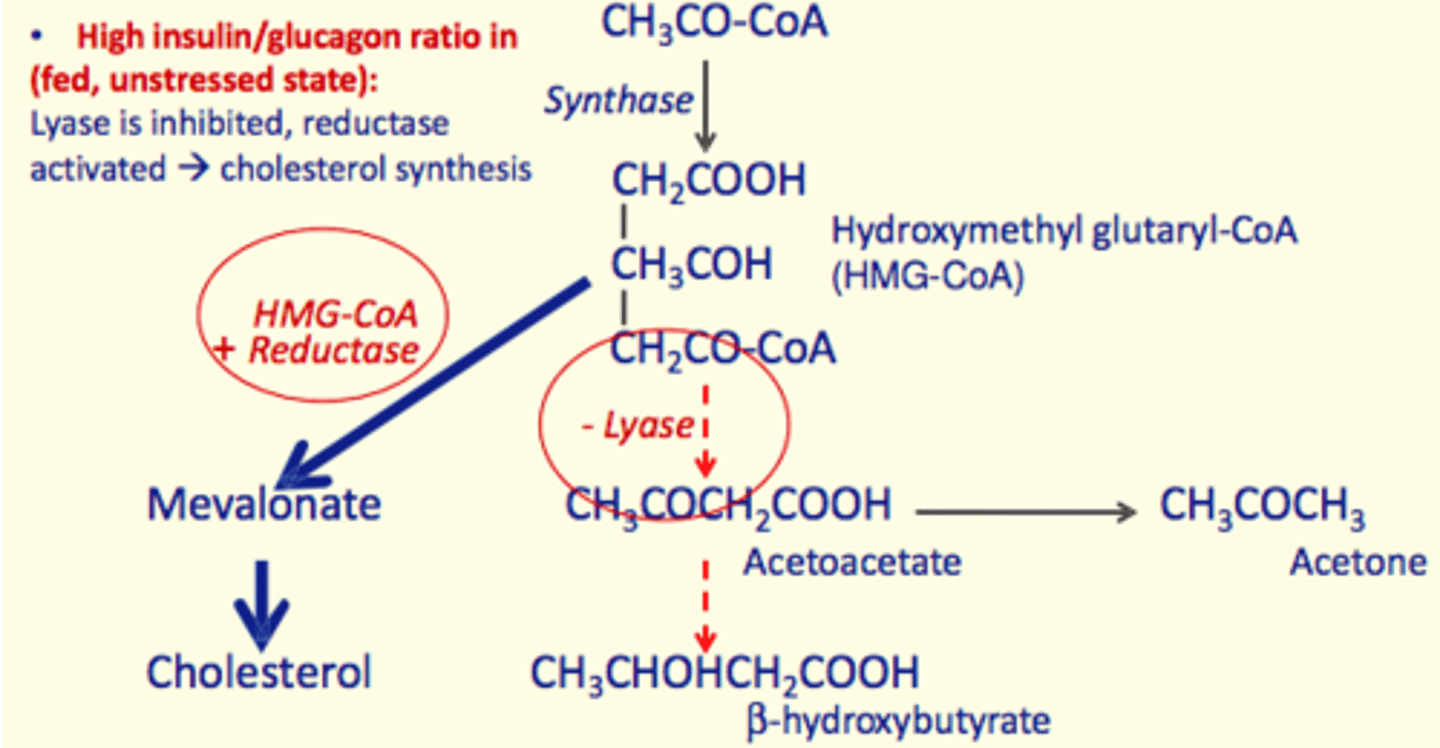
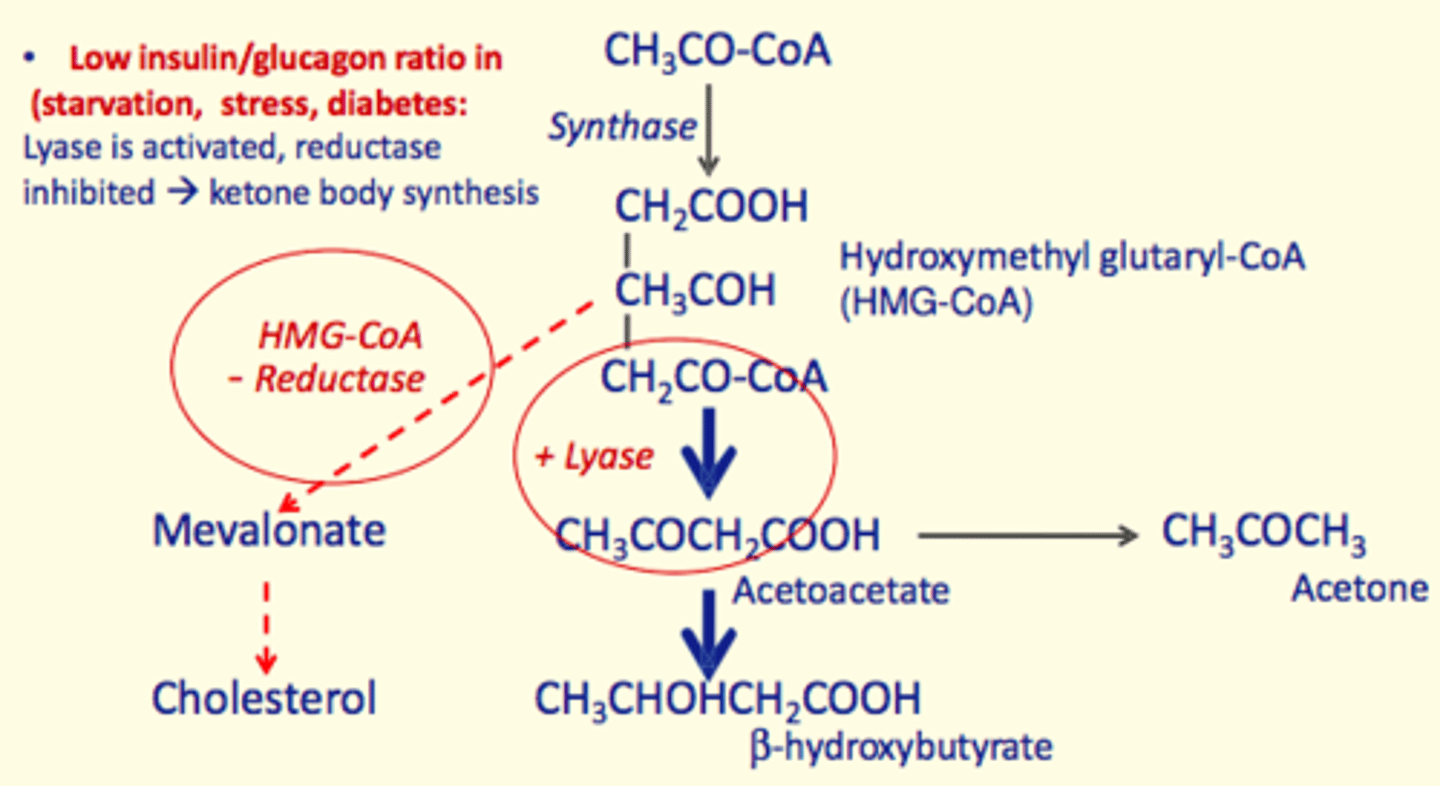
In the fasted state - how is ketogenesis affected?
Fasted State = Low Insulin/Glucagon Ratio
- Lyase activated
- Reductase inhibited
- Hydroxymethyl glutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) + Lyase react
- Production of acetoacetate which forms B-hydroxybutyrate (ketone bodies)
Acetoacetate can also break down spontaneously to form acetone (volatile acetone on the breath of T1D patients)
Ketogenesis in the fed state
Ketogenesis in the fasted state (starvation)
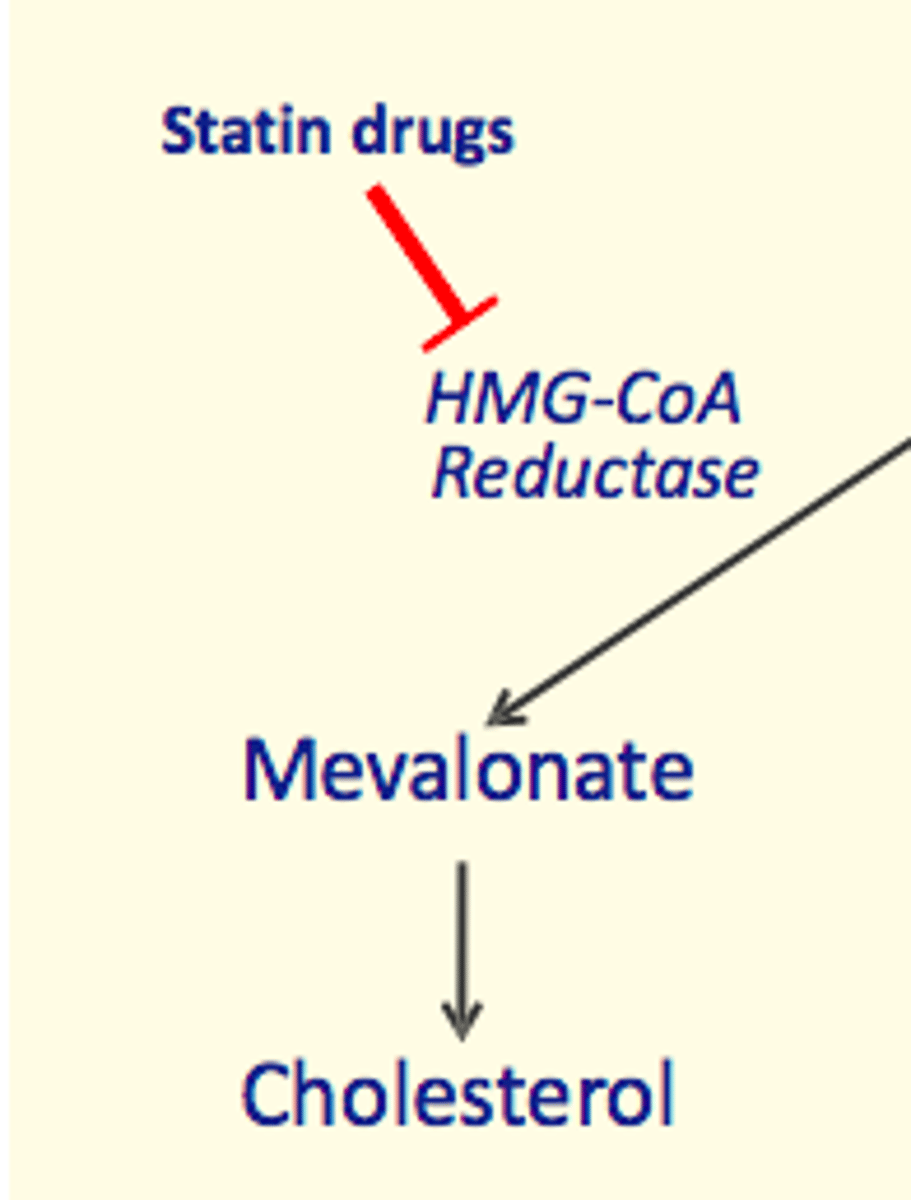
What enzyme does statins drugs inhibit to decrease cholesterol?
HMG-CoA reductase
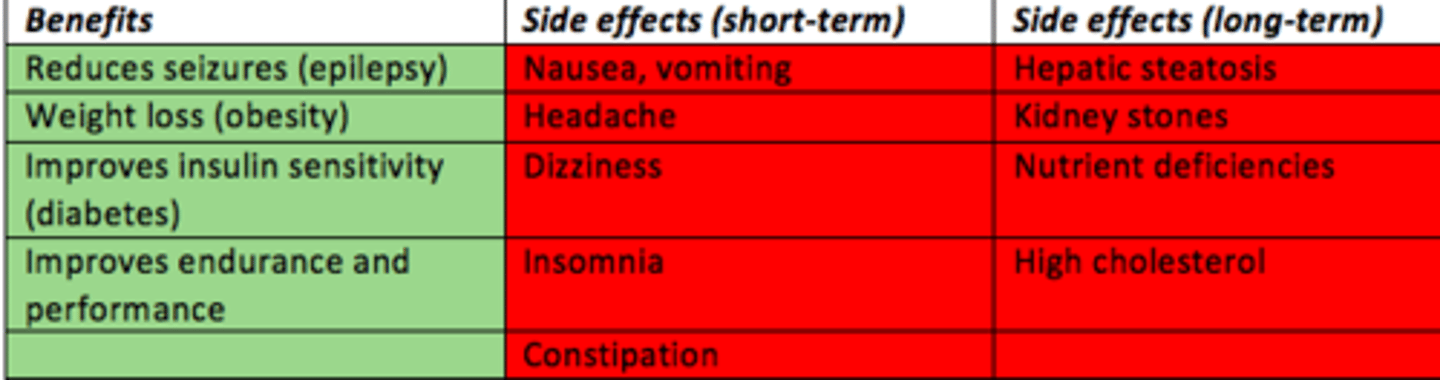
Ketogenic diet benefits
- Epilepsy = reduces seizures
- Obesity = weight loss
- Diabetes = improved insulin sensitivity
- General health = improves endurance and performance
Note =
Ketogenic diets can also benefit individuals who have an X-linked pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) deficiency.
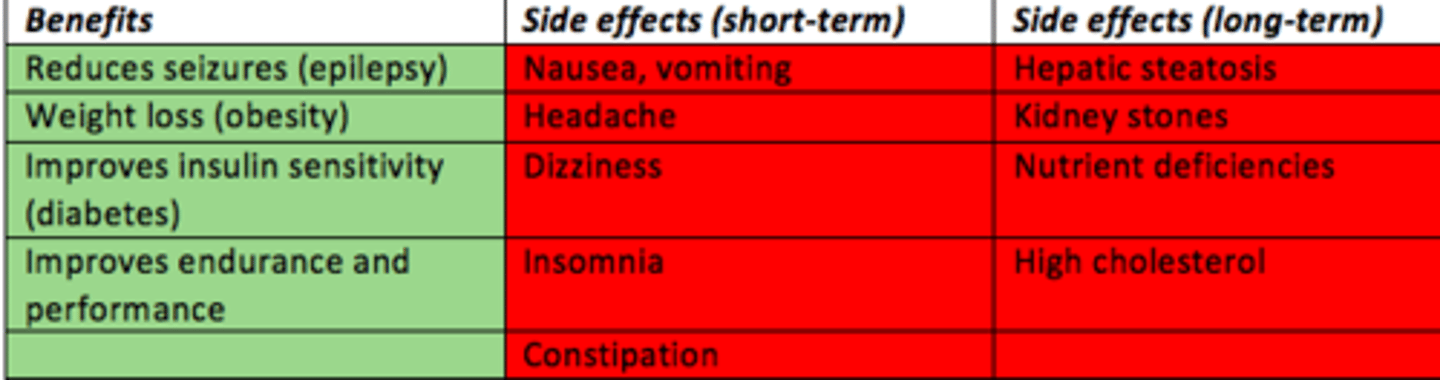
Ketogenic diet short-term side effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- Constipation
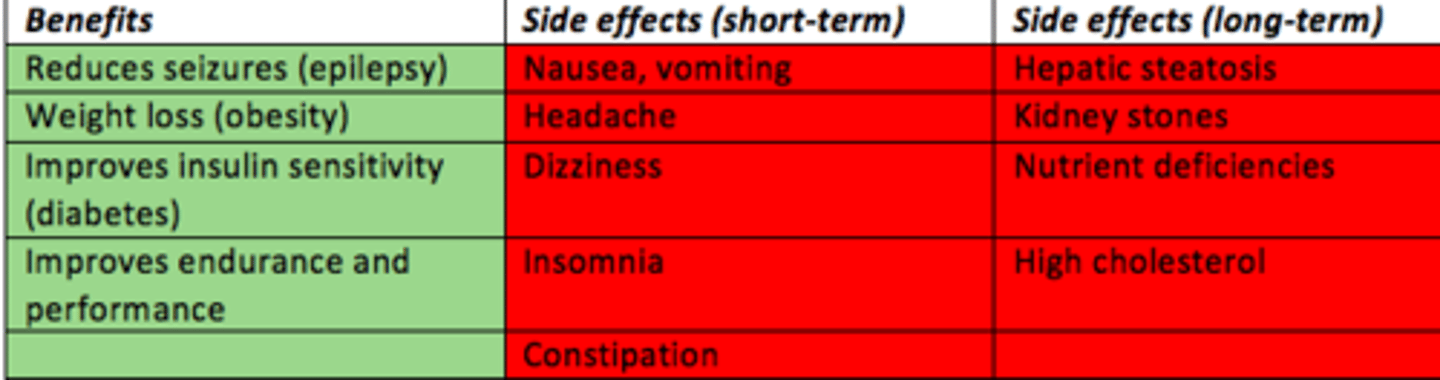
Ketogenic diet long-term side effects
- Hepatic steatosis
- Kidney stones
- Nutrient deficiencies
- High cholesterol
Triacylglycerols are mainly water soluble
True or false?
False
Name the enzyme which hydrolyses dietary triacylglycerols to fatty acids and glycerols in the gastrointestinal tract?
Pancreatic lipase
Unlike fatty acid which is converted to acetyl CoA in order to enter TCA cycle, glycerol needs to enter glycolysis to be processed to pyruvate and then be converted to acetyl CoA
True or false?
True
Name the active transporter which allows transported of activated fatty acids to mitochondria
Carnitine
Fatty acids yield more energy than C6 glucose as they are more reduced.
How many moles of ATP are produced from oxidation of C6 fatty acid?
41 ATP
Where are ketones synthesised in the body?
Liver
Name the volatile ketone which is excreted via lungs in patients with type 1 diabetes
Acetone