midterm 2 review
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure of protein
hydrogen bonds are formed through the backbone atoms
tertiary structure of protein
hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, covalent bonds, are formed between the R-groups
quaternary structure of protein
multiple proteins in the tertiary structure come together to form a larger functioning enzyme
condensation reaction
a reaction that results in the formation of water as an end product
hydrolysis
a reaction that requires water as a reactant
amine
a functional group on an amino acid that is polar, basic, part of the amino acid backbone, and can become positively charged
carboxylic acid
a functional group on an amino acid that is polar, acidic, part of the amino acid backbone, and can become negatively charged
N-terminus
denotes the beginning of a protein chain (first amino acid in the chain)
C-terminus
denotes the end of a protein chain (the last amino acid in the chain)
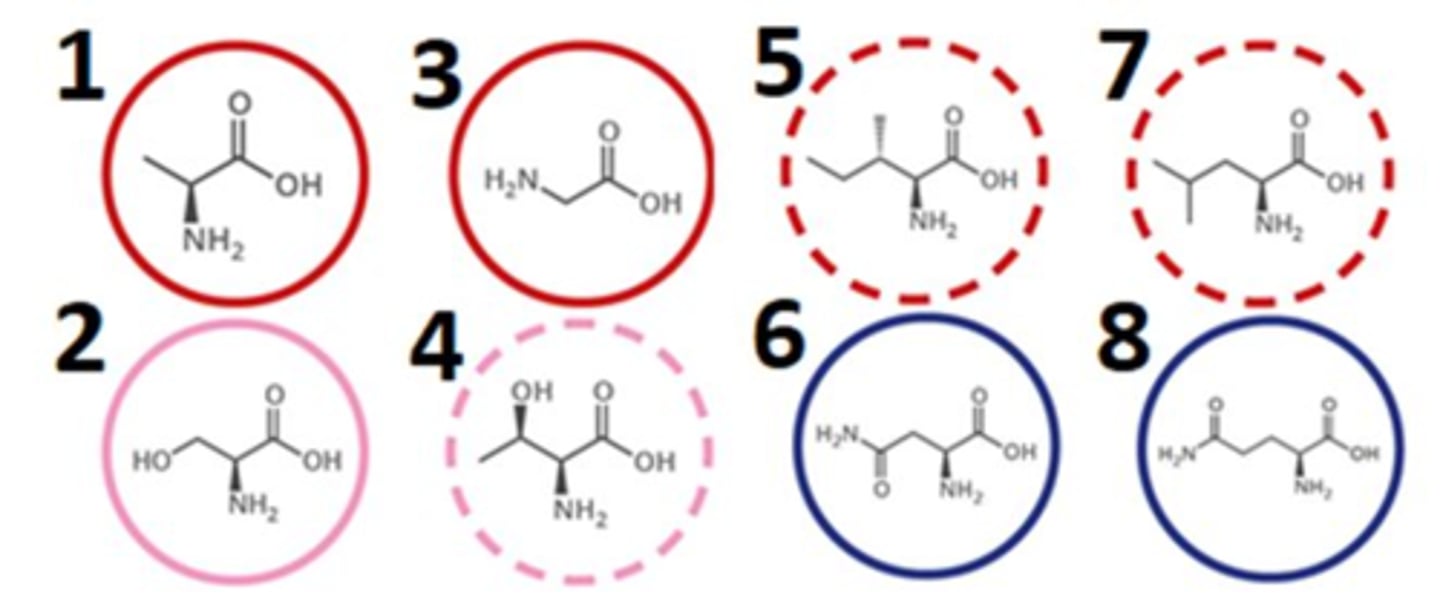
which of the following amino acids contain polar R groups?
2468
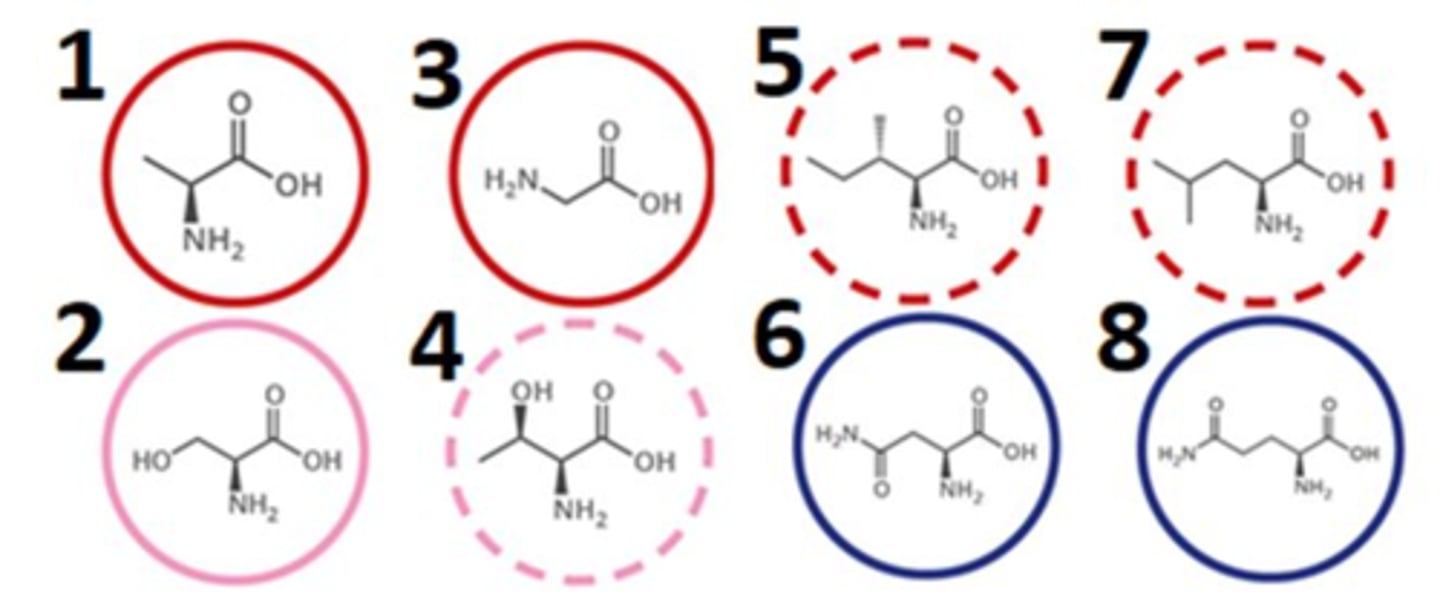
which of the following amino acids contain non-polar R groups?
1357
what is the H2N section called?
amine group
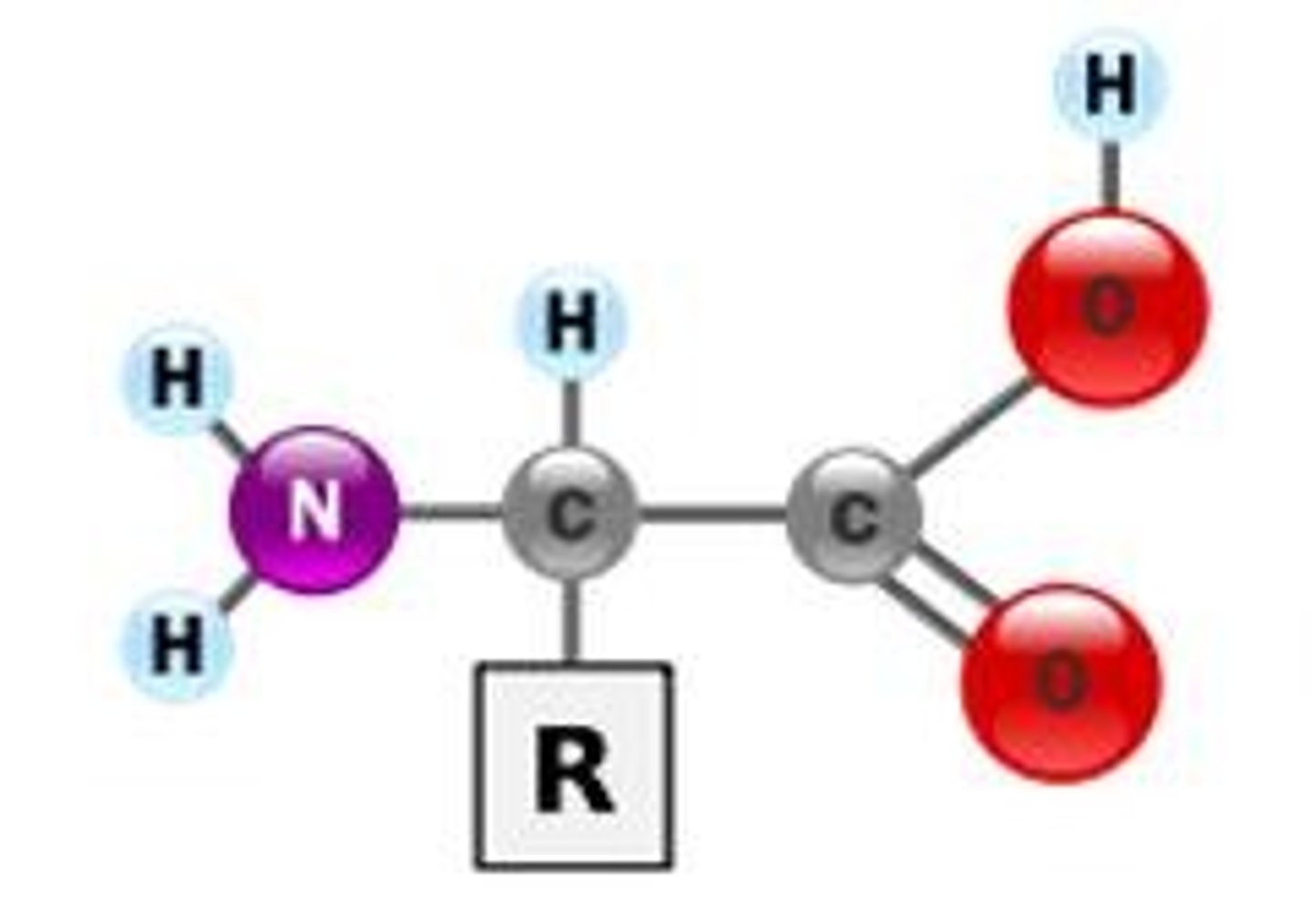
what is the COOH section called?
carboxylic acid
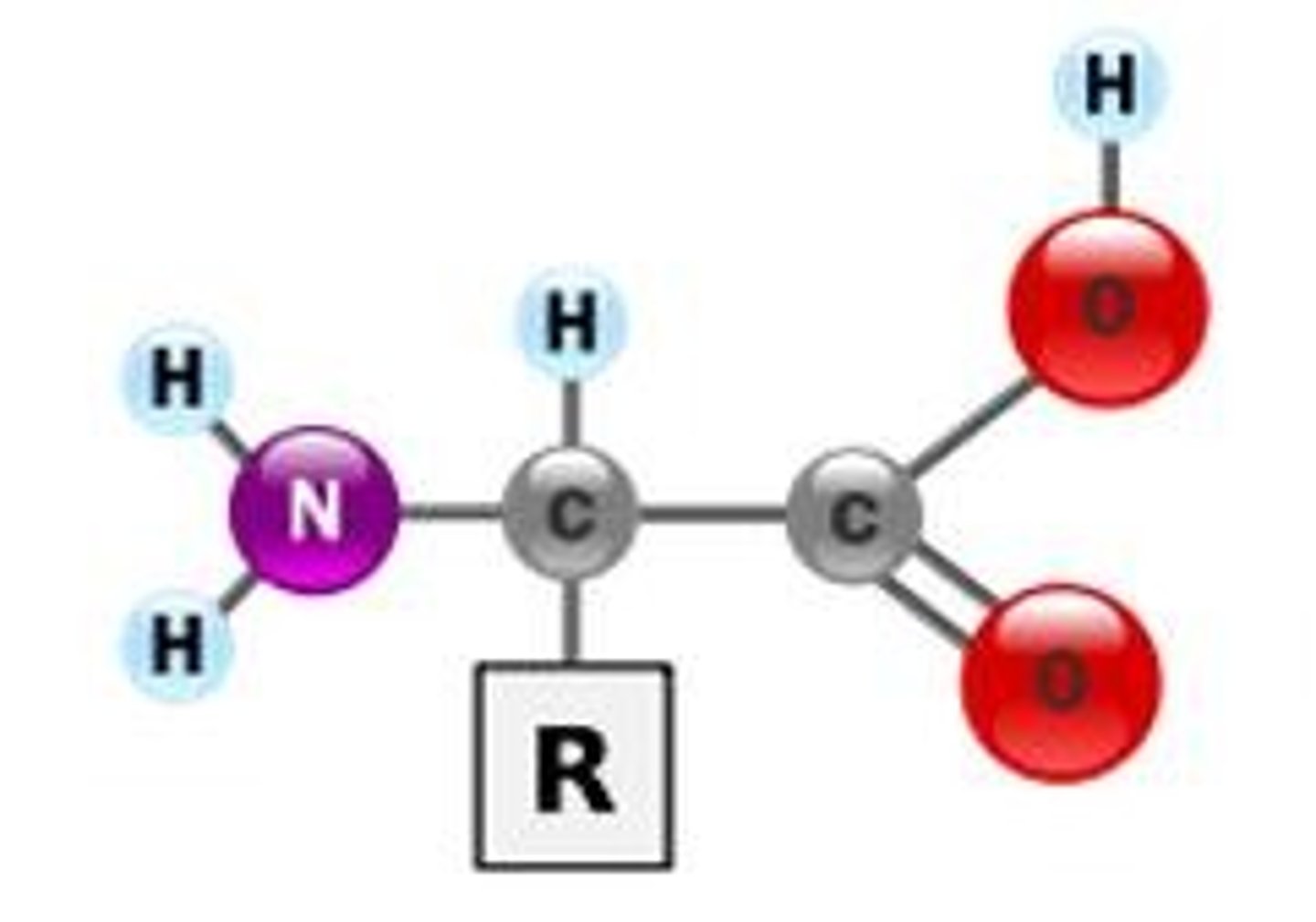
what is the R section called?
variable group
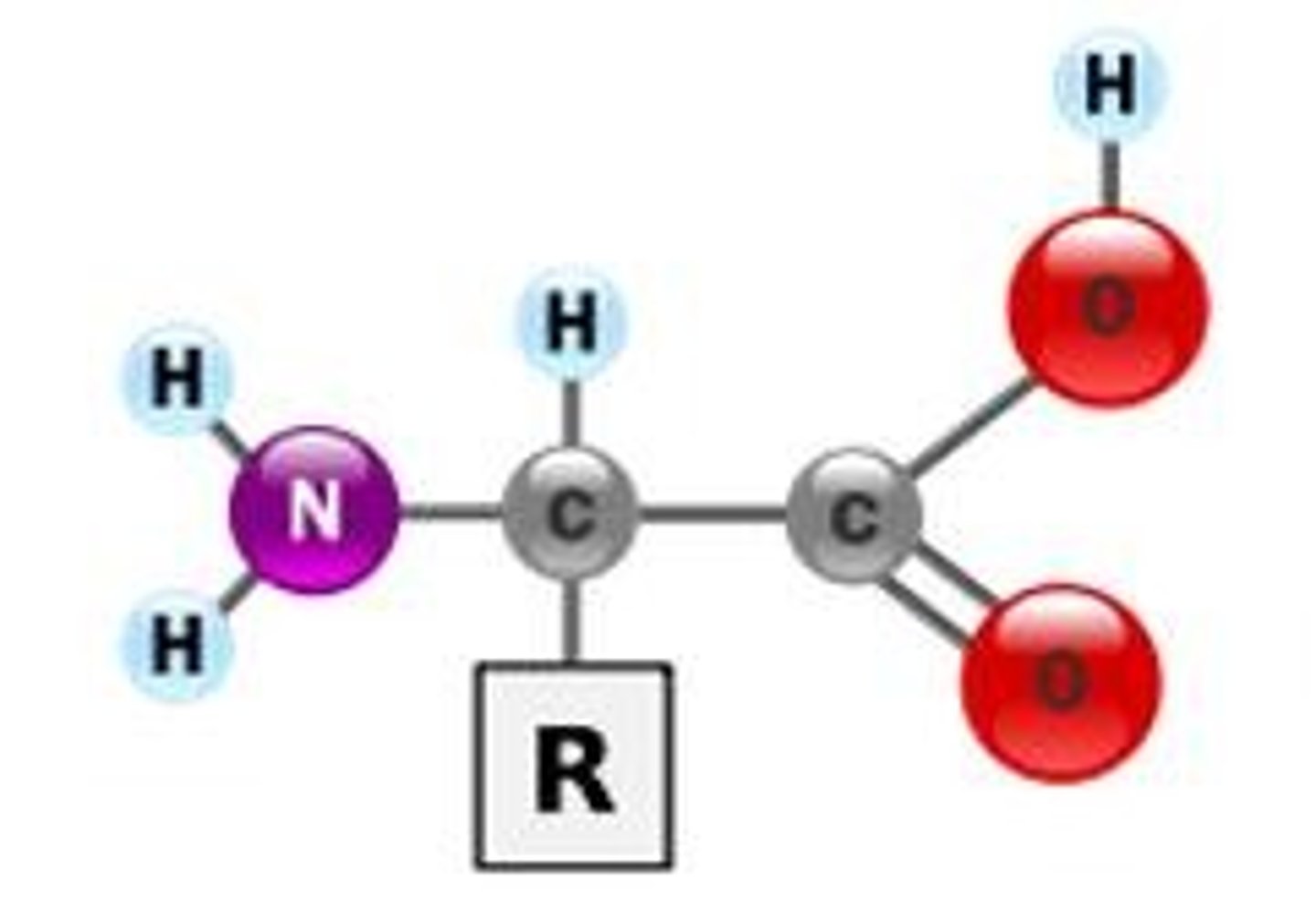
what is the center carbon section called?
alpha carbon
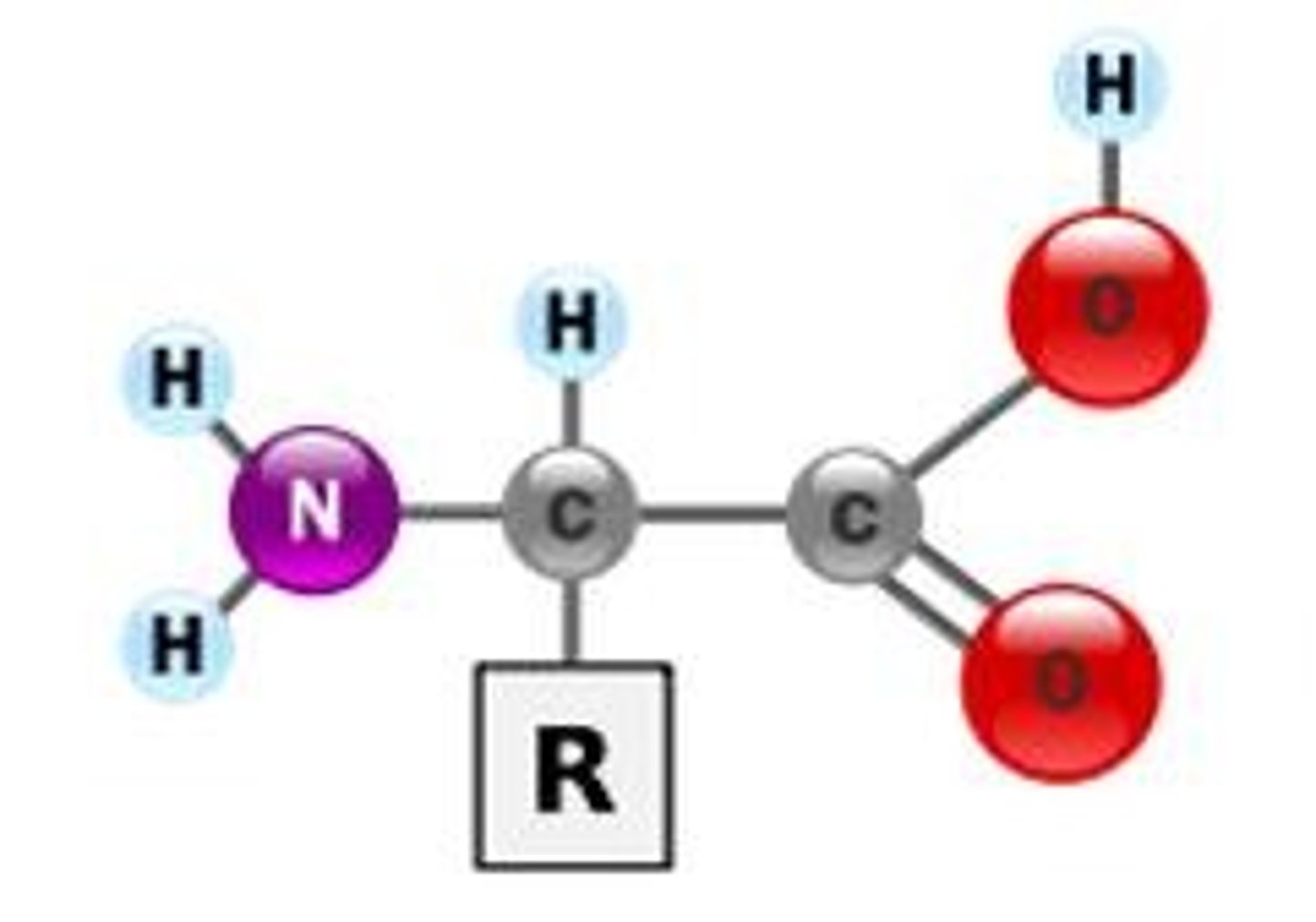
a protein's primary structure is maintained by
covalent bonds
protein cofactors are
required for the function of their protein
a small inhibitory molecule binds to the regulatory site on an enzyme, resulting in a change of the protein's shape. this makes the active site inaccessible to substrate.
this change in shape is probably due to
a rearrangement of the tertiary or quaternary structure, that extends from the regulatory site to the active site
in which compartment of the mitochondria does glycolysis occur?
glycolysis doesn't occur in the mitochondrion
which of the following compartments would be expected to be most acidic when O2 is available?
(a) the outer membrane
(b) the inner membrane
(c) the intermembrane space
(d) the matrix
(e) the entire mitochondrion should be at the same pH
c
in which compartment of the chloroplast does water-splitting occur?
the lumen of the thylakoids
which compartment of the chloroplast is the most acidic when light is available?
the lumen of the thylakoids
a heme cofactor carrying an Fe atom is part of a cytochrome protein involved in electron transfer. two closely related species have different versions of this protein.
one version (A) carries the cytochrome in an active site that has a neutral charge. the other (B) has the cytochrome in an active site that has a net charge of -2.
what would you predict would be the effect, if any, on the ability of the oxidized cytochrome to ACCEPT electrons from other molecules?
the reduction potential of B would be lower (more negative), and it would be a weaker electron acceptor
which of the following parts of metabolism occur in and require the membrane? choose all that apply:
(a) electron transport
(b) light reaction of photosynthesis
(c) pmf formation
(d) atp synthesis
abcd
the cell membrane is considered ------- because it only allows certain compounds to travel through freely
semipermeable
the random movement of molecules down their concentration gradient is called
diffusion
moving down a concentration gradient means moving from a (lower or higher) to a (lower or higher) concentration.
higher, lower
some compounds need to travel into the cell through a membrane protein, this is an example of --------
facilitated diffusion
when compounds are pumped against their concentration gradient they are being moved from (lower or higher) to (lower or higher)
lower, higher
compounds are pumped against their concentration gradient and are being moved from lower to higher concentration by which type of transport?
active transport
the majority of the cell membrane is composed of what type of lipids?
phospholipids
polar compounds are forming bonds with the water on the outside of the membrane. these bonds are called
hydrogen bonds
can polar compounds interact in this same way with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids?
no
do interactions form between polar compounds and the hydrophobic tails?
no
in order for a polar compound to enter into the hydrophobic space of the phospholipid tails, it would need to break the many ------- bonds it has formed with the water and enter into a space where these bonds cannot form.
therefore, it is not a repelling action but a "lack of attraction."
hydrogen
what types of amino acid R groups do you think will line the channel protein interior?
polar
what types of interactions can the polar compound have with the interior of this passage way (channel protein)?
hydrogen bonds
are the hydrogen bonds that polar amino acid R-groups have with the interior of the channel protein the same ones the polar compound can have on the outside of the membrane with water?
yes
when would a cell have to use active transport? (select all that apply)
(a) when the cell needs to move a compound down its concentration gradient
(b) When the cell needs to move a compound against its concentration gradient
(c) When the cell needs to move a polar compound
(d) When the cell needs to move a non-polar compound
(e) When the cell needs to move an ion
b
when would a cell use passive transport? (select all that apply)
(a) when the cell needs to move a compound that cannot move freely through the membrane
(b) when the cell needs to move a compound against its concentration gradient
(c) when the cell needs to move a compound down its concentration gradient
ac
how are the 3 domains of life related?
(a) all prokaryotic species are descended from a single simple eukaryote
(b) prokaryotes are descended from bacteria, while eukaryotes are descended from archeans
(c) bacteria evolved into archeans, which became eukaryotes
(d) a bacterium and an archean became symbionts; some of their descendants later evolved into eukaryotes
d
which strategy for capturing energy came last?
(a) anaerobic respiration
(b) fermentation
(c) methanogenesis
(d) aerobic respiration
(e) oxygenic photosynthesis
d
which of the following is true for both trans-membrane transporter proteins and enzymes?
(a) both transporters and enzymes can be regulated by small metabolites
(b) all are true for both transporters and enzymes.
(c) the rate of transport or catalysis is determined by the number of active proteins available
(d) reactions and transport can be pushed uphill (+∆G) if another reaction/transportation event with sufficient -∆G is coupled to it.
(e) the direction of transport or catalysis is determined by ∆G
b
what is the biological (adaptive) value of a hydrogenosome?
(a) the ability to use methane as an external electron source
(b) the ability to detoxify O2
(c) the ability to generate H2
(d) the ability to oxidize glucose all the way to CO2.
(e) the ability to ferment pyruvate in a way that generates ATP from ADP
e
a cell pumps Na+ out of the cell, resulting in a high concentration of Na+ outside the cell vs a low concentration inside. this is an example of:
(a) active transport
(b) contraflow
(c) facilitated diffusion
(d) proton pumping
(e) diffusion
a
what might provide the energy required to concentrate the sugar lactose within a cell?
(a) the coupled active concentration of Na+ in the cell
(b) the coupled hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi
(c) the coupled synthesis of ATP from AMP + PPi
(d) the coupled concentration of protons
b
why is one of our ancestors thought to have been a methanogen?
(a) because some eukaryotes have hydrogenosomes instead of mitochondria
(b) all responses are correct
(c) because eukaryotes can perform methanogenesis
(d) because the sequence of many eukaryotic nuclear genes is closest to that of an existing methanogen.
a
vesicles are carried as cargo by
(a) kinesins
(b) none are true
(c) dyneins
(d) all are true
(e) myosins
d
dyneins walk where on what?
(a) towards the outside of the cell, on microtubules
(b) towards the inside of the cell, on microtubules
(c) towards the inside of the cell, on microfilaments
(d) towards the outside of the cell, no both microfilaments and microtubules
(e) towards the outside of the cell, on microfilaments
b
which of the following objects requires a motor protein to diffuse across the cytoplasm of a cell at a biologically significant rate?
(a) protons
(b) glucose
(c) dynein
(d) vesicles
(e) Na+
d
if protein DNA polymerase was disrupted, the cell cycle would stop in which phase?
S phase
if the depolymerization of the microtubules was disrupted, the cell cycle would stop in which phase?
metaphase
if the polymerization of actin was disrupted, the cell cycle would stop in which phase?
cytokinesis
if the protein ligase was disrupted, the cell cycle would stop in which phase?
S phase
if the chiasmata formation was disrupted, the cell cycle would stop in which phase?
prophase I
which type of chromosomes are identical?
sister chromatids
which type of chromosomes allow recombination to occur?
homologous chromosomes
in prophase I, homologous chromosomes are held together by -------, which, once resolved, create a cross over event.
chiasmata
in anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate. in anaphase II, what separates?
sister chromatids
the end result of meiosis is 4 (unique/identical) cells
unique
1st phase of mitosis
prophase
2nd phase of mitosis
metaphase
3rd phase of mitosis
anaphase
4th phase of mitosis
telophase
in prophase, the DNA condenses down into compact ------, and the duplicated ------- separate.
chromatin, centrosome
in metaphase, the sister chromatids line up on the -------- plate.
metaphase
in metaphase, the sister chromatids line up through a push and pull motion as they connect to the microtubule spindle fibers emanating from the --------.
centrosomes
in anaphase, the (sister chromatids/homologous chromosomes) are pulled apart.
sister chromatids
in telophase, the nuclear -------- starts to reform and the DNA de-condenses.
membrane
which of the following statements is correct? you can assume that cytokinesis occurs after completion of every meiosis or mitosis.
(a) meiosis is followed by several mitoses, and then fertilization occurs
(b) mitosis is followed by several meioses, and then fertilization occurs
(c) the first cell cycle after fertilization is meiotic
(d) fertilization occurs after meiosis, with no intervening mitoses
d
the hershey-chase experiment was regarded as strong evidence that bacteriophage DNA carried the information needed to build a bacteriophage. they employed bacteriophage that had been grown in a medium that contained radioactive sulfur and phosphorus, and used these to infect bacterial hosts. what specific result(s) supported the 'DNA is inheritance' hypothesis?
(a) only radioactive sulfur was injected into the host cell
(b) both radioactive sulfur and radioactive phosphorus were bound to the exterior of the host cell
(c) both radioactive phosphorus and radioactive sulfur were injected into the host
(d) only radioactive phosphorus were injected into the host
d
kinetochores play an essential role in mitosis by (select all that apply):
(a) pulling the centromere along microtubules
(b) separating the homologs
(c) establishing tension and so allowing the cell to know when the sister chromatids are properly aligned
(d) holding two sister chromatids together
ac
sexual reproduction enhances the rate of evolution, allowing nature to select for novel combinations of alleles. two genes are present on the same chromosome. one homolog carries the dominant A and B alleles, while the other homolog carries the a and b alleles. which specific process of the meiotic cell cycle with result in a recombinant chromosome (for example, A with b)?
(a) crossing over, during meiosis II
(b) segregation of homologs, during meiosis II
(c) the pre-meiotic S phase
(d) crossing over, during meiosis I
(e) segregation of homologs, during meiosis I
d
how does mitosis differ from meiosis I?
(a) the nuclear envelope disappears only in meiosis I
(b) the sister chromatids separate in mitosis, not in meiosis I
(c) homologs align in mitosis but not in meiosis I
(d) chromatin supercoils only in mitosis
(e) crossing over occur in mitosis, but not in meiosis
b
mendel's extremely important contributions to biology was/were (select all that apply):
(a) identification of chromosomes as the subcellular organelle responsible for inheritance
(b) the observation that different kinds of traits segregate independently
(c) the observation that peas carry two copies - and so potentially two version - of what we now call 'genes'
(d) proof that DNA is the molecule of inheritance
bc
in horses, D is a dominant allele of the Dun gene that results in what is considered to be the "wild-type" coat color: dull brown with black mane, tail, legs, and dorsal stripe (called "dun" or "buckskin"). homozygosity for d, a recessive allele, results in a rich, vivid coat color (black, bay, chestnut etc). you have a dun male horse and want to determine whether he is heterozygous or homozygous for D, so you cross him to a bay female. the resulting offspring is bay. from this you can conclude...
(a) your dun horse is homozygous (DD)
(b) your dun horse is homozygous (dd)
(c) your dun horse is heterozygous (Dd)
(d) there are not enough offspring to be able to conclude anything
(e) the male horse's phenotype already tells you his genotype.
c
avery and macleod's experiment strongly suggested that DNA, rather than protein or RNA, is the molecule of inheritance. this experiment involved the identification of a class of molecules that could transform bacteria from harmless to deadly. this transforming molecule was destroyed by...
(a) RNase, but not protease or DNase
(b) DNase, but not protease or RNase
(c) protease, but not RNase or DNase
(d) Both DNase and RNase, but not Protease
(e) Both Protease and RNase, but not DNase
b
looking through a microscope, you see a nucleus that has 6 chromosomes, each chromosome having one chromatid. you conclude that this nucleus is (select all that apply):
(a) in telophase, from a haploid cell with 6 different, non-homologous chromosomes
(b) in telophase, from a diploid cell with 3 pairs of homologous chromosomes
(c) in interphase, and from a diploid cell with 3 pairs of homologous chromosomes
(d) in interphase, and from a haploid cell with 6 different, non-homologous chromosomes
ab
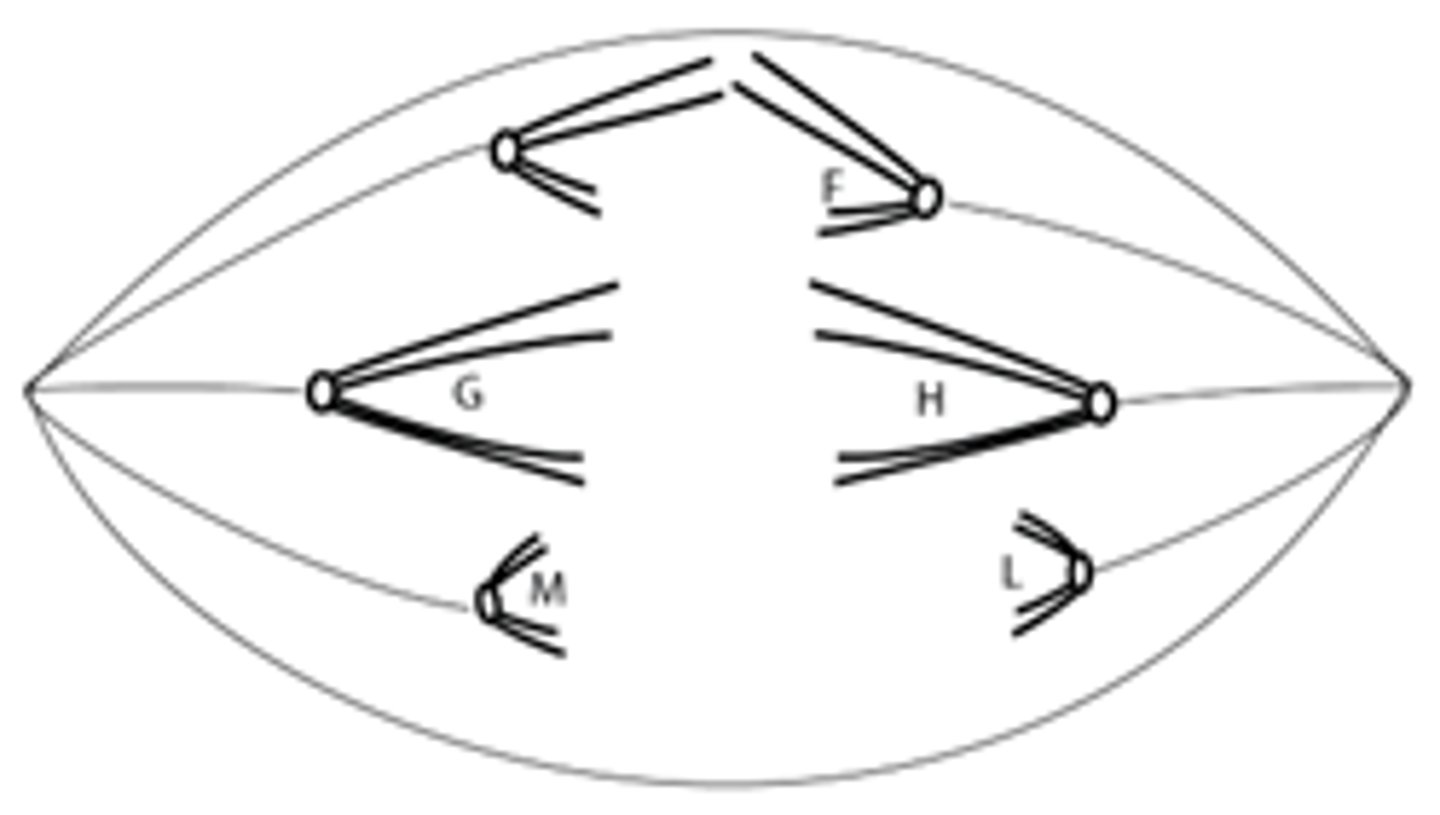
in the cell depicted above, each line represents a chromatid. this cell is in the following stage of the cell cycle:
(a) anaphase of meiosis I
(b) metaphase of mitosis I
(c) prophase of meiosis I
(d) prophase of meiosis II
(e) start of DNA replication (S phase)
a
what are the three components of a nucleotide (select all that apply) ?
(a) nitrogenous base
(b) carboxylic acid group
(c) phosphate group
(d) 5-carbon sugar (ribose)
(e) 6-carbon sugar (glucose)
acd
what functional group is at the 5' end of the DNA?
(a) phosphate group
(b) hydroxyl group
(c) hydrogen
(d) sugar
a
what functional group is at the 3' end of the DNA?
(a) phosphate group
(b) hydroxyl group
(c) hydrogen
(d) sugar
b
what types of molecular interactions are occurring between the base pairs?
(a) covalent bonds
(b) hydrogen bonds
(c) phosphoanhydride bond
(d) ionic bond
b
what is the complementary base sequence to this strand of DNA:
5' - ATGGTCGTAGTGA -3'
TACCAGCATCACT
the two strands of DNA are -------- to each other such that at the end of the DNA, one strand will be 3' paired with a 5' end.
antiparallel
the two strands of the DNA are held together with -------- bonds.
hydrogen
in DNA, A binds with ___ and G binds with ___
T, C
what unwinds the DNA for replication to begin?
helicase
an RNA primer is created by enzyme
primase
the RNA primer supplies the 3' hydroxyl group used by ---------------- to start adding DNA nucleotides
DNA polymerase 3
the DNA strand is made from which end to which end?
5' to 3'
which strand is made in short segments called okazaki fragments (leading/lagging) ?
lagging
which strand is made in one continuous piece (leading/lagging) ?
leading
after replication, the RNA primers are removed by which enzyme before being replaced with DNA nucleotides?
DNA polymerase 1
which enzyme seals the nicks in the sugar-phosphate backbone after the RNA primers are removed?
ligase
which enzyme extends the ends by creating a repeating sequence of nucleotides which helps prevent loss of genetic material with each replication on linear chromosomes?
telomerase
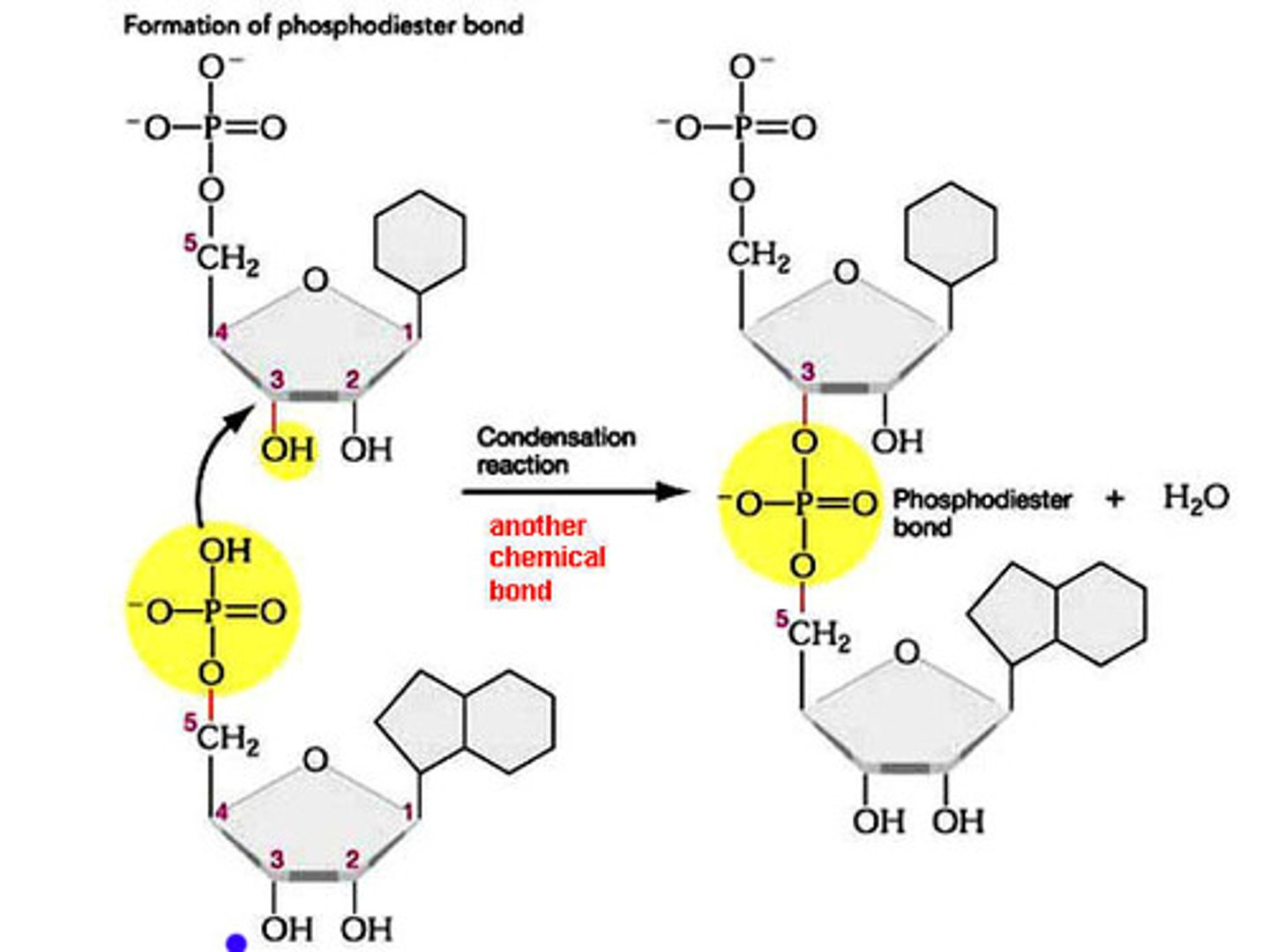
what are the reactants in the formation of the phosphodiester bond in a nucleotide polymerization reaction?
(a) polymer with 3' OH and CTP
(b) polymer with 3' OH and ATP
(c) polymer with 5' OH and CTP
(d) polymer with 3' OH and ATP
a
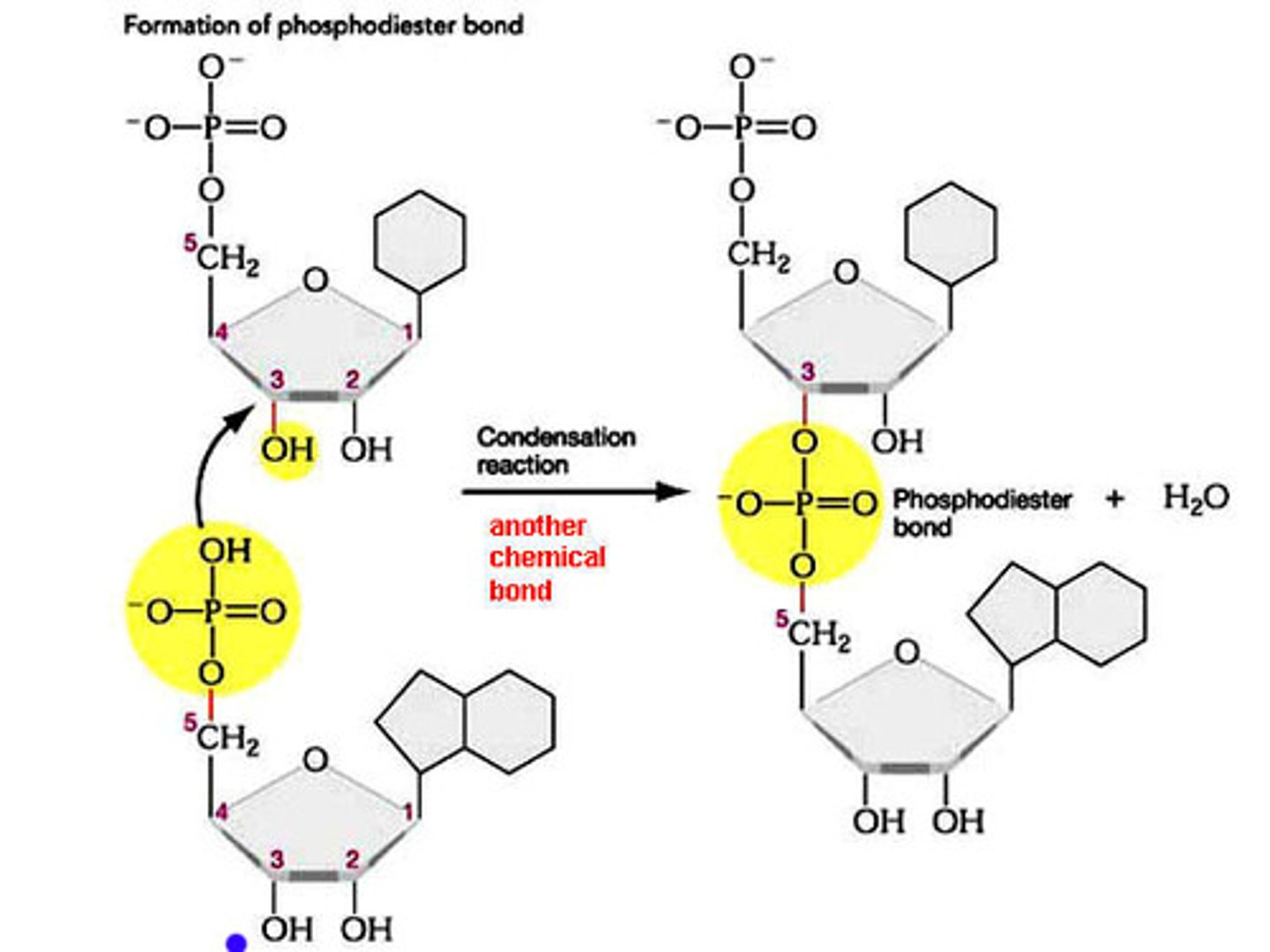
what are the products in the formation of the phosphodiester bond in a nucleotide polymerization reaction?
(a) polymer and pyrophosphate
(b) polymer and energy
(c) pyrophosphate
a
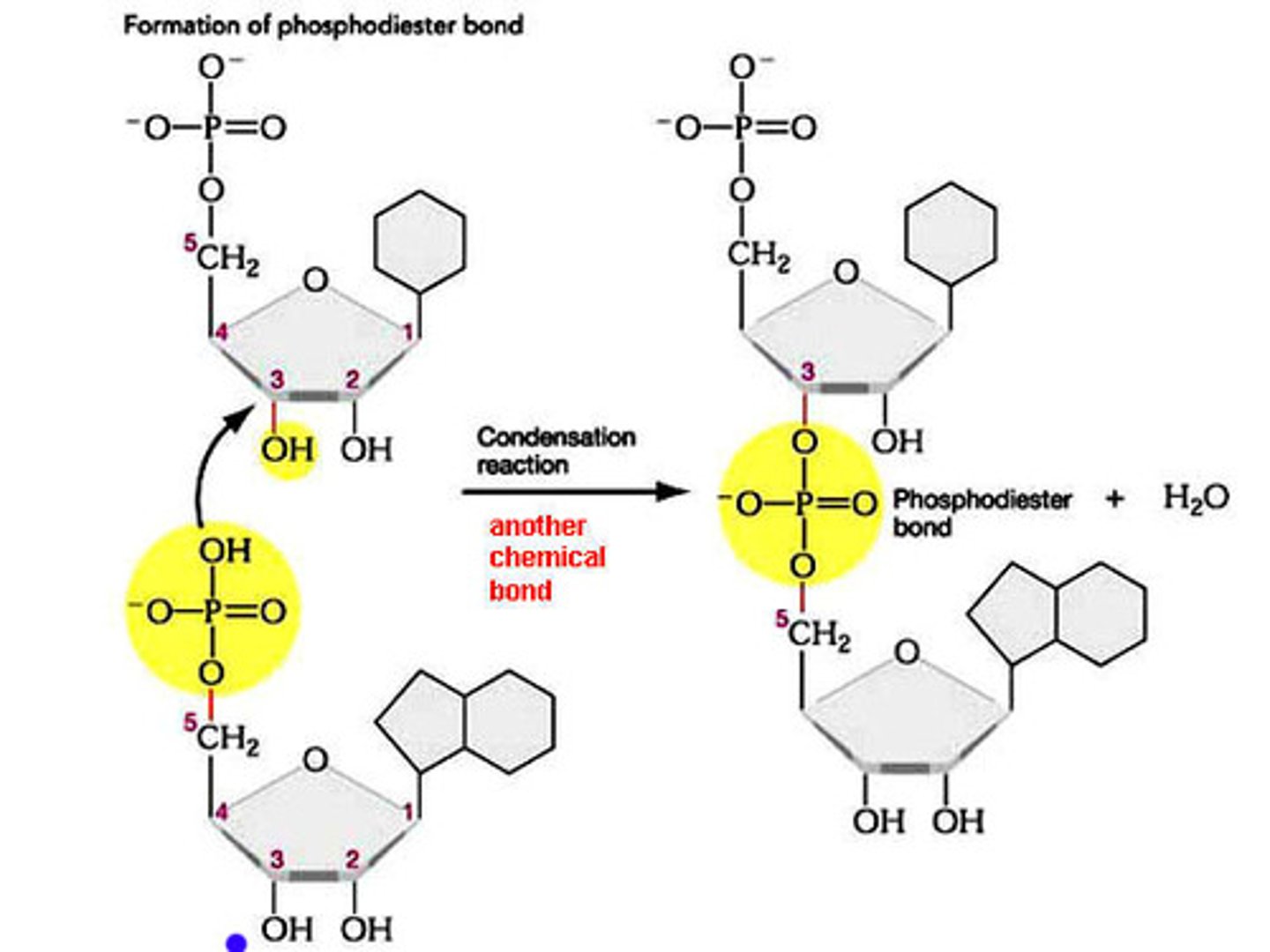
which half reaction is endergonic in this coupled nucleotide polymerization reaction?
(a) hydrolysis of the anhydride bond
(b) catalysis of the phosphodiester bond
b