3- physical exam of CVS
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
“low volume” pulse is also called
“tready” or “weak” pulse
“high volume” pulse is also called
“bounding” or “strong” pulse
during an emergency, pulse volume dictates patient _____
positioning
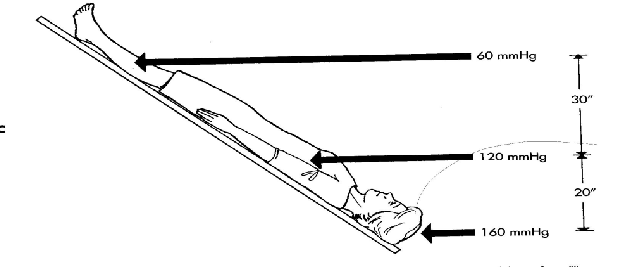
what position should the pt be in if they have a tready pulse
horizontal/head-down/Trendelenburg position → brings blood back to heart
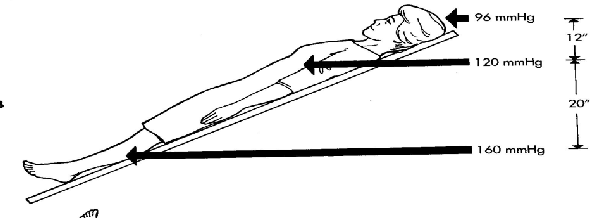
what position should the pt be in if they have a bounding pulse
semi-sitting position → slows return of blood to heart
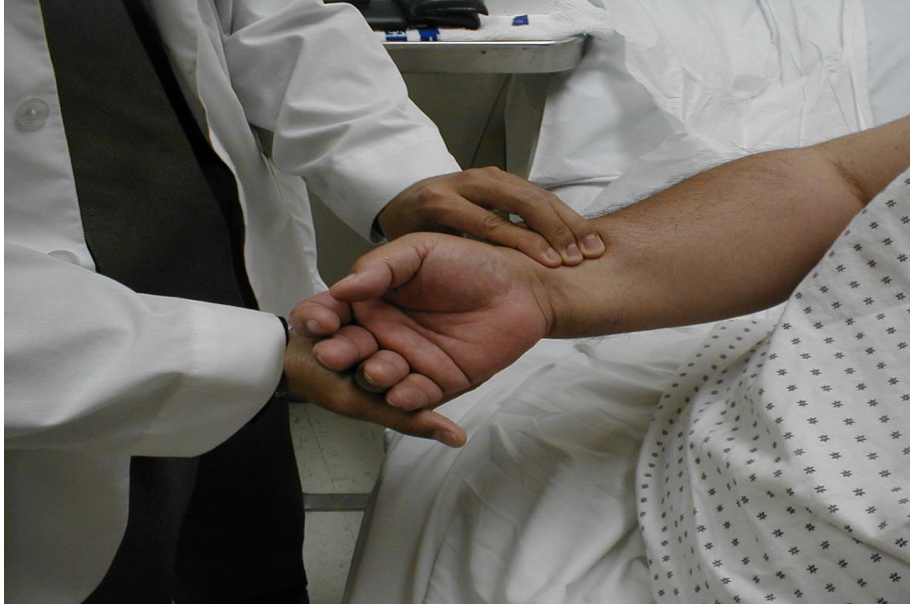
which fingers should you use to feel pulse
index + middle finger
how many fingers do you use to feel pulse on older pts
prevent slipping + stabilize the artery w/ 2-4 fingers
how do you take radial pulse
using 2 or more fingers
T/F: you must count pulse after the pt is relaxed
true
how long do you count pulse for
1 minute
how do you take carotid pulse
have pt flex neck to relax platysma
locate anterior border of SCM
place 2 fingers along border in middle of neck
press down firmly towards midline
why should you never take carotid pulse at angle of the mandible
this can massage the carotid sinus → slowing the pulse
T/F: never take carotid pulse on both sides at the same time
true, can be dangerous esp in older pts
carotid pulse is most frequently used during
medical emergencies
T/F: you should feel each carotid separately
true
what do you do if the HR is not the same on both sides of the carotid
auscultate (listen) for carotid bruit
how do you listen for carotid bruit
have pt hold their breath
place stethoscope over carotid w/ lesser pulse in middle of the neck
listen for “swooshing sound” caused by turbulence of the blood flow through a narrowed or partially obstructed arterial lumen
if there’s a carotid bruit, you should assess for what 2 things
transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
cerebrovascular accidents/strokes (CVAs)
how do you take brachial pulse
position pt’s arm w/ palm facing ceiling
go upwards on medial side on arm, above elbow
support pt’s arm w/ your hand + feel pulse w/ 2 fingers
brachial pulse is taken on what pts
children during medical emergencies
using a stethoscope over the brachial artery monitors what
Korotkoff sounds
what happens if you use a BP cuff that’s too small
overestimation of BP
what happens if you use a BP cuff that’s too big
underestimation of BP
where should the arm be when taking BP
brachial artery must be at cardiac level
what happens if the arm is above heart level when taking BP
underestimation of BP
what happens if the arm is below heart level when taking BP
overestimation of BP
how many BP do you take at the pt’s 1st visit
2
what do you do if the pt has elevated readings at their 1st visit
take 2 more readings at the end of the visit
how many reading are needed for diagnosis of HTN
2-4 readings
what’s the auscultatory gap
absence of Korotkoff sounds between SBP + DBP readings, occurs in some HTN pts
failure to recognize the auscultatory gap can lead to
serious underestimation of the SBP
serious overestimation of the DBP
you must inflate the BP cuff to ___ mmHg in all patients
200 mmHg
what’s pulse pressure
difference between SBP + DBP
high pulse pressure is associated w/ what
uncontrolled hyperthyroidism
low pulse pressure is associated w/ what
uncontrolled hypothyroidism
what’s the BP readings for stage 1 HTN
SBP: 130-139
DBP: 80-89
what’s the BP readings for stage 2 HTN
SBP: >140
DBP: >90
when should you estimate SBP via palpation
during an emergency before BP cuff use
what's the estimate SBP if only carotid pulse is palpable
60-70 mmHg
what's the estimate SBP if carotid + femoral pulse are palpable
70-80 mmHg
what's the estimate SBP if carotid + femoral + radial pulse are palpable
>80 mmHg
clubbing or convexity of the nails may indicate
heart & lung diseases causing chronic hypoxia
spooning or koilonychia of the nails may indicate
iron deficiency anemia
splinter hemorrhage of the nails may indicate
jagged lines seen in subacute bacterial endocarditis
fingers, toes, lips turning blue may indicate
cyanosis associated w/ congenital heart defects
how do you check for ankle edema
press firmly w/ thumb on top of foot near ankle for a few sec + remove thumb
“dent” = edema = congestive heart failure
purpose of palpating chest
detection of parasternal heaves + apex beat
what’s a heave
palpable impulse that noticeably lifts the palpating hand
how do you palpate for a parasternal heave
put R palm against L parasternal region
R ventricular hypertrophy = L parasternal heave
what’s an apex beat
lowest & lateral most point where cardiac impulse can be palpated
displaced apex beat would indicate
L ventricular hypertrophy
how do you percuss a pt’s chest
L hand placed over chest while R hand taps L hand
go lateral → medial, over ICS 2-5
what percussion sound indicates the heart vs. lungs
heart: dull
lungs: resonant
audible S3 in older patients indicates what
congestive heart failure
audible S3 is normal in which pts
young pts + athletes
audible S4 indicates
HTN or aortic stenosis → severely thick + stiff L ventricular wall → vibration of ventricular wall during atrial contraction