Bonding in carbon and homologous series
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Explain the occurrence of carbon compounds in terms of bonding

Tetravalency

Catenation

Hybridization

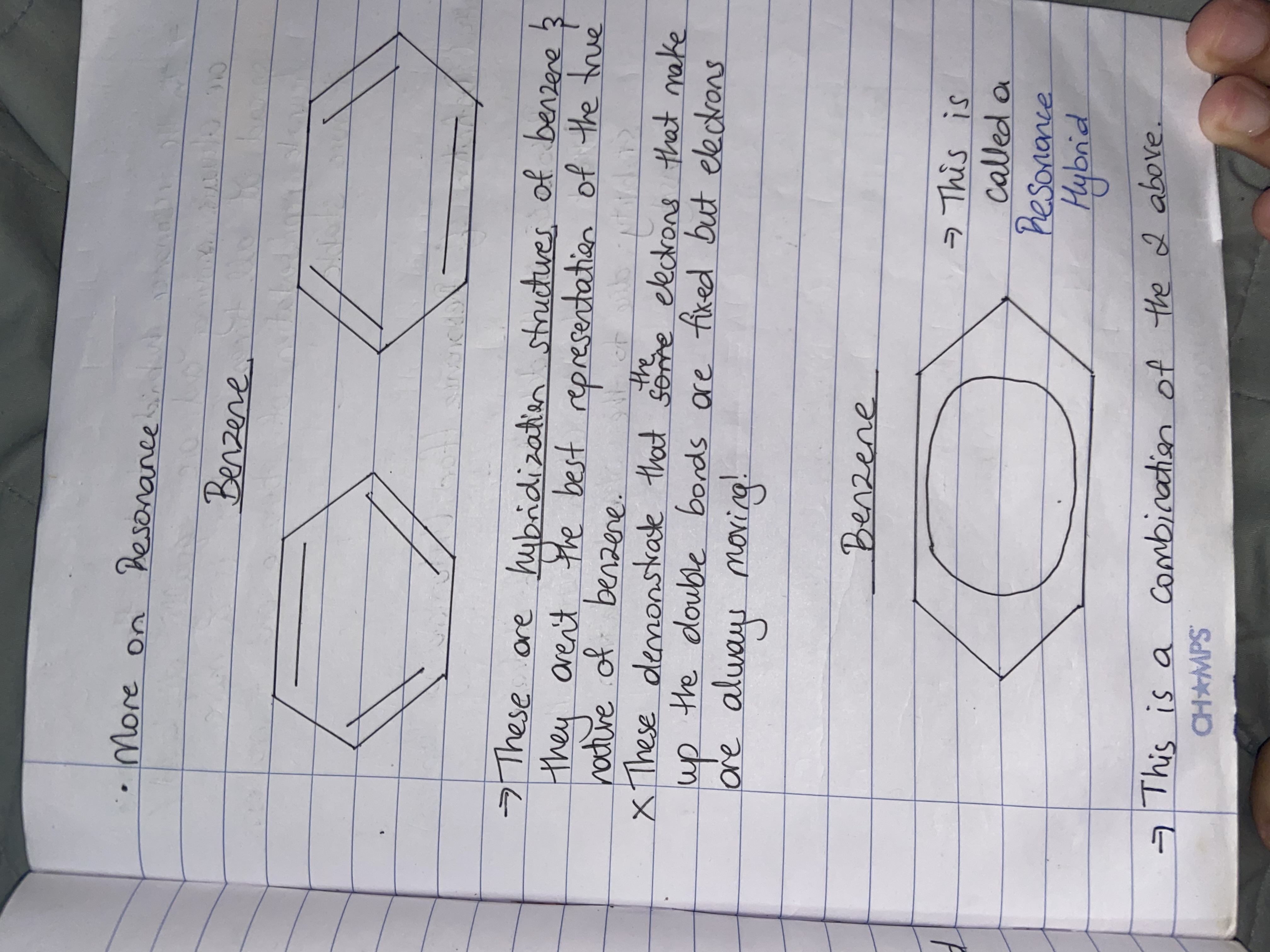
Resonance
Resonance is the delocalization of electrons across multiple atoms in a molecule/ion

Differentiate amongst the types of Hybridization
1. sp³ Hybridisation (tetrahedral):
Definition: Mixing of 1 s orbital and 3 p orbitals to form 4 equivalent sp³ orbitals.
Bond Angle: ~109.5°
Example: Methane (CH₄)
2. sp² Hybridisation (trigonal planar):
Definition: Mixing of 1 s orbital and 2 p orbitals to form 3 equivalent sp² orbitals.
Bond Angle: ~120°
Example: Ethene (C₂H₄)
3. sp Hybridisation (linear):
Definition: Mixing of 1 s orbital and 1 p orbital to form 2 equivalent sp orbitals.
Bond Angle: ~180°
Example: Ethyne (C₂H₂)

Resonance hybrid
A resonance hybrid is the actual structure that results from the combination of all resonance structures of a molecule or ion, showing delocalised electrons.
Explain the meaning of homologous series

Define functional group

Describe the chemical and physical characteristics of homologous series.
Chemical properties:
Same Functional Group, Same Reactions:
All members undergo similar chemical reactions because they have the same functional group.
For example, all alkenes undergo addition reactions due to the C=C double bond.
Reaction Type is Determined by Functional Group:
Alkanes: Mostly unreactive; undergo combustion and substitution.
Alkenes: Undergo electrophilic addition (e.g. with bromine water).
Alcohols: Undergo oxidation, esterification, and can act as weak acids.
Carboxylic acids: React with metals, carbonates, and bases to form salts.
Halogenoalkanes: Undergo nucleophilic substitution.

Define:
Empirical formula
Molecular formula

Give 3 examples of compounds that have the same empirical formula and molecular formula and write the formulas

Define structural formula
Define the types of structural formula

Define skeletal formula

Show the skeletal formula of propane and cyclopropane

Give the displayed structural formula for the Functional groups alkane and alkene

Give the displayed structural formula for the Functional groups alkyne and alcohol
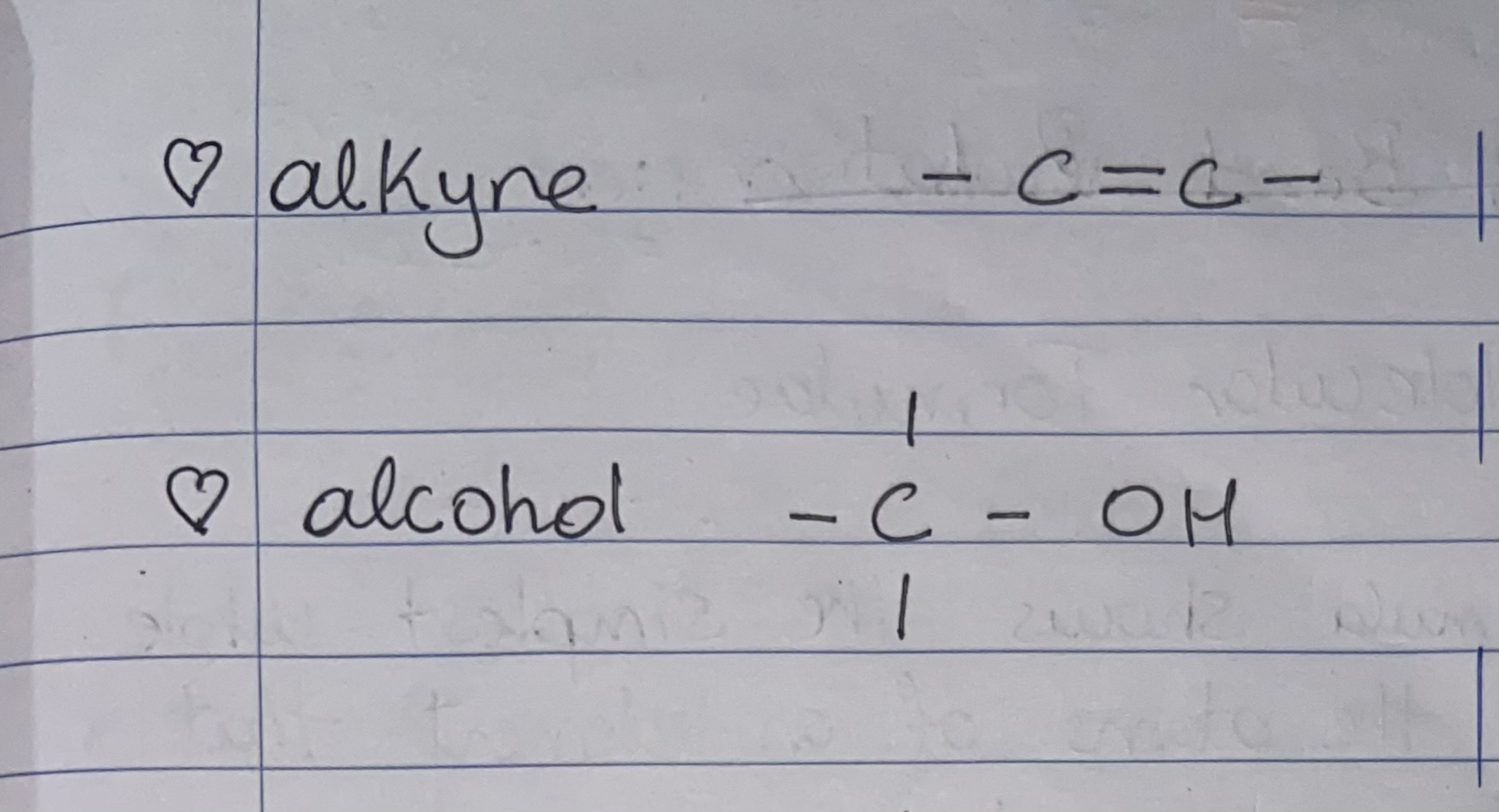
Give the displayed structural formula for the Functional groups
ester
Ether
aldehyde
Ketone

Give the displayed structural formula for the Functional groups
Primary amine
Primary amide
Cyanide
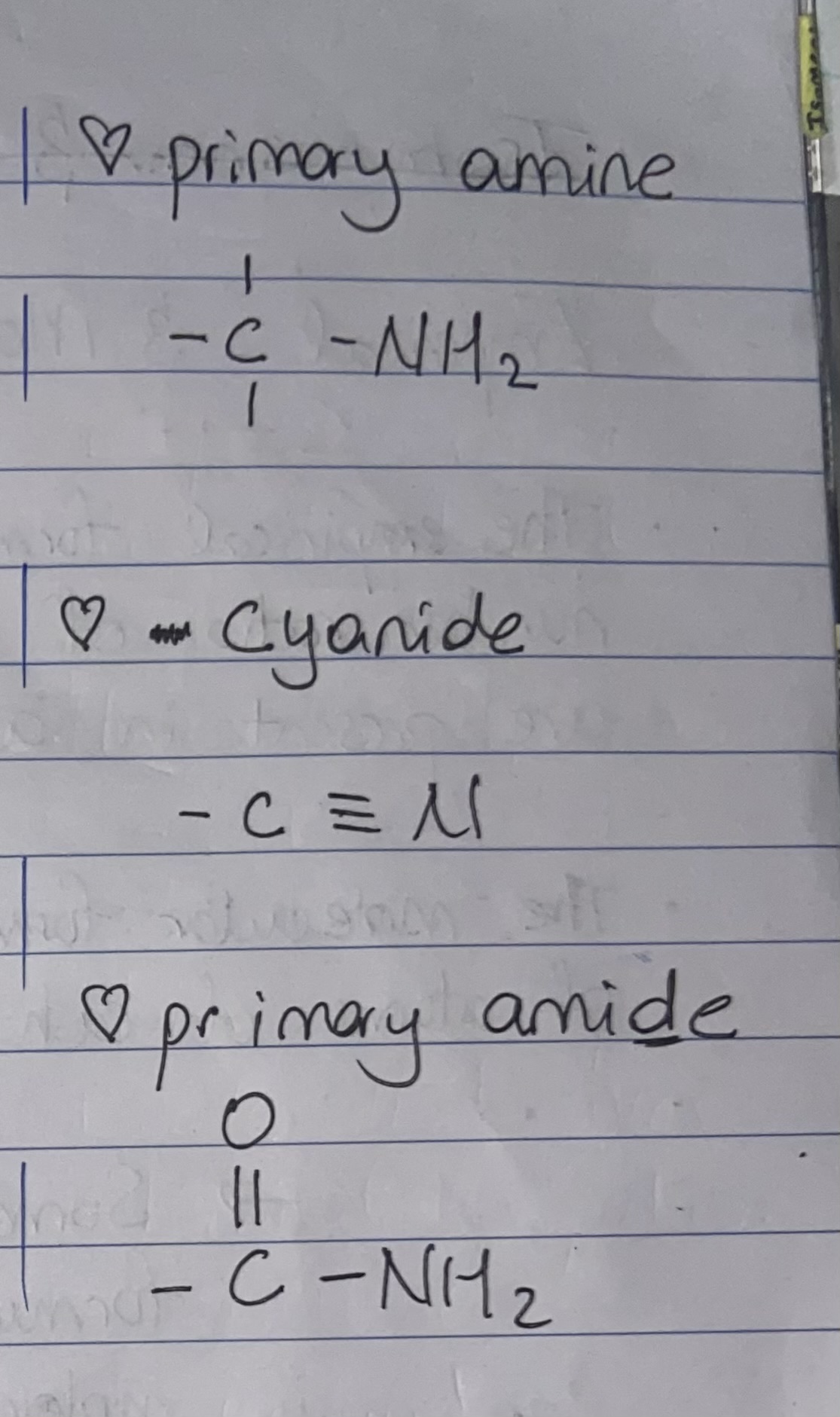
Give the displayed structural formula for the Functional groups thiol and thioester

Give the displayed structural formula for the Functional groups
Carboxylic acid
Carboxyl group
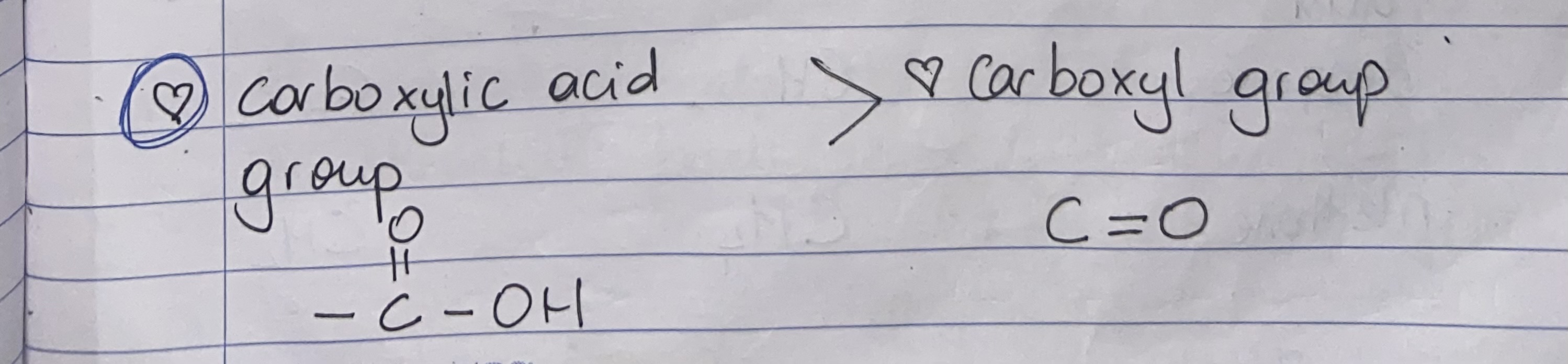
Carbon prefixes 1-10
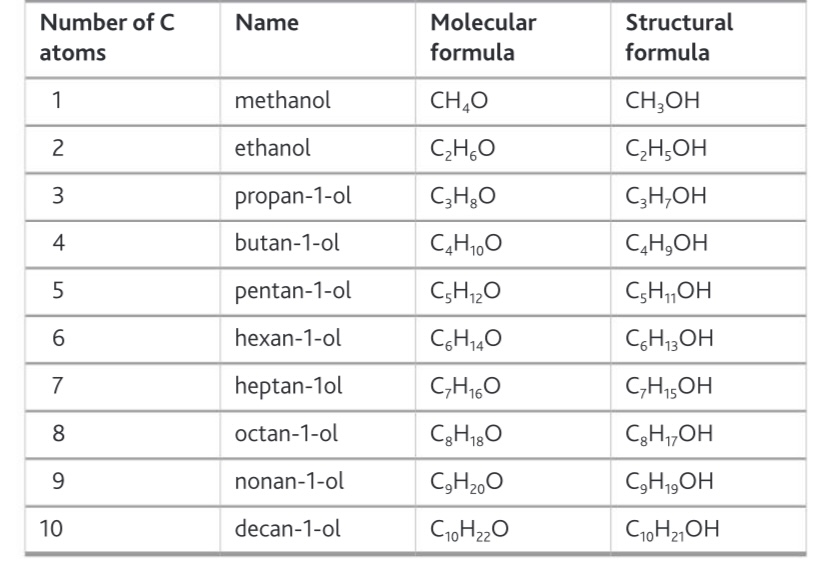
Functional group table for memory
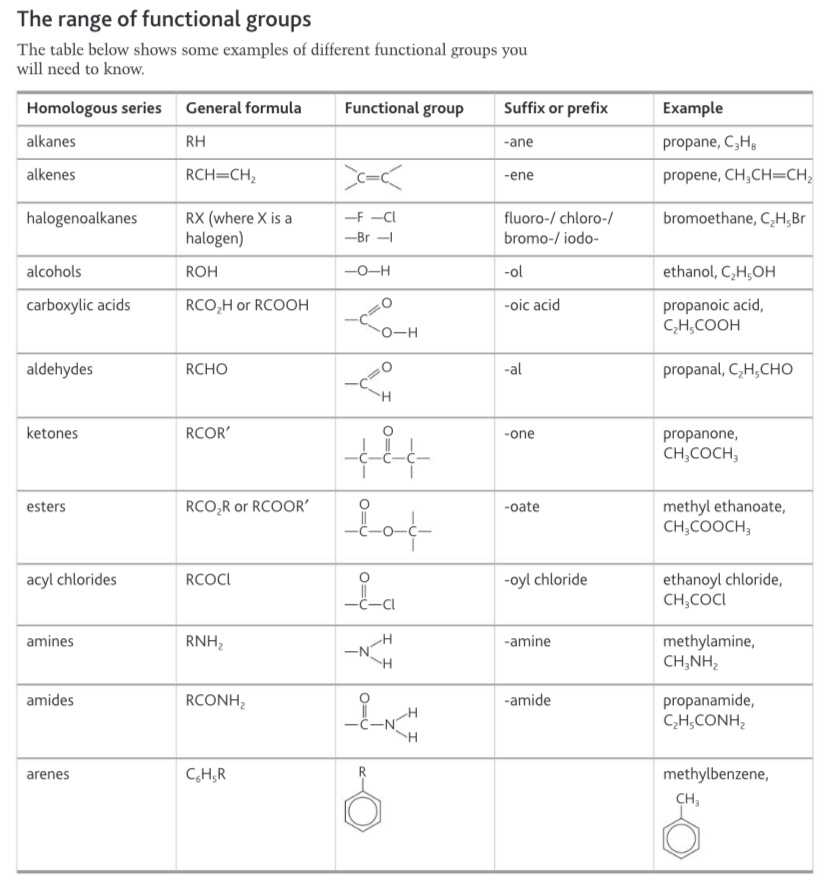


We can find the molecular formula if we know..?





State Avrogardo’s Law
Avogadro’s Law states that equal volumes of all gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules.