McWain - ALL UNITS AP PSYCH 2025 MEGA KAHOOT CHALLENGE!
1/839
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
840 Terms
Experiment
A method of studying behavior with the potential to show cause & effect.
Hindsight Bias
the tendency to believe, AFTER learning an outcome, that they were confident that was what was going to happen all along.
Hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Operational Definition
A carefully worded statement of the exact procedures/variables (operations) used in research for REPLICATION.
Ex: Coffee = 8 oz. caffeinated coffee
Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
Case Study
A non-experimental method in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing truth about larger groups.
Survey
A technique for obtaining self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning random sample of a group
Population
The largest possible group researchers hope to generalize their random sample towards.
Ex: 25 students at this high school hoping it generalizes to ALL students at this high school.
Random Sample
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of being selected.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation.
Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors interact together. Can be a positive, negative, or no correlation.
Correlation Coefficient
The strength of a correlation that ranges from -1 to +1.
-1 and +1 are equally strong. 0 is the weakest.
experiment
a research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process (the dependent variable). By random assignment of participants, the experimenter aims to control other relevant factors
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental & control groups where anyone in the sample has an equal chance to be in any group (randomization).
Double-blind Procedure/Study
An experimental procedure where researchers and participants both don't know which group participants are in until after the study is finished. Aims to eliminate bias.
Placebo Effect
When participants receive a fake version of the treatment, but believe it is real and see real effects.
Ex: Fake headache medicine with flour pill. Headache actually goes away after taking it.
Experimental Group
The group that is exposed to the treatment in an experiment.
They receive one version of the Independent Variable.
Ex: If I drink coffee, then I'm more awake. - The group drinking the caffeinated coffee.
Control Group
The group that is NOT exposed to the treatment in an experiment.
They receive the comparison/baseline version of the Independent Variable.
Ex: If I drink coffee, then I'm more awake. - The group drinking the decaf coffee or no coffee at all.
Independent Variable
The variable being manipulated or changed by the researchers.
Ex: If I drink coffee, then I'm more awake.
IV = Coffee type and amount
Confounding Variable
A BAD variable that ruins the experiment because it impacts the dependent variable. CANNOT be the same as the IV or DV.
Ex: If I drink coffee, then I'm more awake
CV = Amount of sleep
Dependent Variable
The variable researchers are measuring (the outcome).
Ex: If I drink coffee, then I'm more awake
DV = level of awakeness
Mode
The number that appears the MOST in the data set.
Mean
The average in a data set.
Add all numbers together and divide by how many numbers are in the data set.
Median
The middle score in a distribution of numbers. Half of the numbers are above and half are below the median.
Line numbers up from smallest to largest, find the middle number.
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution.
Subtract lowest number from highest number.
Standard Deviation
A number showing how spread out data or scores are.
Smaller standard deviation = scores closer together (stronger)
Larger standard deviation = scores further apart (weaker)
Normal Curve (Normal Distribution)
A normal bell curve.
68% of data within 1 standard deviation of the mean (SD of Mean)
95% of data within 2 SD of Mean
99.7% of data within 3 SD of Mean
Anything else is an outlier
Informed Consent
Ethical Principle: Participants must be told enough info about what they will be doing to help them to choose whether or not they want to participate.
Debriefing
Researchers must explain what the study was about and clear up any deception right away after the study has ended.
Sampling Bias
A flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample (NOT RANDOM)
Regression Toward the Mean
the tendency for extreme or unusual scores to fall back (regress) toward the average.
Skewed Distribution
Very large or very small outliers can skew the data to one side instead of making a bell curve.
Statistical Significance
Whether or not results were accidental (had a confounding variable) or were able to prove cause and effect.
If they ARE statistically significant, we say: Results were NOT due to chance.
If they are NOT statistically significant, we say: Results COULD BE due to chance.
Statistical Significance of .05 OR LESS = Statistically Significant. Anything higher = bad = NOT statistically significant
Informed Assent
A process for minors in research that lets them agree to participate with parent permission, and that they can stop participating at any time.
Bimodal Distribution
When two different data areas have high prevalence. Think "normal bell curve", but with two bumps.
Confederate
A person who appears as a participant, but is in on the study and may be manipulating the situation/other participants on purpose at the researchers request.
Confidentiality
ETHICAL PRINCIPAL: Researchers must not publish any personal or identifying information about their participants.
Confirmation Bias
Looking for information that supports one's beliefs and ignoring anything that doesn't.
Convenience Sampling
Any process for selecting a sample for research that is not random but is chosen by easy access.
Data obtained from this method WILL NOT generalize to the larger population as there may be significant bias.
Cultural Norm
A societal rule, value, or standard that is an accepted and appropriate behavior within a culture.
Deception
Any distortion of or withholding of fact with the purpose of misleading others.
Directionality Problem
In correlational research, a situation where researchers KNOW that two variables are related but DO NOT KNOW which is the cause and which is the effect.
Ethical Guidelines
Rules of acceptable behavior/practices during research.
Falsifiable/Falsifiability
The idea that for a hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be possible to test for evidence that would prove it false.
Generalizability
Degree to which a study's findings (based on a random sample) apply to the entire population (provided the sample is representative and large enough).
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
A committee at each college/university where research is conducted to review every experiment for ethics and methodology.
Meta-analysis
A procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies.
Negative Correlation
A relationship between two variables that shows when one variable increases, the other decreases.
Negative Skew
Low numbered outliers in the data draw the tail/shape of the data to the left.
Non-Experimental Research Methods
4 Types:
-Case Study
-Meta-Analysis
-Naturalistic Observation
-Correlation
Non-experimental methods cannot:
-Randomly assign participants to conditions
-Control or manipulate the independent variable
-Limit the influence of confounding variables.
Positive Correlation
A relationship between two variables where as one variable increases, so does the other.
positive skew
High numbered outliers in the data draw the tail/shape of the data to the right.
Protection from Harm
Reasonable steps taken to avoid and minimize harm (physically, emotional, mental) for research participants whenever possible.
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance (using a method of random selection).
Random Sampling
A smaller group that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion.
Representative Sample
The selection of participants from a larger group (population) in an unbiased way, so the sample reflects the total population.
Self-report Bias
People will respond inaccurately (or with partial truth) to surveys because they want to appear more socially desirable, have poor memory recall, or misunderstand the questions.
Single-blind Study
Research design in which participants don't know whether they are in the experimental or control group.
Social Desirability Bias
A tendency to give socially approved answers to questions about oneself.
8 Perspectives: Psychodynamic
A perspective that explains behavior based on things like childhood experiences, use of defensive mechanisms, and the structure of the mind (ID, Ego, Superego).
Ex: Timmy was overlooked by his parents as a child and now acts out for attention.
8 Perspectives: Cognitive
A perspective that explains behavior based on how we think, interpret, and store information in our brains.
Ex: Timmy waved at a friend in the hallway but they didn't wave back. His behavior/reaction will change based on if he interprets it as disrespect (he doesn't like me) or zoning out (he didn't see me).
8 Perspectives: Behaviorism
A perspective that explains behavior based on things like observing others and copying them, rewards/punishments shaping behavior, or learning from our own experiences.
Ex: Timmy touched a hot stove as a child and burned his fingers. Now he never does that again.
8 Perspectives: Humanism
A perspective that explains behavior based on things that enhance growth potential and our ability to share love, be accepted, and exercise our free will in that process.
8 Perspectives: Biological
A perspective that explains behavior based on things like genetics & body and brain chemicals and processes.
8 Perspectives: Sociocultural
A perspective that explains behavior based on things like social norms, cultural norms, and how we interact with different people in different settings.
8 Perspectives: Evolutionary
A perspective that explains behavior based on things like survival and instincts.
8 Perspectives: Biopsychosocial
A perspective that explains behavior by combining all other perspectives.
Bio = Biological/Evolutionary
Psycho = Psychodynamic, Behaviorism, Cognitive
Social = Sociocultural, Humanism
Actor/Observer Bias
We blame OUR actions on the situation, but blame OTHERS' actions based on their PERSONALITY/TRAITS
Altruism
Caring for others unselfishly - Doing the right thing even if it doesn't obviously benefit us

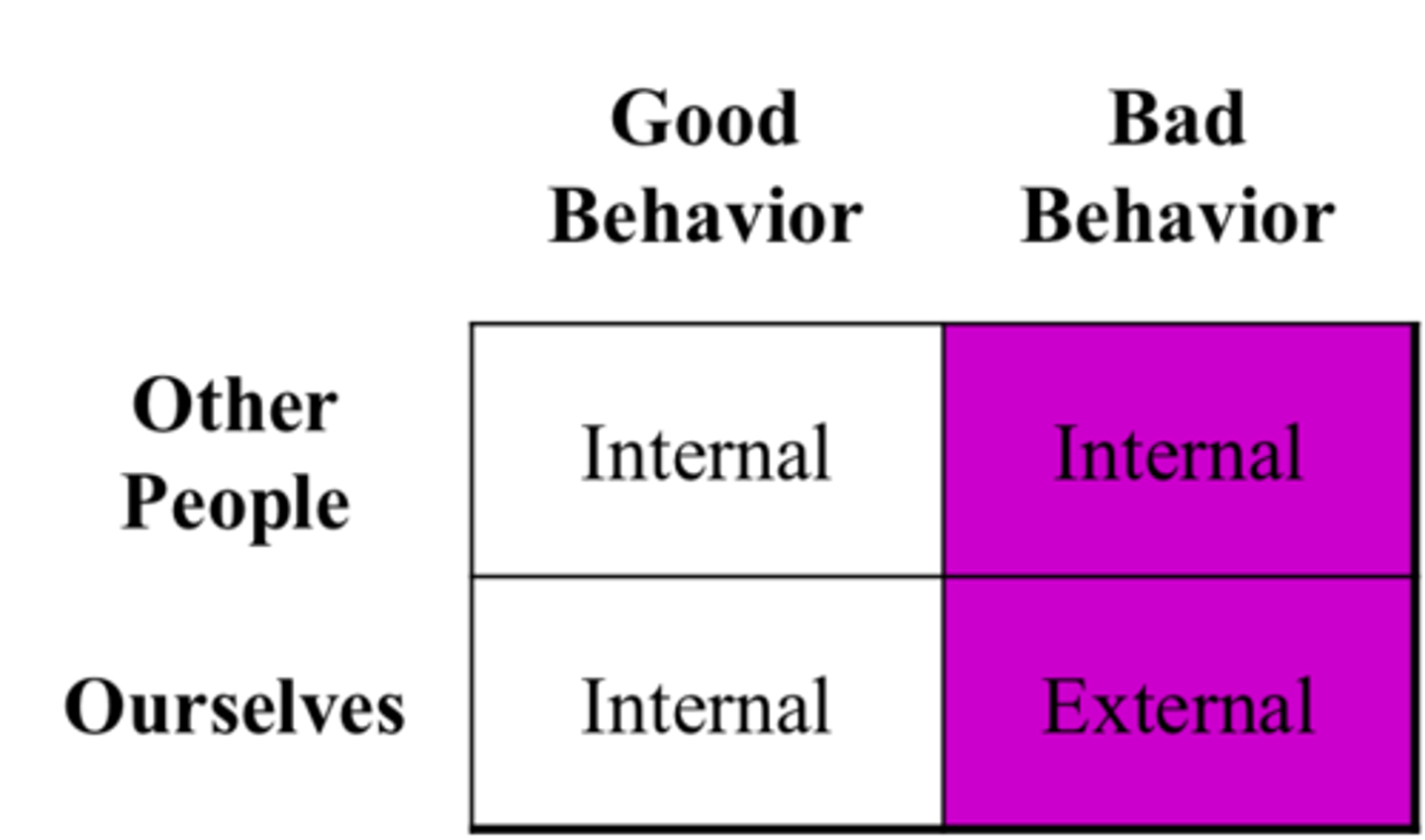
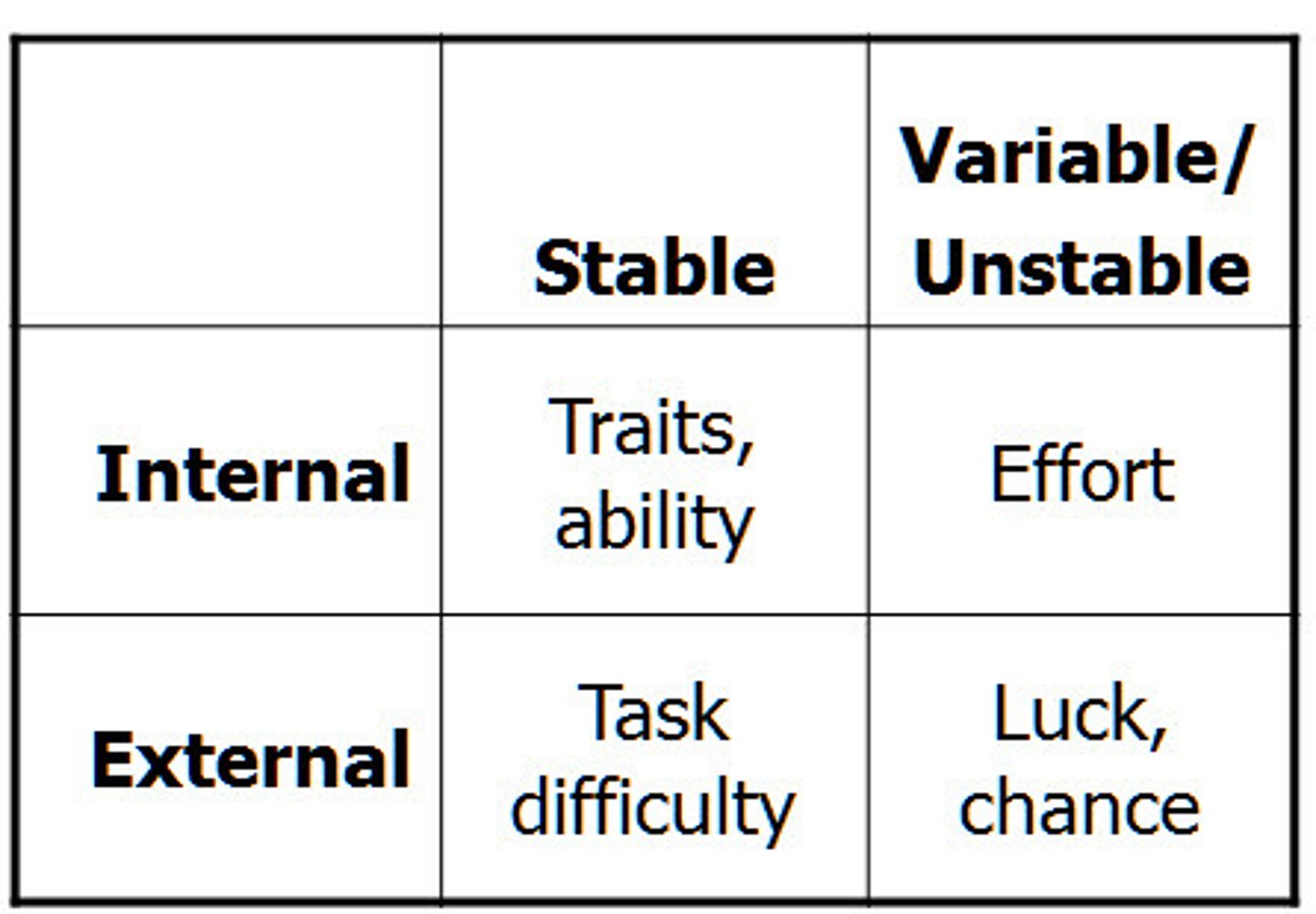
Attributions
How explain what causes behaviors
-Can be internal or external.
Belief Perseverance
Holding onto a belief even when presented with evidence against it
Burnout
physical, emotional, or mental exhaustion accompanied by decreased motivation, lowered performance, and negative attitudes toward oneself and others.

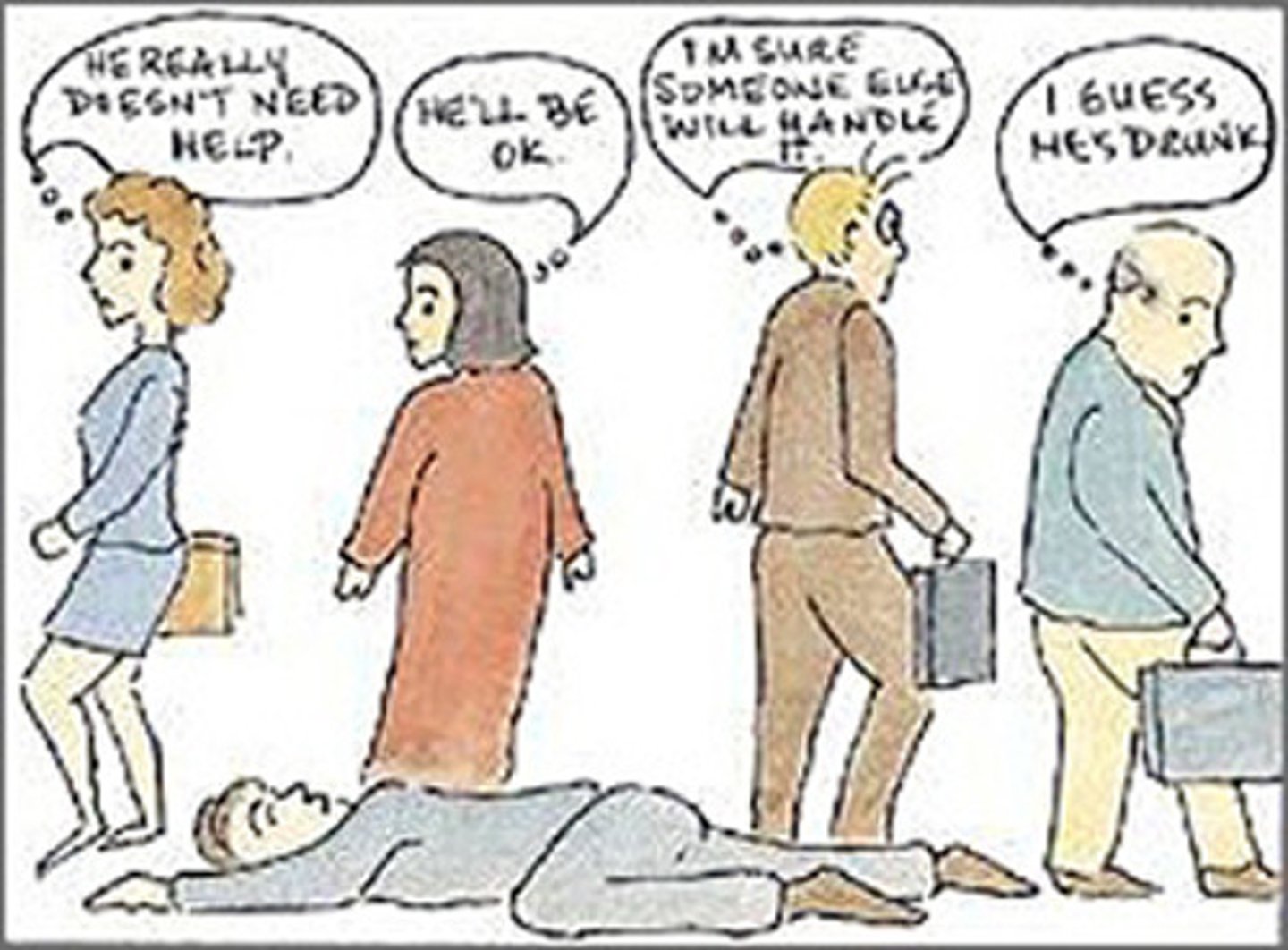
Bystander Effect
People are less likely to help a victim when others are present.

Central Route Persuasion
Persuasion that uses logic and facts to convince people

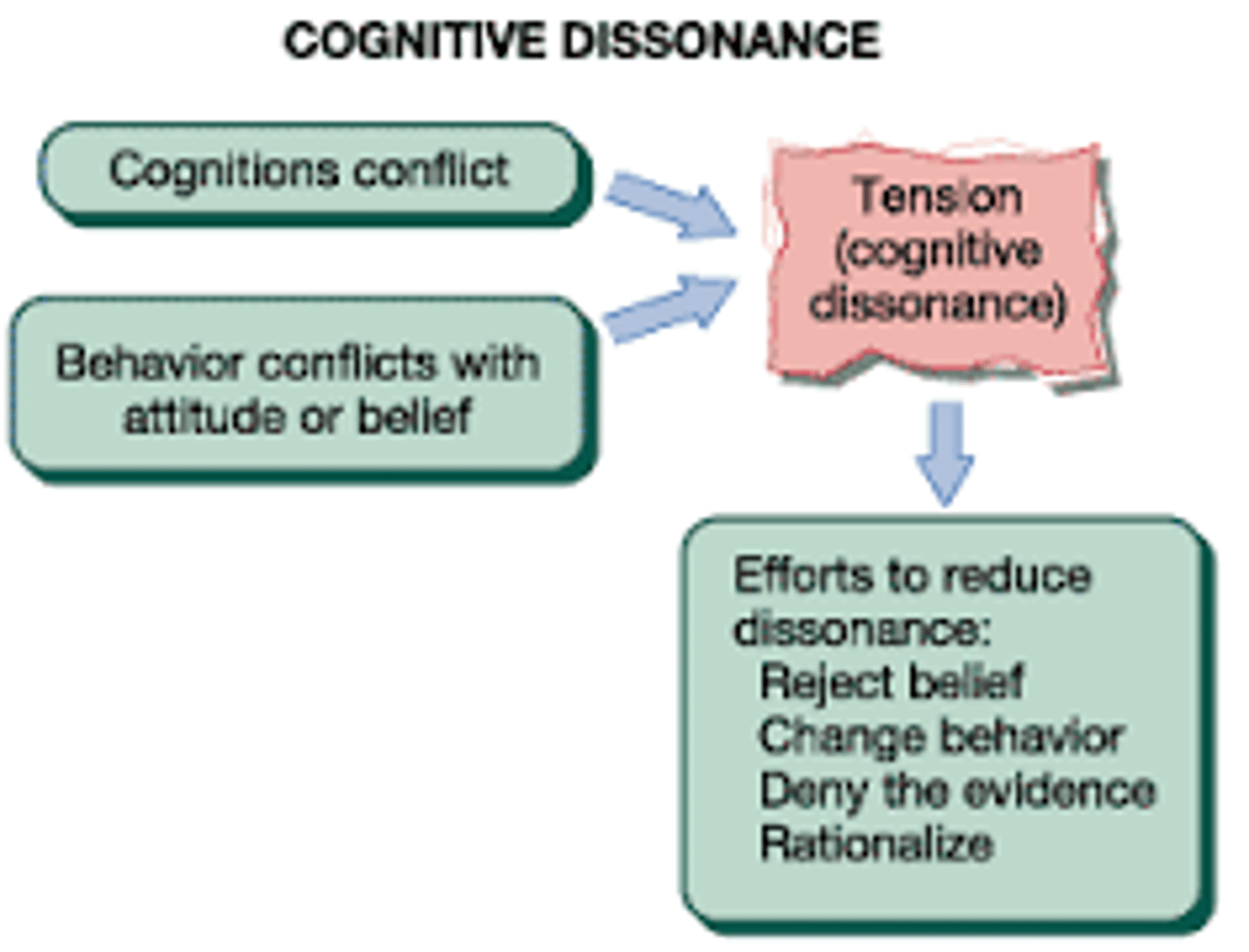
Cognitive Dissonance
When a person's beliefs, values, or attitudes conflict with their actions, so the person feels uncomfortable.
Only ways to get rid of it:
-Change actions to align with beliefs
-Change beliefs to align with actions
Cognitive Load
How much information the human brain's working memory can process at once, and how to avoid overloading it
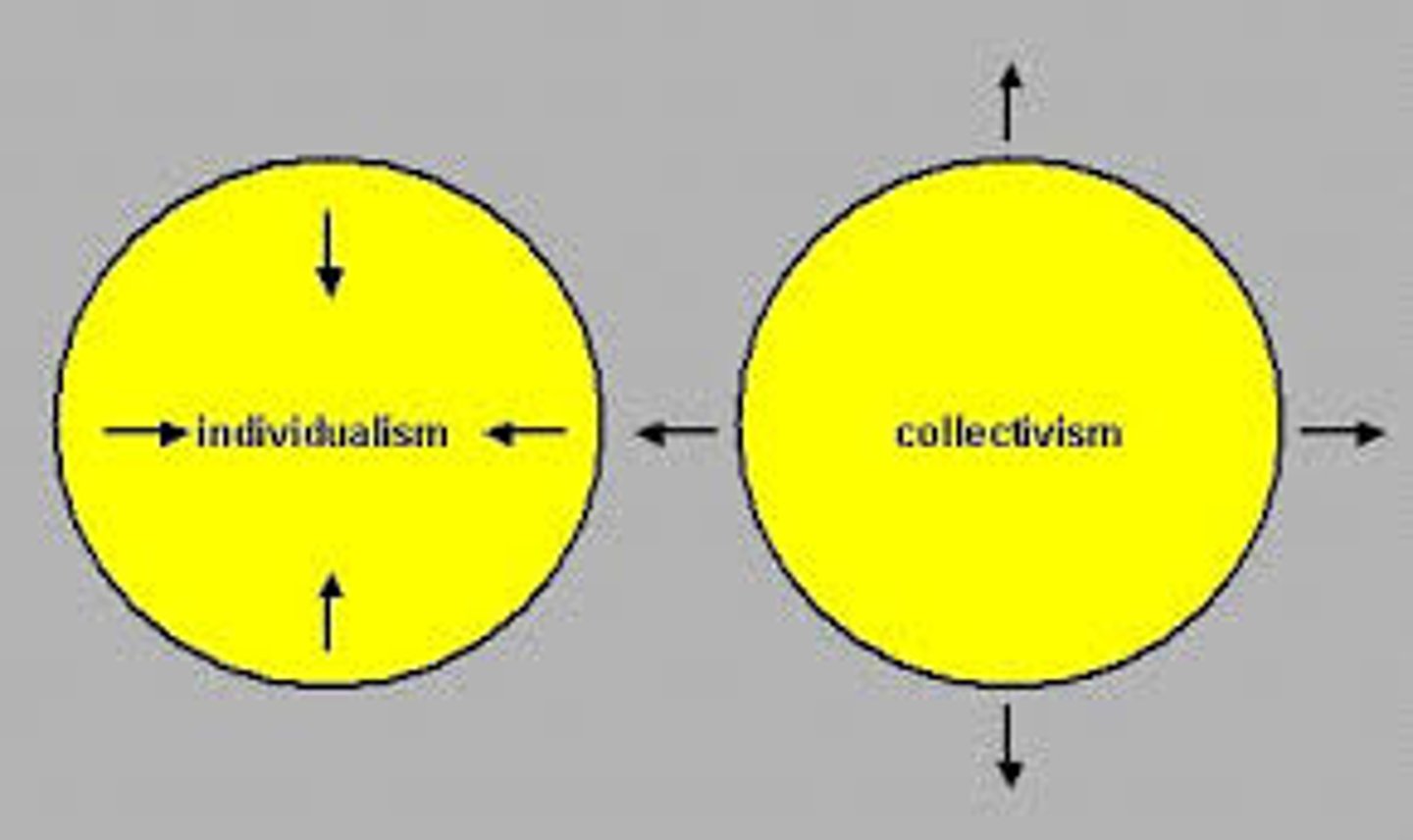
Collectivist Culture
a cultural worldview where people prioritize the goals of a group over their own personal goals.
We > Me
Confirmation Bias
Search for information that supports our beliefs and ignore other ideas.
Conformity
Doing things to fit in - either to appear socially acceptable or avoid being an outcast

Deindividuation
Loss of self-awareness and identity that people experience when they are part of a group or crowd.
-People may feel less accountable and responsible for their actions
-May behave in ways they would not otherwise.

Diffusion of Responsibility
a psychological phenomenon that describes how people are less likely to take action when others are present.
Bystander is an example of a type of diffusion of responsibility
Discrimination
the act of treating people differently based on their identity

Dispositional Attributions
Attributing (explaining) a person's actions to internal characteristics, like their personality.
"They have a bad temper so they ____________".

Door-in-the-Face Technique
Asking for a large commitment and being refused, and then asking for a smaller commitment in order to get what you want
Example: You ask your dad for $20. He says no, so you ask for $10. He agrees to this.

Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.

Explanatory Style
The way a person explains the cause of events in their life.
-Positive (optimistic)
-Negative (pessimistic).
Explanatory styles are usually stable and people tend to use the same style to explain uncontrollable events

External Locus of Control
Belief that external forces (luck, chance, other people) are in control of the outcome of their own life

False Consensus Effect
Bias that causes people to overestimate how much others agree with them

Foot-in-the-Door Technique
People who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request.
Ex: If you give a mouse a cookie, he will want milk to go with it.

Group Polarization
When individuals in a group have similar, though not identical, views, their opinions become more extreme after discussion

Groupthink
When people prioritize harmony over critical analysis and adopt the group's opinion, often at the expense of their own beliefs.

Halo Effect
When overall impression of a person or thing is influenced by a single positive trait/characteristic.
Ex: Trusting medical advice from attractive famous people over the opinions of experts
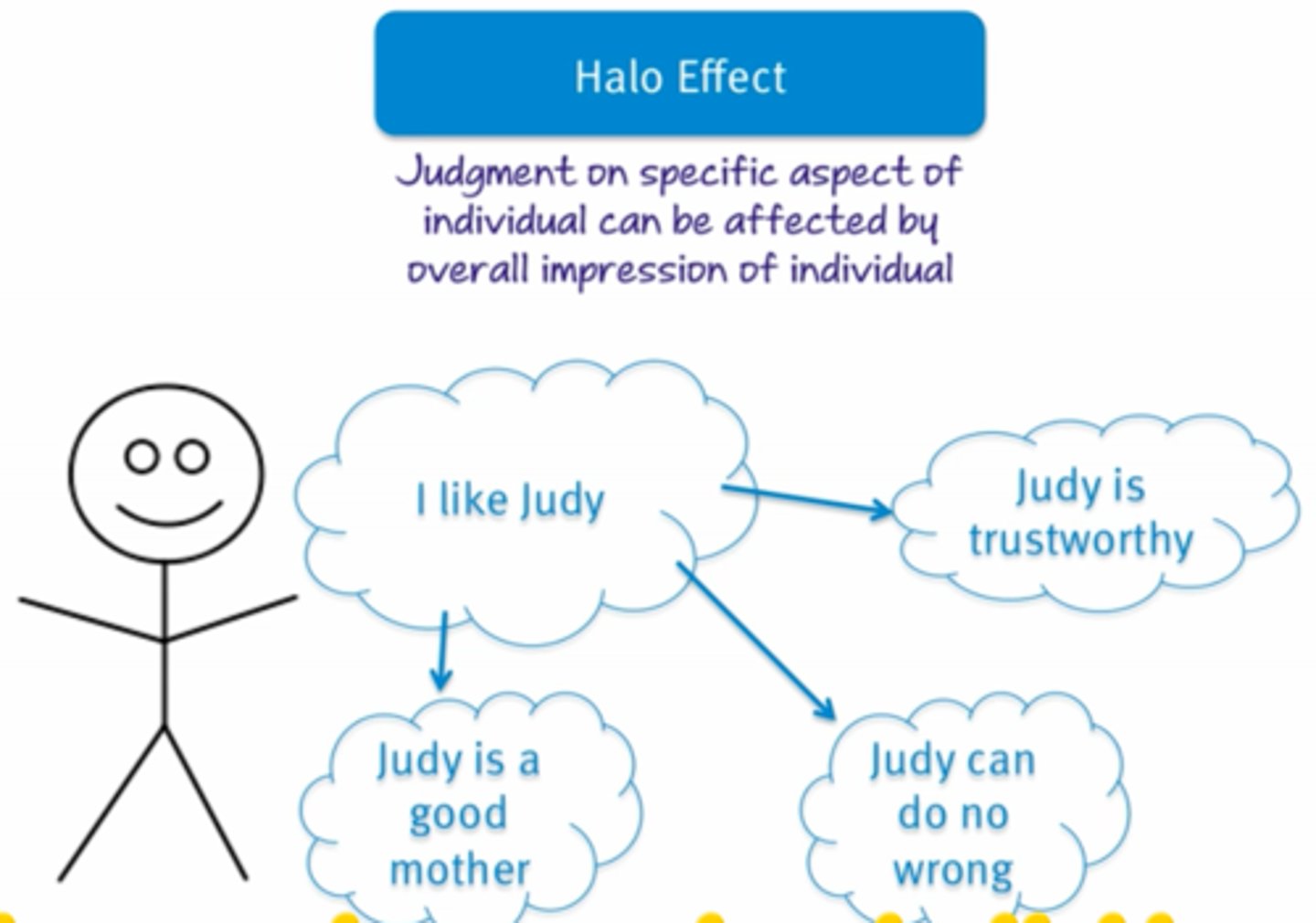
Implicit Attitudes
Attitudes that individuals hold but may be unaware of or may not acknowledge

In-group Bias
The tendency to favor our own group.
Ex: You're a senior and think the senior class is the best class.
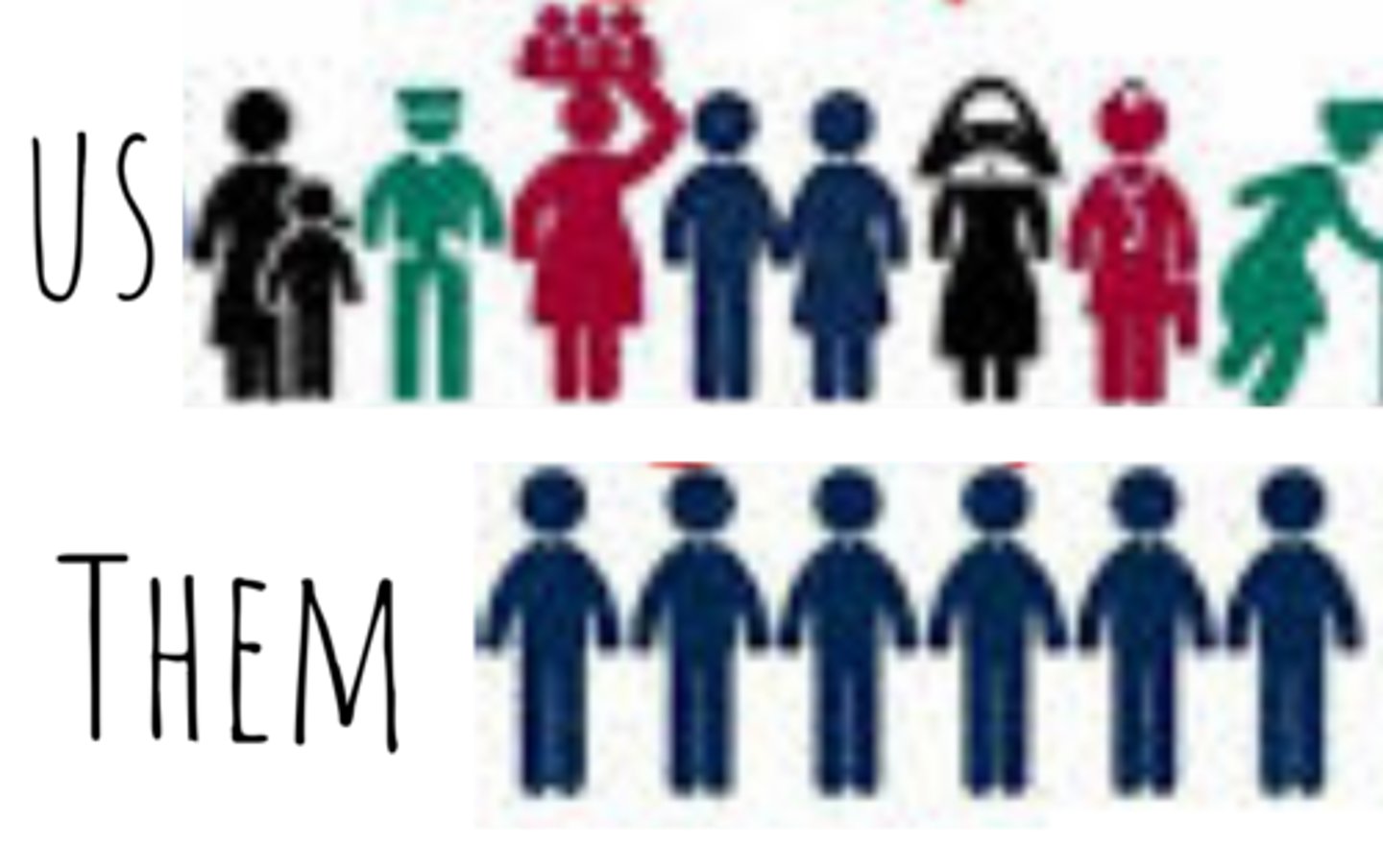
Individualist Culture
A cultural ideology that emphasizes the individual and their rights, independence, and relationships with others

Industrial-organizational (I/O) Psychologists
Branch of psychology - studies human behavior in the work environment and work-related issues

Informational Social Influence
Persuasion type - Influence is based on our willingness to accept others' opinions because we assume they know something we don't.

Internal Locus of Control
The perception that you control your own fate -
You have control in changing the things that happen in your life based on your actions and preparation

Just-world Phenomenon
The belief that the world is fair (just) so we get what we deserve and deserve what we get.

Mere-exposure Effect
People to develop a preference for things because they are familiar with them,
-The more often someone is around something, the more likely they are to end up liking it
