Emotional Health
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
1st step of the decide process
define the problem
2nd step of the decide process
explore the choices
3rd step of the decide process
consider the risks and benefits
4th step of the decide process
identify your values
5th step of the decide process
decide and act
6th step of the decide process
evaluate your results
list 6 steps in the decide process
Define the problem
Explore the choices
Consider the risks and benefits
Identify your values
Decide and act
Evaluate your results
what are the top 3 causes of death for teens?
Accidents
Homicide (murder)
Suicide
top 3 cause of death for adults
Heart disease
Cancer
Accidents
what is the acronym for the three stages of stress response
ARE
what is stage one of the three stages of stress response
alarm (fight or flight)
what is stage two of the three stages of stress response
resistance
what is stage 3 of the three stages of stress response
exhaustion
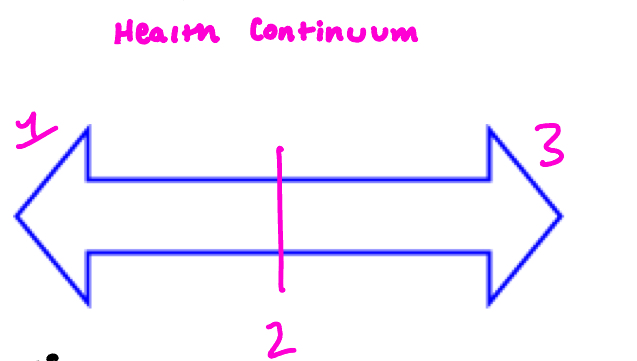
Labels parts of the health continuum; what is 1?
Illness
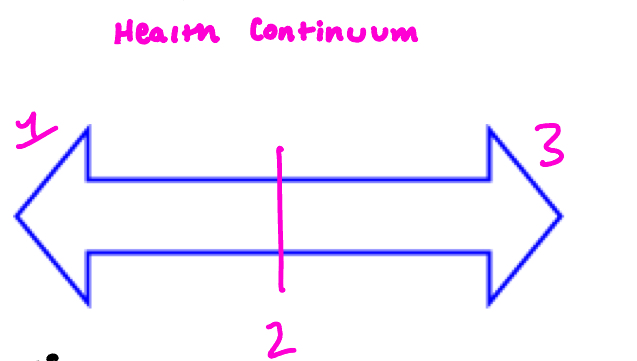
label parts of the health continuum: what is 2?
Mid point
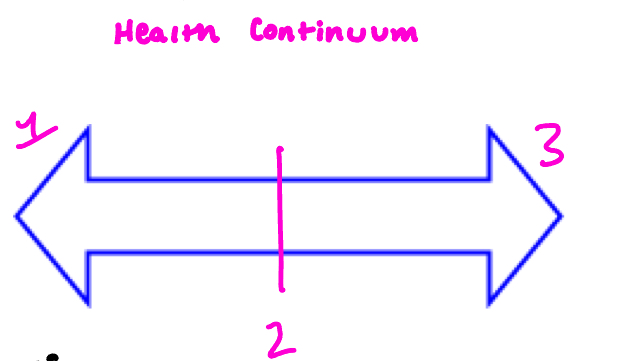
label parts of the health continuum: what is 3?
Wellness
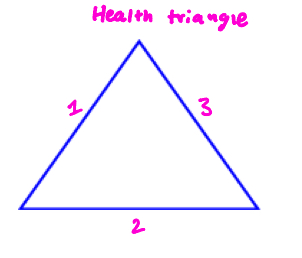
Each side of the health triangle is interchangeable, label the parts
mental health, physical health, social health
How can you help a friend who is depressed/suicidal?
ACT
what does A stand for in ACT
acknowledge
what does C stand for in ACT
care
what does T stand for in ACT
tell/treatment
What are the 3 basic steps to follow when recognizing your emotions?
Name the emotion
Determine what triggered the emotion
Think back to the past on how you handled the emotion in the past
what are the 2 factors used to evaluate health?
Life expectancy
Quality of life
how can you boost your self-esteem?
Maintain positive attitude, focus on strengths, form close relationships, set goals for yourself, avoid risky behaviors, ask for help, help others
How does self-esteem change with age?
usually, self esteem drops in early adolescence, increases gradually during adulthood, and decreases again toward the end of life
what are primary emotions?
Emotions expressed by people in all cultures
examples of primary emotions
Happiness, sadness, anger, and fear
what are learned emotions?
Determined by social environment in which a person grows up
Examples of learned emotions
Love, guilt, and shame
what causes stress?
major life changes, catastrophes, everyday problems, and environmental problems
what are the warning signs of stress?
overeating/hardly eating, sleep problems, unable to concentrate, negative thinking, excessive worrying, headaches, skin rash, anger, etc.
what are some healthy ways you can manage your stress?
Exercise, journaling, drawing, organize w/a calendar, mediation, relaxation techniques
resilience
ability to recover or “bounce back” from stress
what is the key factor in resilience?
Having support of family and friends
what illnesses are related to stress?
Hypertension (blood pressure), stomachaches, asthma, and headaches
what is a mental illness?
An illness that affects the mind and reduces a person’s ability to function
what does the N in NAMI stand for?
National
what does the “A” in NAMI stand for?
alliance
what does the M in NAMI stand for?
mental
what does the “I” in NAMI stand for?
Illness
what are the suicide warning signs?
talks about not being here, killing themselves, being a burden to others, giving away belongings
Healthy People 2030 is a national initiative to help Americans:
provide structure and guidance to live healthy lives
what are examples of uncontrolled risk factors?
age, race, gender, heredity, other people’s behavior
what are examples of controlled risk factors?
Diet, exercise, friends you choose, weight, don’t use ATOD
Decision
making a choice
risk factor
any action or condition that increases the likelihood of injury, disease, or other negative outcomes
consequence
result of an action
goal
aim that requires planning
stressor
any stimulus that produces a stress response
passive
give in or back down
aggressive
communicate feelings in a threatening/ disrespectful way
assertive
stand up for yourself in a firm positive way
distress
negative stress
eustress
positive stres
optimism
being positive, seeing the good side
pessimism
being negative (having an attitude)
clinical depression
persistent hopelessness
anxiety disorder
expressive worrying and feelings of nervousness
procrastination
turns a small problem into a big problem, waits until last minute
time management
scheduling activities well
body language
message without words
stigma
generalization about groups of people
quality of life
degree of overall satisfaction that a person gets from life
life expectancy
number of years a person can expect to live
Lifestyle choices
actions a person takes on a daily basis
lifestyle diseases
can be caused by choices we make in our life (ex: smoking causes cancer)
mental/emotional health
includes feelings about yourself, how well you relate to others, and how well you meet the demands of daily life
physical health
way the parts and systems of your body work together
social health
way you get along with others
spiritual health
values, morals, sense of purpose, connection and something greater than self
wellness
state of high level of health
heredity
traits passed down biologically from parent to child
prevention
taking action to avoid disease, injury, or other negative health outcomes
health literacy
ability to gather, understand, and use health information to improve his/her health
Action plan
series of specific steps you can take to achieve a goal
habit
a behavior that is repeated so often that is becomes almost automatic
What is untreated depression the #1 cause of?
suicide
4 causes of mental illnesses
physical factors, heredity, early experiences, and recent experiences
stress
the response of your body and mind to being challenged or threatened
continuum
gradual progression through many stages between one extreme and another