Cal Poly Bio 263 Final 2018- Lema
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Niche
ecological "role" a species (or population) plays in its broader ecosystem (includes range of resources that can be used, and environmental conditions tolerated)
Biological community
complex assemblage of interacting species within defined area
Community Structure
How combinations of many species interact
What are the 4 two-species interactions, and what are the interspecific effects on fitness of each?
- Commensalism: +/0
- Mutualism: +/+
- Competition: -/-
- Consumption: +/-
Intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
Interspecific competition
competition between members of different species
What are the 3 classifications of consumption?
- Herbivory: plant tissues eaten
- Parasitism: host tissues eaten
- Predation: most/all of another individual eaten
Coevolutionary arms race
a repeating cycle of reciprocal adaptation
Joseph Grinnell
- coined the term 'niche' in 1917
-considered the niche to be the sum of the habitat requirements needed for a species to live and reproduce (emphasize abiotic, physical factors)
Charles Elton
- Defined niche as an "organism's place in the biotic environment, its relation to food and enemies" (1927)
- Emphasized biotic interactions and a species' role in an ecological community
Niche construction
The process whereby an organism alters its own (or another species') environment, often in a way that increases its chances of survival
e.g. Beaver building a dam
What happens when the niches of 2 different species overlap?
interspecific competition
What are the possible outcomes of competition?
1) competition exclusion principle: impossible for species within same niche to coexist
2) Coexistence of species: fitness tradeoffs; niche differentiation
niche differentiation/resource partitioning
an evolutionary change in resource use, caused by competition over generations
competition exclusion principle
impossible for species within same niche to coexist
What happens when one species is a better competitor?
- Asymmetric competition: 1 species suffers greater fitness decline
- Symmetric competition: equal decrease in fitness
What happens when niches are completely overlapping, and asymmetric competition occurs?
weaker competitor becomes extinct
Fundamental niche
resources/conditions used WITHOUT competitors
Realized niche
resources/conditions used WITH competitors
What happens when you have asymmetric competition and incompletely overlapping niches?
The weaker competitor shifts from fundamental to realized niche; cedes resources
character displacement
Species evolve non-overlapping traits to avoid competition
Competition and conservation
-diverse communities more resistant to invasion
-competition can help communities resist invasion
How predictable are communities?
-Frederic Clements: stable, predictable, extensive species interactions, predictable climax community
-Henry Gleason: not stable, not predictable, chance whether similar community develops after disturbance
Keystone species
species that have disproportionately large effects on the structure of an ecological community relative to their abundance
e.g. sea otter
How do keystone species structure communities?
The reduction or loss of a keystone species triggers an ecological chain of reactions resulting in declines in species diversity and community complexity
Foundational Species
Species that have strong interactive effects on their ecological communities, but are too numerous to be keystone species
Disturbance in Ecological communities
Disturbance: removes biomass, alters resource availability
Examples of Natural Disturbances
Fire, wind, blizzard, drought
Disturbance regime
type, frequency, and severity of disturbance
Ecological Succession
response to a disturbance
Successional pathway
specific sequence of species that appears after a disturbance:
1) Pioneering species- small, low to ground, good dispersal, high physiological tolerances, not good competitors
2) Early successional community- weedy species are pushed out
3) Mid successional community- shrubs and short lived trees
4) Climax Community- long-lived tree species mature
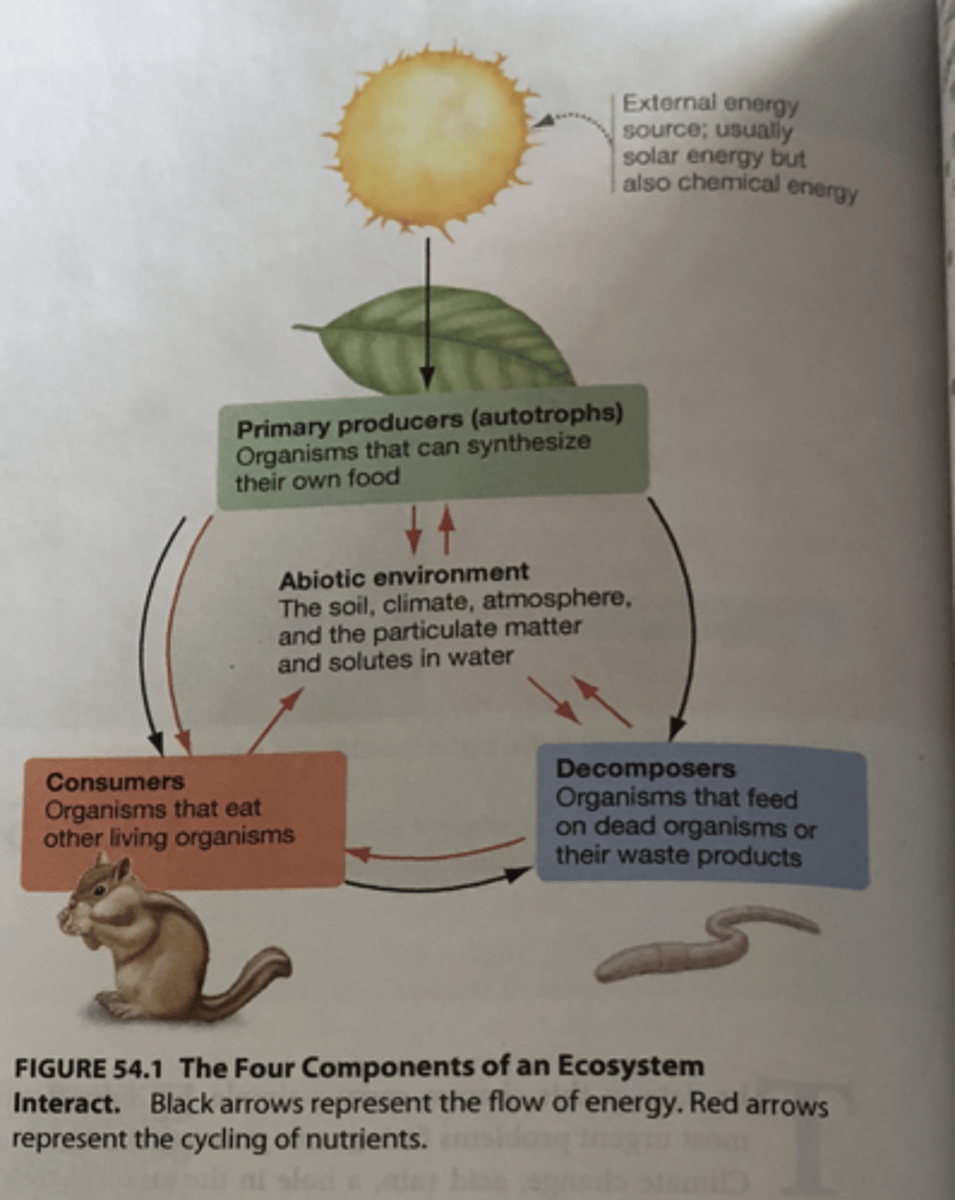
Ecosystem
a community plus its abiotic environment
-includes biogeochemical cycling from abiotic to biotic and back
-ecosystem function relates to flow of nutrients through system
-disruptions to this flow can cause a chain-reaction of effects
What are the six major biomes?
1. tropics
2. grasslands/savannah
3. temperate forests
4. coniferous forests or taiga
5. tundra
6. deserts
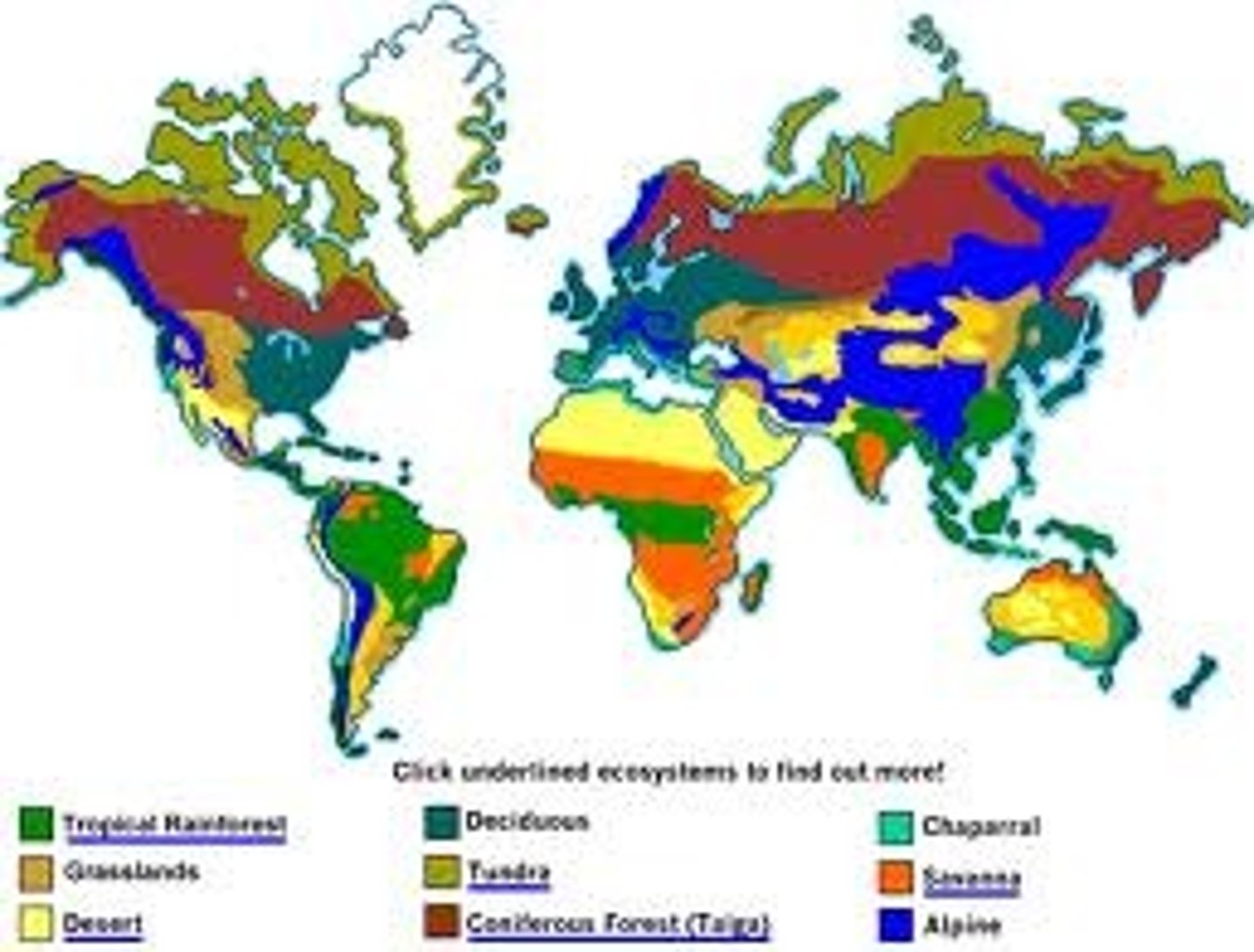
What influences the locations of all major biomes on earth?
Solar insolation and Hadley cells
Circulation cells
large-scale cells in a planet's atmosphere that transport heat between the equator and the poles:
-Warm air rises and cools at the equator, dropping rain
-Cooled air is pushed poleward
-Dense, dry air descends, warms, and absorbs moisture
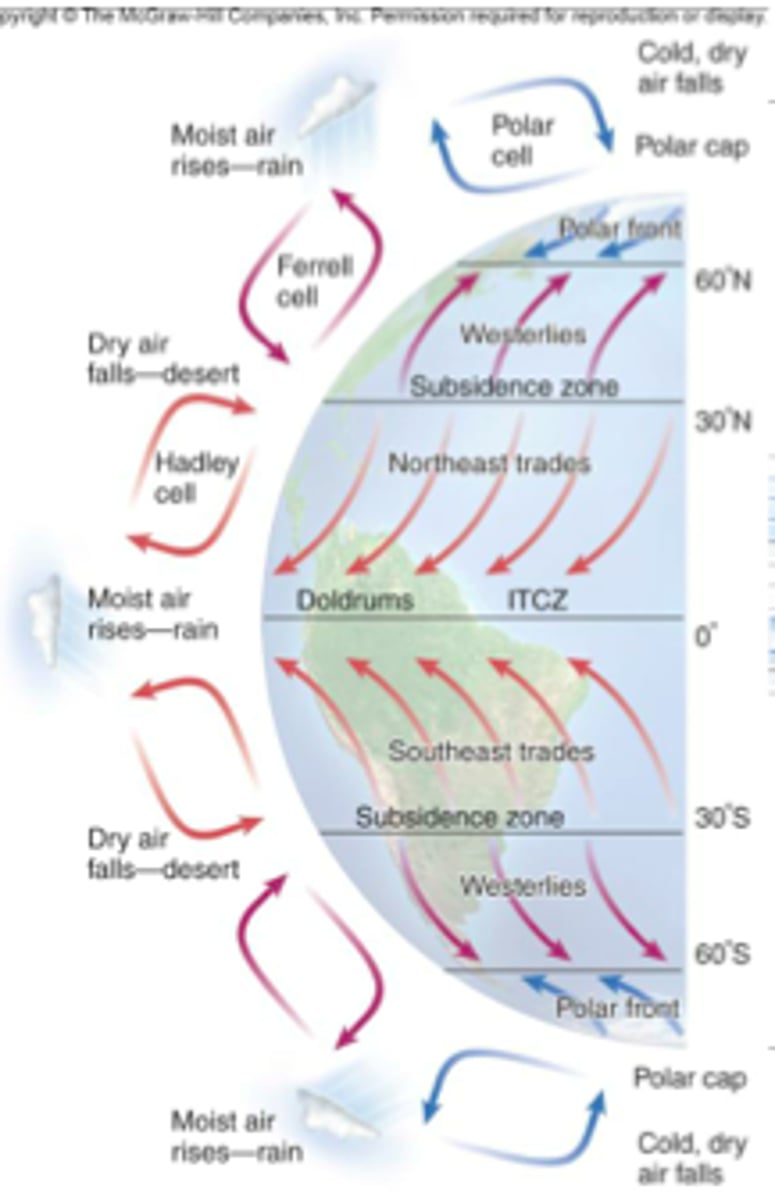
What are the three types of circulation cells called?
-Polar call (above 60 degrees in latitude)
-Ferrel cell (between 60 degrees and 30 degrees in latitude)
-Hadley cell (between 30 degrees and 0 degrees in latitude)
--> there is one of each type of cell on each hemisphere
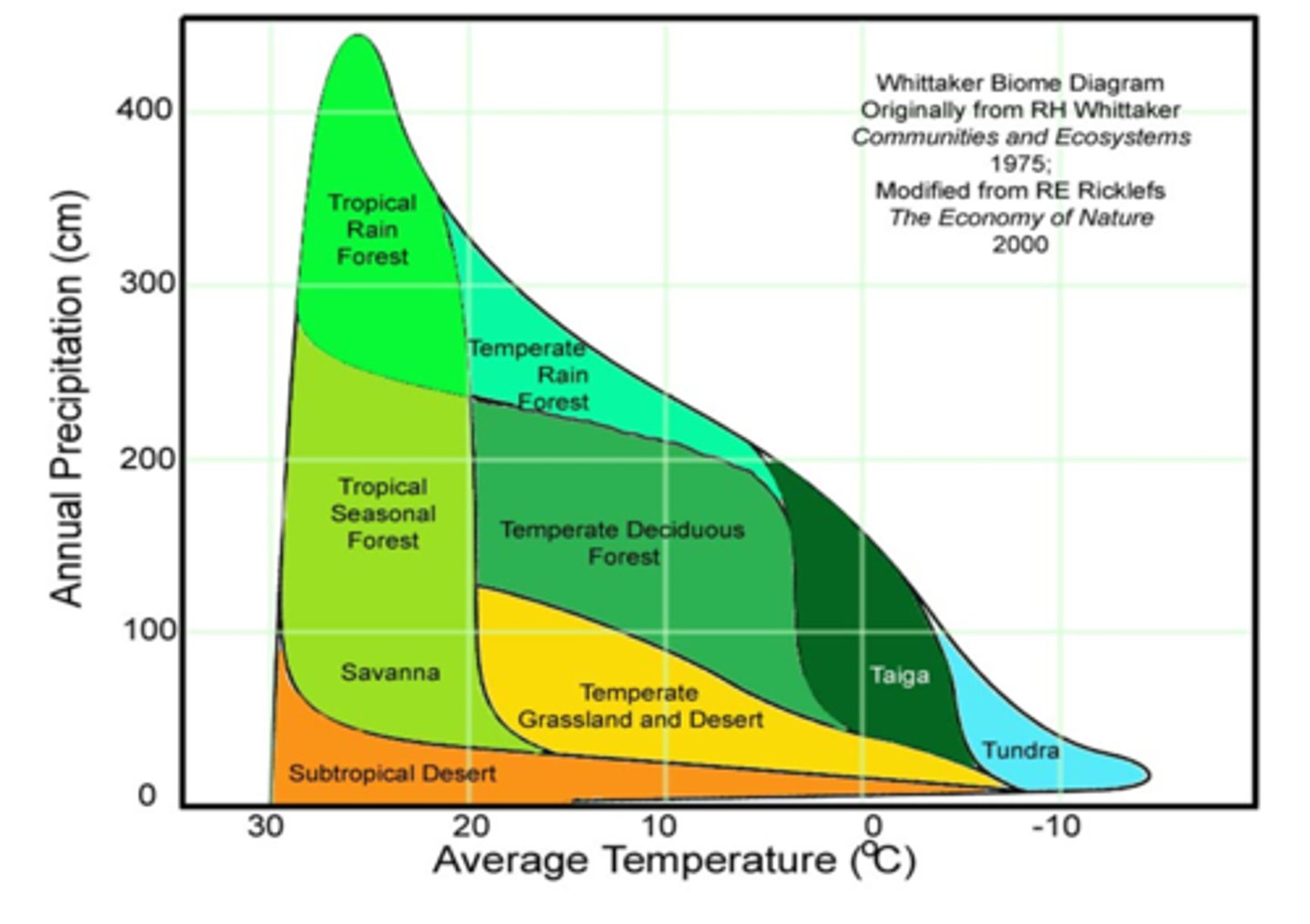
Whittaker Classification of Biomes
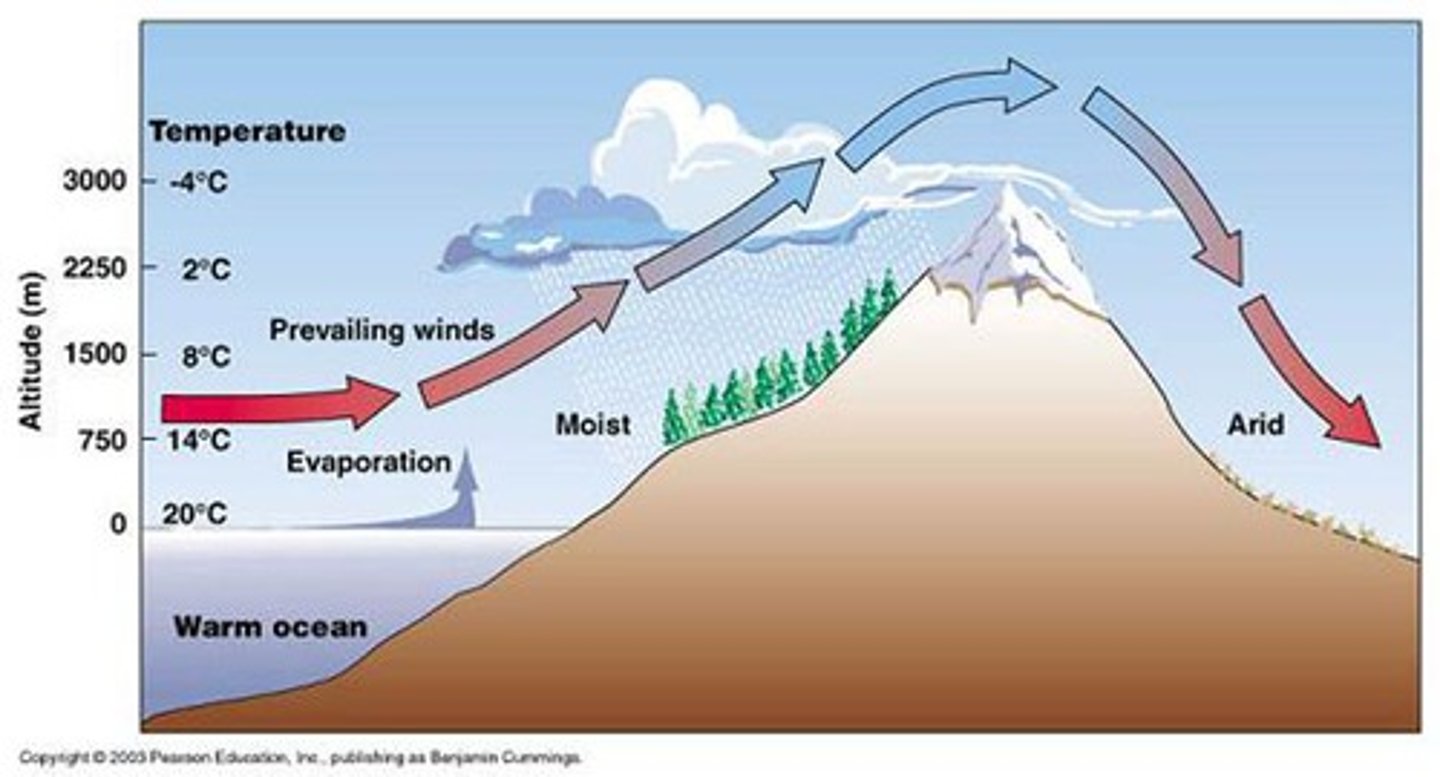
Rainshadow Effect
3 Important points about ecosystems
1) ecosystem boundaries are difficult to define, and change through time
2) organisms within ecosystems are dependent on ecosystem-level biological and physical processes
3) adjacent ecosystems closely interact; interdependent processes maintain the community organization of each ecosystem
Ecosystem ecology
The study of...
-communities of organisms
-trophic dynamics
-nutrient cycling
-biogeochemistry
-energy flow
-hydrology
Net primary productivity
the rate at which photosynthetic organisms produce new 'useful' energy (energy invested in new tissues or offspring)
Where does most of the Earth's net primary productivity come from?
1) open ocean
2) tropical wet forests
Four components of an ecosystem interaction
Pyramid of Productivity
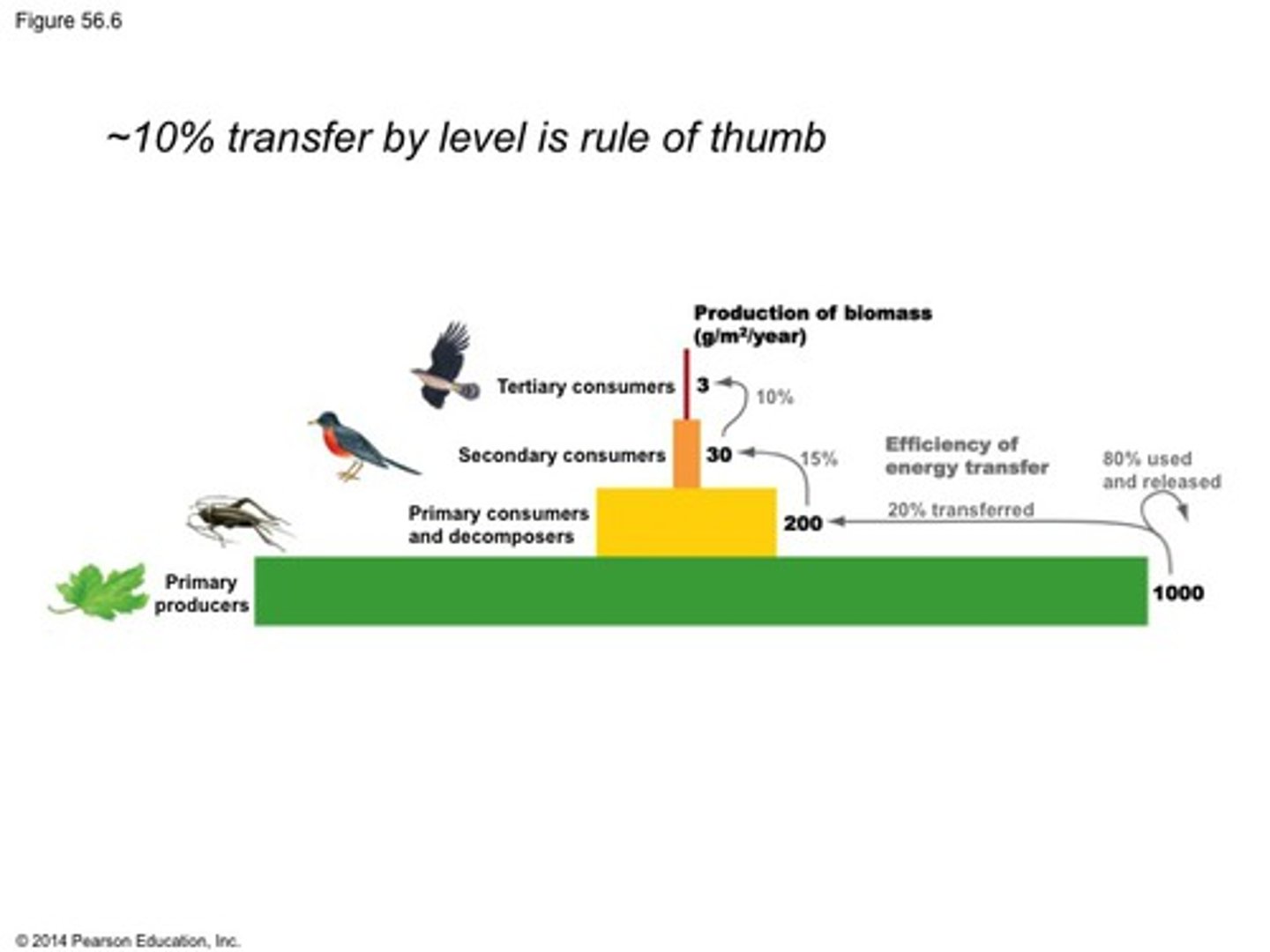
Productivity
Biomass produced per unit of area each year
Efficiency
Fraction of biomass transferred from one level to another
Food webs/ food chains
the connections between trophic levels
Trophic cascade
when predators in a food web suppress the abundance of their prey, thereby releasing the next trophic level down from predation
What is a result of 'top down control'?
trophic cascades (altering top predators affects everything below)
Ecosystem Function affected by:
-resource dynamics (e.g., introduced species disrupt nutrient flow)
-trophic structure (e.g., removal of keystone species, trophic cascades)
-disturbances (e.g., change in frequency of disturbances such as by overgrazing, loss of ESS plants, and topsoil)
Terrestrial Nutrient Cycle
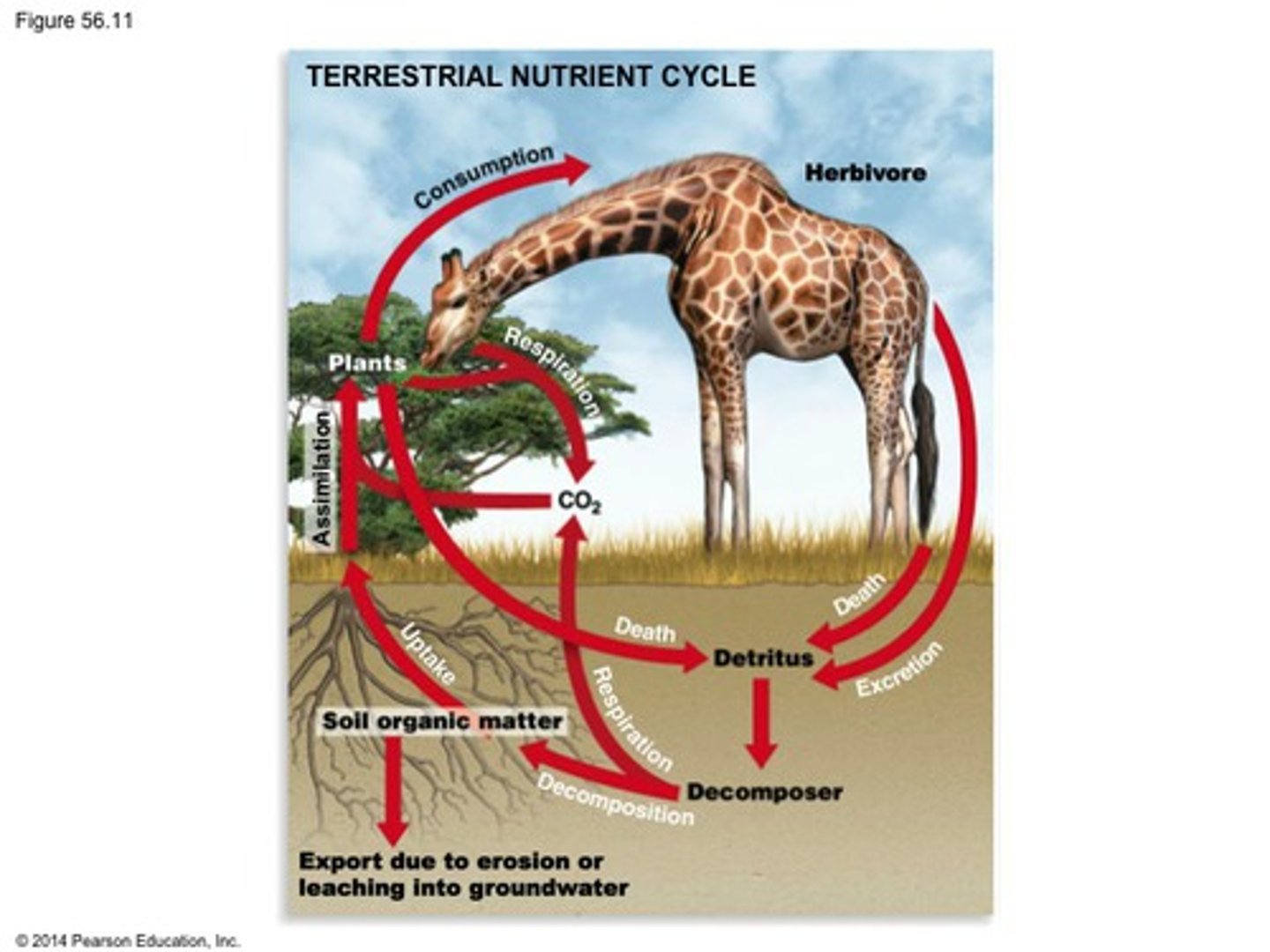
Three examples of biogeochemical cycles
-water cycle
-nitrogen cycle
-carbon cycle
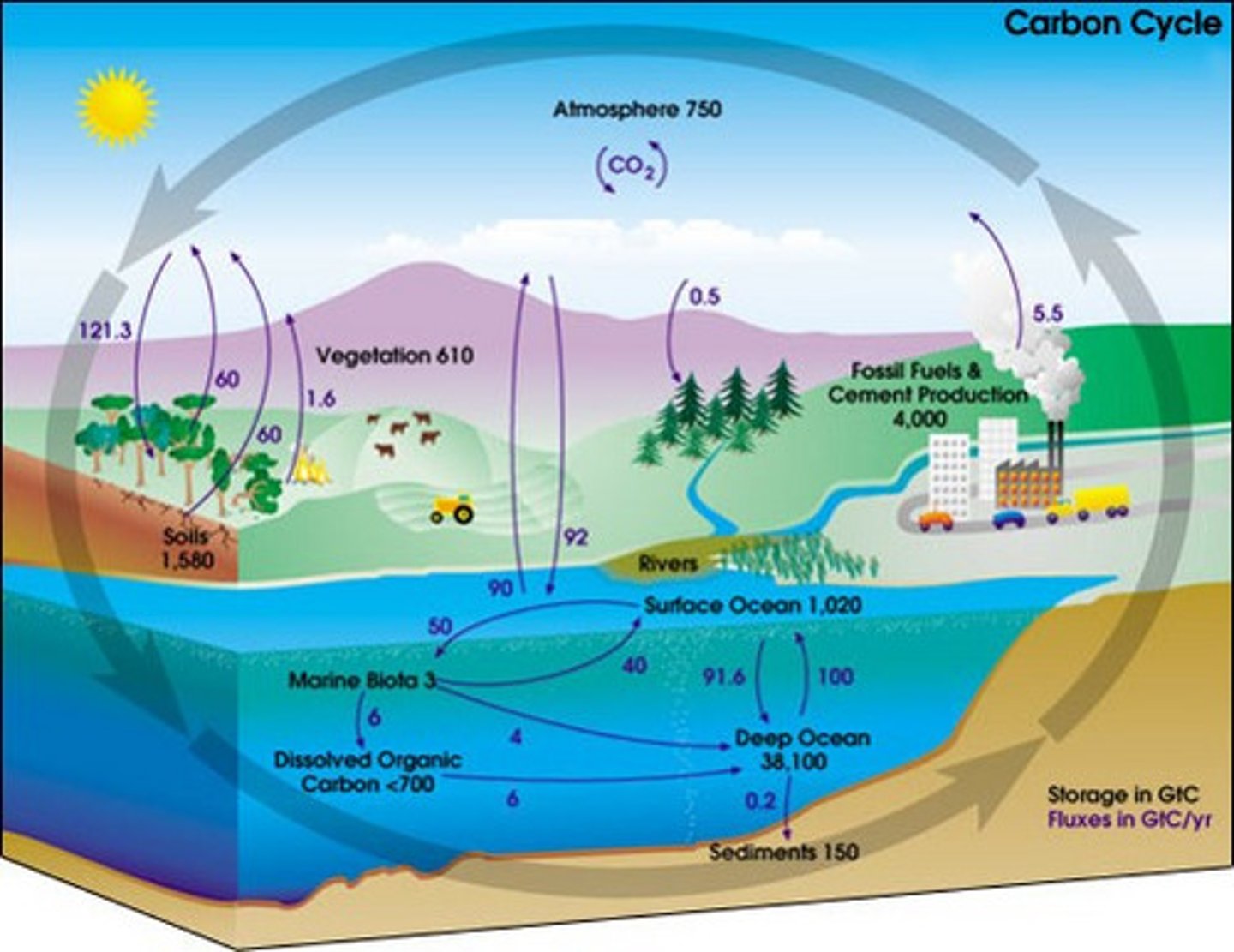
Evidence that the Global Climate is changing
1) increasing global temperatures
2) arctic sea ice declines
--> over 40% decline in 30 years
3) Land ice declines
--> adds water to ocean; raises sea level
4) Sea level rise
Greenhouse effect
Warming resulting from the atmosphere trapping outgoing heat radiating from the Earth toward space
Keeling Curve
Graph measuring carbon dioxide concentration in atmosphere
Human Effects on Global Carbon Cycle
-Fossil Fuels: moves CO2 locked up for hundreds of millions years (petroleum, coal) to atmosphere
-Agriculture, deforestation also add CO2
What is a result of warmer surface waters?
Increased stratification in ocean (surface water is warmer and less dense= currents are less likely to bring nutrient-rich water to surface against the steeper density gradient)
climate change leads to...
-increased intensity and frequency of droughts, flooding, etc
Ice core records
-can tell us when ice formed and what the atmospheric CO2 concentrations were at the time the ice froze
-allows us to make CO2 concentration predictions
photoperiod
the period of time each day during which an organism receives illumination; day length.
What affects photoperiod?
Orbit, tilt, and curvature of earth result in increasing variation in photoperiod throughout the year at higher latitudes.
Biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain