MCA Science Review
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Genetics
the study of how traits are passed on
Heredity
the passing on of traits from parent to offspring (child)
Chromosomes
fine, threadlike structures made of DNA, found in the nucleus, you have 46 in every cell
DNA
contain your genes, the "instructions" for your body, made up of 4 bases (A, G, C, and T)
Gene
a unit of heredity that has a specific location on your DNA/chromosomes and codes for a particular trait
Traits
characteristics of living things (examples: eye color, height, nose shape)
Genotype
genetic code used for each trait; represented as letters
Phenotype
the trait that can be seen; physical appearance
Dominant
traits that present (show) themselves; (uppercase letters)
Recessive
traits that "hide"; will only show themselves if there are two of these genes; (lowercase letters)
Heterozygous
two different versions of a gene (two different sized letters)
Homozygous
two identical versions of a gene (two letters of the same size)
Allele
Different versions of a trait or gene
Ecology
study of relationships of living and non-living things
Environment
our surroundings
Ecologist
a person who studies ecology
Ecosystem
an area where the living and non-living things interact and affect each other
Biome
a large geographic area with a certain climate which determines the plants and animals there (i.e. grassland, desert, rainforest, deciduous forest)
Habitat
the area where a plant or animal lives or grows naturally
Abiotic factor
non-living things
Biotic factor
living things
Community
a group of populations that interact
Population
a group of one kind of organism
Population Density
the number of organisms in a given space
Limiting Factors
something that prevents a population from reaching its biotic potential
Biotic Potential
the maximum population that could be produced under the best possible conditions/resources
Carrying Capacity
the maximum population that could be produced using the resources that are available (not necessarily the best though)
Symbiosis
living together
Mutualism
both organisms benefit from the relationship
Commensalism
one organism benefits and the other has no effect from the relationship
Parasitism
one organism benefits and the other is harmed from the relationship
Parasite
an organism that lives in or on another organism and harms or kills it
Host
the organism that is harmed or killed due to a parasite living on or in it
Biodiversity
the variety of living things in an area
Food Chain
shows what eats what; shows the energy flow
Predator
an organism that hunts an eats another
Prey
an organism that is hunted and eaten
Food Web
many interconnected food chains
Herbivore
consumer that eats plants
Carnivore
consumer that eats animals
Omnivore
consumer that eats plants and animals
Primary Consumer
a consumer that eats plants
Secondary Consumer
eats the primary consumer
Tertiary Consumer
eats the secondary consumer
Producer
organisms that make their own food (plants)
Consumer
organisms that must eat things for energy (can't make their own food)
Decomposer
organisms that break down dead plants and animals
cell membrane
(P & A) surrounds and protects the cell; controls what goes in and out of the cell
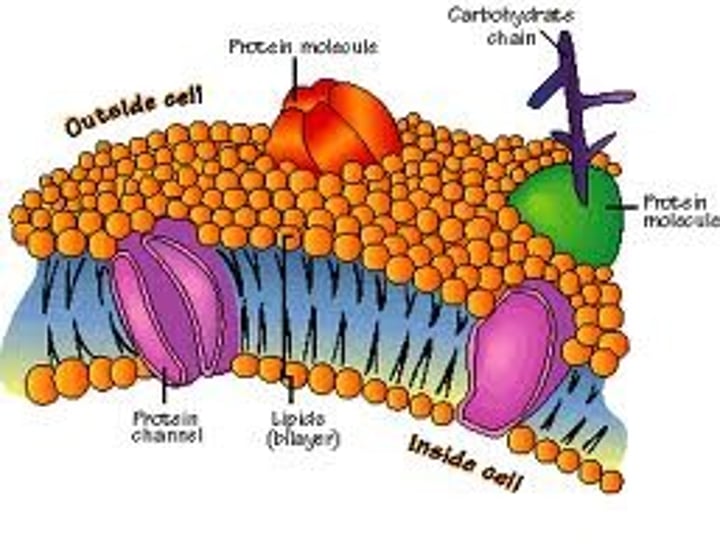
cytoplasm
(P & A) jelly-like substance that fills up the space between the organelles (parts)
vacuoles
(one large in plants & and a few smaller ones in animals) sac that stores water, nutrients, or waste products
cell wall
(P only) strong outer structure that protects a plant cell and gives it support
nucleus
(P & A) contains DNA and controls the activities of the cell
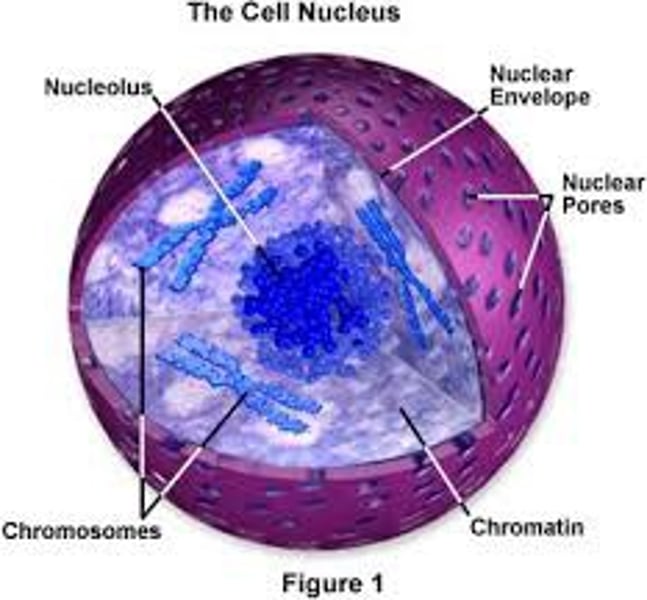
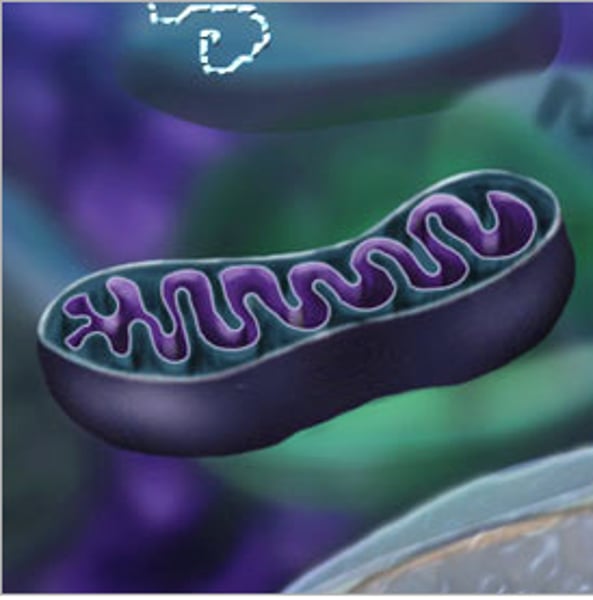
mitochondria
(P & A) powerhouse of the cell; structure that converts food to energy (cellular respiration)
chloroplasts
(P only) produces energy for the cell using energy from the sun (photosynthesis!)

Cell Theory
1. All living things are made of cells
2. Cells are the smallest unit of structure & function
3. All cells come from cells
Alfred Wegener
German scientist. Proposed Continental Drift Theory.
Pangaea
Name of the supercontinent Wegener proposed.
Theory of Continental Drift
Idea that all continents were once together but have separated over time.
Tectonic Plates
Large chunks of lithosphere that cover the Earth.
Crust
Thin, solid, top layer of the Earth.
Mantle
Largest layer of the Earth. Putty-like. Convection occurs here.
Outer Core
Liquid layer of the Earth. Made of iron and nickel.
Inner Core
Hottest layer of the Earth. Solid. Made of iron and nickel.
Convergent Boundary
2 plates come together
Divergent Boundary
Plates move apart
Transform Boundary
Plates slide past each other
Hot Spot
Plates move over a source of magma.
Subduction
Movement of one plate under another.
Shield Volcano
Wide, made of flowing lava, looks like a pile of ketchup
Cinder Cone Volcano
Smallest, made of pyroclastic material
Composite Volcano
Largest volcano, explosive, made of layers of flowing lava and pyroclastic material
Seismic waves
(earthquake) waves of energy that travel through the Earth
Fault
break/crack in the Earth's crust along which an earthquake occurs
Atom
the basic unit of all matter
Element
made of all atoms of the same type; different "flavors" of atoms
Proton
positive charge
Electron
negative charge
Neutron
no charge
Atomic mass
how much the atom weighs; equal to p + n
Compound
2 or more different elements chemically combined
Mixture
physical combinations of pure substances; you can physically separate it
Pure Substance
either an element or a compound (can be written with a chemical formula); it cannot be physically separated;
Chemical Change
substances are changed into new and different substances; usually irreversible
Physical Change
substances change form but nothing new is created; usually reversible
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter cannot be created or destroyed. The mass of your starting substances should be the same as the mass of what is produced.
Volume
how much space an object takes up
Mass
the amount of matter an object has
Length
the distance between two points
Density
mass over volume
Troposphere
layer of the atmosphere where we live
Ozone
the gas responsible for protecting us from solar radiation
Conduction
heat transfer via direct contact
Convection
heat transfer via a circulation of air or liquid
Radiation
heat transfer via waves
Evaporation
liquid water --> gas
Condensation
gas --> liquid water
Precipitation
rain, snow, hail, etc.
Run-off
water flows across the land
Humidity
the amount of water in the air
Stratus
low level cloud