Session 1a: Electronic Principles and Resistors
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is Potential difference (pd)🇦
The difference of potential energy between two points of a load
Unit of measure: volt (V)
Current (I)🇦
The flow of electric charge through a conductor, measured in amperes (A).
It represents the rate at which electric charge is transferred.
Electrons:
Negatively charged particles of an atom
Move from one atom to another to create an electric current
Charge (Q):
quantity of electric charge passing through a given point in a circuit per second
Unit of measure: coulomb (C)
Q=I∙t (coulombs)
Resistance (R)
An opposing force to emf, or current flow, which reduces voltage
Unit of measure: ohm (Ω)
Energy (E)
The total amount of work done; typically transformed into heat
Unit of measure: Joule (J)
Power (P)
The rate (t seconds) of doing work (Joules)
Unit of measure: Watt (W)
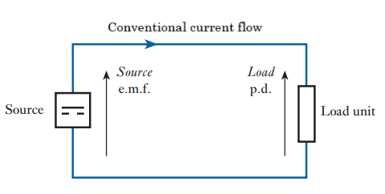
Conventional flow (hole flow)
Used previously to describe current flow, from positive to negative
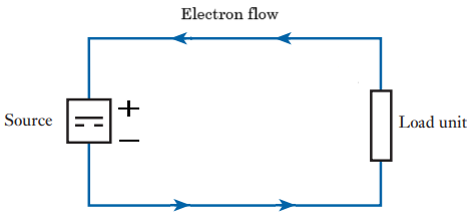
Electron flow
The true flow is from negative to positive
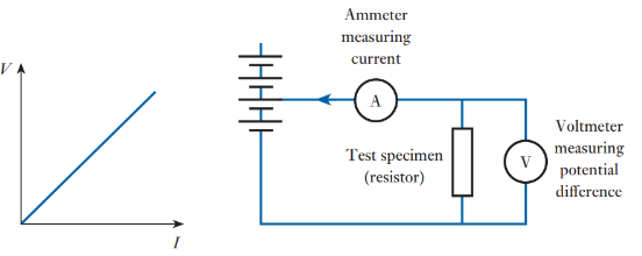
Ohm’s Law
fundamental principle used to relate voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in a circuit
oDescribes how voltage drives current through a resistance
oV=I×R
Ohm’s law relates power (watts), energy (joules), and charge (coulombs) by:
oJ=W∙t
oJ=〖R∙I〗^2∙t
oJ=V^2/R∙t
oJ=V∙C;and C=I∙t
̶Where t is time in seconds
Voltage (V)
is a measure of electric potential energy (Joule) per unit charge (Coulombs) between two points:
What does V equal ?
Joules divided by Coulombs
what does Voltage push?
“pushes” current around a circuit
Current (I) is the measure of…
the amount of charge (Coulomb) flowing per unit time (t in seconds):
Current (I) =
Coulombs/ t
what is Current?
the “movement” of electrons around a circuit
Resistors
Provides a resistance (opposition) to current flow in an electrical circuit
Resistance =
V/I
Resistor Identification
•Resistors come in 4-band or 5-band configurations
•Colour bands allow for the identification of a resistor’s value in Ohms and its tolerance
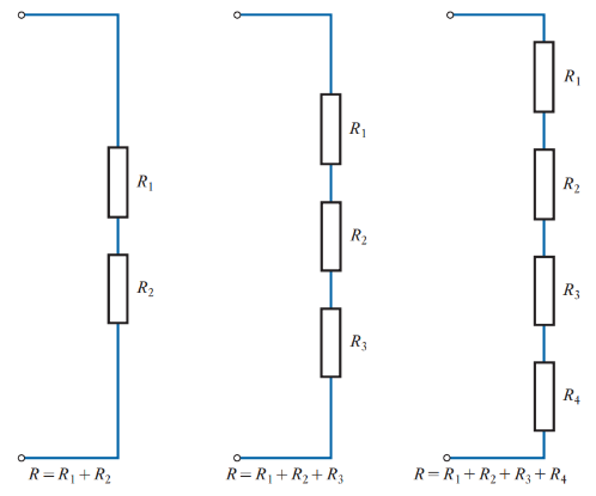
How do you Calculate Resistors ?
R_T=R_1+R_2+R_3+…R_n
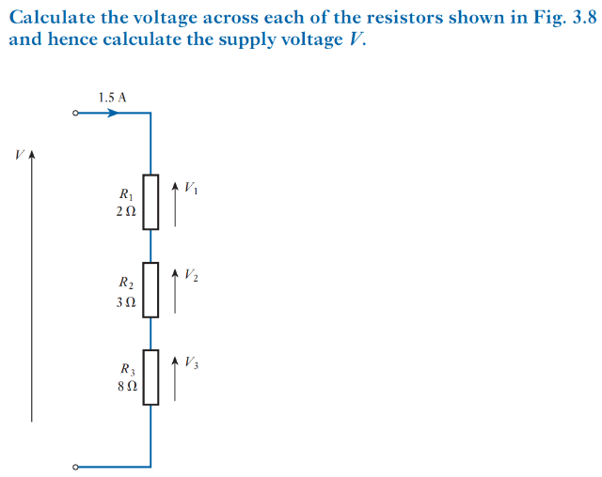
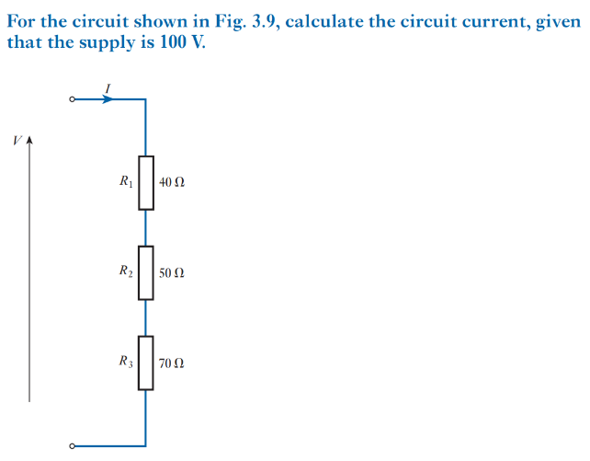
Resistors as a voltage divider
The voltage between only two resistors connected in series can be given as:
V_in=I(R_1+R_2)
V_out=IxR_2
what does ‘I’ equal?
I=V_in/((R_1+R_2))
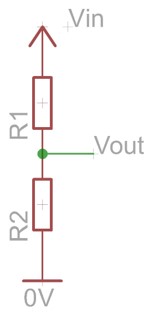
R1=500Ω, R2=100Ω, Vin=6V
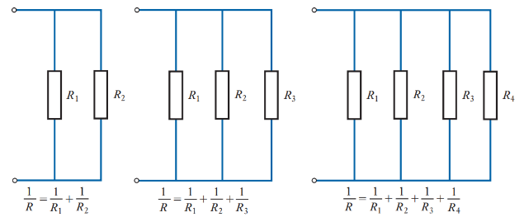
Resistors calculated in parallel
1/R_T =1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3 …1/R_n
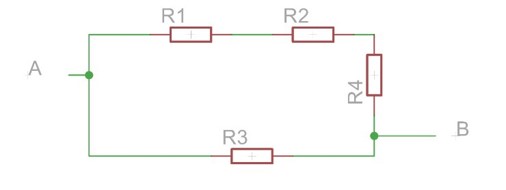
•Calculate the total equivalence between nodes A and B for the resistor combination if:
Parallel: 1/R_T =1/R1+1/R2+…1/Rn
R_Total=1/((1/R1+1/R2+…1/Rn) )
oSeries: R_Total=R1+R2+…Rn
•
•Resistor values:
oR1=5 kΩ
oR2=100 Ω
oR3=470 Ω
oR4=720 Ω
oR_Total=435 Ω
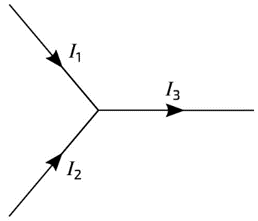
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL):
Current flowing into a node must be the same as the current flowing out of the node
I_3=I_1+I_2
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL):
The algebraic sum of emf (voltage source) acting on a closed loop (circuit) is equal to the algebraic sum of the potential difference (pd) around the loop
E=V_1+V_2+V_3, where E is the emf (voltage source) for the circuit
Calculating power for a resistor
Power=Current∙Voltage
Current=Voltage/Resistance
P=V^2/R
P=R∙I^2