
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What’s Enthalpy’s general formula?
H = E + (P x V)
What’s ΔE?
q + (-P ΔV)
What’s ΔH equal if pressure is held constant?
q
ΔH is?
H final - H initial
what’s q equal to in relation to ΔH?
q = ΔH = (moles reacted) X ΔHrxn
If ΔH is negative then?
system cools down —> exo
If ΔH is positive then?
system heats up —> endo
ΔH is specific to the amount of?
reaction (moles)
Answer Question
C, because the reaction starts at high and ends in low. The system is losing energy.
What’s A? is it Endo or Exo?
Melting/Fusion
Endo
What’s B? Is it Endo or Exo?
Freezing
Exo
What’s C? is it Endo or Exo?
Sublimation
Endo
What’s D? is it Endo or Exo?
Deposition
Exo
What’s E? is it Endo or Exo?
Evaporation
Endo
What’s F? is it Endo or Exo?
Condensation
Exo
A
D
A
A
A
D
A
What’s A-E show in phases?
A. Soild
B. Solid → liquid
C. Liquid
D. liquid → gas
E. gas
What does the line C represent?
Phase
What does the line D represent
phase change
What formula would you need to use for line C & why?
q= m * cp * ΔT
in phase
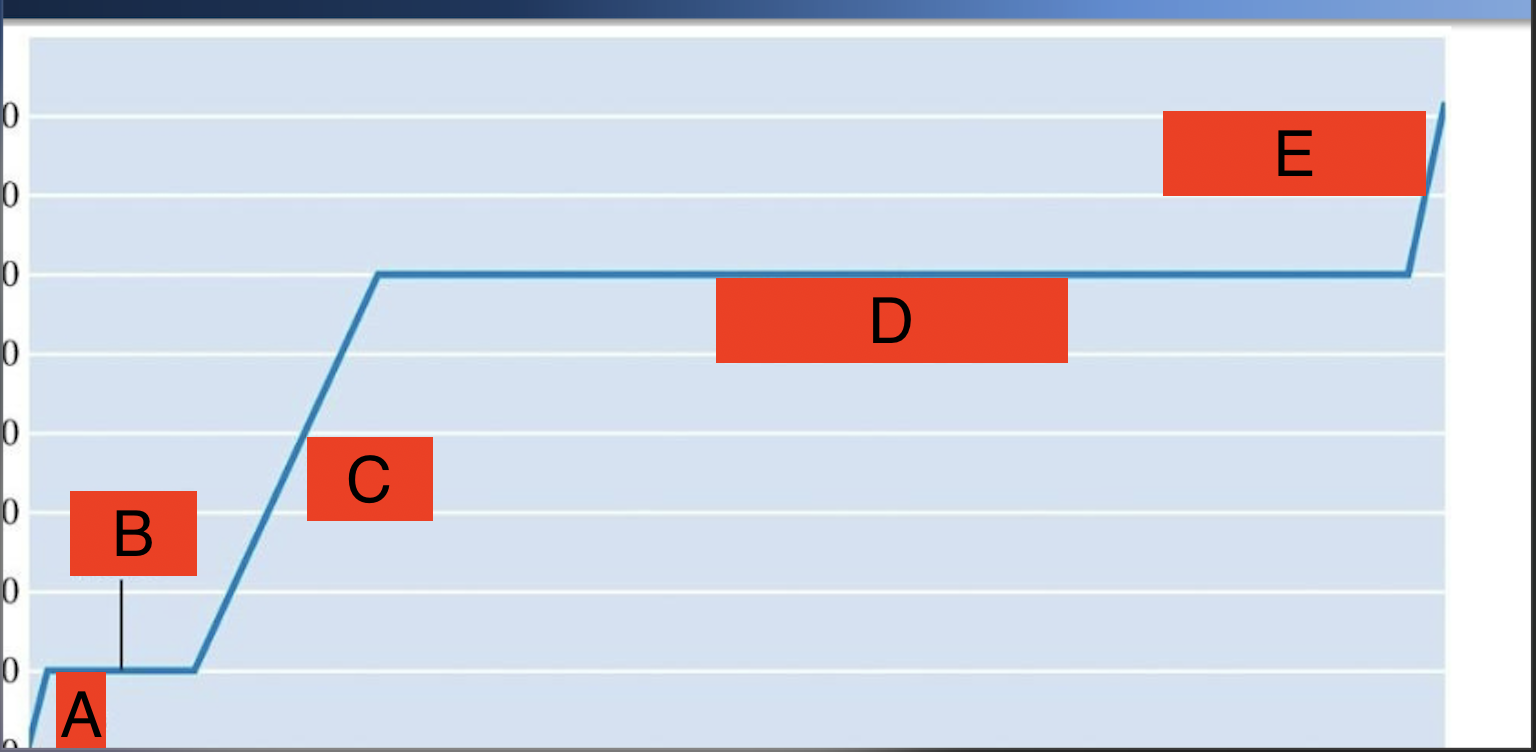
What formula do you need to use for D & Why?
q= n * ΔH
because phase is changing
During the duration of a reaction the q total (heat total) will equal
q1 + q2 + qn (n = amount of times heat changes in corresponding phases)
When Temperature changes what happens to KE?
Changes
When temperature is constant what happens to KE?
KE is constant
PE changes when?
phases changes (flat graph: temperature constant))
PE doesn’t change when?
in phase (slop graph: temperature changing)
What is the 2 rules for manipulating reactions?
if you flip reactions (making the reactants to products instead) you must change the sign of ΔH
What you multiply reaction by is what you multi ΔH by.